Incorporation of halogens (Cl, Br, and I) in an Li–P–S–O system for exploring new sulfide solid electrolytes with high conductivity and superior electrochemical performance in solid-state batteries†
Hari
Raj
 ab,
Audric
Neveu
ab,
Audric
Neveu
 a,
Christian
Jordy
c,
Vincent
Pelé
c and
Valerie
Pralong
a,
Christian
Jordy
c,
Vincent
Pelé
c and
Valerie
Pralong
 *ab
*ab
aUniversité de Caen Normandie, ENSICAEN, CNRS UMR 6508, CRISMAT, Normandie Univ., 14000 Caen, France. E-mail: audric.neveu.kirsch@gmail.com; valerie.pralong@ensicaen.fr; hari.raj@ensicaen.fr
bRéseau sur le Stockage Electrochimique de l’Énergie (RS2E), 80000 Amiens, France
cSAFT, 111-113 Bd Alfred Daney, 33074 Bordeaux, France. E-mail: christian.jordy@saftbatteries.com
First published on 14th October 2024
Abstract
Solid electrolytes (SEs) with high conductivity and better stability against lithium metal are the most important requirements for successful commercialization of solid-state battery (SSB) technology. Therefore, in the search for new SEs with the above-mentioned qualities, halogen elements (Cl, Br, and I) were explored in an Li–P–S–O system to prepare Li10GeP2S12 (LGPS)-structured SEs. Among all the prepared SEs, Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Br0.1 and Li3.3PS3.7O0.3I0.1 compositions showed the highest conductivities of 0.77 mS cm−1 and 0.93 (≈1.0) mS cm−1, respectively, at 25 °C. These compounds also showed superior stability against lithium metal in symmetric and full SSB cells tested with an LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 (NCA) cathode and graphite anode. Generally, the instability of sulfide-based SEs in an ambient environment is a major issue, whereas our prepared compounds Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Br0.1 and Li3.3PS3.7O0.3I0.1 showed 5 times higher stability under ambient environment conditions as compared to non-doped Li3.2PS3.7O0.3. In situ EIS study performed on the as-prepared full SSBs and after charge–discharge cycles revealed the contribution of interfacial reactions to impedance. Higher interfacial resistances in the full SSB with the Li-metal anode compared to those with the graphite anode were also revealed. The in situ EIS study confirmed that the Li3.3PS3.7O0.3I0.1 solid electrolyte formed the most stable interface with NCA, graphite and Li metal. Finally, postmortem analysis of the full SSB cell and an SE–Li interfacial study conducted using SEM and elemental mapping revealed morphological changes in the electrodes and electrolytes before and after charge–discharge cycles. In summary, the present work reports new sulfide-based solid electrolytes with high conductivity, better air/moisture stability, and excellent interfacial stability.
Introduction
Solid-state batteries (SSBs) are considered safer than Li-ion batteries because of the use of solid electrolytes (SEs) in SSBs instead of flammable organic liquid based electrolytes.1 Furthermore, the ultimate goal for SSBs is to use Li metal directly as an anode for achieving high energy density.2,3 However, Li-metal-dendrite formation is a major issue in Li-ion batteries, but it is expected to be suppressed in SSBs owing to the solid nature of the electrolyte.4To achieve this goal, various types of solid electrolytes have already been reported for SSBs, comprising oxides, sulfides, halides, and polymers, which differ in their properties, advantages, and disadvantages.5,6 Among these solid electrolytes, sulfide-based solid electrolytes have certain advantages over others considering their high conductivity and the ductile nature of sulfides.7,8 Because of the ductile nature of sulfide electrolytes, they provide more favorable conditions for solid-state battery fabrication through just cold pressing without any further sintering process needed.9 Kanno et al. reported a Li10GeP2S12 (LGPS)-structured sulfide electrolyte that exhibited an ionic conductivity of 1.2 × 10−2 S cm−1 at room temperature, which was comparable to the conductivity of organic liquid electrolytes.10,11 Despite its high conductivity, the Li10GeP2S12 electrolyte suffers from poor cyclability in solid-state batteries because of the reduction of Ge4+ ions to Ge0 and its instability against the lithium metal anode. Moreover, germanium (Ge) is a rare and expensive element, which limits the industrial application of Li10GeP2S12.12–14 To overcome the issues of the Li10GeP2S12 solid electrolyte, several solutions have been applied, such as replacing Ge with other elements (Sn or Si) to afford Li10SnP2S12,15 Li11Si2PS12,16 and Li10Si0.3Sn0.7P2S12.17 However, the substitution of Ge with Sn or Si cannot solve the issue of instability with the Li metal due to the reduction of M4+ ions to M0 (M = Ge, Sn, Si).18 In the search for a more stable solid electrolyte with an LGPS-type structure, Kanno's group19 reported an electrolyte with the composition Li9.6P3S12 (i.e., Li3.2PS4) by considering the mixed oxidation state (+4.8) of phosphorous (P) instead of +5. The Li3.2PS4 electrolyte demonstrated better stability with Li metal and a higher coulombic efficiency compared to the Li10GeP2S12 electrolyte. Later, to further improve the Li3.2PS4 electrolyte, a partial substitution of S with O was also performed to obtain Li3.2PS3.7O0.3 with an ionic conductivity of ∼1.2 × 10−4 S cm−1 at room temperature.12 The partial substitution of S with O helped attain an LGPS phase with higher purity.
Furthermore, halogen elements have also been incorporated in the structure of LGPS to improve the ionic conductivity, with Li9.54Si1.74P1.44S11.7Cl0.3 showing the highest ion conductivity, i.e., up to 2.5 × 10−2 S cm−1 at room temperature.19,20 Fluorine doping has also been explored in LGPS solid electrolytes to reduce the interfacial reactions and dendrite growth.21,22 Recently, halogen atoms (Br, I) were explored in a Li–P–S system and it was reported that Li10P3S12Br and Li10.25P3S12.25I0.75 offered better conductivity and stability with Li metal.23 Many studies have reported on the doping of different halogen elements in different solid electrolytes to improve the ionic conductivity, capacity, and cycle life, while at the same time, studies have reported reduced interfacial reactions and capacity loss.24–29
It is considered that halogen elements can play an important role in tuning the ionic conductivity of sulfide solid electrolytes due to their unique properties, including (i) weaker interaction of the negative monovalent halogen ions with Li ions compared to divalent S and O, resulting in faster Li-ion conduction, (ii) larger radius of halogen anions (Br, I), leading to longer ionic bonds and higher polarizability, which facilitates Li-ion migration, and (iii) larger ionic radius of Br and I, which can provide additional pathways for Li-ion diffusion.23,30 By considering the reported benefits of halogen doping in solid electrolytes, and further exploring Li3.2PS3.7O0.3 (LPSO), we synthesized a series of solid electrolytes by incorporating halogen atoms (Li, Br, and I) in a Li–P–S–O system with the composition of Li3.2+yPS3.7O0.3Xy (X = Cl, Br, I, y = 0.1, 0.2).
Experimental section
Materials synthesis
The Li3.2+yPS3.7O0.3Xy (X = Cl, Br, I, y = 0, 0.1, 0.2) compounds were synthesized using the precursors Li2S (Alfa Aesar, 99.9%), P2S5 (Sigma Aldrich, 99%), P2O5 (Alfa Aesar, 99.99%), Pred (Sigma Aldrich, 99.99%), LiCl (Sigma Aldrich, >99%), LiBr (Sigma Aldrich, 99.99%), and LiI (Sigma Aldrich, 99.95%) using a mechanochemical method. The synthesis process was motivated by previously reported papers.12,19 The whole synthesis process was performed inside a glove box filled with high purity argon gas with moisture/H2O and O2 levels less than 0.1 ppm. Initially, all the precursors were weighted according to stoichiometry, and a total precursor weight of 2.5 g was transferred to a 20 mL ZrO2 jar for ball milling using ZrO2 balls with a 10 mm diameter. The total ball milling time was 135 h and was carried out using a planetary milling Fritsch Pulverisette 7 system at a speed of 500 rpm. However, in practice the effective ball milling time was actually 45 h as the program used 5 min running intervals with a 10 min pause. The milling process was stopped after every 22.5 h of total ball milling (i.e., 7.5 h of effective ball milling) and the ZrO2 jar was placed inside the glove box for scratching off the material from the jar's walls. The scratched material was ground in a mortar pestle for 10 min and XRD data were collected each time to observe the intermediate changes before starting the next cycle of ball milling. A similar process was repeated multiple times for a total of 45 h (7.5 h × 6) effective ball milling. After 45 h of effective ball milling, the prepared amorphous powder materials were pressed into pellets inside the glove box using 1 ton pressure. These pellets were vacuum-sealed inside the carbon-coated quartz tube and calcined at 220 °C for 4 h at a heating rate of 100 °C h−1. The calcination temperature was selected based on the DSC results. After cooling down to room temperature, the sealed tube was placed inside a glove box and the annealed pellets were ground in a mortar pestle to obtain the final crystalline powder.Materials characterization
XRD measurements of the Li3.2+yPS3.7O0.3Xy (X = Cl, Br, I, y = 0, 0.1, 0.2) compositions were carried out using a Rigaku Miniflex system (Cu Kα1 = 1.5405 Å and Cu Kα2 = 1.5444 Å) using an air-sensitive sample holder, in which the Kapton film was always at 90° to the X-ray beam. The phase identification of the prepared compounds was done using an X'Pert High Score Plus system combined with the COD, PDF-2, and ISCD databases. For detailed structural analysis, Rietveld refinement was performed using FullProf software.The thermal properties of the precursors and crystalline materials of the Li3.3PS3.7O0.3X0.1 (X = Cl, Br, I) and Li3.2PS3.7O0.3 compounds were investigated from 30 °C to 450 °C by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) combined with thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) using a Netzsch STA 449F3 system, in which the powder samples were kept inside the alumina crucible and heated under an argon atmosphere at a heating rate of 2 °C min−1.
The density of the compacted pellets was measured before the conductivity tests by a geometric method. The density was determined using the formula:  , where m is the mass of the pellet and V is the volume of the pellet. The volume of the pellet was calculated using the formula V = (A × h) or πr2h, where, A, r, and h are the surface area, radius, and thickness of the pellets, respectively. The relative densities of the Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Cl0.1, Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Br0.1, Li3.3PS3.7O0.3I0.1, and Li3.2PS3.7O0.3 compounds were 94.0%, 94.0%, 94.5%, and 94.5%, respectively, compared with density of Li3.2PS4 (1.85 g cm−3).
, where m is the mass of the pellet and V is the volume of the pellet. The volume of the pellet was calculated using the formula V = (A × h) or πr2h, where, A, r, and h are the surface area, radius, and thickness of the pellets, respectively. The relative densities of the Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Cl0.1, Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Br0.1, Li3.3PS3.7O0.3I0.1, and Li3.2PS3.7O0.3 compounds were 94.0%, 94.0%, 94.5%, and 94.5%, respectively, compared with density of Li3.2PS4 (1.85 g cm−3).
The ionic conductivity of the newly synthesized materials Li3.3PS3.7O0.3X0.1 (X = Cl, Br, I) and Li3.2PS3.7O0.3 was determined by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) using a BioLogic VMP3 analyzer in the frequency range from 1.0 MHz to 0.1 Hz with an amplitude of 50 mV. For the EIS measurements, first, 200 mg of solid electrolyte powder was pressed into a pellet of 10 mm diameter inside the glove box by applying a pressure of 188 MPa. Then, the pellet was vacuum-sealed inside the plastic bag and further compacted by an isostatic pressure of 9.0 tons. Both sides of the compacted pellet were gold-coated to prepare blocking cells (Au/SE/Au). The pellet sample was placed inside the controlled environment sample holder (CESH) and the sample holder was put inside the intermediate temperature system (ITS) for the conductivity measurements in the range of −40 °C to 80 °C. The samples were placed in the holder inside an argon gas-filled glove box to avoid any potential trace amount of oxygen and moisture inside the holder.
Furthermore, the room temperature ionic conductivity of all the samples was also measured at 25 °C directly inside the battery cell (steel/SE/steel) used for the electrochemical study. For that, 40 mg of solid electrolyte powder was kept inside the battery cell with a 7 mm diameter and pressed at a pressure of 255 MPa. Constant pressure was maintained during the measurement by tightening the screws of the cell.
The measured impedance spectra (Nyquist plots) recorded at −40 °C were fitted to an appropriate electrical equivalent circuit [(R‖Q1) + Q2] for all the samples by the least-squares method using Z-fit Ec-Lab software. However, the total resistance (R) at room temperature was determined from the intersection of the spike and Z-axis of the Nyquist plots. The total conductivity was calculated from the resistance R and geometry of the pellets using the formula  , where R is the total resistance, and l and A are the thickness and area of the pellet, respectively.31
, where R is the total resistance, and l and A are the thickness and area of the pellet, respectively.31
The electrochemical measurements of Li3.3PS3.7O0.3X0.1 (X = Cl, Br, I) and Li3.2PS3.7O0.3 compounds were carried out in a symmetric cell (Li/SE/Li) configuration at different current rates. In the critical current density (CCD) test program, the SSB cells were left to rest for 5 h at OCV to stabilize the solid interface between the lithium metal and solid electrolytes, and a constant current was applied for 30 min at each step before increasing the current. The current was continuously increased until short circuiting of the cells due to lithium dendrites formation.
Electrochemical studies of a full solid-state battery in a (NCA + SE)/SE/(graphite + SE) cell configuration using LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 (NCA) as a cathode and graphite as the anode were conducted on a BioLogic VMP3 analyzer. Both the cathode and anode materials were mixed with the solid electrolyte (SE) in the weight ratio of 70![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30 to ensure good contact among the electrodes and electrolyte materials. For the SSB cell fabrication, about 40 mg of solid electrolyte (SE) powder was pressed inside the battery cell with 255 MPa of pressure for 1 min. Thereafter, about 8.5 mg of a mixture of graphite and SE was put over the surface of the pressed electrolyte and again pressed at 255 MPa for 1 min. Similarly, about 8 mg of a mixture of NCA and SE was put over the other surface of the solid electrolyte, and a similar pressure was applied. Finally, all screws of the cell were tightened to maintain constant pressure on the SSB cell during the measurements. Galvanostatic charge–discharge cycles were recorded using the BioLogic system at a current rate of C/10 (1C = 278.94 mA g−1), corresponding to about 0.39 mA cm−2.
30 to ensure good contact among the electrodes and electrolyte materials. For the SSB cell fabrication, about 40 mg of solid electrolyte (SE) powder was pressed inside the battery cell with 255 MPa of pressure for 1 min. Thereafter, about 8.5 mg of a mixture of graphite and SE was put over the surface of the pressed electrolyte and again pressed at 255 MPa for 1 min. Similarly, about 8 mg of a mixture of NCA and SE was put over the other surface of the solid electrolyte, and a similar pressure was applied. Finally, all screws of the cell were tightened to maintain constant pressure on the SSB cell during the measurements. Galvanostatic charge–discharge cycles were recorded using the BioLogic system at a current rate of C/10 (1C = 278.94 mA g−1), corresponding to about 0.39 mA cm−2.
For the symmetric cell fabrication, about 50 mg of SE powder was pressed inside the battery cell at a pressure of 255 MPa for 1 min. Thereafter, thin layers of Li metal were placed over both sides of the solid electrolyte for making the cell configuration as Li/SE/Li, and finally the battery cell was tightened to ensure adequate pressure during cycling.
The microstructures of the prepared powders and pellets were determined by scanning electron microscopy (ZEISS Supra55 FEG). The microstructures of the pellets were recorded after the EIS study, whereby the pellets were cut in half to record images from cross-sectional areas.
The amount of H2S generated from the prepared solid electrolyte samples was measured with a H2S sensor (Croncow, Gasman) by exposing the samples in ambient atmosphere for 2 h. For the H2S measurements, about 40 ± 5 mg of solid electrolyte powder was pelletized in a die of 6 mm diameter at a pressure of 255 MPa and placed inside a 4000 cm3 air-tight vessel. In order to ensure a constant humidity level, 20 mL of H2O was also placed inside the desiccator. The generated gas was recorded in ppm, which was then converted to cm3 g−1 according to the weight of the sample.
Results and discussion
In the present work, we tried to explore the various possibilities to find new compositions with an LGPS-type structure having the least impurity/secondary phases in the targeted LGPS-structured chemical composition Li3.2+yPS3.7O0.3Xy (X = Cl, Br, I and y = 0, 0.1, 0.2). We started the study with a small amount of single-element doping in the Li3.2PS3.7O0.3 phase, which we further extended for multi-elements and higher contents of the halogen. The XRD patterns of all the prepared samples according to the Li3.2+yPS3.7O0.3Xy (X = Cl, Br, I and y = 0, 0.1, 0.2) composition are given in Fig. 1(a). It can be seen that the samples doped with a small amount of a single element had the maximum purity and adapted LGPS-type structures, which were indexed with ICSD (# 30![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 161) and the space group P42/nmc using references from previously published work.12,19,23,31 However, apart from the Li2S secondary phase that is always observed in LPSO compounds,12 the halogen-doped samples also showed some additional peaks. However, the intensity of the Li2S peak at 31.0° decreased with Cl and Br doping and completely vanished in the LPSOI sample.
161) and the space group P42/nmc using references from previously published work.12,19,23,31 However, apart from the Li2S secondary phase that is always observed in LPSO compounds,12 the halogen-doped samples also showed some additional peaks. However, the intensity of the Li2S peak at 31.0° decreased with Cl and Br doping and completely vanished in the LPSOI sample.
 | ||
| Fig. 1 (a) XRD patterns of Li3.3PS3.7O0.3X0.1 (X = Cl, Br, and I) and Li3.2PS3.7O0.3 compounds, (b) Le Bail Rietveld refinement graphs, (c) change in lattice parameters and cell volume with different halogens, (d) DSC results of the precursors after ball milling, (e) DSC results of the prepared compounds to show the stability temperature range, (f) crystal structure of the original LGPS,32 (g) crystal structure of the LGPS-type Li3.2PS3.7O0.3,33 and (h) crystal structure of the LGPS-type Li3.3PS3.7O0.3X0.1.23 | ||
One additional unidentified XRD peak at 24.45° was observed for Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Cl0.1 and at 25.2° for Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Br0.1, respectively. In addition, the sample Li3.3PS3.7O0.3I0.1 showed impurity peaks at 25.0°, 29.3°, 43.9°, 46.8°, and 51.2°, which were identified as being close to the iodine (I2) phase, according to the ICSD database (Ref. # 01-079-2355). When we tried to perform refinement by including the iodine phase, the refinement did not improve the results. Therefore, we could not reach on a firm conclusion on this phase. We also tried doping two halogen elements together (Br and I, y = 0.1), (Br and I, y = 0.2), (Cl and Br, y = 0.2), and Br with a higher concentration (y = 0.2), and in all cases, the purity of the LGPS phase decreased while the other impurity/secondary phases increased. Therefore, four samples with higher purity, namely Li3.2PS3.7O0.3, Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Cl0.1, Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Br0.1, and Li3.3PS3.7O0.3I0.1, were selected for the further study and the samples were designated as LSPO, LPSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI, respectively. It is to be noted that these compounds likely had some impurity phases, therefore, their actual compositions may be different to the nominal compositions quoted. However, since quantification of the impurity phases was not done in the present study, for simplicity, the nominal compositions are used throughout this paper.
For the detailed analysis, Le Bail refinement analysis was performed on the selected samples, as shown in Fig. 1(b). The refinement results suggested that all the compounds adopted the LGPS-type structure with some impurity peaks in LPSOI, which needs further detailed investigation. However, we succeeded in performing Rietveld refinement analysis on the LPSO sample using initial parameters from the literature,12,19 and the refinement graph and the results are given in Fig. S1 and Table S2 of the ESI.† The atomic positions, occupancy of Li, and thermal parameters of all the atoms were fixed during the refinement. The refinement results suggested about 3.5 wt% of Li2S as a secondary/impurity phase, which was also present in the halogen-doped samples. Therefore, a 3.5 wt% Li2S secondary phase was assumed to be present in all the samples. The lattice parameters and cell volume increased with the doping of Br and I in the LPSO compound, whereas, opposite results were found for the Cl-doped sample, as shown in Fig. 1(c). The increment/decrement in lattice parameters and cell volume of the halogen-doped compounds were due to the differences in the ionic radii of the doped elements (Cl, Br, I) from the S and O atoms. The order of the ionic radii (Å) of the anions was O2− (1.35) < Cl− (1.81) < S2− (1.84) < Br− (1.96) < I− (2.20),34 which was consistent with the order of changes in the lattice parameters and cell volumes of the samples, i.e., LPSOCl < LPSO < LPSOBr < LPSOI. The change in the cell volumes of LPSO and LPSOCl was smaller compared to in LPSOBr and LPSOI, which could be due to the very small difference in ionic radii of Cl− (1.81) and S2− (1.84). According to these results, it can be assumed that halogen atoms occupy the position of S atoms in the structure. However, another study reported new sites for Br and I in the LGPS-type structure.23 A separate detailed structural analysis is being carried out by transmission electron microscopy/neutron diffraction to find out the impurity peaks and positions of the halogen atoms in LPSO compounds, and the work purely based on structural analysis will be published in a separate study in the future. Le Bail Rietveld refinement graphs of other compositions, namely Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Br0.05I0.05, Li3.4PS3.7O0.3Cl0.1Br0.1, Li3.4PS3.7O0.3Br0.1I0.1, and Li3.4PS3.7O0.3Br0.2, are given in the ESI Fig. S3.†
The calcination temperature of the precursors after ball milling was selected based on the DSC results of the precursors, as shown in Fig. 1(d). All the compounds showed major exothermic peaks in the range of 210 °C to 230 °C. Therefore, the calcination temperature for all the compounds was selected as 220 °C. The compounds Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Br0.1 and Li3.2PS3.7O0.3 showed two exothermic peaks, whereas Li3.3PS3.7O0.3X0.1 (X = Cl, I) showed only one peak. The stability of the compounds was also checked by DCS measurements and the results are shown in Fig. 1(e). Broad endothermic peaks were observed for all the compounds near 100 °C, which could be due to moisture absorbance on the powder surface. Thereafter, no activity was noticed up to 315 °C, which shows the stability of the compounds over this temperature range. However, a major reactivity was noticed after 315 °C in all the compounds due to decomposition of the materials. To find out the decomposition compounds, samples LPSO and LPSOBr were calcined at 350 °C in a quartz tube under similar conditions. The XRD results showed that β-Li3PS4 was a major phase in both samples, with the results shown in the ESI (Fig. S4).† A similar β-Li3PS4 phase was obtained in a previous study also.23
Crystal structure models of LGPS, LPSO, and LPSOX were drawn and are shown in Fig. 1(f and g). While synchrotron and neutron diffractions data are required to determine the atomic positions of atoms, we did not use these large-scale facilities in our study, and therefore, for drawing the crystal structure, the atomic positions used were obtained from prior literature.23,32,33
The densities of the compacted pellets are given in Table 1, as measured before the conductivity test by a geometric method, as explained in the experimental section. AC impedance measurements were performed to determine the electrical conductivity of the prepared electrolytes in the form of compacted pellets. Fig. 2(a and b) show the Nyquist plots at 25 °C and −40 °C, respectively, of the cells in an Au/SE/Au geometry. It can be seen from the Nyquist plots recorded at 25 °C that the samples did not show proper semicircles due to their low impedance, and a similar phenomenon has been previously reported.10,35 Therefore, the total resistance of the samples was determined by intersection of the spike and Z-axis. The LPSOI and LPSOBr samples showed lower resistances compared to LPSO, while the LPSOCl sample showed the highest resistance. This suggests that Cl doping is not beneficial for the conductivity improvement of LPSO electrolytes, whereas Br and I doping showed a positive impact on the conductivity of the LSPO compound. When the EIS data were recorded at a lower temperature than room temperature, a semicircle started to appear and a proper semicircle was observed at −40 °C due to the slow kinetics of Li ions at low temperatures.17 The resistance at −40 °C was calculated by Z-fitting using an electrical equivalent circuit [(R‖Q1) + Q2], where R is the resistance related to the solid electrolyte (SE), which is combination of grain/bulk resistance and grain boundary resistance, and Q1 represents the capacitive behavior of a non-ideal capacitor, called the constant phase element. The non-ideal capacitive behavior of the constant phase element is not yet fully understood, but it is generally assigned to the inhomogeneity, surface roughness, porosity, and tortuosity of materials.36,37 The spike in the low-frequency region appeared due to charge build-up at the blocking electrodes (Au in this case)38 and is represented by the constant phase element Q2 (also denoted by ZCPE). The ZCPE can be calculated by the relation: ZCPE = Q−1 × (iω)−n, where n ≤ 1, and the corresponding capacitance can be estimated by C = [R1−n × Q]1/n.17,39 The capacitance of a semicircle can be calculated by the relation (ωmax = R × C),where  is angular frequency at the maximum of the semicircle and R is the resistance of the semicircle.17 It is generally found in sulfide electrolytes that due to their high conductivity, ductile nature, and better compaction, the signal responses from grains and gain boundaries overlap, making it hard to distinguish the resistances of the grains and grain boundaries.37,40 In our case also, we got only one semicircle, even at low temperature (−40 °C), whereas some other studies were able to distinguish grain and grain boundary resistance at low temperature.12,40 The sample LPSOI showed the highest conductivity of 0.55 mS cm−1 at 25 °C, while LPSOCl showed the lowest value, as given in Table 1. The activation energies (Ea) of the samples were calculated from linear extrapolation of the Arrhenius plot, as shown in Fig. 2(c). The lower Ea values of the LPSOI and LPSOBr samples were consistent with the conductivity values, which means I and Br doping facilitate ionic diffusion inside the structure. A lower activation energy implies that a lower potential energy barrier is required for ions to jump to adjacent lattice sites, resulting in more active lithium-ion jumps.41
is angular frequency at the maximum of the semicircle and R is the resistance of the semicircle.17 It is generally found in sulfide electrolytes that due to their high conductivity, ductile nature, and better compaction, the signal responses from grains and gain boundaries overlap, making it hard to distinguish the resistances of the grains and grain boundaries.37,40 In our case also, we got only one semicircle, even at low temperature (−40 °C), whereas some other studies were able to distinguish grain and grain boundary resistance at low temperature.12,40 The sample LPSOI showed the highest conductivity of 0.55 mS cm−1 at 25 °C, while LPSOCl showed the lowest value, as given in Table 1. The activation energies (Ea) of the samples were calculated from linear extrapolation of the Arrhenius plot, as shown in Fig. 2(c). The lower Ea values of the LPSOI and LPSOBr samples were consistent with the conductivity values, which means I and Br doping facilitate ionic diffusion inside the structure. A lower activation energy implies that a lower potential energy barrier is required for ions to jump to adjacent lattice sites, resulting in more active lithium-ion jumps.41
| Sample | Abbr. | Results in the Au/SE/Au cell | Results in the steel/SE/steel cell | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R Total (Ω) | σ (mS cm−1) | E a (eV) | ρ Rel. (%) | R Total (Ω) | σ (mS cm−1) | ρ Rel. (%) | ||
| Li3.2PS3.7O0.3 | LPSO | 650 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 94.0 | 272 | 0.5 | 94 |
| Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Cl0.1 | LPSOCl | 753 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 94.0 | 295 | 0.45 | 94 |
| Li3.3PS3.7O0.3Br0.1 | LPSOBr | 480 | 0.53 | 0.34 | 94.5 | 195 | 0.77 | 94 |
| Li3.3PS3.7O0.3I0.1 | LPSOI | 459 | 0.55 | 0.33 | 94.5 | 152 | 0.93 | 94 |
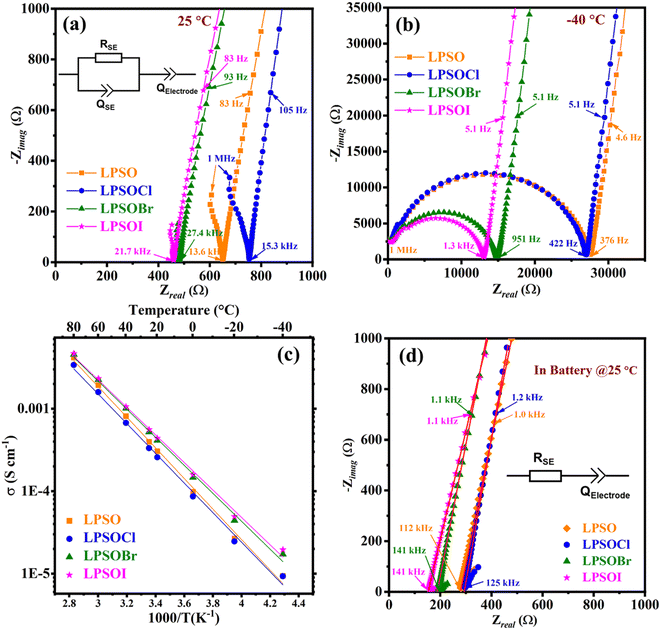 | ||
| Fig. 2 Nyquist plots recorded in Au/SE/Au cells at (a) 25 °C and (b) −40 °C. (c) Arrhenius conductivity plots in between −40 °C and 80 °C. (d) Nyquist plots recorded in steel/SE/steel cells at 25 °C. | ||
The conductivity and activation results also support the hypothesis that the doping of larger anions may provide additional space inside the structure for lithium diffusion as the ionic radii of I and Br are larger than that of S, with similar results also found earlier,23 whereas we observed the opposite results in the case of Cl doping.
We further measured the conductivity at 25 °C directly using the battery cell in a steel/SE/steel configuration at a constant pressure of 255 MPa to co-relate the performance of the solid-state battery with the conductivity of the solid electrolytes, and the results are shown in Fig. 2(d). The conductivity of the samples followed a similar trend as observed for the pelletized samples (Fig. 2(a)). The maximum conductivity of 0.93(≈1.0) mS cm−1 was obtained for the LPSOI sample, while LSPOCl showed the lowest value. The total resistance (bulk + grain boundary) and conductivity (ionic + electronic) of all the samples are given in Table 1. The conductivities of all the samples in the steel/SE/steel configuration were found to be higher than in the Au/SE/Au cell because of the lower interfacial/contact resistance due to the applied pressure. In the steel/SE/steel cell, a continuous pressure of 255 MPa was applied during the measurements, which provided better contact between the solid electrolyte and current collectors. This means the conductivity of the material also depends on the measurement method and applied pressure.42 We also measured the conductivity for other samples with lower purity in the steel/SE/steel configuration and the results are given in the ESI (Fig. S4 and Table S5).†
Next, the DC polarization method was used to measure the electronic conductivities of LPSO, LPSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI in an Au/SE/Au configuration. A constant voltage of 0.5 V was applied to the samples with gold-blocking electrodes (Au/SE/Au) for the measurements. Initially, a large current polarization was observed, which became almost stable after 10 min. To determine the electrical conductivity, the resistance (R) was calculated using Ohm's law (V = IR), which used the current value after 10 min. The electrical conductivities were measured using the formula σ = l/RA, where l and A are the thickness and surface of the sample. The values of electronic conductivities of the LPSO, LPSOCl, LPSOBr, LPSOI were 0.7 × 10−7, 0.6 × 10−7, 1.2 × 10−7, and 1.4 × 10−7 S cm−1, respectively. The DC polarization graphs are given in the ESI (Fig. S7).†
The microstructures of the prepared powder samples and pelletized samples (after the EIS test) were determined by SEM analysis and the results are shown in Fig. 3. The powder samples showed a large range of particle sizes, starting from less than 1 μm to 10 μm, and some particles even looked more than 10 μm, as shown in Fig. 3(a–d). However, the closer view of the bigger particles in the magnified images given in the inset suggests that the bigger particles were formed by the agglomeration of smaller particles. Therefore, the actual particle size might be lower than that observed in the images.
 | ||
| Fig. 3 (a–d) Microstructures of the powder samples, and (e–h) microstructures of the pellet samples. | ||
The microstructures of the pellets showed a highly dense microstructure that can be linked to more than 94% of the relative density of all the pellets. Therefore, highly dense pellets could be obtained from the halogen-doped solid electrolytes by cold pressing. However, the microstructures showed some micro cracks. These cracks might have formed during the EIS measurement when the pellets were heated up to 80 °C and cooled down to −40 °C. The morphologies of the halogen-doped samples were found to be different (e.g., cuboid) in pellet form compared to in the powder. Furthermore, the pellet sample of LPSOI showed a morphology like French fries in Fig. 3(h), whereas the powder sample did not. To verify the composition of the French fries' morphology and whether it is a new phase or LPSOI, SEM-EDS compositional analysis was carried out and the results are given in the ESI (Fig. S8).† The EDS results showed a similar composition as LSPOI, which means the change in morphology will have occurred during either pelletizing the powder or during the EIS measurement. To find the origin of the morphology change, a pellet of LPSOI was prepared in a similar way, and SEM and elemental compositional analysis were performed before the EIS measurement. The microstructure of the pellet (cross-sectional view) is shown in Fig. S9(a and b) of the ESI.† The microstructure of the LPSOI layer in the full SSB was also measured before charge–discharge cycling, as shown in Fig. S9(e) of the ESI.† In both cases, the morphology of the LPSOI was observed as being like French fries. Therefore, the morphology of LPSOI was changed due to the applied pressure, either applied unidirectional or isostatic. The elemental compositional analysis of the LPSOI pellet before EIS also confirmed similar compositions of both the French fries- and bulk-shaped samples, as shown in the ESI (Fig. S9).† To further confirm the phase, XRD was conducted on pellets of LPSOI and the results showed similar results to the powder samples.
CV measurements of a Li/SE/Au cell were recorded in the potential range of 0–5 V at a scan rate of 0.1 mV s−1 and the results are shown in Fig. 4(a). The CV results show the excellent electrochemical stability of the electrolytes up to 5 V, with no redox peaks observed throughout the range except between 0 and 0.6 V. The cathodic peaks observed between 0 and 0.2 V (before the dotted line) were due to lithium deposition on the Au electrode and the formation of a Li–Au alloy.43,44 Three anodic peaks were also noticed in the potential range of 0.2–0.6 V due to the de-alloying or dissolution of lithium from the Au electrode through the following reactions: Li3Au to Li5Au3, Li5Au3 to Li3Au2, and Li3Au2 to Li3Au5.45–47 From the intensities of the anodic and cathodic peaks, it can be hypothesized that the halogen-doped samples were stable than LSPO during Li-alloying/de-alloying. The intensities of the anodic and cathodic peaks were lowest for LPSOI, which supports the stability of the sample. We also recorded CV curves of Li/SE/Au cells in two extended voltage limits from −0.01 to 7 V and from −0.05 to 10 V. However, we did not observe any significant change at higher voltage. The results are included in the ESI as Fig. S10.†
The final goal of solid-state batteries is to use lithium metal as an anode; therefore, the stability of the prepared solid electrolytes against lithium metal was determined by plotting the polarization vs. time profiles in symmetric cells (Li/SE/Li), as shown in Fig. 4(b–e). First, a critical current density (CCD) test of the solid electrolyte was performed, which defines the power density of batteries, as shown in Fig. 4(b). The CCD test helps to understand the interfacial reactivity between solid electrolytes and lithium metal, dendrites formation, and the maximum acceptable current for solid electrolytes before a short circuit or battery failure.48 It can be seen that the LPSOI electrolyte bore a maximum current of 0.80 mA cm−2 before failure, whereas LPSOCl could tolerate only up to 0.60 mA cm−2 with high polarization due to the soft short circuit.48 The current-bearing capacities of LPSOBr and LPSO were observed to be 0.65 and 0.70 mA cm−2, respectively. The CCD results suggest that the high conductivity of the LPSOI sample assisted smooth lithium diffusion, which allowed it to bear the maximum current density and also slowed down dendrite formation.23,43,44
We further tested the critical current density for a longer time, as shown in Fig. 4(c), which also showed the lower polarization and better stability of the Br- and I-doped LSPO samples. Fig. 4(d) shows the interfacial stability of the prepared solid electrolytes with lithium metal in terms of polarization up to 250 h, and these results also validated the better stabilities of the LPSOI and LPSOBr samples with lower polarization. The LPSOI solid electrolyte showed the best stability among all the samples; therefore, it was further tested for a very long time of 1150 h, and it was found that the cell worked smoothly without any short circuit, as shown in Fig. 4(e).
After proving the stability of the solid electrolytes against lithium metal, full solid-state batteries (SSBs) were prepared in the (NCA![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) SE, 70
SE, 70![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30)/SE/(graphite
30)/SE/(graphite![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) SE, 70
SE, 70![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30) cell configuration, with the details of the SSBs fabrication given in the experimental section. Galvanostatic charge–discharge cycles were recorded at a current rate of C/10 rate (1C = 278.94 mA g−1) calculated according to the weight of active material in the composite cathode and the results are shown in Fig. 5(a–c). The first charge capacities of LPSO, LPSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI were 162, 182, 182, and 179 mA h g−1, while the discharge capacities were 110, 124, 129, and 126 mA h g−1, respectively. The large irreversible capacity noticed for all the samples could be due to lithium consumption in the interfacial reactions to form the solid electrolyte interface (SEI).19,49 The capacity losses during the first cycle for the samples LPSO, LPSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI were 32%, 32%, 29%, and 29%, respectively. Sample LPSO showed the lowest charge and discharge capacities, but the capacity loss was equal for the LPSO and LPSOCl samples; while LPSOI and LPSOBr not only showed minimum capacity losses but also higher charge–discharge capacities due to the superior conductivity of the materials. Fig. 5(b) shows the charge–discharge capacities of the second cycle, where a very small difference could be noticed in the charge–discharge capacities. From the second cycle, the coulombic efficiency was found to be quite stable (about 95%) for up to 20 cycles, indicating a very stable SEI was formed during the first cycle, as shown in Fig. 5(c). However, a continuous capacity loss was noticed for all samples and reached near 50%, except for LSPOI, which showed a loss of only 40%. Achieving a stable cycle life in SSBs is still a challenge and very limited literature is available on a long cycling life for SSBs. The capacity loss may depend on many factors, such as the selection of the electrode material, the ratio of the cathode and anode materials, the thickness of the solid electrolyte layer, and the applied current. It should be noted that we used a non-coated NCA cathode, which is more prone to react with sulfide solid electrolytes compared to LiNbO3-coated NCA.42,50
30) cell configuration, with the details of the SSBs fabrication given in the experimental section. Galvanostatic charge–discharge cycles were recorded at a current rate of C/10 rate (1C = 278.94 mA g−1) calculated according to the weight of active material in the composite cathode and the results are shown in Fig. 5(a–c). The first charge capacities of LPSO, LPSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI were 162, 182, 182, and 179 mA h g−1, while the discharge capacities were 110, 124, 129, and 126 mA h g−1, respectively. The large irreversible capacity noticed for all the samples could be due to lithium consumption in the interfacial reactions to form the solid electrolyte interface (SEI).19,49 The capacity losses during the first cycle for the samples LPSO, LPSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI were 32%, 32%, 29%, and 29%, respectively. Sample LPSO showed the lowest charge and discharge capacities, but the capacity loss was equal for the LPSO and LPSOCl samples; while LPSOI and LPSOBr not only showed minimum capacity losses but also higher charge–discharge capacities due to the superior conductivity of the materials. Fig. 5(b) shows the charge–discharge capacities of the second cycle, where a very small difference could be noticed in the charge–discharge capacities. From the second cycle, the coulombic efficiency was found to be quite stable (about 95%) for up to 20 cycles, indicating a very stable SEI was formed during the first cycle, as shown in Fig. 5(c). However, a continuous capacity loss was noticed for all samples and reached near 50%, except for LSPOI, which showed a loss of only 40%. Achieving a stable cycle life in SSBs is still a challenge and very limited literature is available on a long cycling life for SSBs. The capacity loss may depend on many factors, such as the selection of the electrode material, the ratio of the cathode and anode materials, the thickness of the solid electrolyte layer, and the applied current. It should be noted that we used a non-coated NCA cathode, which is more prone to react with sulfide solid electrolytes compared to LiNbO3-coated NCA.42,50
Galvanostatic charge–discharge cycles of SSBs with LPSOCl. LPSOBr, and LPSOI solid electrolytes in the (NCA![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) SE, 70
SE, 70![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30)/SE/Li cell configuration were also recorded at a current rate of C/10 rate (1C = 278.94 mA g−1), as shown in Fig. 5(d–f). The charge and discharge capacities of SSBs with Li metal were lower than the capacities of cells with graphite composite due to the well-known instability of sulfide electrolytes with Li metal. The capacity loss during the first cycle was also higher due to the occurrence of side reactions.51 The capacity retention of LPSOCl appeared to be better than that of LPSOBr and LPSOI, but this was because the SSB with LPSOCl had already lost most of its capacity in the first cycle; while the capacity retentions of LPSOI and LPSOBr were significantly higher and stabilized after the initial capacity loss.
30)/SE/Li cell configuration were also recorded at a current rate of C/10 rate (1C = 278.94 mA g−1), as shown in Fig. 5(d–f). The charge and discharge capacities of SSBs with Li metal were lower than the capacities of cells with graphite composite due to the well-known instability of sulfide electrolytes with Li metal. The capacity loss during the first cycle was also higher due to the occurrence of side reactions.51 The capacity retention of LPSOCl appeared to be better than that of LPSOBr and LPSOI, but this was because the SSB with LPSOCl had already lost most of its capacity in the first cycle; while the capacity retentions of LPSOI and LPSOBr were significantly higher and stabilized after the initial capacity loss.
The stability of sulfide-based solid electrolytes in ambient environments is very necessary for the safety and wide commercialization of these materials. Therefore, the H2S gas generated from the newly prepared solid electrolytes in ambient conditions was recorded, as shown in Fig. 5(d). It can be seen clearly from the graphs that the halogen-doped samples were more stable compared to LPSO. Furthermore, the samples LPSOBr and LPSOI were very stable, which implies that Br and I doping not only increased the conductivity of LPSO but also improved its stability in the ambient environment.
For better understanding the stability and the H2S gas evolution, we compared our compounds with other reported compounds with the LGPS structure, glassy Li3PS4, or thio-LISICON. Muramatsu et al. reported a 75Li2S·25P2S5 glass-ceramic solid electrolyte that demonstrated a conductivity of 1.9 × 10−4 S cm−1 at room temperature in an argon atmosphere. The conductivity of the compound was reduced to 1.5 × 10−4 S cm−1 after air exposure.52 Hayashi et al. tried to improve the chemical stability of the Li3PS4 glass electrolyte by adding ZnO, Fe2O3, and Bi2O3. The composite electrolyte 90Li3PS4–10ZnO (mol%) demonstrated an ionic conductivity of 3 × 10−4 S cm−1 and better stability in air.8 The conductivity (6.7 × 10−4 S cm−1) of our LPSOI compound at room temperature is higher than both those reported similar compounds. Tufail et al.53 reported an air-induced degradation mechanism for the Li7P3S11 solid electrolyte. The compound generated about 2.7 × 10−2 cm3 per g per min H2S and this continued to increase even after 50 min, whereas our compound LPSOI did not show any H2S generation after 30 min (as shown in Fig. 5(d)). Xu et al.33 performed an H2S gas evolution study on the LGPS-type solid electrolytes M-Li9P3S9O3 and Q-Li9P3S9O3 prepared by a mechanochemical and melt quench process, respectively. The samples M-Li9P3S9O3 and Q-Li9P3S9O3 released about 0.8 wt% and 0.3 wt% H2S gas upon exposure to air for 6 h. Neveu et al.54 also reported the H2S gas evolution of LGPS-type compounds with the formula Li3P1−xBxS4−x, and compared this with Li3BS3, β-Li3PS4, and Li10GeP2S12 after exposure to air versus time. The Li3P1−xBxS4−x compounds showed very high reactivity and the H2S gas value reached 30 cm3 g−1 in just 5–10 min. In comparison to these studies, our LPSOI compound showed better stability. However, many studies have chosen different parameters and experimental approaches, and also selected different representation methods, so direct comparisons are difficult.
XRD analysis of the LPSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI samples was conducted after exposing them to air and moisture for 30 min to assess their stability. We observed only minor changes in the diffraction peaks, with the LGPS structure remaining intact. The Le Bail refinement results are presented in Fig. 5(h).
To understand the interfacial behaviors of the halogen-doped solid electrolytes with the NCA cathode and graphite anode in a full solid-state battery, an in situ EIS study was performed on the battery cells during charge–discharge cycling and the results are shown in Fig. 6. Nyquist plots of battery cells prepared with LOSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI were recorded for as the prepared battery, and after the 1st, 4th, and 10th charge–discharge cycles. The data interpretation/analysis was done using an equivalent circuit model by Z-fit software and a possible understanding of the charge–discharge process inside the battery cells. During the charge–discharge process, the following steps are involved and might be responsible for various interfacial reactions: (i) Li-ion diffusion and migration in solid electrolytes, (ii) diffusion of ions and electrons in particles of the active materials (e.g., NCA and graphite), (iii) migration of ions and electrons across the composite cathode/anode thickness, (iv) migration of ions and electrons through the solid electrolyte interface (SEI) or solid–solid interface, (v) double-layer formation at the electrode/electrolyte interface, and (vi) transfer of electrons from the current collector to the cathode/anode composite.55 However, the multiple processes occurring in a full cell are difficult to deconvolute from a single experimental spectrum due to overlapping of the information.55,56 The high-frequency region is often disturbed by inductance; therefore, some of the data points in the high-frequency region were removed for a reliable fitting. A similar perturbation in data at higher frequency has also been reported earlier.35
The Nyquist plots of the as-prepared full battery cells with LPSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI are shown in Fig. 6(a, e and i), respectively. The as-prepared battery cells were in a discharge stage or 0% SOC (OCV = ∼400 mV), during which the graphite anode behaves like a blocking electrode; therefore, the impedance contribution in the high-frequency region would only be from the solid electrolyte. The value of RSE is related to the total resistance due to the solid electrolytes (bulk + grain boundary) calculated from the intersection between the x-axis and spikes (in the high-frequency region). In this case, the equivalent circuit model RSE + Qelectrode was used for the fitting. The value of RSE increased upon cycling from the as-prepared state to the 10th cycle for all three materials (shown by the shaded area in the plots). Increasing RSE values may be possible due to repeated Li insertion and de-insertion in solid electrolytes leading to crack formation, which increases the low contact points. The low contact points inside the solid electrolytes cause a higher grain boundary resistance. Pressure modification or pressure relaxation during cycling may also contribute to a higher grain boundary resistance. It is well known that the conductivity of sulfide-based solid electrolytes varies with applied pressure.42 The increment in RSE values of LPSOI was lower compared to for LPSOBr and LPSOCl due to the higher conductivity and better stability of the LPSOI solid electrolyte; while the sample LPSOCl showed the highest RSE resistance, even though an incomplete semicircle in the high-frequency region started appearing after the first cycle, which further grew up to the 10th cycle due to the increasing impedance from the grains and grain boundaries of LPSOCl. The first incomplete semicircle of LPSOCl in Fig. 6(b–d) showed a capacitance value in the range of 10−12 F, which was associated with the bulk resistance; however, it also had a contribution from the grain boundaries due to the poorly resolved contributions of the bulk and grain boundary separately.37 The overlapping of the bulk and grain boundary contributions is common due to the high-conducting grain boundaries of sulfide solid electrolytes.42,57 The resistance due to the anode and cathode composites in the as-prepared cells were calculated from the difference between R2 (intersection of the line drawn parallel to the low-frequency and high-frequency regions) and R1 (intersection of the high frequency and x-axis). The values of resistance (R = R2 − R1) for LPSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI were observed as 1827, 707, and 622 Ω, respectively. The high resistance was due to the state of charge of the active materials (0% SOC for the as-prepared cells).58 The total ionic conductivity of the composite electrodes (anode + cathode) was calculated by the formula  ; where R is the total resistance due to the anode and cathode composites, l is the sum of thicknesses of the cathode and anode layers, and A is the surface area of the electrodes layers. The total ionic conductivities of LPSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI in full SSBs were found to be 3.2 × 10−5, 8.0 × 10−5, and 9.1 × 10−5 S cm−1, respectively.
; where R is the total resistance due to the anode and cathode composites, l is the sum of thicknesses of the cathode and anode layers, and A is the surface area of the electrodes layers. The total ionic conductivities of LPSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI in full SSBs were found to be 3.2 × 10−5, 8.0 × 10−5, and 9.1 × 10−5 S cm−1, respectively.
However, depressed semicircles in the mid-frequency range having capacitance values in the order of 10−6 F appeared for all three samples recorded after the 1st, 4th, and 10th cycles due to the impedance contribution from the solid–solid interface (SSI). The impedance of the SSI is the sum of both the anode and cathode composites. Regarding the values of RSSI of LPSOBr and LPSOI, the full battery cell prepared with LPSOBr showed lower RSSI values recorded after the 1st and 4th cycles compared to the case with LPSOI. This could be possible due to more stable interface between LPSOBr and NCA in the beginning compared to the LPSOI electrolyte, which is also related to the higher initial capacity of the LPSOBr battery cell, as shown in Fig. 5(a and b). However, the interfacial resistance of LPSOI became almost constant from the 4th to the 10th cycle with a minimal increment in RSSI from 320 Ω to 323 Ω, while the RSSI of LPSOBr increased from 282 Ω to 323 Ω during the same interval. This characteristic can be understood by the interlayer hypothesis of the formation of byproducts of the NCA cathode and LPSOI/LPSOBr electrolytes. In this hypothesis, the byproducts of the LPSOI and NCA cathode form a stable interlayer, which prevents further reactivity of both materials, leading to a constant RSSI, whereas the interface between LPSOBr and NCA continuously reacts due to the unstable interlayer or contact loss within the cathode composites.59 This phenomenon can also be related to the cycling stability results shown in Fig. 5(c), even though the LPSOBr battery showed an initial higher capacity than LPSOI, though after 10 cycles the capacity of the LPSOI battery surpassed this and showed a more stable capacity compared to LPSOBr. However, the RSSI of the LPSOCl battery was the highest in all the samples due to the higher reactivity of the electrodes materials, which was already revealed by the lower capacity and cycle life of LPSOCl, as shown in Fig. 5. The impedance spectrum of LPSOCl after the 10th cycle (as shown in Fig. 6(d)) showed an imperfect third semicircle in the low-frequency region (∼1 Hz), which was due to the contribution from the charge-transfer resistance at the electrodes and electrolyte interface. The charge-transfer resistance was very high (Rct = 1061 Ω) due to the higher reactivity of LPSOCl. A schematic diagram of the full solid-state battery is shown in Fig. 6(m) along with the equivalent circuits used for the different Nyquist plots.
To observe the interfacial stability with Li metal, full cells were prepared in a similar way using Li metal as the anode instead of graphite, as shown in Fig. 7. In the battery cell prepared with Li metal, the impedance difference was too high between LPSOCl, LPSOBr, and LPSOI; therefore, we used a different scale for plotting the data for all three samples to better visualize the changes in impedance with cycling. The Nyquist plots of the as-prepared battery cells (shown in Fig. 7a, e, and i) also show both SE and SSI contributions due to the Li metal (source of Li), and the battery cells behaved as if already in the charge stage (OCV = ∼2.85 V), which was not the case with the graphite anode. All three samples followed a similar trend as for the results shown in Fig. 6. However, the impedance was much higher in the cells with the Li metal compared to the graphite anode due to the reactivity of sulfide materials with Li metal.35,60 Furthermore, the stacking pressure was lower in the battery cells with Li metal to avoid short circuit due to piercing of the Li metal through the electrolyte layer. However, the possibility of an imperfect contact between the solid electrolyte and Li metal cannot be neglected because the stack pressure also influences the impedance values.42,61 The value of RSS and RSSI increased very rapidly from the 1st to the 10th cycle, suggesting high interfacial reactions in the solid electrolytes as well as at both electrodes sides, respectively. The increasing RSS values were due to the above-mentioned reasons related to the formation of cracks due to the repeated Li insertion and de-insertion in the solid electrolyte during the charge–discharge cycling and pressure relaxation. The particle-size distribution also plays an important role in reducing the porosity of the solid electrolyte, which can affect the impedance. Generally, hot pressing is used to improve the porosity,42 while we used cold pressing only; therefore, low compaction could also be the reason for the increasing RSS values;61 whereby the increasing RSSI values were due to the instability of the sulfide electrolytes against Li metal. The rate of interfacial reactions also depends on the composition of the solid electrolytes along with other factors;57,62 therefore, LPSOI was found to be most stable against Li metal compared to LPSOBr and LPSOCl, which was in good agreement with the polarization data for the symmetric cells shown in Fig. 4. Due to the anode limitation by Li metal, the contribution of the cathode in the low-frequency range was difficult to determine. Therefore, the diffusion tails in the low-frequency region were poorly resolved in the Li/SE/NCA cells compared to cells with the graphite anode.
To further analyze the impedance of the solid electrolyte and the effect of pressure relaxation, we recorded Nyquist plots of LPSOI, LPSOBr, and LPSOCl after different time intervals from the as-prepared state to 160 h. The results show the increasing impedance of all three samples with time, as shown in Fig. S11 of the ESI.†
The microstructural and elemental analysis of the full SSB prepared by LPSOI (cross-sectional view) before (as-prepared) and after charge–discharge cycling were measured and the results are shown in Fig. 8. The thickness of all three layers (anode, cathode, and electrolyte) of the SSB are shown in the micrograph in Fig. 8(a). The thickness of the LPSOI layer was 503 μm, while the thicknesses of the anode and cathode composites layers were 127 μm and 91 μm, respectively. The SEM-EDX elemental analysis results for Ni, C, P, and S are shown in Fig. 8(b and c). Since the solid electrolyte LPSOI was mixed in both the anode (graphite + SE) and cathode (NCA + SE) composites, therefore a S content was observed in all three layers. Fig. 8(d) shows a magnified view of the cathode composite, while the elemental mapping results for Ni and S show the mixing of NCA and LPSOI in the composite, as depicted in Fig. 8(e and f). Similar microstructure and elemental analysis were performed for the anode composite, as shown in Fig. 8(g–i).
A postmortem analysis of the full SSB of LPSOI was carried out after 20 charge–discharge cycles by SEM and elemental mapping and the results are shown in Fig. 8(j–o). To perform the postmortem analysis, the SSB cell was recovered and cut to obtain a cross-sectional view. Fig. 8(j) shows a magnified image of the composite cathode, in which the changes in the morphology of the composite can be seen clearly. A gel-like morphology was observed after cycling, which was different from the fresh composite, and which may be due to the reaction between NCA and LPSOI, and the formation of the SEI layer. Previous studies have also shown interfacial reactions between the NCA cathode and sulfide electrolytes, and their byproducts, such as LiCl, Li2S, Li3PO4, Li2SO4, and Ni3S4.50,63 However, while the solid electrolytes used in reported studies were different than LPSOI, still we can presume similar reactions for our compound. In the elemental mapping of the composite, a homogeneous network of solid electrolyte (shown by S mapping) around the NCA particles (shown by Ni mapping) could be observed, as shown in Fig. 8(k and l).
However, the microstructure of the anode composite showed more stability between graphite and LPSOI, as shown in Fig. 8(m) as a similar morphology of the composite was observed after cycling as it observed for the as-prepared cell. The graphite and LPSOI material were visible in their original state as before cycling. The elemental mappings of graphite (C) and LPSOI (S) are shown in Fig. 8(n and o).
During the microstructure analysis of the cathode composite in the fresh SSB, we noticed micro gaps between the NCA particles and LPSOI electrolyte (shown by arrows), as shown in Fig. S12 of the ESI.† However, these micro gaps vanished in the cathode composite in the cycled SSB due to the complete layer of LPSOI that was formed over the NCA particles, as shown in Fig. 7(k and l). These micro gap formed in the fresh SSB and the gel-like layer in the cycled SSB could be due to reactions between NCA and LPSOI.50,63 Since, there is no reported study available for reference due to the newness of our LPSOI solid electrolyte, further study by XPS or XAS is required to confirm the reaction products.
Furthermore, an interface of the solid electrolyte and Li metal with time was observed by SEM, and the micrographs are shown in Fig. 9. To measure the cross-sectional view, Li foil was mounted on LPSOX pellets at 0.5 ton (127.5 MPa) of pressure and cut by a sharp knife. After cutting, the samples were transferred to a SEM chamber and micrographs were recorded after 1, 7, and 68 h. We did not observe any changes in the LPSOI–Li interface, confirming the stability of the materials. However, we noticed a healing of some of the microcracks in LPSOCl and LPSOBr (shown by arrows) after 7 and 68 h. These changes in the LPSOCl and LPSOBr samples could be related to the reactivity of the materials with Li metal, leading to modification of the cracks.
 | ||
| Fig. 9 SEM analysis of the SE–Li metal interface after 1 h, 7 h and 68 h of contact for (a–c) LPSOCl, (d–f) LPSOBr, and (g–i) LPSOI. | ||
Conclusion
In summary, we report a series of new solid electrolytes with halogen (Cl, Br, I) doping in the LGPS-structured LPSO compound. The study shows that Br and I doping increased the lattice volume, resulting in additional space for Li-ion diffusion. The iodine-doped sample LPSOI not only showed the highest electrical conductivity of 0.93 mS cm−1 but also superior stability against Li metal in the symmetric cell. Higher initial charge–discharge capacities were also found for the halogen-doped samples compared to LPSO. The halogen-doped samples also showed better stability in the ambient environment compared to LPSO, with LPSOI showing the highest stability upon exposure to air and moisture. The in situ EIS study revealed the least interfacial resistance was between the LPSOI and NCA composite, and also the same compound showed the lowest interfacial resistance with the Li-metal anode in all the SEs. Structural and elemental studies were also performed on the as-prepared and post-cycled SSB, and the results showed the interfacial stability between the NCA cathode and LPSOI solid electrolyte. Therefore, halogen, especially Br and I, doping of sulfide electrolytes provides a possible solution to the battery industry for commercializing solid-state batteries.Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the ESI.†Author contributions
Hari Raj: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, synthesis and investigation, characterization methodology, visualization, writing – original draft, funding acquisition, writing & editing. Audric Neveu: formal analysis, and scientific discussion. Christian Jordy: formal analysis, validation, review & editing, and scientific discussion. Vincent Pelé: formal analysis, and scientific discussion. Valerie Pralong: supervision, resources, investigation, formal analysis, validation, review & editing, and scientific discussion, project administration. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.Acknowledgements
Funding was received from the European Union through the Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska Curie Action grant agreement no. 101034329 and the WINNINGNormandy Program. The authors thank Mahima Chaudhary, V. Kovrugin, A. P. Q. Le, S. Duffourt, J. Lecourt, S. Gascoin, H. Laurence, and X. Larose for technical help. Hari Raj and Valerie Pralong gratefully acknowledge the CNRS, Normandy region and European Union for the funding.References
- Q. Wang, L. Jiang, Y. Yu and J. Sun, Progress of Enhancing the Safety of Lithium Ion Battery from the Electrolyte Aspect, Nano Energy, 2019, 55, 93–114, DOI:10.1016/J.NANOEN.2018.10.035.
- K.-H. Kim and S. W. Martin, Structures and Properties of Oxygen-Substituted Li10SiP2 S12−x Ox Solid-State Electrolytes, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31(11), 3984–3991, DOI:10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b00505.
- J. Janek and W. G. Zeier, A Solid Future for Battery Development, Nat. Energy, 2016, 1(9), 1–4, DOI:10.1038/nenergy.2016.141.
- H. D. Lim, J. H. Park, H. J. Shin, J. Jeong, J. T. Kim, K. W. Nam, H. G. Jung and K. Y. Chung, A Review of Challenges and Issues Concerning Interfaces for All-Solid-State Batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 25, 224–250, DOI:10.1016/J.ENSM.2019.10.011.
- B. Zhang, R. Tan, L. Yang, J. Zheng, K. Zhang, S. Mo, Z. Lin and F. Pan, Mechanisms and Properties of Ion-Transport in Inorganic Solid Electrolytes, Energy Storage Mater., 2018, 10, 139–159, DOI:10.1016/J.ENSM.2017.08.015.
- H. Raj, T. Fabre, M. Lachal, A. Neveu, J. Jean, M. C. Steil, R. Bouchet and V. Pralong, Stabilizing the NASICON Solid Electrolyte in an Inert Atmosphere as a Function of Physical Properties and Sintering Conditions for Solid-State Battery Fabrication, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2023, 6(3), 1197–1207, DOI:10.1021/ACSAEM.2C02464.
- Z. Jiang, T. Liang, Y. Liu, S. Zhang, Z. Li, D. Wang, X. Wang, X. Xia, C. Gu and J. Tu, Improved Ionic Conductivity and Li Dendrite Suppression Capability toward Li7P3S11-Based Solid Electrolytes Triggered by Nb and O Cosubstitution, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(49), 54662–54670, DOI:10.1021/ACSAMI.0C15903.
- A. Hayashi, H. Muramatsu, T. Ohtomo, S. Hama and M. Tatsumisago, Improvement of Chemical Stability of Li3PS4 Glass Electrolytes by Adding MxOy (M = Fe, Zn, and Bi) Nanoparticles, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(21), 6320–6326, 10.1039/C3TA10247E.
- T. Yu, B. Ke, H. Li, S. Guo and H. Zhou, Recent Advances in Sulfide Electrolytes toward High Specific Energy Solid-State Lithium Batteries, Mater. Chem. Front., 2021, 5(13), 4892–4911, 10.1039/D1QM00474C.
- N. Kamaya, K. Homma, Y. Yamakawa, M. Hirayama, R. Kanno, M. Yonemura, T. Kamiyama, Y. Kato, S. Hama, K. Kawamoto and A. Mitsui, A Lithium Superionic Conductor, Nat. Mater., 2011, 10(9), 682–686, DOI:10.1038/nmat3066.
- M. Tatsumisago, M. Nagao and A. Hayashi, Recent Development of Sulfide Solid Electrolytes and Interfacial Modification for All-Solid-State Rechargeable Lithium Batteries, J. Asian Ceram. Soc., 2013, 1(1), 17–25, DOI:10.1016/J.JASCER.2013.03.005.
- A. Neveu, V. Pelé, C. Jordy and V. Pralong, Exploration of Li–P–S–O Composition for Solid-State Electrolyte Materials Discovery, J. Power Sources, 2020, 467, 228250, DOI:10.1016/J.JPOWSOUR.2020.228250.
- H. Wan, S. Liu, T. Deng, J. Xu, J. Zhang, X. He, X. Ji, X. Yao and C. Wang, Bifunctional Interphase-Enabled Li10GeP2S12Electrolytes for Lithium-Sulfur Battery, ACS Energy Lett., 2021, 6(3), 862–868, DOI:10.1021/ACSENERGYLETT.0C02617.
- W. D. Richards, L. J. Miara, Y. Wang, J. C. Kim and G. Ceder, Interface Stability in Solid-State Batteries, Chem. Mater., 2016, 28(1), 266–273, DOI:10.1021/ACS.CHEMMATER.5B04082.
- P. Bron, S. Johansson, K. Zick, J. S. A. Der Günne, S. Dehnen and B. Roling, Li10SnP2S12: An Affordable Lithium Superionic Conductor, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(42), 15694–15697, DOI:10.1021/JA407393Y.
- A. Kuhn, O. Gerbig, C. Zhu, F. Falkenberg, J. Maier and B. V. Lotsch, A New Ultrafast Superionic Li-Conductor: Ion Dynamics in Li 11 Si 2 PS 12 and Comparison with Other Tetragonal LGPS-Type Electrolytes, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16(28), 14669–14674, 10.1039/C4CP02046D.
- P. Bron, S. Dehnen and B. Roling, Li10Si0.3Sn0.7P2S12 – A Low-Cost and Low-Grain-Boundary-Resistance Lithium Superionic Conductor, J. Power Sources, 2016, 329, 530–535, DOI:10.1016/J.JPOWSOUR.2016.08.115.
- P. Bron, B. Roling and S. Dehnen, Impedance Characterization Reveals Mixed Conducting Interphases between Sulfidic Superionic Conductors and Lithium Metal Electrodes, J. Power Sources, 2017, 352, 127–134, DOI:10.1016/J.JPOWSOUR.2017.03.103.
- Y. Kato, S. Hori, T. Saito, K. Suzuki, M. Hirayama, A. Mitsui, M. Yonemura, H. Iba and R. Kanno, High-Power All-Solid-State Batteries Using Sulfide Superionic Conductors, Nat. Energy, 2016, 14(4), 1–7, DOI:10.1038/nenergy.2016.30.
- T. Ito, S. Hori, M. Hirayama and R. Kanno, Liquid-Phase Synthesis of the Li10GeP2S12-Type Phase in the Li–Si–P–S–Cl System, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10(27), 14392–14398, 10.1039/D2TA02834D.
- N. Zhang, Q. He, L. Zhang, J. Zhang, L. Huang and X. Yao, Homogeneous Fluorine Doping toward Highly Conductive and Stable Li10GeP2S12 Solid Electrolyte for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries, Adv. Mater., 2024, 2408903, 1–9, DOI:10.1002/adma.202408903.
- Y. Jin, Q. He, G. Liu, Z. Gu, M. Wu, T. Sun, Z. Zhang, L. Huang and X. Yao, Fluorinated Li10GeP2S12 Enables Stable All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries, Adv. Mater., 2023, 35(19), 1–8, DOI:10.1002/adma.202211047.
- S. Song, S. Hori, Y. Li, K. Suzuki, N. Matsui, M. Hirayama, T. Saito, T. Kamiyama and R. Kanno, Material Search for a Li10GeP2S12-Type Solid Electrolyte in the Li-P-S-X (X = Br, I) System via Clarification of the Composition-Structure-Property Relationships, Chem. Mater., 2022, 34(18), 8237–8247, DOI:10.1021/ACS.CHEMMATER.2C01608.
- C. Sun, J. Liu, Y. Gong, D. P. Wilkinson and J. Zhang, Recent Advances in All-Solid-State Rechargeable Lithium Batteries, Nano Energy, 2017, 33(January), 363–386, DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.01.028.
- Y. Lu, X. Meng, J. A. Alonso, M. T. Fernández-Díaz and C. Sun, Effects of Fluorine Doping on Structural and Electrochemical Properties of Li 6.25 Ga 0.25 La 3 Zr 2 O 12 as Electrolytes for Solid-State Lithium Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(2), 2042–2049, DOI:10.1021/acsami.8b17656.
- J. Liu, F. Yin, Y. Mao and C. Sun, Fluorine-Doped Li7La3Zr2O12 Fiber-Based Composite Electrolyte for Solid-State Lithium Batteries with Enhanced Electrochemical Performance, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2024, 16(24), 31191–31200, DOI:10.1021/acsami.4c05217.
- K. Tuo, C. Sun and S. Liu, Recent Progress in and Perspectives on Emerging Halide Superionic Conductors for All-Solid-State Batteries, Electrochem. Energy Rev., 2023, 6, 17, DOI:10.1007/s41918-023-00179-5.
- S. Li, Z. Huang, Y. Xiao and C. Sun, Chlorine-Doped Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3as an Electrolyte for Solid Lithium Metal Batteries, Mater. Chem. Front., 2021, 5(14), 5336–5343, 10.1039/d1qm00241d.
- J. Wu, S. Liu, F. Han, X. Yao and C. Wang, Lithium/Sulfide All-Solid-State Batteries Using Sulfide Electrolytes, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(6), 1–31, DOI:10.1002/adma.202000751.
- Y. He, W. Chen, Y. Zhao, Y. Li, C. Lv, H. Li, J. Yang, Z. Gao and J. Luo, Recent Developments and Progress of Halogen Elements in Enhancing the Performance of All-Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2022, 49, 19–57, DOI:10.1016/J.ENSM.2022.03.043.
- K. Suzuki, M. Sakuma, S. Hori, T. Nakazawa, M. Nagao, M. Yonemura, M. Hirayama and R. Kanno, Synthesis, Structure, and Electrochemical Properties of Crystalline Li–P–S–O Solid Electrolytes: Novel Lithium-Conducting Oxysulfides of Li10GeP2S12 Family, Solid State Ionics, 2016, 288, 229–234, DOI:10.1016/J.SSI.2016.02.002.
- R. Iwasaki, S. Hori, R. Kanno, T. Yajima, D. Hirai, Y. Kato and Z. Hiroi, Weak Anisotropic Lithium-Ion Conductivity in Single Crystals of Li10 GeP2 S12, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31(10), 3694–3699, DOI:10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b00420.
- M. Xu, S. Song, S. Daikuhara, N. Matsui, S. Hori, K. Suzuki, M. Hirayama, S. Shiotani, S. Nakanishi, M. Yonemura, T. Saito, T. Kamiyama and R. Kanno, Li10GeP2S12-Type Structured Solid Solution Phases in the Li9+δP3+δ′S12-KOkSystem: Controlling Crystallinity by Synthesis to Improve the Air Stability, Inorg. Chem., 2022, 61(1), 52–61, DOI:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c01748.
- R. D. Shannon and IUCr, Revised Effective Ionic Radii and Systematic Studies of Interatomic Distances in Halides and Chalcogenides, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A: Found. Crystallogr., 1976, 32(5), 751–767, DOI:10.1107/S0567739476001551.
- I. Tarhouchi, V. Viallet, P. Vinatier and M. Ménétrier, Electrochemical Characterization of Li10SnP2S12: An Electrolyte or a Negative Electrode for Solid State Li-Ion Batteries?, Solid State Ionics, 2016, 296, 18–25, DOI:10.1016/j.ssi.2016.08.016.
- W. H. Mulder, J. H. Sluyters, T. Pajkossy and L. Nyikos, Tafel Current at Fractal Electrodes. Connection with Admittance Spectra, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1990, 285(1–2), 103–115, DOI:10.1016/0022-0728(90)87113-X.
- L. Zhang, Y. Dai, C. Li, Y. Dang, R. Zheng, Z. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Cui, H. Arandiyan, Z. Shao, H. Sun, Q. Zhuang and Y. Liu, Recent Advances in Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy for Solid-State Batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2024, 69(March), 103378, DOI:10.1016/j.ensm.2024.103378.
- J. T. S. Irvine, D. C. Sinclair and A. R. West, Electroceramics: Characterization by Impedance Spectroscopy, Adv. Mater., 1990, 2(3), 132–138, DOI:10.1002/adma.19900020304.
- G. J. Brug, A. L. G. van den Eeden, M. Sluyters-Rehbach and J. H. Sluyters, The Analysis of Electrode Impedances Complicated by the Presence of a Constant Phase Element, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1984, 176(1–2), 275–295, DOI:10.1016/S0022-0728(84)80324-1.
- P. Bron, S. Dehnen and B. Roling, Li10Si0.3Sn0.7P2S12 – A Low-Cost and Low-Grain-Boundary-Resistance Lithium Superionic Conductor, J. Power Sources, 2016, 329, 530–535, DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.08.115.
- K. S. Kim, R. Rajagopal and K. S. Ryu, The Improvement of Electrochemical Performance by Mixing InF3 in Li5.3PS4.3Cl1.7 Solid Electrolyte, J. Alloys Compd., 2024, 992(April), 174620, DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom.2024.174620.
- J. M. Doux, Y. Yang, D. H. S. Tan, H. Nguyen, E. A. Wu, X. Wang, A. Banerjee and Y. S. Meng, Pressure Effects on Sulfide Electrolytes for All Solid-State Batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8(10), 5049–5055, 10.1039/c9ta12889a.
- Y. Lu, C. Z. Zhao, H. Yuan, X. B. Cheng, J. Q. Huang and Q. Zhang, Critical Current Density in Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries: Mechanism, Influences, and Strategies, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(18), 2009925, DOI:10.1002/ADFM.202009925.
- R. Sudo, Y. Nakata, K. Ishiguro, M. Matsui, A. Hirano, Y. Takeda, O. Yamamoto and N. Imanishi, Interface Behavior between Garnet-Type Lithium-Conducting Solid Electrolyte and Lithium Metal, Solid State Ionics, 2014, 262, 151–154, DOI:10.1016/J.SSI.2013.09.024.
- R. Raj and J. Wolfenstine, Current Limit Diagrams for Dendrite Formation in Solid-State Electrolytes for Li-Ion Batteries, J. Power Sources, 2017, 343, 119–126, DOI:10.1016/J.JPOWSOUR.2017.01.037.
- J. Li, W. Liu, X. Zhang, Y. Ma, Y. Wei, Z. Fu, J. Li and Y. Yan, Heat Treatment Effects in Oxygen-Doped β-Li3PS4 Solid Electrolyte Prepared by Wet Chemistry Method, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2021, 25(4), 1259–1269, DOI:10.1007/S10008-021-04904-2.
- P. Bach, M. Stratmann, I. Valencia-Jaime, A. H. Romero and F. U. Renner, Lithiation and Delithiation Mechanisms of Gold Thin Film Model Anodes for Lithium Ion Batteries: Electrochemical Characterization, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 164, 81–89, DOI:10.1016/J.ELECTACTA.2015.02.184.
- P. Bach, I. Valencia-Jaime, U. Rütt, O. Gutowski, A. H. Romero and F. U. Renner, Electrochemical Lithiation Cycles of Gold Anodes Observed by in Situ High-Energy X-Ray Diffraction, Chem. Mater., 2016, 28(9), 2941–2948, DOI:10.1021/ACS.CHEMMATER.5B04719.
- M. Sakuma, K. Suzuki, M. Hirayama and R. Kanno, Reactions at the Electrode/Electrolyte Interface of All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries Incorporating Li–M (M = Sn, Si) Alloy Electrodes and Sulfide-Based Solid Electrolytes, Solid State Ionics, 2016, 285, 101–105, DOI:10.1016/J.SSI.2015.07.010.
- A. Banerjee, H. Tang, X. Wang, J. H. Cheng, H. Nguyen, M. Zhang, D. H. S. Tan, T. A. Wynn, E. A. Wu, J. M. Doux, T. Wu, L. Ma, G. E. Sterbinsky, M. S. D'Souza, S. P. Ong and Y. S. Meng, Revealing Nanoscale Solid-Solid Interfacial Phenomena for Long-Life and High-Energy All-Solid-State Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(46), 43138–43145, DOI:10.1021/ACSAMI.9B13955.
- Y. Kato, S. Hori, T. Saito, K. Suzuki, M. Hirayama, A. Mitsui, M. Yonemura, H. Iba and R. Kanno, High-Power All-Solid-State Batteries Using Sulfide Superionic Conductors, Nat. Energy, 2016, 1(4), 1–25, DOI:10.1038/nenergy.2016.30.
- H. Muramatsu, A. Hayashi, T. Ohtomo, S. Hama and M. Tatsumisago, Structural Change of Li2S-P2S5 Sulfide Solid Electrolytes in the Atmosphere, Solid State Ionics, 2011, 182(1), 116–119, DOI:10.1016/j.ssi.2010.10.013.
- M. Khurram Tufail, N. Ahmad, L. Zhou, M. Faheem, L. Yang, R. Chen and W. Yang, Insight on Air-Induced Degradation Mechanism of Li7P3S11 to Design a Chemical-Stable Solid Electrolyte with High Li2S Utilization in All-Solid-State Li/S Batteries, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 425(March), 130535, DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2021.130535.
- A. Neveu, H. Raj, V. Pelé, C. Jordy and V. Pralong, Effect of the Boron Element in a Li-P-S System, Dalton Trans., 2023, 52(47), 18045–18052, 10.1039/d3dt02883f.
- M. Gaberšček, Understanding Li-Based Battery Materials via Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 19–22, DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-26894-5.
- J. Moškon, J. Žuntar, S. Drvarič Talian, R. Dominko and M. Gaberšček, A Powerful Transmission Line Model for Analysis of Impedance of Insertion Battery Cells: A Case Study on the NMC-Li System, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2020, 167(14), 140539, DOI:10.1149/1945-7111/abc769.
- S. Hori, R. Kanno, X. Sun, S. Song, M. Hirayama, B. Hauck, M. Dippon, S. Dierickx and E. Ivers-Tiffée, Understanding the Impedance Spectra of All-Solid-State Lithium Battery Cells with Sulfide Superionic Conductors, J. Power Sources, 2023, 556(November), 232450, DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.232450.
- N. Kaiser, S. Spannenberger, M. Schmitt, M. Cronau, Y. Kato and B. Roling, Ion Transport Limitations in All-Solid-State Lithium Battery Electrodes Containing a Sulfide-Based Electrolyte, J. Power Sources, 2018, 396(April), 175–181, DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.05.095.
- M. Shin and A. A. Gewirth, Incorporating Solvate and Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Li2S Batteries with High Capacity and Long Cycle Life, Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9(26), 1–11, DOI:10.1002/aenm.201900938.
- S. Wenzel, S. Randau, T. Leichtweiß, D. A. Weber, J. Sann, W. G. Zeier and J. Janek, Direct Observation of the Interfacial Instability of the Fast Ionic Conductor Li10GeP2S12 at the Lithium Metal Anode, Chem. Mater., 2016, 28(7), 2400–2407, DOI:10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b00610.
- H. Yamauchi, J. Ikejiri, K. Tsunoda, A. Tanaka, F. Sato, T. Honma and T. Komatsu, Enhanced Rate Capabilities in a Glass-Ceramic-Derived Sodium All-Solid-State Battery, Sci. Rep., 2020, 10(1), 1–12, DOI:10.1038/s41598-020-66410-1.
- A. Sakuda, H. Kitaura, A. Hayashi, K. Tadanaga and M. Tatsumisago, Modification of Interface Between LiCoO[Sub 2] Electrode and Li[Sub 2]S–P[Sub 2]S[Sub 5] Solid Electrolyte Using Li[Sub 2]O–SiO[Sub 2] Glassy Layers, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2009, 156(1), A27, DOI:10.1149/1.3005972.
- H. W. Kwak and Y. J. Park, Cathode Coating Using LiInO2-LiI Composite for Stable Sulfide-Based All-Solid-State Batteries, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1), 1–9, DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-44629-x.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Supplementary figures including refinement pattern and result's table, XRD patterns, SEM-EDS graphs, conductivity graphs, table of conductivity data. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ta04904g |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |





