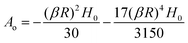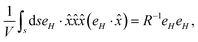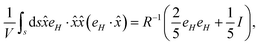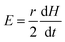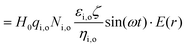DOI:
10.1039/D4TB00362D
(Paper)
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2024,
12, 7348-7356
On the origin of the biological effects of time varying magnetic fields: quantitative insights
Received
21st February 2024
, Accepted 10th June 2024
First published on 10th June 2024
Abstract
In a number of recently published experimental studies from our research group, the positive impact of magnetic stimuli (static/pulsed) on cell functionality modulation or bactericidal effects, in vitro, has been established. In order to develop a theoretical understanding of such magnetobiological effects, the present study aimed to present two quantitative models to determine magnetic Maxwell stresses as well as pressure acting on the cell membrane, under the influence of a time varying magnetic field. The model predicts that magnetic field-induced stress on the cell/bacteria is dependent on the conductivity properties of the extracellular region, which is determined to be too low to cause any significant effect. However, the force on the cell/bacteria due to the induced electric field is more influential than that of the magnetic field, which has been used to determine the membrane tension that can cause membrane poration. With a known critical membrane tension for cells, the field parameters necessary to cause membrane rupture have been estimated. Based on the experimental results and theoretically predicted values, the field parameters can be classified into three regimes, wherein the magnetic fields cause no effect or result in biophysical stimulation or induce cell death due to membrane damage. Taken together, this work provides some quantitative insights into the impact of magnetic fields on biological systems.
1. Introduction
The influence of magnetic field stimulation, either in static or pulsed mode, on biological systems has been experimentally studied at cellular, pre-clinical and clinical levels.1,2 The influence of a magnetic field on antitumor activity has also been analysed in vitro, in vivo and on human subjects.3–5In vitro experiments were conducted to understand the role of magnetic field parameters (e.g., intensity, frequency, and modulation) on two transformed cell lines (WiDr human colon adenocarcinoma, and MCF-7, human breast adenocarcinoma) and a non-transformed cell line (MRC-5 embryonal lung fibroblasts).6 Increased cell death that was morphologically consistent with apoptosis has been reported in these two transformed cell lines. As far as in vivo studies are concerned, 31% increase in survival time was obtained in mice that were exposed daily for 70 min to a modulated magnetic field (static field with superimposition of 50 Hz) of a time average total intensity of 5.5 mT. However, the mice bearing tumours were subjected to the same treatment for four weeks consecutively, where 40% inhibition of tumour growth was reported, along with a decrease in tumour cell mitotic index and proliferation activity.
Several effects of magnetic field stimulation at the cellular level have been reported using in vitro models. The exposure to a static field is known to reduce cell viability and inhibits cell growth. In bacterial cultures, application of a static magnetic field of 100 mT, applied at the log phase of bacterial growth, has been shown to inhibit the growth of S. epidermidis and E. coli on biomaterials.7 It has also demonstrated potential in the intelligent design of biomaterials using magnetoactive phase (such as Fe3O4).8 Some of the earlier studies reported conflicting results. For example, Tsuchiya et al. (1996) suggested that the growth of E. coli can be affected by a strong homogenous static magnetic field (7 T) and homogenous field strengths (5.2–6.1 T or 3.2–6.7 T).9 In the stationary growth phase, the cell number was two to three times higher than that of the control under a high magnetic field.
The effect of the homogenous field was weaker than inhomogeneous fields. Strong inhomogeneous static magnetic fields of 5.2–6.1 T improved the transcription activity of E. coli. Horiuchi et al. (2001) showed that in the presence of a strong inhomogeneous static magnetic field of 5.2–6.1 T, E. coli cell death occurred in the stationary phase. The suppression was found to depend on the addition of amino acids to the LB medium.10 In the case of pulsed magnetic fields, the effect on bacterial growth rate has been shown to be more drastic. For example, Boda et al.11 demonstrated that S. aureus and E. coli cultures, exposed to a high strength pulse magnetic field (≈4 T, 30 ms pulse), could exhibit up to 70% reduction in bacterial cell viability. Interestingly, the study recorded signs of necrotic cell death such as high ROS levels and bacterial membrane damage, while at the same time noting the absence of these effects in eukaryotes. Clearly, the effect of a magnetic field varies with the cell type and the stimulating field parameters (frequency and strength) induce an adverse response to prokaryotes, when compared to eukaryotes. This was further confirmed after an intermittent static magnetic field of 100 mT was found to enhance the differentiation of stem cells towards bone-like cells on HA-Fe3O4 magnetoactive biocomposites.1 These sets of reports indicate that there is a possible connection between the cellular effects of magnetic field (inhibition of bacterial growth, promoting stem cell differentiation) and clinical applications, such as in mending fractures and cranial stimulation. However, there is no consensus on the subject in the scientific community to date.
It needs to be reiterated here that several experimental studies were carried out with magnetic stimulation at several length scales in organisms (bacteria, cell, in vivo models, clinical applications), but the physical insights into the biomagnetic effects are not sufficiently understood. A few studies proposed a trans-membrane potential model for magnetic field effects,12,13 where the transmembrane potential changes across the membrane of a eukaryote or a prokaryote due to the presence of a non-uniform (and/or time varying field) field. Similar models can successfully explain observed cell responses such as deformation, orientation and membrane rupture in electric field stimulated conditions.14 Among other models to rationalise magneto-biological effects, the most widely applicable are the ion-interference model, which describes the interaction between a pulsed magnetic field and ion-protein complexes in the membrane, stochastic resonance, eddy current and magnetohydrodynamic models.15 There are also reports of magnetic field-induced stress on the membrane. For example, Krichen et al.16 reported that magnetic field-induced Maxwell stress can cause compressive strain on the cell membrane and can cause a reduction in cell membrane thickness. Based on the mathematical model, they showed that the membrane thickness decreases from 5 nm to 4.88 nm with an increase in the magnetic field strength from 0 to 50 A m−1. The lower the relative magnetic permeability, the higher the reduction in membrane thickness due to the magnetic field. Therefore, it is expected that below a certain thickness, the cell membrane will undergo poration at high stress, due to the applied magnetic field.
The impact of magnetic field treatment for cancer treatment was also investigated at the cellular level, in animal models and on human subjects. In a pilot study, human subjects with previously treated advanced cancer were exposed to static magnetic fields. Based on follow up clinical assessment of the exposed subjects, the study outcomes indicated that magnetic field exposure schedules can be safely prescribed for cancer treatment.3,4 A deeper examination of the published studies indicates that both microscopic (ion spin effects, ion-complex interactions, stochastic effects) and macroscopic (eddy currents, polarization and magnetohydrodynamics, magnetic pressure) models are necessary to describe the observed effects of magnetic field, in addition to the electromagnetic model in the biological context.17–19 Against this background, the present study attempted to quantitatively describe some of the macroscopic effects of both static and non-uniform magnetic fields, using a spherical cell model.20 We shall first determine the magnetic Maxwell stresses, considering the cell as an electrically conducting biological object, being placed in a magnetic field. Other objectives of the present study are to quantitatively analyse the induced Lorentz forces and pressure around a biological cell, when exposed to a static magnetic field (without any induced electric field). In developing our understanding, we will consider two specific cases, (i) where no electric current is present in the system and (ii) where an ionic current is present. We will be particularly interested in the magnitude and nature of such induced Lorentz forces/pressure, as that will potentially impact the mechanotransduction processes involved in cellular signalling-mediated functionality changes, i.e., differentiation. Another objective of this study is to develop a similar quantitative understanding on the influence of the pulsed magnetic field on cell membrane tension, where the effect of the induced eddy current will be considered. With the basis on these theoretical results, we will make an attempt to correlate our earlier experimental results on the effect of a magnetic field on cells, in vitro.
2. Maxwell stress and Lorentz force on a spherical cell due to an oscillating magnetic field
In establishing the theoretical foundation of the magnetobiological effect on a cell in a cellular microenvironment, we first consider a biological cell to be spherical and immersed in a culture medium. A time varying magnetic stimulus of the form H(t) is delivered to the cellular microenvironment. The electrical conductivities of the media inside and outside the cell membrane are taken to be σi and σo, respectively. The radius of the cell and the cell membrane thickness are ‘R’ and ‘d’, respectively, and ‘r’ is taken as an arbitrary radial distance from the centre.
The cell and the culture media are kept in a uniform magnetic field H, directed along the Z axis, which is perpendicular to the paper's plane (XY plane), as shown schematically in Fig. 1. In our model, we assume that the cell/bacteria have no inherent magnetic properties implying that the relative magnetic permeability is zero and that there are no significantly large permanent magnetic moments in our system. Under such an assumption, the applied magnetic field is uniform. In this calculation, we have also assumed the absence of any ionic currents. Therefore, in the presence of a static magnetic field, there are no electric currents in the system and hence, there is no induced stress on the cell membrane, while a time varying magnetic field will have both the induced electric field and the associated stress.
 |
| | Fig. 1 Model of a spherical cell under the influence of time varying magnetic field (H) inducing an electric field (E), which results in a force (F) on the membrane and a corresponding stress Sk which also acts on the membrane. The electrical parameters are conductivity (σ) and permittivity (ε) with subscripts ‘i’ and ‘o’ denoting inside and outside the cell, respectively. ‘ds’ is a differential surface element at a distance ‘r’ and ‘R’ is cell radius. | |
2.1 Maxwell stress on a cell/bacteria in an oscillating magnetic field
Based on the assumptions for the model described earlier, the electric and magnetic fields in the vicinity of the cell/bacteria under the influence of an oscillating magnetic field H = H0![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) cos
cos![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ωt can be written in terms of Maxwell equations in the absence of free charges as,
ωt can be written in terms of Maxwell equations in the absence of free charges as,| |  | (1) |
| |  | (2) |
where, J is the current density, μ0 is the magnetic permeability of free space and ε is the dielectric permittivity of the system.
Substituting J = σE and neglecting the ε∂E/∂t term (since εω ≪ σ) and taking the curl of eqn (2) in terms of H, we get the following relationship between the system properties and the applied magnetic field,
| |  | (3) |
Simplifying this for the case, when
εω ≪
σ, the second term in the RHS of
eqn (3) goes to zero and by inserting the curl of the electric field, this becomes,
| |  | (4) |
For an oscillating magnetic field of the form
H =
Ho![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif)
cos
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ωt
ωt = (
Ho/2)(e
iωt + e
−iωt), we get,
where, the parameter is defined as
β = √(−
iσωμ0)
This magnetic field can be expressed in terms of magnetic potential (A), which satisfies H = ∇ × A. ‘A’ can be further represented as a pseudovector whose direction depends on the direction (eH) of the applied magnetic field H as, A = Ai∇ × (ϕr)eH, where ϕr = sin(βr)/r is a spherically symmetric solution for the Poisson equation,
The solution for the magnetic field in the cell/bacteria, which is treated here as a conducting particle can be expressed in terms of magnetic potential
A and
ϕ and is presented in Appendix A.
Following the determination of Maxwell stress, used in our previous study,14 we can write the expression for the instantaneous stress ‘S’ on the cell/bacteria due to a magnetic field as,
| |  | (7) |
This stress is due to the action of the magnetic field on the entire volume of the cell/bacteria and
eqn (7) is a general expression that can be used to determine the stress at any given point in the vicinity of the particle. However, to determine the total extracellular stress due to the external magnetic field on the bacteria/particle, the instantaneous stress must be averaged over the entire surface of the particle, which can be written as,
21| |  | (8) |
where,
V is the particle volume and ‘
s’ is the surface of the particle and ‘
n’ is a unit vector pointing outward and normal to the surface. The expression for the stress on the particle can be further simplified and is presented in Appendix B. The deviatoric component of the Maxwell stress, which is responsible for fluctuations in the membrane, will then be
| | 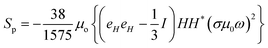 | (9) |
The total stress on the cell/bacteria that causes membrane deformation can be directly calculated from the above expression and it depends on the magnetic field and system properties.
2.2 Lorentz force on a cell/bacteria in an oscillating magnetic field
In order to estimate the force on a cell/bacteria due to magnetic field stimulation, we first consider an oscillating magnetic field H of the form,| | H = H0![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) sin(ωt) sin(ωt) | (10) |
where, H0 and ω are the amplitude and angular frequency, respectively.
Following Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, there will be an induced electric field E at a radial distance r, in the anti-clockwise direction (for a positive direction of H), as shown in Fig. 1. If ds is the differential element along the perimeter of the eddy-current circle with the radius r, one can write the expression for the induced electric field by integrating along the loop of length, s = rθ (see Appendix C).
The drift current density owing to this electric field, J(r), will be in a specific direction, as shown in Fig. 1. The electrophoretic charge mobility, by assuming an infinitesimally small Debye layer width, around a moving charge is given by
| |  | (11) |
Here,
μ,
ε,
η and
ζ are the mobility, dielectric permittivity, dynamic viscosity and zeta potential across the Debye layer, respectively. Also, o and i are suitable suffixes, depending on whether one is considering the parameter outside or inside the cell, as per
Fig. 1. Considering the ionic charge and number of ions per unit volume to be
q and
N, respectively, we have the ionic conductivity as,
| |  | (12) |
The induced current density J(r), therefore is,
| |  | (13) |
The total Lorentz force, from which the Maxwell stress can be derived, can be written as,
| | | Fi,o(r) = Ji,o(r) × H(r) | (14) |
Applying the right-hand rule, one sees that the AC magnetic field compresses and stretches the cell membrane along its diameter(s). In our calculation, we consider no lag of this ‘cell membrane oscillation’ with respect to the applied AC magnetic field as a first approximation. The cell membrane oscillates with the same angular frequency ω. The magnitude of the Lorentz force, responsible for this oscillating stress is F, as shown in Fig. 1.
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of magnetic field induced Maxwell stress
The magnitude of the stress on the cell/bacteria derived in Section 2.1 is very small. An estimate of the stress for a cell/bacteria of size of the order of 1 μm with the extracellular region having conductivity, σ = 0.1 S m−1 exposed to a magnetic field of the order of 1 T at a frequency of 10 Hz results in a Sp ≈ 10−8 Pa, with |βR| ≪ 1 being satisfied for this system. It is more useful to look at how this parameter |βR| varies with the system properties to get a better idea of how changes in system properties influence the effect of the magnetic field. We can define a parameter ‘(βR)2’ that relates the stress with the characteristic system properties, magnetic field stimulation and size of the cell/bacteria as,where, μ is the permeability of the extracellular matrix/substrate, σ is the conductivity of the culture media/substrate and R is the size of the cell/bacteria and ω is the angular frequency of the stimulating field. This parameter (βR)2, when plotted with respect to the frequency of the magnetic field for different conductivities (highly conducting 104 S m−1, moderately conducting 0.1 S m−1 and insulating 10−5 S m−1) with R = 1 μm, is shown in Fig. 2. This provides an important insight into how the material properties affect cells/bacteria during magnetic field stimulation. Based on the parameter, it is possible to predict the effectiveness of stress due to magnetic fields. In this case, the effect of magnetic field induced stresses will be significant when (βR)2 ≈ 1.0. Assuming that the cell/bacteria is surrounded by ECM or it is adhered on a biomaterial substrate, it is possible to predict the effect of magnetic field by looking at the variation in (βR)2. It is seen that in all three types of extracellular matrices (ECM) or biomaterial substrates with different conductivity properties, the term (βR)2 is not close to 1, especially at higher frequencies. However, it is seen that lower frequency stimulation with conducting ECM results in higher values implying that magnetic stimulation leads to more stress in a conducting environment (ECM) at lower frequencies.
 |
| | Fig. 2 Variation of the parameter (βR), a measure of the stress effect of magnetic field on a cell/bacteria with a size of the order of 1 μm at various frequencies for three different types of substrates differentiated based on their conductivity viz. good conductor – 104 S m−1, moderate conductor – 0.1 S m−1 and insulator – 10−6 S m−1. | |
3.2 Effect of frequency and magnetic field on Lorentz force on the cell
Oscillating magnetic fields induce electric fields in the system that can cause membrane damage due to electric field induced force/tension in cells/bacteria. Following the theoretical framework presented in the previous section for the determination of induced current density (Section 2.3), one can find the following explicit expression for the Lorentz force starting from eqn (14) (see Appendix C),| |  | (16) |
Therefore, the mathematical expression for the Lorentz force at the cell membrane will be as follows,| |  | (17) |
The divergence of this force per unit volume will lead to mechanical oscillations, resulting in a pressure wave, which obeys the following inhomogeneous wave equation,22| |  | (18) |
Here, cS is the velocity of sound in the medium. It can be easily verified that the right-hand side of the above equation is space independent,| |  | (19) |
Of course, a trial solution can be a pressure which is time dependent but space independent. This also makes Pascal's law valid (i.e., absence of any pressure gradients in the ionic liquid).
Then, the evaluation of the wave eqn (18) by substituting for P = P0·sin(2ωt) and Fi,o will be,
| |  | (20) |
Then, the magnetically induced pressure becomes,
| |  | (21) |
Therefore, the entire volume of the ionic liquid (cell culture media), which revolves about the central axis of the spherical cell, will get radially displaced – creating a vortex in the immediate cellular microenvironment. It is also borne in mind that this picture is compatible with that of the incompressible fluid. Therefore, the pressure on the cell membrane (P) is,
| |  | (22) |
The variation of this pressure can be visualized by plotting the maximum pressure [sin(2
ωt) = 1] with respect to the magnetic field (
Ho) at different frequencies, as shown in
Fig. 3. This analysis assumes that the speed of sound in media (1525 m s
−1) is similar to that of water at 37 °C. It is to be noted here that as the frequency of the signal increases, the pressure effect diminishes, indicating that higher frequency field stimulation exerts a negligible force on the cell membrane. Furthermore, the effect of this pressure on the whole cell can be deduced. At zero magnetic field, the volume of the cell
V0 and in the presence of a magnetic field, the pressure in the cell as well as the change in cell volume, and the situation qualitatively resemble that of a balloon, wherein, air is being pumped in or out and follows the ideal gas law,
PbVb =
Mb. Here, the subscript b is for balloon. The right-hand side of the above equation,
M is a function of the number of (air) molecules inside the balloon. When air is blown into the balloon, its inside pressure and size both increase. In the above equation, Boyle's law does not hold, and each parameter,
Pb,
Vb, and
Mb increases. Similarly, the periodic volume change of the cell in an alternating magnetic field depends critically on the value of
M. At zero magnetic field, let us assume that the equilibrium pressure on the cell membrane is
P0. Until now, we were assuming
P0 to be zero, however, in reality,
P0 has a finite value which can be modelled to be independent of the magnetic field.
 |
| | Fig. 3 The maximum membrane tension for sinusoidal magnetic field stimulation with varying frequency, determined using eqn (24), showing three different regions based on the effect of magnetic field on the biological material and the corresponding variation in pressure at the membrane due to the Lorentz force with respect to magnetic field (H) at different frequencies as determined using eqn (22). | |
Therefore, the two equations that govern the pressure and volume change of the cell in the absence and presence of AC magnetic fields are, P0V0 = M0 and (P0 + P)V = M. In these equations, P0, V0, and P are known. Therefore, if one can know the change in the number of molecules inside the cell, ΔM, determining V from the above equations become straightforward. Such consideration allows us to write the following expression, ΔM = M − M0. Once the volume V is known, one can calculate whether the AC magnetic field induced pressure will deform or rupture the cell membrane. This can be done by considering the elastic stiffness of the cell membrane (Y), and the tensile strength per unit length of the membrane material (T0). From the new volume V, the new cell radius r/ and the new cell perimeter S/ along the XY plane can be calculated as, 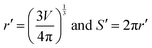 .
.
Therefore, the strain in the cell membrane material can be calculated and from there, one can derive the stress as,
| |  | (23) |
Here, S = 2πR.
Such a concept of ions, entering or exiting a cell, from or to the cellular microenvironment is valid in the biological context. This is because the cells communicate chemically with each other via the cell signalling process. The ions move through the cell membrane following a diffusion dominated mechanism.
However, the force at the cell membrane, owing to the AC magnetic field induced intracellular pressure change can be quantified using the standard relation between hoop stress/circumferential stress (PH) and radial stress (P) as,  . The hoop stress is also given, in terms of the membrane tensile strength per unit length (T),
. The hoop stress is also given, in terms of the membrane tensile strength per unit length (T),  . From these relationships, one can arrive at an expression for membrane tension (T) as,
. From these relationships, one can arrive at an expression for membrane tension (T) as,  . Substituting for the magnetic field induced intra-cellular pressure P,
. Substituting for the magnetic field induced intra-cellular pressure P,
| | 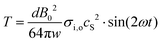 | (24) |
Putting the values such as,
d = 10 nm,
σ ∼ 10
−1 S m
−1,
B0 ∼ 4 T, and
w = 2π
f, where,
f = 10 Hz, and
cS ∼ 1520 m s
−1, one has maximum
T,

, which is negligible as compared to the known critical membrane tension which is of the order of 1 mN m
−1.
In order to get a complete picture of this effect of magnetic field over a wider range of frequencies, the behaviour of Tmax, similar to that of pressure, is plotted together in Fig. 3. The dependence of membrane tension on magnetic field strength and frequency is shown in Table 1. The results plotted in Fig. 3 clearly show regions where the parameters of magnetic field stimulation can be predicted to have no effect in addition to the regions with parameters usually used for biological stimulation. Assuming a critical tension for the cell membrane to be about 1 mN m−1, a magnetic field of 10 T, applied at a frequency of 0.1 Hz can cause membrane rupture. It follows from the behaviour of pressure and membrane tension due to magnetic field that only high intensity and low frequency stimulation can induce rupture in the cell membrane, whereas higher frequency signals (even at high magnetic field) exhibit a negligible effect.
Table 1 Frequency and magnetic field strength dependence of membrane tension on a cell under the influence of a magnetic field, as determined using theoretical analysis presented in this study
| 10 Hz magnetic field (mT) |
Membrane tension (mN m−1) |
AC frequency of 100 mT magnetic field (Hz) |
Membrane tension (mN m−1) |
| 25 |
1.9 × 10−5 |
0.05 |
0.6 |
| 50 |
3.8 × 10−5 |
0.075 |
0.4 |
| 75 |
5.6 × 10−5 |
0.1 |
0.3 |
| 100 |
7.5 × 10−5 |
0.25 |
0.12 |
| 250 |
1.9 × 10−4 |
0.5 |
0.06 |
| 500 |
3.8 × 10−4 |
0.75 |
0.04 |
| 750 |
5.6 × 10−4 |
1 |
0.03 |
| 1000 |
7.5 × 10−4 |
25 |
1.2 × 10−3 |
| 2000 |
1.5 × 10−3 |
50 |
6 × 10−4 |
| 3000 |
2 × 10−3 |
75 |
4 × 10−4 |
| 4000 |
3 × 10−3 |
100 |
3 × 10−4 |
3.3 Comparison between theoretical predictions and experimental observations
As can be seen in Section 3.1, the effect of magnetic field in terms of pressure causing membrane tension, depends not only on the field parameters (intensity, frequency, shape), but also on the electrical properties of the medium and the size of the living system (cell/bacteria). However, the size effects are not apparent while examining the pressure and membrane tension due to magnetic field stimulation. This effect of size is apparent in the observed effects of magnetic field stimulation on bacterial cells and tissues, as summarized in Table 2. Fig. 3 shows the linear variation of membrane pressure with magnetic field strength (H) for different frequencies. Since the cell, in general, is broadly non-magnetic, the relationship between magnetic field and membrane pressure is linear. With the knowledge of membrane pressure, we have determined the membrane tension, which is the shear component of pressure. Based on the membrane tension, magnetic fields can be divided into three broad regions with respect to the effect it has on biological systems viz. region (a) where no magnetic field effect is observed (B < 10−3 T), (b) which is relevant to biophysical stimulation is between 10−3 and 1 T and (c) beyond the order of magnitude of 1 T, membrane rupture and its associated effects (cell apoptosis, necrosis) are observed (Fig. 3). This is in close agreement with experimental results with a static magnetic field (100 mT) and time varying magnetic fields (pulse, 1 T),1,7,8,10,11 and magnetic fields less than 1 T elicit a favourable effect on cells in culture whereas higher strength pulse magnetic fields result in a higher degree of destructive effects such as apoptosis in smaller sized bacteria as compared to larger eukaryotic cells.
Table 2 Summary of observed magnetobiological effects in vitro, as published in recent studies
| Magnetic field parameters |
Cells/bacteria |
Observed effects |
Ref. |
| 4 T, 30 successive pulses |
S. aureus, E. coli |
Reduction in bacterial viability, membrane rupture |
11
|
| 100 mT, static magnetic field, 4 h exposure |
S. aureus, E. coli |
Reduction in bacterial viability |
7 and 8
|
| 100 mT, static magnetic field, 30 minutes exposure every 24 h for 28 days |
Human mesenchymal stem cells |
Differentiation towards bone-like cells |
1
|
4. Conclusions
This study presents quantitative models to determine the effect of time varying magnetic fields on biological cells, as they experience magnetic field induced Maxwell stress and Lorentz forces due to the induced electric field in the cellular microenvironment. While the magnitude of the Maxwell stress was found to be small in this case, of importance were analyzed in more detail. Based on such ab initio calculations, we note that the parameter, βR (a combination of field stimulation and properties of the cell/bacteria) determines the extent of the effect of magnetic field on cells/bacteria. This commensurates well with the published experimental studies, where bactericidal effects are observed for βR ≈ 1. Furthermore, theoretical predictions of the forces of the cell/bacteria experience were made along with the field parameters that are necessary to overcome membrane tension and cause poration. In analysing experimentally observed magnetobiological effects, the force and resulting tension on the cell membrane were determined using the theoretical model. Such analyses allow the prediction of field parameters, needed to cause membrane breakdown. Based on magnetic field parameters, the existence of three distinct regions in the observed field effects viz. negligible effect, biophysical stimulation, and membrane poration, were predicted, that agree reasonably well with the experimental results.
Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the equations, appendices and relevant references.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Appendices
Appendix A: Solution for the magnetic field in terms of magnetic potential
| |

| (A1) |
where, ϕ′ and ϕ′′ refer to the first and second derivatives of the potential ϕ(r) and ![[x with combining circumflex]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0078_0302.gif) is the unit normal vector along x and is defined by
is the unit normal vector along x and is defined by  . Since, ϕ(r) is a solution to the Poisson equation, the second derivative can be expressed in terms of ϕ and ϕ′ as,
. Since, ϕ(r) is a solution to the Poisson equation, the second derivative can be expressed in terms of ϕ and ϕ′ as,
Substituting this back in the expression for H, we get,
| |  | (A2) |
The magnetic field outside the cell/bacteria satisfies both, ∇·
H = 0 and ∇ ×
H = 0 and the field can be expressed as a gradient of a potential, since the curl is 0. This implies that the potential satisfies the Laplace equation (solenoidal condition). The magnetic field outside the cell/bacteria can be described by the following expression,
| |  | (A3) |
The boundary condition for the continuity of the magnetic field at the surface of the cell/bacteria at
r =
R provides the conditions for the relationship between the constants
Ai and
Ao,
These two equations can be solved for Ai and Ao to get,
| |  | (A4) |
| |  | (A5) |
The limiting value of Ao at |βR| ≪ 1 is,
and at |
βR| ≫ 1 the constant
Ao is,
Appendix B: Derivation of Maxwell stress due to magnetic field
We start with the definition of total stress on the particle due to the magnetic field,| |  | (B1) |
The expression for total stress can be simplified using indicial notation as follows,
| |  | (B2) |
Similarly,
| | 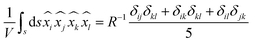 | (B3) |
Using these identities in the expression for the stress, we get,
| | 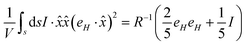 | (B4) |
With these transformations, we can expand the expression for Sp as,
| | 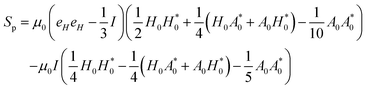 | (B5) |
Here, the terms proportional to

correspond to the uniform normal stress difference due to the magnetic field in the absence of cell/bacteria. With this correction, the deviatoric stress on the cell/bacteria due to the magnetic field is,
| |  | (B6) |
In the limit |βR| ≪ 1, the expression for Sp reduces to,
Substituting for
β, we get the final expression for the deviatoric stress on cell/bacteria due to the magnetic field in terms of H and system parameters,
| |  | (B7) |
Appendix C: Determination of Lorentz force due to magnetic field
Consider E due to the presence of an oscillating magnetic field that can be written as| |  | (C1) |
Here, s = rθ, since the closed loop integral is with respect to θ, where r is constant, ds = r·dθ.
Therefore, one arrives at the following expression,
or
The time-derivative of the magnetic field can be written as,
| |  | (C2) |
The force due to the induced current density can be written as,
| | | Fi,o(r) = Ji,o(r) × H(r) | (C3) |
The above equation simplifies to the following form,
| |  | (C4) |
Acknowledgements
BB acknowledges the financial support from Abdul Kalam National Innovation Fellowship of Indian National Academy of Engineering. In addition, AKD and BB acknowledge the SPARC research program, “Electrical stimulation with electroactive biomaterials as therapeutic strategy for intractable bone and neurodegenerative diseases”, funded by the Government of India.
References
- S. K. Boda, G. Thrivikraman and B. Basu, Magnetic field assisted stem cell differentiation–role of substrate magnetization in osteogenesis, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015, 3(16), 3150–3168 RSC.
- S. Naskar, Chandan, D. Baskaran, A. N. Roy Choudhury, S. Chatterjee, S. Karunakaran, B. S. Murthy and B. Basu, Dosimetry of pulsed magnetic field towards attaining bacteriostatic effect on Enterococcus faecalis: Implications for endodontic therapy, Int. Endod. J., 2021, 54(10), 1878–1891 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Tofani, M. Cintorino, D. Barone, M. Berardelli, M. M. De Santi, A. Ferrara, R. Orlassino, P. Ossola, K. Rolfo and F. Ronchetto, Increased mouse survival, tumor growth inhibition and decreased immunoreactive p53 after exposure to magnetic fields, Bioelectromagnetics, 2002, 23(3), 230–238 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Tofani, D. Barone, M. Berardelli, E. Berno, M. Cintorino, L. Foglia, P. Ossola, F. Ronchetto, E. Toso and M. Eandi, Static and ELF magnetic fields enhance the in vivo anti-tumor efficacy of cis-platin against Lewis lung carcinoma, but not of cyclophosphamide against B16 melanotic melanoma, Pharmacol. Res., 2003, 48(1), 83–90 CAS.
- C. Sun, H. Yu, X. Wang and J. Han, A pilot study of extremely low-frequency magnetic fields in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Effects on survival and palliation of general symptoms, Oncol. Lett., 2012, 4(5), 1130–1134 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Tofani, D. Barone, M. Cintorino, M. M. de Santi, A. Ferrara, R. Orlassino, P. Ossola, F. Peroglio, K. Rolfo and F. Ronchetto, Static and ELF magnetic fields induce tumor growth inhibition and apoptosis, Bioelectromagnetics, 2001, 22(6), 419–428 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Bajpai, N. Saha and B. Basu, Moderate intensity static magnetic field has bactericidal effect on E. coli and S. epidermidis on sintered hydroxyapatite, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part B, 2012, 100(5), 1206–1217 CrossRef PubMed.
- I. Bajpai, K. Balani and B. Basu, Synergistic effect of static magnetic field and HA-Fe3O4 magnetic composites on viability of S. aureus and E. coli bacteria, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part B, 2014, 102(3), 524–532 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Tsuchiya, K. Nakamura, K. Okuno, T. Ano and M. Shoda, Effect of homogeneous and inhomogeneous high magnetic fields on the growth of Escherichia coli, J. Ferment. Bioeng., 1996, 81(4), 343–346 CrossRef CAS.
- S.-i Horiuchi, Y. Ishizaki, K. Okuno, T. Ano and M. Shoda, Drastic high magnetic field effect on suppression of Escherichia coli death, Bioelectrochemistry, 2001, 53(2), 149–153 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. K. Boda, K. Ravikumar, D. K. Saini and B. Basu, Differential viability response of prokaryotes and eukaryotes to high strength pulsed magnetic stimuli, Bioelectrochemistry, 2015, 106, 276–289 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Ye, M. Cotic, E. E. Kang, M. G. Fehlings and P. L. Carlen, Transmembrane potential induced on the internal organelle by a time-varying magnetic field: a model study, J. Neuroeng. Rehabil., 2010, 7, 1–15 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Ye, M. Cotic and P. L. Carlen, Transmembrane potential induced in a spherical cell model under low-frequency magnetic stimulation, J. Neural Eng., 2007, 4(3), 283 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Ravikumar, V. Kumaran and B. Basu, Biophysical implications of Maxwell stress in electric field stimulated cellular microenvironment on biomaterial substrates, Biomaterials, 2019, 209, 54–66 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
-
V. N. Binhi, Magnetobiology: Underlying physical problems, 2002 Search PubMed.
- S. Krichen, L. Liu and P. Sharma, Biological cell as a soft magnetoelectric material: Elucidating the physical mechanisms underpinning the detection of magnetic fields by animals, Phys. Rev.
E, 2017, 96(4), 042404 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Binhi, Y. D. Alipov and I. Y. Belyaev, Effect of static magnetic field on E. coli cells and individual rotations of ion–protein complexes, Bioelectromagnetics, 2001, 22(2), 79–86 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Zablotskii, T. Polyakova, O. Lunov and A. Dejneka, How a high-gradient magnetic field could affect cell life, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6(1), 37407 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Zablotskii, T. Polyakova and A. Dejneka, Cells in the non-uniform magnetic world: how cells respond to high-gradient magnetic fields, BioEssays, 2018, 40(8), 1800017 CrossRef PubMed.
-
L. D. Landau, J. S. Bell, M. Kearsley, L. Pitaevskii, E. Lifshitz and J. Sykes, Electrodynamics of continuous media, Elsevier, 2013 Search PubMed.
- V. Kumaran, A suspension of conducting particles in a magnetic field–the particle stress, J. Fluid Mech., 2020, 901, A36 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Ziolkowski, S. Gratkowski and A. R. Zywica, Analytical and numerical models of the magnetoacoustic tomography with magnetic induction, COMPEL Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng., 2018, 37(2), 538–548 CrossRef.
|
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |
Click here to see how this site uses Cookies. View our privacy policy here.  c,
V.
Kumaran
c,
V.
Kumaran
 d and
Bikramjit
Basu
d and
Bikramjit
Basu
 *e
*e
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) cos
cos![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ωt can be written in terms of Maxwell equations in the absence of free charges as,
ωt can be written in terms of Maxwell equations in the absence of free charges as,



![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) cos
cos![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ωt = (Ho/2)(eiωt + e−iωt), we get,
ωt = (Ho/2)(eiωt + e−iωt), we get,

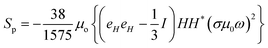
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) sin(ωt)
sin(ωt)










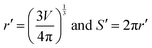 .
.
 . The hoop stress is also given, in terms of the membrane tensile strength per unit length (T),
. The hoop stress is also given, in terms of the membrane tensile strength per unit length (T),  . From these relationships, one can arrive at an expression for membrane tension (T) as,
. From these relationships, one can arrive at an expression for membrane tension (T) as,  . Substituting for the magnetic field induced intra-cellular pressure P,
. Substituting for the magnetic field induced intra-cellular pressure P,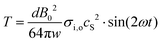
 , which is negligible as compared to the known critical membrane tension which is of the order of 1 mN m−1.
, which is negligible as compared to the known critical membrane tension which is of the order of 1 mN m−1.

![[x with combining circumflex]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0078_0302.gif) is the unit normal vector along x and is defined by
is the unit normal vector along x and is defined by  . Since, ϕ(r) is a solution to the Poisson equation, the second derivative can be expressed in terms of ϕ and ϕ′ as,
. Since, ϕ(r) is a solution to the Poisson equation, the second derivative can be expressed in terms of ϕ and ϕ′ as,





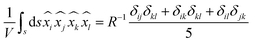
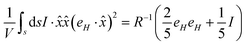
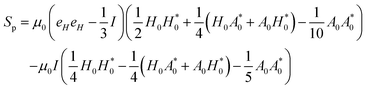
 correspond to the uniform normal stress difference due to the magnetic field in the absence of cell/bacteria. With this correction, the deviatoric stress on the cell/bacteria due to the magnetic field is,
correspond to the uniform normal stress difference due to the magnetic field in the absence of cell/bacteria. With this correction, the deviatoric stress on the cell/bacteria due to the magnetic field is,