Near-infrared Cr3+-doped lead-free halide perovskite microcrystals for information encryption and temperature thermometry†
Wei
Zhao
a,
Li
Li
 *a,
Faling
Ling
*a,
Faling
Ling
 a,
Yongjie
Wang
a,
Yongjie
Wang
 *a,
Guotao
Xiang
*a,
Guotao
Xiang
 a,
Xianju
Zhou
a,
Xianju
Zhou
 a,
Sha
Jiang
a,
Zhiyu
Yang
a,
Yongbin
Hua
a,
Sha
Jiang
a,
Zhiyu
Yang
a,
Yongbin
Hua
 b and
Jae Su
Yu
b and
Jae Su
Yu
 *b
*b
aSchool of Science, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Chongqing, 400065, P. R. China. E-mail: lilic@cqupt.edu.cn; wangyj@cqupt.edu.cn
bDepartment of Electronics and Information Convergence Engineering, Institute for Wearable Convergence Electronics, Kyung Hee University, Yongin-si, Gyeonggi-do 17104, Republic of Korea. E-mail: jsyu@khu.ac.kr
First published on 20th February 2024
Abstract
Lead-free double perovskite materials have attracted lots of interest because they can be doped with luminescence activators to modify their optical characteristics and improve photoluminescence performances. Herein, a solvothermal method was utilized to synthesize single Cr3+-doped Cs2NaInCl6 phosphors. Under 292 nm excitation, Cr3+-doped Cs2NaInCl6 microparticles exhibited a strong broad near-infrared emission with a good photoluminescence quantum yield of 42.9%. The prepared sample exhibited a prominent peak at 960 nm and a full width at half maximum of 138 nm, which can be attributed to the spin-allowed transition (4T2 → 4A2) of Cr3+ ions. Additionally, the emission band of Cr3+ displayed a noticeable red shift as temperature increased owing to the variations in the strength of the crystal field. The thermometry based on the bandwidth and band-shift modes showed good sensitivities of 0.337 nm K−1 and 0.272 nm K−1, respectively. Finally, the security ink was made for information encryption.
1. Introduction
Metal halide perovskites have exhibited remarkable potential for numerous applications, including solar cells,1 light-emitting diodes,2 photodetectors,3 and more, owing to their exceptional optoelectronic properties.4 CsPbBr3 is a representative Pb-based perovskite that has garnered significant interest due to its high quantum yield.5,6 However, the widespread commercialization of these substances has been impeded because of their instability and toxicity.7 To address this, researchers have explored various strategies to replace lead with non-toxic or low-toxic elements.8 Among these methods, using a monovalent metal cation (B+) and a trivalent metal cation (B3+) simultaneously for the heterovalent replacement of Pb2+ ions stands out as one of the most efficient approaches.9,10 In this instance, the double perovskite is represented by A2B(I)B(II)X6 (A = Cs+; B(I) = Ag+, Na+; B(II) = In3+, Sb3+, Bi3+; X = Cl−, Br−) with a distinctive structure and superior performance, which can be distinguished by a three-dimensional framework consisting of vicissitudinary corner-sharing octahedra [B+X6] and [B3+X6].11,12 Although the optical properties of those lead-free metal halide perovskite hosts is significantly inferior to that of Pb-based materials, there are more methods to modify the composition and spectrum by involving ion doping and alloying.13 Recently, Cs2NaInCl6 with excellent moisture, light, and thermal stabilities has attracted plenty of attention as one of the direct band gap double perovskites.14 Zeng et al. incorporated Sb3+ ions into Cs2NaInCl6 to adjust the band structure for obtaining efficient blue light.15 Nie et al. used Er3+ and Ho3+ ion co-doped Cs2NaInCl6:Sb3+ to achieve adjustable white light emission.16 As we know, the near-infrared (NIR) emission spectra of common rare earth activated ions Pr3+, Nd3+, Tm3+ and Yb3+ are too narrow, and the raw materials are expensive.17 Therefore, incorporating Cr3+ ions into lead-free metal halide perovskites is a wise decision because they have the capability to generate a broad range of emissions, spanning from 650 to 1350 nm when situated within a crystal field of weak octahedral coordination.18,19 Meanwhile, the selective capturing of invisible NIR light information encryption modes was expected to enable greater security levels and has widespread usage in daily life.Temperature, as a fundamental physical quantity, plays an important role in our daily lives.20 Therefore, temperature measurement technology has received significant attention and been developed.21 Optical temperature measurement is a non-contact, fast, and accurate method for measuring temperature, which has plenty of applications in industries, healthcare, and environmental sectors, providing us with an efficient and convenient means of temperature monitoring.22,23 The utilization of the luminescence intensity ratio (LIR) from the 4f–4f transitions of lanthanide elements is extensively employed as a widely adopted approach in optical temperature measurement for temperature sensing.24,25 Lanthanide elements have unique optical properties, for instance, longer emission lifetimes and narrower absorption/emission lines.26 However, the utilization of bandwidth (full width at half maximum (FWHM)) or spectral position (peak centroid) of emission bands for temperature sensing has been relatively limited in previous studies.27 Possible reasons include the minor temperature-induced band shifts or FWHM variations for 4f–4f transitions.28 To effectively overcome these limitations, a promising approach involves harnessing transition metal ions that demonstrate high sensitivity towards local coordination environments and consequently respond to the changes in lattice volume caused by variations in temperatures.29
In this study, we successfully synthesized a highly efficient phosphor that emits NIR light by incorporating Cr3+ ions into the Cs2NaInCl6 double perovskite structure using a convenient hydrothermal method. Using X-ray diffraction (XRD), the crystal structure of Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ double perovskite was determined, while morphological characterization was conducted by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis. Additionally, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) were performed to further analyze the electronic and crystal structures. The Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ double perovskite exhibited broadband NIR emission (λem = 960 nm, FWHM = 138 nm) under 292 nm excitation. Eventually, this material showcased its potential in NIR information encryption and optical temperature measurement in this work.
2. Experimental section
2.1 Materials
CsCl (99.9%, Aladdin), NaCl (99.9%, Aladdin), InCl3 (99.9%, Aladdin), CrCl3·6H2O (analytical pure, Chengdu Kelong Chemical Reagent Factory, China), hydrochloric acid (HCl, 37%, Chongqing Chuandong Chemical, China), and ethanol (analytical pure, Chongqing Chuandong Chemical, China) were used. The chemicals are procured commercially and employed without undergoing additional purification.2.2 Synthesis of Cs2NaInCl6:xCr3+ phosphors
Cs2NaInCl6:xCr3+ (x = 0, 0.03, 0.06, 0.09, 0.12, and 0.15) phosphors were synthesized via the solvothermal method. 2 mmol CsCl, 1 mmol NaCl, 1 − x mmol InCl3, and x mmol CrCl3·6H2O were dissolved in 12.5 mL of hydrochloric acid and then transferred into a 50 mL Teflon autoclave. The solution was heated at 180 °C for 12 h and then cooled to room temperature at a slow and consistent speed. Finally, the microcrystals were collected, washed multiple times with ethanol, and dried overnight in a vacuum furnace.2.3 Characterization
The utilized powders were all obtained by grinding in a mortar. The powder samples were subjected to the XRD (Cu Kα radiation λ = 1.54 Å) measurements at a constant scanning rate of 2° min−1. The Rietveld refinement was carried out with the assistance of the universal structure analysis system (Fullprof) program. The morphology and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analyses of the as-synthesized phosphor were performed by SEM. The XPS was performed by Thermo Scientific K-Alpha. The EPR measurements were carried out by using a conventional Bruker EMX PLUS spectrometer. Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) absorbance spectroscopy was carried out on a Agilent Carry 5000 spectrophotometer supplied with an integrating sphere. In addition, the photoluminescence excitation (PLE) spectra, photoluminescence (PL) emission spectra, PL quantum yield (PLQY), and decay lifetime were measured using a FLS1000 fluorescence spectrophotometer (Edinburgh Instruments Ltd, UK). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed through a Thermogravimetric Analyzer TGA STD Q600. Meanwhile, a standard Nikon Z30 camera and a NIR camera (Basler a2A1280-125μm) were employed to acquire visible and NIR images correspondingly.2.4 Computational method
We utilized density functional theory (DFT) to perform preliminary calculations.30 To account for the exchange–correlation effects among electrons, we utilized the generalized gradient approximation (GGA-PBE).31 A plane wave cut-off energy of 500 eV was employed for both structural optimizations and electronic calculations. The Monkhorst–Pack scheme was utilized to generate k-point meshes for various structures within the Brillouin zones, with a size of 12 × 12 × 12 for primitive Cs2NaInCl6.3. Results and discussion
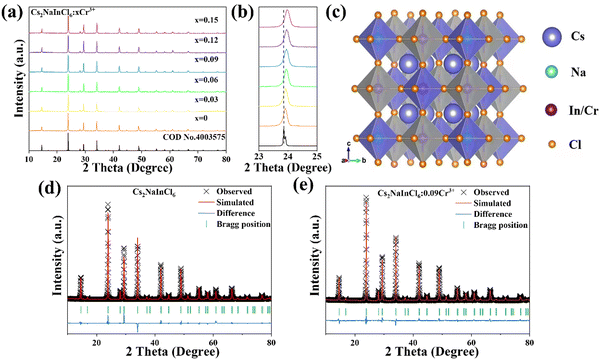
The XRD patterns of the prepared Cs2NaInCl6:xCr3+ (x = 0, 0.03, 0.06, 0.09, 0.12, and 0.15) samples are depicted in Fig. 1a. There are no observable additional diffraction peaks present in any of the samples, demonstrating that the doping of Cr3+ ions has no significant influence on the crystal structure of Cs2NaInCl6. Simultaneously, it is found that the characteristic diffraction peak (220) alters monotonically to a higher angle with an increase in the Cr3+ ion concentration (Fig. 1b). According to the known Bragg theory, Cr3+ (0.615 Å, CN = 6) with a smaller ionic radius replaces In3+ (r = 0.81 Å, CN = 6) with a larger ionic radius, resulting in the reduction of cell volume. Meanwhile, according to previous reports, it is suggested that the Cr3+ ion takes up the In3+ sites, which balances the charge and follows the rule of matching ionic radii.32 Therefore, the crystal structure diagram of Cs2NaInCl6:xCr3+ is shown in Fig. 1c, illustrating the face-centered cubic space group (Fm![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m) consisting of corner-connected octahedra [NaCl6] and [InCl6], with Cs+ occupying the outside spaces, which results in a three-dimensional structure. The Rietveld XRD refinements were conducted using the structural data for COD no. 4003575 as an original model for analyzing the cell parameters of the prepared samples, as illustrated in Fig. 1d and e. The excellent quality of refinement results (Rwp < 15%, Rp < 10%) revealed the single-phase structure of the as-prepared materials, as shown in Table 1. Additionally, the decrease in cell volume from 1167.917 to 1166.186 Å3 demonstrates that Cr3+ ions have been successfully acquired into the positions of In3+ ions.
m) consisting of corner-connected octahedra [NaCl6] and [InCl6], with Cs+ occupying the outside spaces, which results in a three-dimensional structure. The Rietveld XRD refinements were conducted using the structural data for COD no. 4003575 as an original model for analyzing the cell parameters of the prepared samples, as illustrated in Fig. 1d and e. The excellent quality of refinement results (Rwp < 15%, Rp < 10%) revealed the single-phase structure of the as-prepared materials, as shown in Table 1. Additionally, the decrease in cell volume from 1167.917 to 1166.186 Å3 demonstrates that Cr3+ ions have been successfully acquired into the positions of In3+ ions.
| Parameters | Cs2NaInCl6 | Cs2NaInCl6:0.09Cr3+ |
|---|---|---|
| Radiation type λ (Å) | X-ray, 1.5406 | X-ray, 1.5406 |
| 2 theta range (degree) | 10–80 | 10–80 |
| Space group |
Fm![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m m |
Fm![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m m |
| Crystal system | Cubic | Cubic |
| a = b = c (Å) | 10.53103 | 10.52582 |
| Volume (Å3) | 1167.917 | 1166.186 |
| α = γ = β (°) | 90.0000 | 90.0000 |
| R wp | 12.0% | 10.2% |
| R p | 9.23% | 7.37% |
| χ 2 | 4.27 | 3.17 |
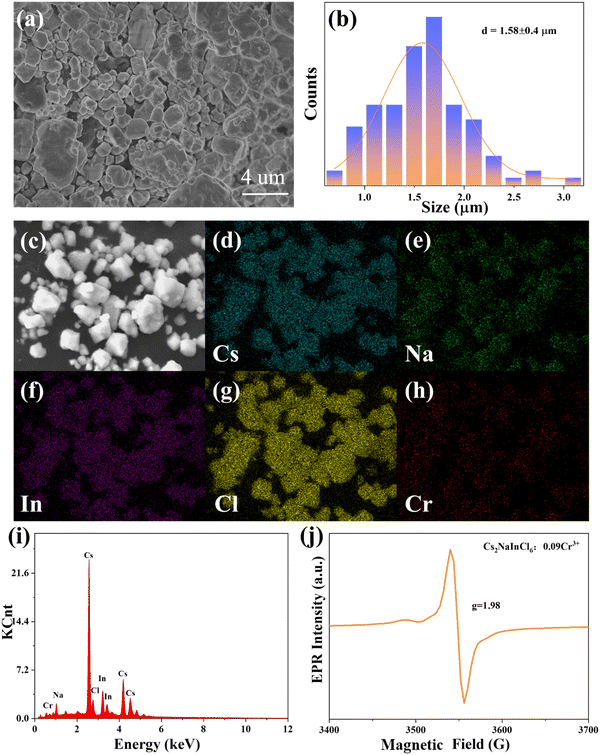
The morphology of the Cs2NaInCl6:0.09Cr3+ sample, which exhibited an irregular form with an average diameter of 1.58 ± 0.4 μm, is displayed in Fig. 2a and b. The Cs, Na, In, Cl, and Cr were uniformly dispersed over the surface of the sample, as portrayed in Fig. 2c–h. Moreover, Fig. 2i shows the EDS spectrum of the Cs2NaInCl6:0.09Cr3+ phosphor, revealing the existence of Cs, Na, In, Cl, and Cr peaks. The chemical environment of the oxidation state of the Cr ion in the host can be studied by EPR spectroscopy. The EPR spectrum of Cs2NaInCl6:0.09Cr3+ is presented in Fig. 2j, and the coupling pattern structure with a distinctive g-factor of 1.98 may demonstrate the presence of Cr3+ ions.33
The XPS analysis was conducted to further investigate the electronic properties and elemental construction of Cs2NaInCl6:0.09Cr3+. The obtained results confirmed the presence of all the basic elements in Cs2NaInCl6:0.09Cr3+ as illustrated in Fig. 3a–e. Specifically, the Cs 3d peak exhibited two components at the states of 3d3/2 (738.1 eV) and 3d5/2 (724.1 eV).34 Similarly, the In 3d core level exhibited two peaks at the binding energy at 452.8 and 445.2 eV, as specified to the states of In3+ 3d3/2 and 3d5/2.35 A peak at 1071.7 eV was assigned to Na 1s.36 The Cr 2p spectrum exhibited two separate peaks at 585.2 and 576.4 eV, corresponding to the orbitals of Cr3+ ions at the states of 2p1/2 and 2p3/2, respectively. The observed binding energy of the Cr 2p electrons was consistent with previous research conducted on octahedral Cr3+ ions.37 The above results clearly verify the successful preparation of Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ phosphors.
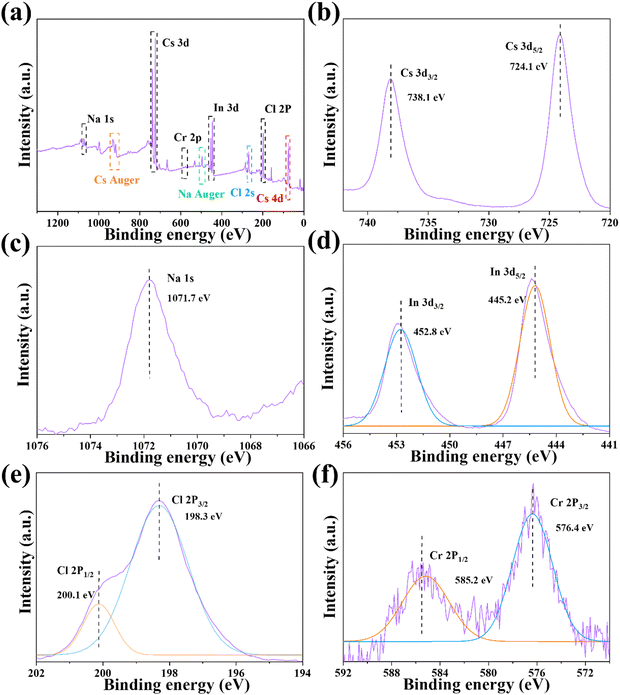 | ||
| Fig. 3 (a) XPS core-level spectra of the (b) Cs+ 3d, (c) Na+ 1s, (d) In3+ 3d, (e) Cl− 2p, and (f) Cr3+ 2p for the Cs2NaInCl6:0.09Cr3+ phosphor. | ||
The pristine and Cr3+ substituted compounds were analyzed for their electronic band structures using DFT simulation. Fig. 4a and b display the electronic band structures of Cs2NaInCl6. The Cs2NaInCl6 exhibits a direct electronic transition with the calculated band gap (Eg) of 3.04 eV, which is approximately equal to the previously calculated result (Eg = 2.96 eV).38 The Cl 3p orbitals are the primary origin of the valence band maximum, while the conduction band minimum was predominantly contributed by both the Cl 3p and In 5s orbitals. From the band structures of Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ as illustrated in Fig. 4c, the band gap for Cs2NaInCl6 host decreases from 3.04 to 2.79 eV. Meanwhile, we observe the formation of Cr 3d states in the proximity of the Fermi energy (Fig. 4d). The band gap change may be associated with a modification in strength as well as the nature of the host crystal and the effect of the energy level of doping ions.39 Even though it is semiqualitative in nature, the interpretation at the DFT level of theory provides crucial details on the placement of the chrome ion orbitals in the host band gap and provides insights into the performance of this material as a phosphor.
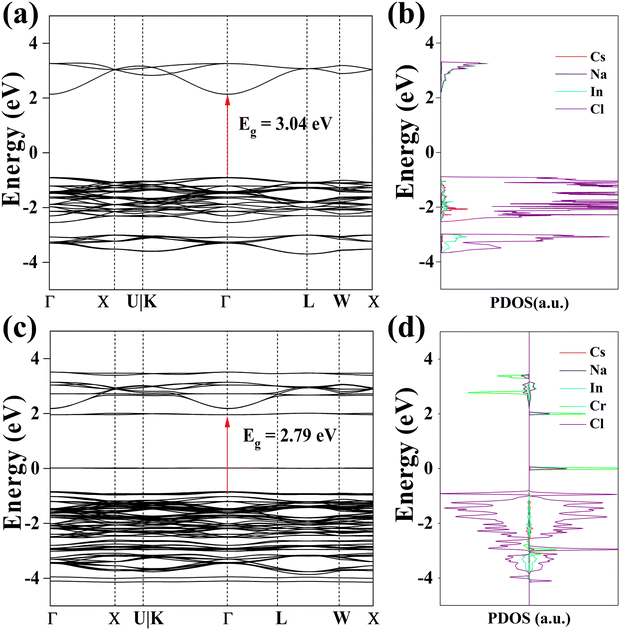 | ||
| Fig. 4 (a) Calculated band structure and (b) density of state of Cs2NaInCl6 host. (c) Calculated band structure and (d) density of state of Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+. | ||
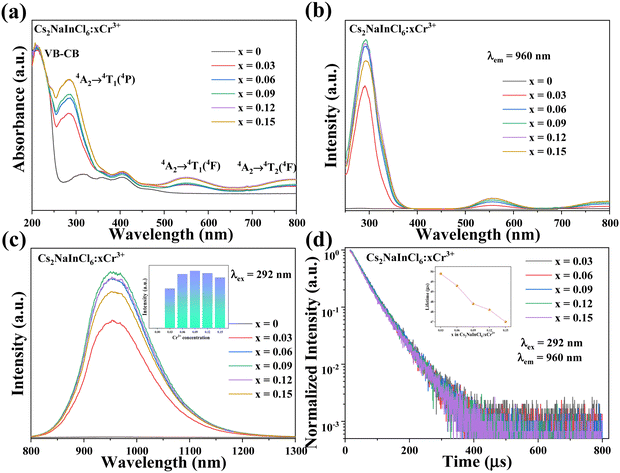
The PL properties of the synthesized products were subsequently investigated. Fig. 5a displays the UV-Vis absorption spectra of all the Cs2NaInCl6:xCr3+ (x = 0, 0.03, 0.06, 0.09, 0.12, and 0.15) samples. It is unambiguous from the absorption spectra that there is a peak apparent at around 221 nm, which belongs to the electron transitions from the host valence band to its conduction band. Meanwhile, the absorption bands at 285, 552, and 795 nm could be credited to the d–d transitions of 4A2 → 4T1(4P), 4A2 → 4T1(4F) and 4A2 → 4T2(4F) of Cr3+ ions.40 Furthermore, Fig. 5b shows the PLE spectra of Cs2NaInCl6:xCr3+. There are three excitation peaks that could be well matched to the Cr3+ absorption bands of the UV-Vis absorption under the emission wavelength of 960 nm. Specifically, these three bands were in the violet (about 292 nm), green (around 558 nm), and deep red (around 797 nm) regions. The correlation between concentration of Cr3+ ions and the intensity of PL emission is presented in Fig. 5b and c. The PL emission intensity exhibits an increased tendency with the increment of Cr3+ ion concentration and the maximum intensity was obtained at x = 0.09. At this concentration, the PL spectrum exhibited strong NIR emission centered at 960 nm with the FWHM of 138 nm assigned to the spin-allowed 4T2 → 4A2 transition of octahedrally coordinated Cr3+ ions.41,42 Meanwhile, the PL emission spectra do not exhibit noticeable alteration, which suggests that there is no effect of the Cr3+ ion concentration on the crystal field environment.43 Additionally, Fig. S1 (ESI†) illustrates a measured PLQY value of approximately 42.9% for Cs2NaInCl6:0.09Cr3+. By comparing some recent reports (Table 2), it is reasonable to consider that the obtained samples may be suitable for some optical applications.
| Sample | λ ex/λem (nm) | FWHM (nm) | Dq/B | PLQY (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr2InSbO6:Cr3+ | 558/955 | — | 1.96 | 14.5 | 18 |
| Cs2AgInCl6:Cr3+/Yb3+ | 365/1000 | 188 | 2.25 | 45.0 | 34 |
| Cs2AgInCl6:Cr3+ | 353/1010 | 180 | — | 22.0 | 50 |
| Ca2InTaO6:Cr3+ | 440/880 | 200 | 2.26 | 33.6 | 55 |
| NaGaP2O7:Cr3+ | 460/793 | 115 | 1.98 | 56.4 | 56 |
| KGaP2O7:Cr3+ | 460/815 | 127 | 1.96 | 74.7 | 57 |
| Sr9Ga(PO4)7:Cr3+ | 485/850 | 140 | — | 66.3 | 58 |
| Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ | 292/960 | 138 | 2.28 | 42.9 | This work |
The decay curves of Cs2NaInCl6:xCr3+ were measured at 960 nm emission wavelength and 292 nm excitation wavelength (Fig. 5d). Furthermore, the average lifetime could be calculated using the following eqn (1) and (2):44
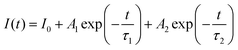 | (1) |
| τave = (A1τ12 + A2τ22)/(A1τ1 + A2τ2) | (2) |
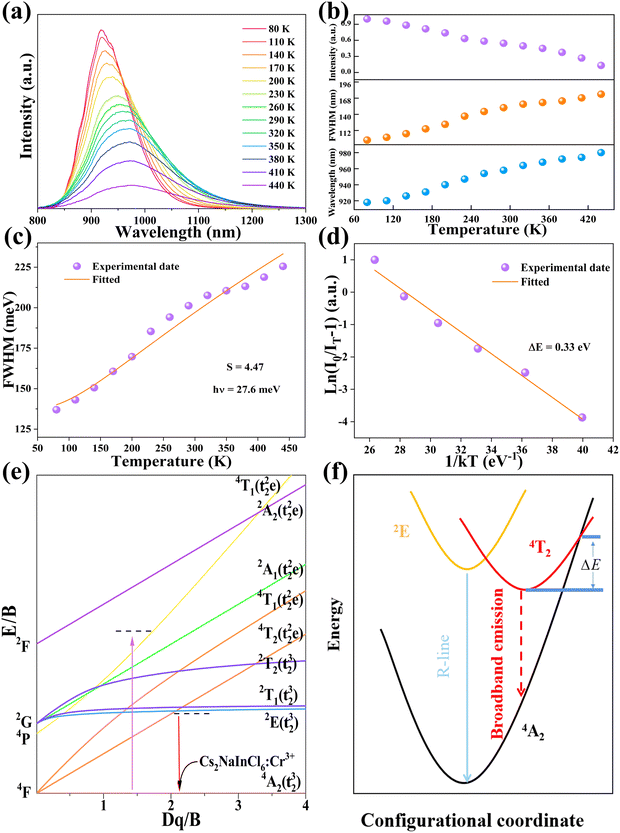
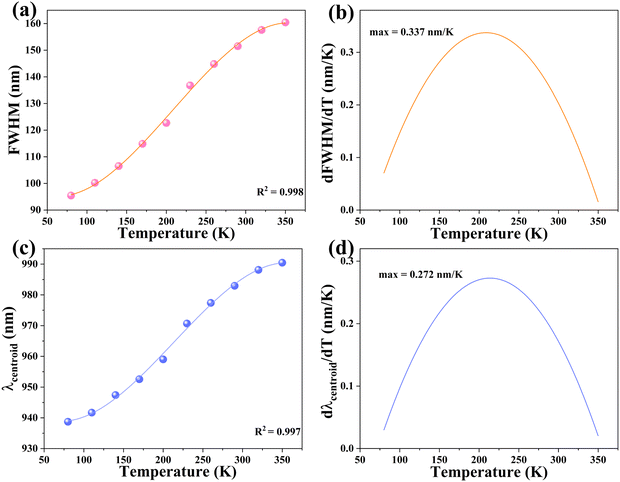
Temperature-dependent PL spectra of Cs2NaInCl6:0.09 Cr3+ are seen in Fig. 6a. It is visible that different temperatures result in the measurement of a wide emission band corresponding to the 4T2 → 4A2 spin-allowed transition of Cr3+ ions. The peak wavelength of PL spectra was red-shifted as the temperature was raised from 80 to 440 K, but the PL emission intensity was declined and the FWHM of the PL spectra was increased from 95 to 183 nm (Fig. 6b). Typically, by finding the relationship between FWHM and temperature, the coupling effect between electrons and phonons can be defined using eqn (3):46
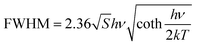 | (3) |
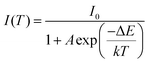 | (4) |
The PL characteristics of the Cr3+ ions are highly dependent on the crystal environment because they have the 3d3 configuration, in which the 3d electrons are not protected from their surroundings by outer-filled shells. Due to the lower crystal field stabilization energy of an octahedron compared to a tetrahedron in coordination, the Cr3+ ion prefers to occupy one in a crystal material.49 When Cr3+ ions are positioned in the core of coordinated octahedra, the effect of the host lattice on the luminescence properties of Cr3+ ions may be represented by the parameters of Dq and B, which are ascertained by using the subsequent eqn (5)–(7):49
| 10Dq = E(4T2) = E(4A2 → 4T2) | (5) |
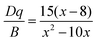 | (6) |
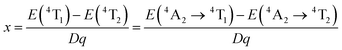 | (7) |
To assess the possible application in optical thermometers, the thermometric performance was evaluated by implementing the bandwidth (FWHM) and band shift of the 4T2 → 4A2 emission band of Cr3+ ions. Noteworthy is the fact that at 350 K, the FWHM and band centroid deviated from their temperature dependence, implying that the working temperature range was selected to be 80–350 K. The band-shift and FWHM parameters were both related to temperature and effectively fitted to polynomial formulas, with R2 = 0.998 and 0.997, respectively (Fig. 7a and c). In Table S1 (ESI†), the relevant fitting parameters are presented. The determined temperature are sensitivity values for the bandwidth (d(FWHM)/dT) as a relation of temperature are exhibited in Fig. 7b, revealing the maximal rate of the band broadening was 0.337 nm K−1 at 208 K. The sensitivity values based on the band-shift (d(λcentroid)/dT) were also calculated (Fig. 7d), showing that the maximal rate of the band-shifting was 0.272 nm K−1 at 213 K. Furthermore, the obtained sample has better sensitivity than previously discovered lanthanide-based luminous thermometers with the aid of the FWHM and emission band-shift.51–54
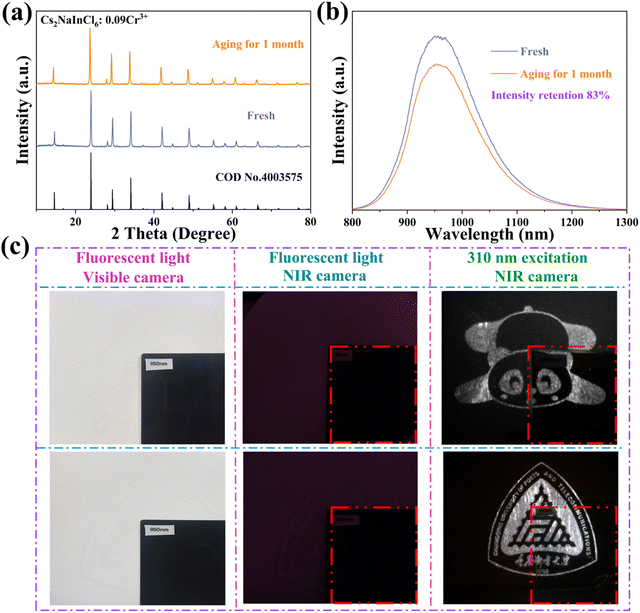
Along with the aforementioned optical properties, ensuring long-term stability in both the perovskite structure and its optical characteristics is essential for practical applications. To assess the resilience of the sample towards chemical and thermal stabilities, Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ was aged at room temperature for one month, after which the samples were retested. The obtained results demonstrate negligible changes in XRD patterns after this duration of aging (Fig. 8a). Furthermore, even after this period, the integrated PL intensity of Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ remained at 83% of its initial value (Fig. 8b). In addition, the thermal stability test of Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ was performed by TGA. The TGA curve of the Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ was measured from 25 to 800 °C (Fig. S2, ESI†). The results imply that the sample demonstrates exceptional thermal stability, as there is no weight fluctuation shift below 580 °C. Compared with organic–inorganic hybrid materials, Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ has higher stability against high temperatures.
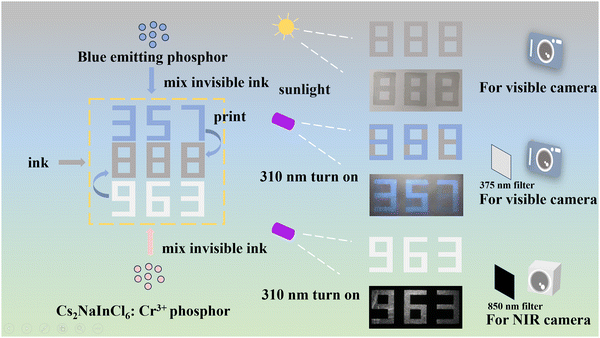
Eventually, the security ink based on the Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ powder was fabricated, and a screen printing technique was further utilized to produce intricate patterns. The luminescence patterns with NIR emission are displayed in Fig. 8c. Furthermore, we designed an information encryption mode using the material in conjunction with commercial blue phosphor (Fig. 9). In visible light, the “888” pattern was displayed. Under 310 nm excitation, the “357” pattern was displayed, indicating the emanated light from the blue phosphor, which reveals the first encryption mode. Simultaneously, using the NIR camera, the “963” pattern shows a second encryption mode that is imperceptible to the human eye. The NIR optical properties of the material improve the security of the information encryption, exhibiting unique advantages in the fields of anti-counterfeiting and information encryption.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, this work successfully synthesizes Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ double perovskite using the solvothermal method, and its structures, optical properties, luminescence mechanism, and applications were studied. Cs2NaInCl6:Cr3+ phosphors exhibit a broad range of NIR emission of 800–1300 nm upon excitation at 292 nm. The temperature-dependent PL emission spectra were analyzed to investigate the sensing sensitivity in both bandwidth and band-shift thermometry modes, achieving high sensitivity values of 0.337 nm K−1 for bandwidth thermometry and 0.272 nm K−1 for band-shift thermometry. Additionally, the material can be used to create patterns that demonstrate its potential for NIR information encryption applications.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The project was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (12004062), the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (KJZD-M202300601, KJZD-K202300612, and KJQN202100615) and the Venture and Innovation Support Program for Chongqing Overseas Returnees (CX2019085 and CX2022024).References
- A. Ho-Baillie, M. Zhang, C. F. J. Lau, F.-J. Ma and S. Huang, Untapped Potentials of Inorganic Metal Halide Perovskite Solar Cells, Joule, 2019, 3, 938–955 CrossRef CAS.
- X.-K. Liu, W. Xu, S. Bai, Y. Jin, J. Wang, R. H. Friend and F. Gao, Metal halide perovskites for light-emitting diodes, Nat. Mater., 2021, 20, 10–21 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Wang, S. Li, X. Liu, Z. Shi, X. Fang and J. He, Low-Dimensional Metal Halide Perovskite Photodetectors, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2003309 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Xiang, S. (Frank) Liu and W. Tress, A review on the stability of inorganic metal halide perovskites: challenges and opportunities for stable solar cells, Energy Environ. Sci., 2021, 14, 2090–2113 RSC.
- B. Zhang, L. Goldoni, J. Zito, Z. Dang, G. Almeida, F. Zaccaria, J. De Wit, I. Infante, L. De Trizio and L. Manna, Alkyl Phosphonic Acids Deliver CsPbBr3 Nanocrystals with High Photoluminescence Quantum Yield and Truncated Octahedron Shape, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 9140–9147 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Shi, Y. Wang, S. Zeng, Y. Cui and Y. Xiao, Surface Regulation of CsPbBr3 Quantum Dots for Standard Blue-Emission with Boosted PLQY, Adv. Opt. Mater., 2020, 8, 2000167 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Xiao, Z. Song and Y. Yan, From Lead Halide Perovskites to Lead-Free Metal Halide Perovskites and Perovskite Derivatives, Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, 1803792 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Chu, W. Ahmad, W. Liu, J. Yang, R. Zhang, Y. Sun, J. Yang and X. Li, Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskite Materials: A New Superstar Toward Green and Stable Optoelectronic Applications, Nano-Micro Lett., 2019, 11, 16 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Zhu, G. Pan, J. Zhao, K. Liu, W. Xue, Y. Wang, W. You, H. Gao, W. Xu and Y. Mao, High-Efficiency Dual-Mode Polychromatic Emission of Rare-Earth-Based Double Perovskite with Low Phonon Energy toward High-Level Anti-Counterfeiting and Information Encryption, Adv. Opt. Mater., 2023, 11, 2202019 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Igbari, Z. Wang and L. Liao, Progress of Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskites, Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9, 1803150 CrossRef.
- J. Luo, X. Wang, S. Li, J. Liu, Y. Guo, G. Niu, L. Yao, Y. Fu, L. Gao, Q. Dong, C. Zhao, M. Leng, F. Ma, W. Liang, L. Wang, S. Jin, J. Han, L. Zhang, J. Etheridge, J. Wang, Y. Yan, E. H. Sargent and J. Tang, Efficient and stable emission of warm-white light from lead-free halide double perovskites, Nature, 2018, 563, 541–545 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Ji, J. Klarbring, F. Wang, W. Ning, L. Wang, C. Yin, J. S. M. Figueroa, C. K. Christensen, M. Etter, T. Ederth, L. Sun, S. I. Simak, I. A. Abrikosov and F. Gao, Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskite Cs2AgBiBr6 with Decreased Band Gap, Angew. Chem., 2020, 132, 15303–15306 CrossRef.
- F. Locardi, M. Cirignano, D. Baranov, Z. Dang, M. Prato, F. Drago, M. Ferretti, V. Pinchetti, M. Fanciulli, S. Brovelli, L. De Trizio and L. Manna, Colloidal Synthesis of Double Perovskite Cs2AgInCl6 and Mn-Doped Cs2AgInCl6 Nanocrystals, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 12989–12995 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Zhou, Z. Liu, S. Fang, H. Zhong, B. Tian, Y. Wang, H. Li, H. Hu and Y. Shi, Efficient White Photoluminescence from Self-Trapped Excitons in Sb3+/Bi3+-Codoped Cs2NaInCl6 Double Perovskites with Tunable Dual-Emission, ACS Energy Lett., 2021, 6, 3343–3351 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Zeng, L. Zhang, Y. Xue, B. Ke, Z. Zhao, D. Huang, Q. Wei, W. Zhou and B. Zou, Highly Efficient Blue Emission from Self-Trapped Excitons in Stable Sb3+-Doped Cs2NaInCl6 Double Perovskites, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2020, 11, 2053–2061 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Nie, B. Zhou, S. Fang, H. Zhong, H. Li and Y. Shi, Efficient Multicolor and White Photoluminescence in Erbium- and Holmium-Incorporated Cs2NaInCl6:Sb3+ Double Perovskites, Chem. Mater., 2022, 34, 6288–6295 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Liu, G. Li, P. Dang, Q. Zhang, Y. Wei, H. Lian, M. Shang, C. C. Lin and J. Lin, Simultaneous Broadening and Enhancement of Cr3+ Photoluminescence in LiIn2SbO6 by Chemical Unit Cosubstitution: Night-Vision and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Detection Applications, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 14644–14649 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Zhao, L. Li, Z. Wu, Y. Wang, Z. Cao, F. Ling, S. Jiang, G. Xiang, X. Zhou and Y. Hua, Bifunctional near-infrared-emitting phosphors of chromium(III)-activated antimonates for NIR light-emitting diodes and low-temperature thermometry, J. Alloys Compd., 2023, 965, 171370 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhang, D. Huang, C. Huang, S. Liang and H. Zhu, Investigation on the Luminescent Property and Application of In2BP3O12: Cr3+ Broadband Near-Infrared Phosphor, Acta Chim. Sin., 2022, 80, 453–459 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wu, S. Zhan, J. Han and Y. Liu, Nanoscale Ultrasensitive Temperature Sensing Based on Upconversion Nanoparticles with Lattice Self-Adaptation, Nano Lett., 2021, 21, 272–278 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. B. Nair, A. Kumar, S. J. Dhoble and H. C. Swart, Synergistic effect from the dual oxidation states of europium in the color-tuning of Ca3Mg3(PO4)4: Eu2+, Eu3+ thermometric phosphor, Mater. Res. Bull., 2020, 122, 110644 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Wang, M. Liao, Q. Lin, M. Xiong, Z. Mu and F. Wu, A review on fluorescence intensity ratio thermometer based on rare-earth and transition metal ions doped inorganic luminescent materials, J. Alloys Compd., 2021, 850, 156744 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Wang, Z. Liang, J. Luo, Y. Yang, Z. Mu, X. Zhang, H. Dong and F. Wu, Ratiometric optical thermometer with high sensitivity based on dual far-red emission of Cr3+ in Sr2MgAl22O36, Ceram. Int., 2020, 46, 5008–5014 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Wu, L. Li, Y. Wang, F. Ling, Z. Cao, S. Jiang, G. Xiang, X. Zhou, Y. Hua and J. S. Yu, High-sensitivity luminescent thermometer based on Mn4+/Sm3+ dual-emission centers in double-perovskite tellurate, Ceram. Int., 2022, 48, 27664–27671 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhang, H. Zheng, J. Hu, F. Lu, X. Peng, R. Wei, F. Hu and H. Guo, Enhanced up-conversion luminescence and temperature sensing property of Ba Sr Lu4O9:Tm3+/Yb3+ phosphors, Ceram. Int., 2021, 47, 32290–32296 CrossRef CAS.
- C. D. S. Brites, P. P. Lima, N. J. O. Silva, A. Millán, V. S. Amaral, F. Palacio and L. D. Carlos, A Luminescent Molecular Thermometer for Long-Term Absolute Temperature Measurements at the Nanoscale, Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 4499–4504 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. M. Diaz-Rodriguez, D. A. Gálico, D. Chartrand, E. A. Suturina and M. Murugesu, Toward Opto-Structural Correlation to Investigate Luminescence Thermometry in an Organometallic Eu(II) Complex, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 912–921 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- U. Rocha, C. Jacinto Da Silva, W. Ferreira Silva, I. Guedes, A. Benayas, L. Martínez Maestro, M. Acosta Elias, E. Bovero, F. C. J. M. Van Veggel, J. A. García Solé and D. Jaque, Subtissue Thermal Sensing Based on Neodymium-Doped LaF3 Nanoparticles, ACS Nano, 2013, 7, 1188–1199 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. K. Amarasinghe and F. A. Rabuffetti, Bandshift Luminescence Thermometry Using Mn4+: Na4Mg(WO4)3 Phosphors, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 10197–10204 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Hafner, Ab-initio simulations of materials using VASP: Density-functional theory and beyond, J. Comput. Chem., 2008, 29, 2044–2078 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Kresse and J. Furthmüller, Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1996, 54, 11169–11186 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Zhang, Y. Liu, G. Liu and Z. Xia, Dopant and Compositional Modulation Triggered Broadband and Tunable Near-Infrared Emission in Cs2Ag1–xNax InCl6: Cr3+ Nanocrystals, Chem. Mater., 2022, 34, 3006–3012 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Mironova-Ulmane, M. G. Brik, J. Grube, G. Krieke, M. Kemere, A. Antuzevics, E. Gabrusenoks, V. Skvortsova, E. Elsts, A. Sarakovskis, M. Piasecki and A. I. Popov, EPR, optical and thermometric studies of Cr3+ ions in the α-Al2O3 synthetic single crystal, Opt. Mater., 2022, 132, 112859 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Chen, X. Zhang, J. Wei, L. Zhou, P. Chen, Q. Pang and J. Z. Zhang, Simultaneous enhancement of near infrared luminescence and stability of Cs2AgInCl6: Cr3+ double perovskite single crystals enabled by a Yb3+ dopant, Inorg. Chem. Front., 2022, 9, 4695–4704 RSC.
- F.-J. Meng and X.-M. Guo, Tuning the oxygen defects and Fermi levels via In3+ doping in SnO2-In2O3 nanocomposite for efficient CO detection, Sens. Actuators, B, 2022, 357, 131412 CrossRef CAS.
- M. A. Muñoz-Márquez, M. Zarrabeitia, E. Castillo-Martínez, A. Eguía-Barrio, T. Rojo and M. Casas-Cabanas, Composition and Evolution of the Solid-Electrolyte Interphase in Na2Ti3O7 Electrodes for Na-Ion Batteries: XPS and Auger Parameter Analysis, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7, 7801–7808 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Zhou, J. Luo, J. Fan, H. Pan, S. Zeng, L. Zhou, Q. Pang and X. Zhang, Luminescent properties and LED Application of Broadband Near-Infrared Emitting NaInGe2O6:Cr3+ phosphors, Ceram. Int., 2021, 47, 25343–25349 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhou, X. Rong, P. Zhang, M. S. Molokeev, P. Wei, Q. Liu, X. Zhang and Z. Xia, Manipulation of Bi3+/In3+ Transmutation and Mn2+-Doping Effect on the Structure and Optical Properties of Double Perovskite Cs2NaBi1−x InxCl6, Adv. Opt. Mater., 2019, 7, 1801435 CrossRef.
- K. Indumathi, S. Tamilselvan, L. Rajasekaran, A. D. J. David, G. S. Muhammad, G. Ramalingam and M. Biruntha, Structural and optical properties of Eu3+ doped Sr3Gd[PO4]3 phosphor white-LED application, Mater. Lett., 2022, 309, 131371 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Shao, X. Zhou, L. Li, Y. Wang, F. Ling, C. Jing, X. Tang and Z. Cao, Broadband near-infrared double-perovskite phosphor Sr2ScTaO6:Cr3+,Yb3+ for NIR pc-LED applications, Ceram. Int., 2023, S0272884223021995 Search PubMed.
- C.-H. Lu, Y.-T. Tsai, T.-L. Tsai, T.-S. Chan, X. Zhang and C. C. Lin, Cr3+-Sphere Effect on the Whitlockite-Type NIR Phosphor Sr9Sc(PO4)7 with High Heat Dissipation for Digital Medical Applications, Inorg. Chem., 2022, 61, 2530–2537 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Wang, S. Wang, T. Tan, J. Wang, R. Pang, D. Li, C. Li and H. Zhang, Efficient Cr3+-activated NaInP2O7 phosphor for broadband near-infrared LED applications, Inorg. Chem. Front., 2022, 9, 3692–3701 RSC.
- T. Yu, H. Sheng, S. Chen, J. Yuan, T. Deng, M. Wu, Y. Guo and Q. Zeng, A broadband near-infrared Sc1−x(PO3)3: X Cr3+ phosphor with enhanced thermal stability and quantum yield by Yb3+ codoping, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2022, 105, 3403–3417 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Miao, Y. Liang, Y. Zhang, D. Chen and X. Wang, Blue LED-Pumped Broadband Short-Wave Infrared Emitter Based on LiMgPO4: Cr3+, Ni2+ Phosphor, Adv. Mater. Technol., 2022, 7, 2200320 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Zhao, Z. Song and Q. Liu, Novel Cr3+-activated far-red emitting phosphors with β-Ca3(PO4)2-type structure for indoor plant cultivation, Int. J. Miner., Metall. Mater., 2022, 29, 1286–1294 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Y. Zhao, H. Cai, S. Y. Zhang, Z. Song and Q. L. Liu, Octahedron-dependent near-infrared luminescence in Cr3+-activated phosphors, Mater. Today Chem., 2022, 23, 100704 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Feng, L. Lin, R. Duan, J. Qiu and S. Zhou, Transition metal ion activated near-infrared luminescent materials, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2022, 129, 100973 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Malysa, A. Meijerink and T. Jüstel, Temperature dependent photoluminescence of Cr3+ doped Sr8MgLa(PO4)7, Opt. Mater., 2018, 85, 341–348 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Miao, Y. Liang, Y. Zhang, D. Chen, S. Yan, J. Liu and X.-J. Wang, Spectrally tunable and thermally stable near-infrared luminescence in Na3Sc2(PO4)3:Cr3+ phosphors by Ga3+ co-doping for light-emitting diodes, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2022, 10, 994–1002 RSC.
- F. Zhao, Z. Song, J. Zhao and Q. Liu, Double perovskite Cs2AgInCl6:Cr3+: broadband and near-infrared luminescent materials, Inorg. Chem. Front., 2019, 6, 3621–3628 RSC.
- A. Ćirić, S. Stojadinović and M. D. Dramićanin, Time-integrated luminescence thermometry of Eu3+ and Dy3+ doped YVO4, Sens. Actuators, Phys., 2019, 295, 450–455 CrossRef.
- J. Periša, Z. Ristić, W. Piotrowski, Ž. Antić, L. Marciniak and M. D. Dramićanin, All near-infrared multiparametric luminescence thermometry using Er3+, Yb3+-doped YAG nanoparticles, RSC Adv., 2021, 11, 15933–15942 RSC.
- T. Zheng, M. Runowski, N. Stopikowska, M. Skwierczyńska, S. Lis, P. Du and L. Luo, Dual-center thermochromic Bi2MoO6:Yb3+,Er3+,Tm3+ phosphors for ultrasensitive luminescence thermometry, J. Alloys Compd., 2022, 890, 161830 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Zheng, M. Sójka, M. Runowski, P. Woźny, S. Lis and E. Zych, Tm2+ Activated SrB4O7 Bifunctional Sensor of Temperature and Pressure—Highly Sensitive, Multi-Parameter Luminescence Thermometry and Manometry, Adv. Opt. Mater., 2021, 9, 2101507 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhang, W. Zhao, X. Zhang, Y. Li, W. Zhang, H. Wen and J. Zhong, Ultra-broadband near-infrared emission in the double-perovskite Ca2InTaO6:Cr3+ phosphor for light-emitting-diode applications, J. Lumin., 2023, 255, 119581 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhang, C. Li, J. Zhong, J. Wen and W. Zhao, Thermally Robust Broadband Near-Infrared Luminescence in the NaGaP2O7:Cr3+ Phosphor, ACS Appl. Opt. Mater., 2023, 1, 85–93 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhong, C. Li, W. Zhao, S. You and J. Brgoch, Accessing High-Power Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Using Cr3+ -Substituted Metal Phosphate Phosphors, Chem. Mater., 2022, 34, 337–344 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Zhao, H. Cai, Z. Song and Q. Liu, Structural Confinement for Cr3+ Activators toward Efficient Near-Infrared Phosphors with Suppressed Concentration Quenching, Chem. Mater., 2021, 33, 3621–3630 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3tc04453j |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |