Prediction of Henry's law constants for CO2 and CH4 in levulinic acid via different Monte Carlo approaches
Prasil
Kapadiya
 and
Jhumpa
Adhikari
and
Jhumpa
Adhikari
 *
*
Department of Chemical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Powai, Mumbai – 400076, India. E-mail: adhikari@iitb.ac.in
First published on 16th October 2025
Abstract
Henry's law constants of CO2 and CH4 in levulinic acid are predicted at 313.15 K and 101.325 kPa. The Widom test particle insertion method (which is based on excess chemical potential computation) in the NPT ensemble via two different Monte Carlo approaches, viz., CBMC and CFCMC, is implemented. GEMC-NVT simulations are performed to calculate Henry's law constants from the slope of the line fitted to the plot of partial pressure of solute (CO2 or CH4) in the vapour phase versus the mole fraction of solute in liquid levulinic acid. Henry's law constants estimated via all three Monte Carlo methods and for both the solutes show good agreement within statistical uncertainties. The negative value of the Gibbs free energy of transfer (ΔGtrans) of CO2 from the vapour to the solvent (levulinic acid) phase suggests a preference of CO2 for liquid levulinic acid over the vapour phase. The solvation number computed from solute–solvent centre-of-mass radial distribution functions (RDFs) shows a higher value for CH4 than CO2, contrary to the trend in Henry's law constant. Therefore, the local environment around the solute molecule is investigated by computing the solute–solvent site–site intermolecular RDFs. The number integral calculated (up to the first minimum) from site–site intermolecular RDFs of the C(CO2)–methyl group of levulinic acid (CH3(1)) is more than that calculated from the CH4–CH3(1) RDF, confirming the higher solubility of CO2 in levulinic acid than CH4.
1. Introduction
The Henry's law constant (H2,1(T, p)) is generally employed to provide a measure of the solubility of a gas (solute species 2) in a liquid solvent (species 1) and is defined as the ratio of the equilibrium partial pressure of the solute in the gas phase (pgas2) to its mole fraction in the liquid solvent (xliq2) at infinite dilution as described in eqn (1).1,2 | (1) |
Determination of the Henry's law constant at a given temperature and pressure via molecular simulation techniques often includes the computation of the excess chemical potential of the solute at infinite dilution. The Widom test-particle insertion method (TPI)7 and staged free-energy perturbation (FEP) technique9,10 are usually employed for calculation of the excess chemical potential. The Widom TPI technique computes the excess chemical potential as the difference in the free energy of the (N + 1) particle system and the system containing N particles by inserting a test or ghost particle during the perturbation move.7 The Widom TPI method is a simple and elegant technique; however, since the method involves insertion of the test particle, longer simulation runs may be required (for example, at low temperatures) or other more efficient methods may be needed when a solvent contains a large solute molecule and/or the solvent fluid is extremely dense.11 In the staged FEP method, the interaction between the solute particle and solvent particles is gradually varied using a coupling parameter λ which varies from 0 to 1.9,10 Corresponding to the sequence of increasing λ values, a set of independent isobaric isothermal (NPT) sub-ensembles are considered.9,10 This method expresses the Boltzmann factor of the excess chemical potential at infinite dilution as the product of the contributions (which are functions of the difference in configurational energy between two consecutive sub-ensembles) from the sequence of sub-ensembles.9,10 Here, the value of free energy difference depends upon the direction of the perturbation either from the reference system to the target system or vice versa.3,8 The application of FEP methods requires careful consideration of the phase–space relationship between the reference and target systems, as highlighted by Kofke and Cummings.3,8 Alternatively, Gibbs ensemble Monte Carlo (GEMC) simulations can be used for direct calculation of Henry's law constants, analogous to experiments, without the use of excess chemical potential.2 This two-box method allows for the simultaneous determination of the vapour pressure and the mole fractions of solutes in both the vapour and liquid phases.2 Using these values, the Henry's law constant can be calculated as the slope of the pgassolutevs. xliqsolute plot2 (as described in eqn (1)). The expanded ensemble approach12–14 is another commonly employed approach for free energy calculations where two systems of interest are connected via a collection of sub-ensembles. These sub-ensembles are transformed gradually from one system of interest to another via Monte Carlo trials attempting to change the identity of the sub-ensemble and from the probability distribution obtained, the relative free energy of each sub-ensemble can be determined.12–14 The expanded ensemble technique was coupled with the self-adaptive transition matrix Monte Carlo (TMMC) method by Cichowski et al.3 for the efficient computation of Henry's law constants of a wide-range of solutes in numerous solvents. This combination provides a powerful tool for calculating the balancing factors and, hence, the relative free energies for each sub-ensemble, with high efficiency.3
The above discussed Monte Carlo methods can be applied in conjunction with configurational-bias Monte Carlo (CBMC)15 and continuous fractional component Monte Carlo (CFCMC)16 algorithms. The CBMC algorithm developed by Siepmann and Frenkel,15 based on the Rosenbluth and Rosenbluth scheme,17 includes a Monte Carlo move that explores the large-scale conformational changes of a molecule in a single trial move. Here, we first discuss some examples reported in the literature for the computation of Henry's law constants using CBMC. Lísal et al.11 estimated the Henry's constant of CO2 in water over a wide range of temperatures, starting from 0 °C to the critical temperature of water via Monte Carlo simulations in the NPT ensemble. The effect of the number of interaction sites on the value of the Henry's constant was investigated by employing two three-site potentials for CO2 (EPM2 and Errington and Panagiotopoulos) and various water models with three (SPC, SPC/E, MSPC/E, and Errington and Panagiotopoulos), four (TIP4P), and five (TIP5P) interaction sites.11 The Widom TPI and staged FEP methods were used to compute the Henry's constant.11 The Henry's constants predicted using Errington and Panagiotopoulos models were in good agreement with the experimental values.11 While extremely long simulation runs at lower temperatures were required for accurate prediction of the Henry's law constant of CO2 in water, the FEP method allows further analysis of Henry's law constants for both low and high temperature calculations.11 CBMC simulations in the canonical (NVT) version of the Gibbs ensemble have been performed by Zhang and Siepmann2 to compute the Henry's law constants and the Gibbs free energies of transfer for O2, N2, CH4, and CO2 in ethanol at 323 and 373 K. The solvent, ethanol, was modelled using the TraPPE-UA (transferable potentials for phase equilibria–united atom) force field, CH4 was modelled by TraPPE-UA and TraPPE-EH (transferable potentials for phase equilibria–explicit hydrogen) force fields, rigid models were used for CO2 (three LJ and three partial charge sites) and N2 (two LJ and three partial charge sites), and the model developed by Coon et al. was used for O2.2 Most of their simulations involved systems containing 1000 solvent molecules and 1, 2, 4 or 8 solute molecules.2 An excellent agreement between the GEMC data with predictions made utilizing the transition matrix Monte Carlo method was observed.2 A mean unsigned error of 15% was observed for the data predicted using the TraPPE-UA force field with experiments.2 Zhang and Siepmann2 determined that employing the united-atom representation (TraPPE-UA) for methane results in more accurate predictions of the Henry's law constant in united-atom (TraPPE-UA) ethanol compared to those obtained using the explicit-hydrogen (TraPPE-EH) methane. On the other hand, predictions for O2 showed higher deviations from the experimental data as compared to N2 and CO2.2 Cichowski et al.3 estimated Henry's law constants of CH4, O2, N2, and CO2 in ethanol at 323 and 373 K using an expanded NPT ensemble coupled with the self-adaptive TMMC method. Infinite-dilution excess chemical potential values for the solute were calculated.3 Molecular interactions were described by the TraPPE force field for all molecules except O2, where the model developed by Coon et al. was employed.3 For N2 in addition, the force field developed by Galassi and Tildesley was also used to investigate the sensitivity of the results to the molecular models employed.3 The Henry's law constant of O2 in ethanol estimated using this approach showed the highest deviation from the experimental data.3 Shah and Maginn18 used the Widom TPI method and expanded ensemble Monte Carlo approach in the NPT ensemble to compute the Henry's law constants of H2O, CO2, C2H6, O2, and N2 in the ionic liquid 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([bmim][PF6]). The force field for the ionic liquid was based on a UA model, while H2O, CO2, C2H6, O2, and N2 were modelled using SPC/E, TraPPE-small, TraPPE-UA, Miyano and TraPPE-small force fields, respectively.18 The predicted values of solubilities of the solutes in the ionic liquid were higher than the experimental values.18 Additionally, the temperature dependency of the Henry's law constants for CO2, O2 and water was investigated using the Widom TPI method.18 While the simulations using the Widom TPI method accurately predicted the trend where solubility of H2O and CO2 decreases with increasing temperature, the method failed to show the increase in solubility of O2 with temperature due to entropic effects governing the dissolution of O2.18
The CFCMC algorithm, introduced by Shi and Maginn,16 overcomes the difficulties encountered with the insertion and deletion of molecules in simulations, especially for dense systems. The method achieves efficient insertion and deletion of molecules by employing a continuously changing coupling parameter and an adaptive bias potential.16 This scaling factor (λ) modulates the strength of intermolecular interactions between the fractional molecule and its neighbouring molecules within the system.16λ ranges from 0 to 1, λ = 0 represents no interactions between the fractional molecule and surrounding whole molecules, and λ = 1 implies that interactions are fully developed.16 Examples of studies reported in the literature where CFCMC has been employed to compute the Henry's law constant are described here. The solubilities of CO2, CH4, C2H6, CO, H2, N2, N2O and H2S in various commercial solvents, like Rectisol, Selexol, Purisol and Fluor, were studied by Chen et al.5 using CFCMC simulations in the osmotic ensemble. CH4, C2H6, CO2 and N2 were modelled by the standard TraPPE force fields,5 and molecular models for CO, H2, N2O and H2S developed by Martin-Calvo et al., Cracknell et al., Lachet et al. and Guiterrez-Sevillano et al., respectively, were used.5 Overall, a good agreement between the experimental values and the estimated Henry's law constants for these gases was observed by Chen and co-workers.5 Ramdin et al.6 computed the solubilities and Henry's law constants of CO2, CH4, CO, H2, N2, and H2S in the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide ([bmim][TF2N]) at 333.15 K using CFCMC simulations in the osmotic ensemble. For the ionic liquid, the force field developed by Liu and Maginn was used.6 As in the study by Chen et al., the standard TraPPE force fields were adopted for CH4, CO2 and N2, and CO and H2 were represented using the Martin-Calvo et al. and Cracknell et al. models, respectively.6 Ramadin and co-workers examined three different force fields for H2S, viz., a three-site model developed by Kamath et al., a four-site model by Kristof and Lizi and a five-site model by Guiterrez-Sevillano et al.6 The predicted gas solubilities and Henry's law constants aligned well with the experimental data.6 Solubilities of CO2, CH4, CO, H2, N2, and H2S in green deep eutectic solvents, namely, choline chloride urea and choline chloride ethylene glycol, were estimated by Salehi et al.19 using CFCMC simulations in the NPT ensemble via the open source Brick-CFCMC software package. Two force fields, namely, GAFF (general Amber force field) and OPLS (optimized potentials for liquid simulations), were used to estimate the solubility at 328 K.19 It was observed that the OPLS force field yielded higher average Henry's constants in the case of choline chloride with ethylene glycol compared to GAFF.19 Furthermore, the solubility order for these solutes in choline chloride urea and choline chloride ethylene glycol deep eutectic solvents was observed to be in reasonable agreement with experimental values.19
Chemocatalytic conversion of cellulose (through glucose), as well as a one-pass catalytic process in the presence of a multifunctional catalyst, produces a wide range of molecules, from large molecules such as furfural, 5-hydroxy-2-methylfurfural and levulinic acid to small molecules with one carbon atom such as CO2 and CH4.20 To the best of our knowledge, there is no reported value for the Henry's constants of CO2 or CH4 in levulinic acid in the literature. Thus, we have performed molecular simulations to compute the Henry's law constants of CO2 and CH4 in levulinic acid at 313.15 K and 101.325 kPa. We have compared the results obtained from CBMC and CFCMC simulations in the NPT ensemble via the Widom TPI method. Moreover, this provides us with an opportunity to compare the computational resources required by the two algorithms (namely, CBMC and CFCMC). Additionally, canonical version of Gibbs ensemble Monte Carlo (GEMC-NVT) simulations in conjunction with CBMC moves with 1000 levulinic acid molecules and 1, 2, 4 or 8 CO2 or CH4 molecules are performed for the estimation of Henry's law constant. All CBMC simulations are performed using the MCCCS Towhee software package,21 whereas CFCMC simulations are performed using the Brick-CFCMC software.22 Furthermore, we have performed Metropolis MC simulations in the canonical ensemble with 1 molecule of each CO2 and CH4 in 300 molecules of levulinic acid (such that solute–solute interactions are absent) at 313.15 K. Solvation of CH4 and CO2 molecules in levulinic acid, which is a keto-acid containing two functional groups (keto-group and carboxylic acid group), is studied via computing the solute–solvent centre-of-mass (COM) radial distribution functions (RDFs), site–site intermolecular RDFs and their corresponding number integrals (NIs).
This article is organized as follows: a detailed description of the force fields and simulation methodologies adopted here is presented in Sections 2 and 3, respectively. The results are analysed and discussed in Section 4. The conclusions are summarised in the last section.
2. Force fields
The selection of the appropriate force field is crucial for any molecular simulation method, as the accuracy of the simulation results depends on the force field and combining rules employed to describe the interactions present in the system of interest. The force fields adopted in this study have been described here.2.1. TraPPE-UA force field
The interactions present in levulinic acid23–25 (refer to Scheme 1) and CH426 (refer to Scheme 2a) are described using the TraPPE-UA force field. The nonbonded interactions are modelled by 12-6 Lennard-Jones (LJ) and Coulombic potentials as shown in eqn (2),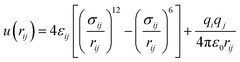 | (2) |
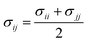 | (3) |
 | (4) |
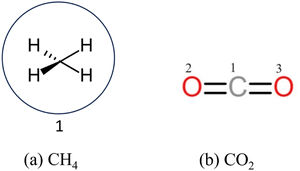 | ||
| Scheme 2 Structure of (a) CH4 for the TraPPE-UA force field and (b) CO2 for the TraPPE-small force field. | ||
All the bond lengths are kept rigid and modelled as
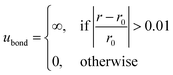 | (5) |
The bond bending is modelled by the harmonic potential specified as
 | (6) |
The torsional interactions are modelled using eqn (7), depending on the four united atoms involved.
utorsion(ϕ) = c0 + c1[1 + cos![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ϕ] + c2[1 + cos ϕ] + c2[1 + cos![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2ϕ] + c3[1 + cos 2ϕ] + c3[1 + cos![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3ϕ] 3ϕ] | (7) |
The TraPPE-UA force field parameters for levulinic acid and CH4 are reported in Tables S1 and S2 of the SI, respectively.
2.2. TraPPE-small force field
The TraPPE-small force field is used to model CO227,28 (refer to Scheme 2b). The nonbonded interactions between atoms are represented using the 12-6 LJ potential given in eqn (2). The cross-interactions between unlike atoms are modelled using the Lorentz–Berthelot combining rules and defined in eqn (3) and (4). The bonded interactions (bond stretching and bond bending) in the CO2 molecule are held rigid and are described by eqn (5) and (8), respectively. | (8) |
The nonbonded and bonded parameters for CO2 modelled using the TraPPE-small force field are reported in Table S3 of the SI.
3. Methodology
At temperature T and pressure p, the Henry's constant for solute i in a solvent j is given as29 | (9) |
![[f with combining circumflex]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0066_0302.gif) Li is the fugacity of the solute, i, in the mixture. Based on standard thermodynamic relationships, the expression can be written as1,11
Li is the fugacity of the solute, i, in the mixture. Based on standard thermodynamic relationships, the expression can be written as1,11 | (10) |
3.1. Widom test-particle insertion (TPI) method
The Widom test particle insertion method is a notably simple and elegant approach for measuring the chemical potential of a species in a pure fluid or a mixture. Here, the infinite dilution chemical potential is calculated using the Widom test-particle insertion (TPI) method.7,11 In this method, a solute particle (also called the “test” particle) is randomly inserted into a pure solvent. This insertion of the “test” particle can be either via CBMC or CFCMC moves. The exponential term containing the excess chemical potential of the solute at infinite dilution in eqn (10) can be computed either using eqn (11) when the CBMC algorithm is employed or eqn (12) for the CFCMC approach.In the NPT ensemble simulation in conjunction with the CBMC algorithm, the excess chemical potential of the solute at infinite dilution is computed using eqn (11).7,11,30
 | (11) |
In the CFCMC algorithm, the excess chemical potential term can be calculated using the following expression:22,31
 | (12) |
3.2. Gibbs ensemble Monte Carlo method in the canonical ensemble
Similar to experiments, the GEMC-NVT32 simulation technique allows for the direct calculation of Henry's law constants.2 A two-phase system facilitates the direct measurement of both the vapour pressure and the solute mole fractions in both the vapour and liquid phases. The values of xliqsolute and pgassolute for computing the Henry's law constant using this method can be determined simply by computing the ensemble averages of these properties. Using these values, the Henry's law constant can be calculated from the slope of the line fitted to the plot of pgassolutevs. xliqsolute (as described in eqn (1)).23.3. Simulation details
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5
5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 25
25![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30
30![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30. The system is allowed to equilibrate over at least 1
30. The system is allowed to equilibrate over at least 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500
500![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 MC cycles with averages computed over 100
000 MC cycles with averages computed over 100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles of the production run.
000 cycles of the production run.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30
30![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20. The system is equilibrated over at least 2
20. The system is equilibrated over at least 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000
000![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 MC cycles, followed by another 100
000 MC cycles, followed by another 100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 MC cycles for the production run.
000 MC cycles for the production run.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5
5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5
5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5
5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5
5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20
20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 25
25![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 25. The total volume of the two simulation boxes is adjusted such that on average approximately half of the total number of solute molecules can be found in the vapour box and half in the liquid box. The system is allowed to equilibrate for at least 450
25. The total volume of the two simulation boxes is adjusted such that on average approximately half of the total number of solute molecules can be found in the vapour box and half in the liquid box. The system is allowed to equilibrate for at least 450![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 MC cycles with averages computed over 50
000 MC cycles with averages computed over 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 MC cycles of the production run.
000 MC cycles of the production run.
4. Results and discussion
4.1. Liquid phase density
The liquid density of levulinic acid is computed at 313.15 K and 100 kPa using single box NPT MC simulations via CBMC and CFCMC approaches separately. The values of the liquid densities are reported in Table 1 and compared with the experimental value of 1123 kg m−3 reported in the literature.34 The density of levulinic acid predicted via NPT Metropolis MC simulations in conjunction with the CBMC approach and the CFCMC approach is in good agreement with the experimental data (within 4.5%), with the value from the CFCMC approach being in better agreement with the experimental value. However, the values from the two approaches do not overlap within the statistical uncertainties associated with each average value; the difference between the two average values is less than 0.7%. This suggests the suitability of the TraPPE-UA force field and its parameters to model the interactions present in levulinic acid in the liquid phase.| Simulation (kg m−3) | Experiment34 (kg m−3) | % Relative deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBMC | 107![[5 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0035_0332.gif) (1) (1) |
1123 | 4.1% |
| CFCMC | 108![[2 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0332.gif) (3) (3) |
3.6% | |
4.2. Henry's law constants via the Widom test-particle insertion technique
For the estimation of Henry's law constants of CO2 and CH4 in levulinic acid at 313.15 K and 101.325 kPa, we have carried out NPT simulations using the Widom TPI technique via the use of both the CBMC and CFCMC algorithms. Table 2 shows the values of Henry's law constants predicted using CBMC and CFCMC approaches. The values of the Henry's law constant of CO2 in levulinic acid using CBMC and CFCMC approaches are in excellent agreement. The Henry's constants for the same solvent (i.e., levulinic acid) with CH4 as the solute using both CBMC and CFCMC approaches are found to be close and within the error bars. We note here that there is no reported value for the Henry's constant of CO2 or CH4 in levulinic acid in the literature for comparison.| Solute | CBMC | CFCMC |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 | 1![[2 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0332.gif) (1) (1) |
12.![[1 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0332.gif) (4) (4) |
| CH4 | 1![[1 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0332.gif) ![[3 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0332.gif) (19) (19) |
1![[1 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0332.gif) ![[8 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0038_0332.gif) (20) (20) |
4.3. Henry's law constants via GEMC-NVT simulations
Additionally, we have carried out GEMC-NVT simulations using CBMC moves to calculate Henry's law constants of CO2 and CH4 in levulinic acid. Fig. 1 and 2 show the relationship between the partial pressure of CO2 (modelled using the TraPPE-small force field) and CH4 (modelled using the TraPPE-UA force field), and their corresponding liquid-phase mole fractions in levulinic acid (solvent) at 313.15 K. The four markers in each plot illustrate the simulation results for systems corresponding to the number of solute molecules varying as 1, 2, 4 and 8. The average values of Henry's law constants obtained from pgassolute and xliqsolute for each solute have been determined from the GEMC-NVT simulations. Furthermore, a linear regression of pgassolutevs. xliqsolute that is constrained to pass through the origin has been carried out and the slope of this fitted straight line provides the value of the Henry's law constant. We note here that the results for all four concentrations are accurately represented by a linear fit for both the solutes, viz., CO2 (refer to Fig. 1) and CH4 (refer to Fig. 2). The values of Henry's law constants derived from the GEMC-NVT simulations are presented in Table 3. In the case of CO2 as a solute, the Henry's law constant is determined to be 11 MPa, whereas the same for CH4 as a solute is 128 MPa. These are similar to the corresponding values obtained from CBMC and CFCMC approaches via the Widom TPI method. | ||
| Fig. 1 Partial pressure versus liquid-phase mole fraction for CO2 in levulinic acid obtained via GEMC-NVT simulations. | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 2 Partial pressure versus liquid-phase mole fraction for CH4 in levulinic acid obtained via GEMC-NVT simulations. | ||
| Solute | Henry's law constant (MPa) |
|---|---|
| CO2 | 1![[1 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0332.gif) (2) (2) |
| CH4 | 1![[2 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0332.gif) ![[8 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0038_0332.gif) (18) (18) |
The value of the Henry's law constant for CH4 is higher than that for CO2 in levulinic acid as obtained from all the methods discussed above (i.e., CBMC and CFCMC simulations in the NPT ensemble via the Widom TPI method and GEMC-NVT simulations using CBMC moves). This suggests less solubility of CH4 compared to CO2 in levulinic acid. We again note here that there are no experimental data nor any simulation studies available in the literature for the Henry's constant of CO2 and CH4 in levulinic acid for comparison here.
1000 MC cycles performed using the CBMC and CFCMC approaches in the NPT ensemble simulations (in the case of CO2 in levulinic acid) require approximately 5304 and 2856 s of CPU time, respectively, and GEMC simulations with the CBMC approach in the case of 1000 levulinic acid molecules with 8 CO2 molecules require about 44![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 076 s of CPU time on an Intel® Xenon® Silver processor at 2.40 GHz. Based on the total computational time requirement, the Widom TPI method in the NPT ensemble in conjunction with the CFCMC algorithm is recommended to compute the Henry's law constant via molecular simulations. We note here that the GEMC simulations allow us to additionally compute the Gibbs free energy of transfer of the solute.
076 s of CPU time on an Intel® Xenon® Silver processor at 2.40 GHz. Based on the total computational time requirement, the Widom TPI method in the NPT ensemble in conjunction with the CFCMC algorithm is recommended to compute the Henry's law constant via molecular simulations. We note here that the GEMC simulations allow us to additionally compute the Gibbs free energy of transfer of the solute.
4.4. Gibbs free energy of transfer of the solute
We have calculated the Gibbs free energy of transfer (ΔGtrans) of the solute (CO2 or CH4) from the vapour box (initially containing 1, 2, 4 or 8 solute molecules) to the liquid box (containing 1000 levulinic acid molecules) using the results obtained from the GEMC-NVT simulations. This can be expressed in terms of the number densities of the solute in the two phases as given in eqn (13).35 | (13) |
Table 4 reports the values of ΔGtrans of solute from the vapour phase to the liquid phase for various number ratios of levulinic acid to solute in the case of each solute. The ΔGtrans of CO2 from the vapour phase to the liquid levulinic acid phase is negative indicating a preference for the liquid phase in contrast to the positive values noted for CH4, confirming our previously stated results for the Henry's law constant values.
Levulinic acid![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) solute (in terms of number of molecules) solute (in terms of number of molecules) |
ΔGtrans (kJ mol−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 | CH4 | |
1000![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
−![[4 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0034_0332.gif) (1) (1) |
3.![[9 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0039_0332.gif) (8) (8) |
1000![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 2 |
−3.![[1 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0332.gif) (4) (4) |
![[4 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0034_0332.gif) (1) (1) |
1000![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 4 |
−![[3 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0332.gif) (1) (1) |
4.![[6 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0036_0332.gif) (9) (9) |
1000![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8 8 |
−2.![[2 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0332.gif) (7) (7) |
![[5 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0035_0332.gif) (1) (1) |
4.5. Radial distribution functions
Molecular simulations also allow us to gain molecular-level insights into the underlying reasons for the relative solubilities of the solutes, viz., CO2 and CH4, in the solvent, levulinic acid. We have performed Metropolis MC simulations in the NVT ensemble to investigate the solvation of CO2 and CH4 in levulinic acid at 313.15 K with a system consisting of 300 levulinic acid molecules and 1 molecule of CO2 or CH4 (to maintain the dilute nature of the system such that solute–solute interactions are absent). Prior to the NVT ensemble simulations, we have performed NPT ensemble MC simulations at 313.15 K and 101.325 kPa for at least 250![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles to determine the average box volume (which is then input to the NVT MC simulations). The densities are found to be 107
000 cycles to determine the average box volume (which is then input to the NVT MC simulations). The densities are found to be 107![[6 with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0036_0332.gif) (2) kg m−3 for the mixtures of either CO2 or CH4 as solutes in levulinic acid. We have first plotted solute–solvent COM RDFs and the corresponding NIs for levulinic acid–solute interactions. The proximity of CH4 and CO2 molecules to the individual groups of the levulinic acid molecule (a ketoacid containing two functional groups: keto–group and carboxylic acid group, see Scheme 1) is assessed via site–site intermolecular RDFs and the corresponding NIs. We discuss each of these types of RDFs in separate sub-sections.
(2) kg m−3 for the mixtures of either CO2 or CH4 as solutes in levulinic acid. We have first plotted solute–solvent COM RDFs and the corresponding NIs for levulinic acid–solute interactions. The proximity of CH4 and CO2 molecules to the individual groups of the levulinic acid molecule (a ketoacid containing two functional groups: keto–group and carboxylic acid group, see Scheme 1) is assessed via site–site intermolecular RDFs and the corresponding NIs. We discuss each of these types of RDFs in separate sub-sections.
4.5.2.1. C(CO2)–levulinic acid interactions. The site–site intermolecular RDFs for the carbon of CO2 represented as C(CO2) and the various united atoms of the carbon containing groups of levulinic acid (i.e., CH3(1), C2, CH2(3), CH2(5) and C6 groups as shown in Scheme 1) are plotted in Fig. 4(a). Fig. 4(b) shows the RDFs for the different O atoms of levulinic acid (i.e., O4, O7, and O8 in Scheme 1) and the H9 atom (refer to Scheme 1) with C(CO2). We find that the first peak heights are above unity for all the site–site intermolecular RDFs in Fig. 4(a) and (b). The first peak heights from site–site RDFs arranged in descending order are as follows: CH3(1) > C2 > CH2(5) > C6 > O4 > CH2(3) > O7 > H9 > O8. The highest peak height is observed in the case of C(CO2)–CH3(1) (at the separation distance of 4.543 Å). The highest peak height for the C(CO2)–CH3(1) site–site intermolecular RDF corresponds to the highest value of well depth (of the 12-6 LJ potential which describes the van der Waals interactions) for C(CO2)–CH3(1) interactions obtained using the Lorentz–Berthelot combining rule (eqn (4)). The value of NI calculated up to a separation distance of 6.08 Å (distance corresponding to the first minimum) is 5.42 (refer to Fig. 5). We have also shown the snapshots from our simulation for two different configurations of the local environment around the CO2 molecule in Fig. 5. We see that a CO2 molecule is surrounded by six levulinic acid molecules at a separation distance of 6.08 Å.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Site–site intermolecular RDFs for the C(CO2)–levulinic acid system: (a) CH3(1), C2, CH2(3), CH2(5) and C6 groups of levulinic acid and (b) O4, O7, O8 and H9 groups of levulinic acid. | ||
Fig. 4(b) shows that the heights of the first peak in the C(CO2)–O4, C(CO2)–O7, and C(CO2)–O8 RDFs are in descending order and the partial charges (in the Coulomb potential modelling the electrostatic interactions listed in Table S1 of the SI) of O4, O7 and O8 atoms also exhibit a decreasing trend. Moreover, the first peaks in the RDFs of the C(CO2) with O4, O7, O8 and H9 (Fig. 4(b)) appear before the first peaks in the RDFs of the C(CO2) with CH3(1), C2, CH2(3), CH2(5) and C6 united atoms (Fig. 4(a)) suggesting that the C(CO2) atom is near the oxygen atoms of the carboxylic acid and the keto groups of the levulinic acid molecule. We note here that the minimum separation distances as calculated from the Lorentz–Berthelot combining rule (eqn (3)) are less in the case of van der Waals interactions (represented by the 12-6 LJ potential) of C(CO2) with O4, O7, O8 and H9 than with carbon containing united atoms of levulinic acid. Levulinic acid molecules in the liquid phase adopt different conformations, some of which are illustrated in Fig. 5 and we observe from Fig. 5(b) that the CO2 molecule is in close proximity to the carboxylic acid group of levulinic acid. We note the presence of two peaks in the C(CO2)–O8 and the C(CO2)–H9 RDFs with the first peak in both cases appearing at a separation distance of 3.17 Å. In the C(CO2)–O8 RDF, the two peak heights (with g(r) = 1.237 and g(r) = 1.244) are almost the same, implying that there are two preferred locations of the CO2 molecule with respect to O8. A third peak with g(r) = 1.173 at 5.53 Å is also observed in the C(CO2)–O8 RDF.
4.5.2.1. O(CO2)–levulinic acid interactions. Additionally, we have computed the site–site intermolecular RDFs for the oxygen of CO2 represented as O(CO2) and the different united atoms representing the carbon containing groups of levulinic acid (Scheme 1) and these RDFs are presented in Fig. 6(a). The plots of the RDFs for O4, O7, O8 and H9 of levulinic acid (Scheme 1) with O(CO2) are shown in Fig. 6(b). The central C(CO2) atom is bonded to the two O(CO2) atoms in the CO2 molecule and any association of C(CO2) with the sites on the levulinic acid molecule will involve associations with the two O(CO2) atoms also. Here, the heights of the first peaks, except for the O(CO2)–H9 RDF, are observed to be greater than one. The value of NI calculated from the O(CO2)–CH3(1) RDF up to the first coordination shell (with a separation distance of 4.71 Å) is 2.07. As in Fig. 4(b), we find that Fig. 6(b) also shows that the heights of the first peak in the O(CO2)–O4, O(CO2)–O7, and O(CO2)–O8 RDFs in descending order are in correspondence with the decreasing trend in the partial charges (in the Coulomb potential modelling the electrostatic interactions given in Table S1 of the SI) of O4, O7 and O8 atoms.
 | ||
| Fig. 6 Site–site intermolecular RDFs for the O(CO2)–levulinic acid system: (a) CH3(1), C2, CH2(3), CH2(5) and C6 groups of levulinic acid and (b) O4, O7, O8 and H9 groups of levulinic acid. | ||
The O(CO2)–O8 RDF exhibits features distinct from the C(CO2)–O8 RDF, with the first peak (with g(r) = 1.428 which is slightly higher than the first two peaks of the C(CO2)–O8 RDF) displaying one pronounced peak at a separation distance (r) of 3.00 Å, a first shoulder with g(r) > 1.0 at r = 3.34 Å and a second shoulder which appears with g(r) ≈ 1.0 at r = 3.86 Å. From Fig. 4(b), we note that the third peak of the C(CO2)–O8 RDF (with peak height g(r) = 1.173) is at r = 5.23 Å, and this peak corresponds to the second peak (with a slightly higher peak height of g(r) = 1.234) of the O(CO2)–O8 RDF at r = 5.06 Å in Fig. 6(b).
5. Conclusions
In this study, the Henry's law constants of CO2 and CH4 in levulinic acid at 313.15 K and 101.325 kPa have been estimated via three different Monte Carlo approaches. The interactions present in levulinic acid and CH4 are modelled using the TraPPE-UA force field, whereas the TraPPE-small force field is used to describe interactions present in CO2. First, the suitability of the force field is checked by computing the liquid density of levulinic acid at 313.15 K and 100 kPa using NPT MC simulations via both CBMC and CFCMC approaches. We find that the values of the liquid densities estimated using CBMC and CFCMC approaches are in good agreement with the experimentally reported value (within 4.5%) with the prediction via the CFCMC approach being closer to the experimental value. First, we have implemented the Widom TPI method (which is based on the calculation of excess chemical potential) in the NPT ensemble using two Monte Carlo algorithms, viz., CBMC and CFCMC. We find that the values of Henry's law constant via both CBMC and CFCMC are in excellent agreement for each solute. Additionally, we have performed GEMC-NVT simulations including the CBMC moves to calculate Henry's law constants of CO2 and CH4 in levulinic acid, because this method does not require calculation of excess chemical potential. From the slope of the line fitted to the plot of pgassolutevs. xliqsolute, the values of the Henry's law constant in the case of each solute are calculated. The values obtained via GEMC-NVT simulations are similar to the values obtained from CBMC and CFCMC approaches via the Widom TPI method. Moreover, from GEMC-NVT simulations, ΔGtrans of solutes (viz., CO2 and CH4) can also be estimated. The negative value of ΔGtrans of CO2 from the vapour phase to the liquid (levulinic acid) phase suggests an obvious preference of CO2 for the liquid levulinic acid phase over the vapour phase. We note that there are no experimental data nor any prior simulation studies available in the literature for Henry's constants of CO2 and CH4 in levulinic acid for comparison here. This knowledge of Henry's law constants is useful in the various industrial processes for design, optimization and modelling of separation equipment.We have also studied the solvation of CH4 and CO2 molecules in liquid levulinic acid by performing single box NVT simulations at 313.15 K using one solute molecule (viz., CO2 or CH4) in 300 levulinic acid molecules such that solute–solute interactions are absent. The site–site intermolecular RDFs for C(CO2), O(CO2) and CH4 with the various united atoms representing the carbon containing groups of levulinic acid and those with O4, O7, O8 and H9 atoms of levulinic acid (Scheme 1) are computed to investigate the local environment around the solute molecule. From the solute–solvent site–site RDFs, we can conclude that CO2 shows a preference for the carboxylic acid and keto groups of levulinic acid, whereas CH4 shows a tendency to reside in the proximity of the CH3(1) group of levulinic acid. The NIs calculated from the integration of the site–site intermolecular RDFs up to the first minima of the C(CO2)–CH3(1) and CH4–CH3(1) RDFs show that the solvation number of CO2 in levulinic acid is more than that of CH4. This observation (which is in contrast to the respective solvation numbers computed from the solute–solvent COM RDFs) aligns well with the lower Henry's law constant of CO2 in levulinic acid as compared to CH4 at 313.15 K and atmospheric pressure. This is also consistent with the negative value of ΔGtrans of CO2 from the vapour phase to the liquid phase, confirming a preference for the dissolution of CO2 in levulinic acid over CH4.
Author contributions
Prasil Kapadiya: conceptualization (equal); data curation (lead); formal analysis (lead); funding acquisition; investigation (equal); methodology (equal); software (lead); validation; visualization (lead); roles/writing – original draft (lead); and writing – review & editing (equal). Jhumpa Adhikari: conceptualization (equal); data curation (supporting); formal analysis (supporting); funding acquisition; investigation (equal); methodology (equal); project administration; resources (lead); software (supporting); supervision (lead); validation; visualization; roles/writing – original draft (supporting); and writing – review & editing (equal).Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.Data availability
Data will be made available on request.Supplementary information (SI): nonbonded and bonded interaction parameters for the TraPPE-UA force field for levulinic acid and CH4 are provided in Tables S1 and S2, respectively. The parameters for the TraPPE-small force field in the case of CO2 are reported in Table S3. Site–site intermolecular radial distribution functions for CO2–levulinic acid and CH4–levulinic acid systems are presented in Fig. S1–S3. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5cp02630j.
Acknowledgements
P. K. acknowledges funding support from the Prime Minister's Research Fellowship (PMRF), Ministry of Education, Government of India. Computational resources and funding for this project have been provided by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology, India (Sanction Order #: CRG/2022/000148 of Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF)).References
-
S. I. Sandler, Chemical, Biochemical, and Engineering Thermodynamics, 5th edn, John Wiley & Sons, 2017 Search PubMed
.
- L. Zhang and J. I. Siepmann, Direct calculation of Henry's law constants from Gibbs ensemble Monte Carlo simulations: Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and methane in ethanol, Theor. Chem. Acc., 2006, 115(5), 391–397, DOI:10.1007/s00214-005-0073-1
.
- E. C. Cichowski, T. R. Schmidt and J. R. Errington, Determination of Henry's law constants through transition matrix Monte Carlo simulation, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2005, 236(1–2), 58–65, DOI:10.1016/j.fluid.2005.05.001
.
- K. Sumida, D. L. Rogow, J. A. Mason, T. M. McDonald, E. D. Bloch, Z. R. Herm, T. H. Bae and J. R. Long, Carbon dioxide capture in metal–organic frameworks, Chem. Rev., 2012, 112(2), 724–781, DOI:10.1021/cr2003272
.
- Q. Chen, M. Ramdin and T. J. Vlugt, Solubilities of CO2, CH4, C2H6, CO, H2, N2, N2O, and H2S in commercial physical solvents from Monte Carlo simulations, Mol. Simul., 2023, 49(13–14), 1341–1349, DOI:10.1080/08927022.2023.2228918
.
- M. Ramdin, S. P. Balaji, J. M. Vicent-Luna, J. J. Gutierrez-Sevillano, S. Calero, T. W. de Loos and T. J. Vlugt, Solubility of the precombustion gases CO2, CH4, CO, H2, N2, and H2S in the ionic liquid [bmim][Tf2N] from Monte Carlo simulations, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118(41), 23599–23604, DOI:10.1021/jp5080434
.
- B. Widom, Some topics in the theory of fluids, J. Chem. Phys., 1963, 39(11), 2808–2812, DOI:10.1063/1.1734110
.
- D. A. Kofke and P. T. Cummings, Quantitative comparison and optimization of methods for evaluating the chemical potential by molecular simulation, Mol. Phys., 1997, 92(6), 973–996, DOI:10.1080/002689797169600
.
- N. Lu, J. K. Singh and D. A. Kofke, Appropriate methods to combine forward and reverse free-energy perturbation averages, J. Chem. Phys., 2003, 118(7), 2977–2984, DOI:10.1063/1.1537241
.
- N. Lu and D. A. Kofke, Optimal intermediates in staged free energy calculations, J. Chem. Phys., 1999, 111(10), 4414–4423, DOI:10.1063/1.479206
.
- M. Lísal, W. R. Smith and K. Aim, Analysis of Henry's constant for carbon dioxide in water via Monte Carlo simulation, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2005, 228, 345–356, DOI:10.1016/j.fluid.2005.03.005
.
- A. P. Lyubartsev, A. A. Martsinovski, S. V. Shevkunov and P. N. Vorontsov-Velyaminov, New approach to Monte Carlo calculation of the free energy: Method of expanded ensembles, J. Chem. Phys., 1992, 96(3), 1776–1783, DOI:10.1063/1.462133
.
- A. P. Lyubartsev, A. Laaksonen and P. N. Vorontsov-Velyaminov, Determination of free energy from chemical potentials: Application of the expanded ensemble method, Mol. Simul., 1996, 18(1–2), 43–58, DOI:10.1080/08927029608022353
.
- A. P. Lyubartsev, O. K. Førrisdahl and A. Laaksonen, Solvation free energies of methane and alkali halide ion pairs: An expanded ensemble molecular dynamics simulation study, J. Chem. Phys., 1998, 108(1), 227–233, DOI:10.1063/1.475374
.
- J. I. Siepmann and D. Frenkel, Configurational bias Monte Carlo: A new sampling scheme for flexible chains, Mol. Phys., 1992, 75(1), 59–70, DOI:10.1080/00268979200100061
.
- W. Shi and E. J. Maginn, Continuous fractional component Monte Carlo: An adaptive biasing method for open system atomistic simulations, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2007, 3(4), 1451–1463, DOI:10.1021/ct7000039
.
- M. N. Rosenbluth and A. W. Rosenbluth, Monte Carlo calculation of the average extension of molecular chains, J. Chem. Phys., 1955, 23(2), 356–359, DOI:10.1063/1.1741967
.
- J. K. Shah and E. J. Maginn, Monte Carlo simulations of gas solubility in the ionic liquid 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109(20), 10395–10405, DOI:10.1063/1.1741967
.
- H. S. Salehi, R. Hens, O. A. Moultos and T. J. H. Vlugt, Computation of gas solubilities in choline chloride urea and choline chloride ethylene glycol deep eutectic solvents using Monte Carlo simulations, J. Mol. Liq., 2020, 316, 113729, DOI:10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113729
.
- C. H. Zhou, X. Xia, C. X. Lin, D. S. Tong and J. Beltramini, Catalytic conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to fine chemicals and fuels, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40(11), 5588–5617 RSC
.
- M. G. Martin, MCCCS Towhee: a tool for Monte Carlo molecular simulation, Mol. Simul., 2013, 39(14–15), 1212–1222, DOI:10.1080/08927022.2013.828208
.
- R. Hens, A. Rahbari, S. Caro-Ortiz, N. Dawass, M. Erdos, A. Poursaeidesfahani, H. S. Salehi, A. T. Celebi, M. Ramdin, O. A. Moultos and D. Dubbeldam, Brick-CFCMC: Open source software for Monte Carlo simulations of phase and reaction equilibria using the continuous fractional component method, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2020, 60(6), 2678–2682, DOI:10.1021/acs.jcim.0c00334
.
- J. M. Stubbs, J. J. Potoff and J. I. Siepmann, Transferable potentials for phase equilibria. 6. United-atom description for ethers, glycols, ketones, and aldehydes, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108(45), 17596–17605, DOI:10.1021/jp049459w
.
- G. Kamath, F. Cao and J. J. Potoff, An improved force field for the prediction of the vapor-liquid equilibria for carboxylic acids, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108(37), 14130–14136, DOI:10.1021/jp048581s
.
- T. Chakraborti, A. Desouza and J. Adhikari, Prediction of Thermodynamic Properties of Levulinic Acid via Molecular Simulation Techniques, ACS Omega, 2018, 3(12), 18877–18884, DOI:10.1021/acsomega.8b02793
.
- M. G. Martin and J. I. Siepmann, Transferable potentials for phase equilibria. 1. United-atom description of n-alkanes, J. Phys. Chem. B, 1998, 102(14), 2569–2577, DOI:10.1021/jp972543
.
- J. J. Potoff and J. I. Siepmann, Vapor-liquid equilibria of mixtures containing alkanes, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen, AIChE J., 2001, 47(7), 1676–1682, DOI:10.1002/aic.690470719
.
- B. L. Eggimann, Y. Sun, R. F. DeJaco, R. Singh, M. Ahsan, T. R. Josephson and J. I. Siepmann, Assessing the quality of molecular simulations for vapor–liquid equilibria: An analysis of the TraPPE database, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2019, 65(3), 1330–1344, DOI:10.1021/acs.jced.9b00756
.
-
J. M. Smith, H. C. Van Ness and M. M. Abbott, Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, 7th edn, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 2005 Search PubMed
.
-
D. Frenkel and B. Smit, Understanding Molecular Simulation, 2nd edn, Academic Press, San Diego, 2001 Search PubMed
.
- A. Rahbari, R. Hens, M. Ramdin, O. A. Moultos, D. Dubbeldam and T. J. H. Vlugt, Recent advances in the continuous fractional component Monte Carlo methodology, Mol. Simul., 2021, 47(10–11), 804–823, DOI:10.1080/08927022.2020.1828585
.
- A. Z. Panagiotopoulos, Direct determination of phase coexistence properties of fluids by Monte Carlo simulation in a new ensemble, Mol. Phys., 1987, 61(4), 813–826, DOI:10.1080/00268978700101491
.
- MCCCS Towhee. https://towhee.sourceforge.net/.
- H. Guerrero, C. Lafuente, F. Royo, L. Lomba and B. Giner, PρT behavior of several chemicals from biomass, Energy Fuels, 2011, 25(7), 3009–3013, DOI:10.1021/ef200653s
.
- S. J. Keasler, J. L. Lewin, J. I. Siepmann, N. M. Gryska, R. B. Ross, N. E. Schultz and M. Nakamura, Molecular insights for the optimization of solvent-based selective extraction of ethanol from fermentation broths, AIChE J., 2013, 59(8), 3065–3070, DOI:10.1002/aic.14055
.
| This journal is © the Owner Societies 2025 |





