Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCompetition between CH4 hydrate formation and phase separation in a wetted metal–organic framework MIL-101 at moderate subcooling: molecular insights into CH4 storage†
Zhongjin
He
 a,
Jianwen
Jiang
a,
Jianwen
Jiang
 b,
Guosheng
Jiang
a and
Fulong
Ning
b,
Guosheng
Jiang
a and
Fulong
Ning
 *a
*a
aNational Center for International Research on Deep Earth Drilling and Resource Development, Faculty of Engineering, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China
bDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 117576, Singapore. E-mail: nflzx@cug.edu.cn
First published on 1st February 2024
Abstract
Adsorption-hydration hybrid technology has emerged as a promising technology to store CH4 in porous materials, as it synergistically improves CH4 storage capacity by combining CH4 adsorption and hydrate formation. However, the fundamental mechanism involved in this technology remains elusive. Herein, we perform systematic molecular dynamics simulations to explore CH4 hydrate formation in a metal–organic framework MIL-101 at moderate subcooling. Simulation results reveal that at moderate subcooling, CH4 hydrate formation and phase separation of CH4 to form nanobubbles occur simultaneously, and these two processes compete with each other for CH4 molecules in the solution. The outcome of the competition is primarily governed by the relative stabilities of CH4 hydrate solids and CH4 nanobubbles, which are closely related to their sizes. It is revealed that CH4 hydrate formation occurs exclusively in the outer space of MIL-101 cavities, whereas phase separation of CH4 to form nanobubbles takes place in the MIL-101 cavities and their outer space simultaneously. The small nanobubbles in the MIL-101 cavities gradually shrink and finally disappear, as CH4 molecules therein diffuse out and grow into large nanobubbles and large hydrate solids in the outer space. Moderate subcooling appears to facilitate the formation of large ordered CH4 hydrate solids containing sI and sII domains. Additionally, it is found that lower subcooling and presence of MIL-101 both promote phase separation of CH4. In the evolution of large and small nanobubbles during phase separation, coalescence of CH4 nanobubbles and an interesting phenomenon similar to Ostwald ripening are observed. The molecular insights into the effects of the degree of subcooling on CH4 hydrate formation in MIL-101 provide bottom-up guidance on optimizing pressure-temperature conditions for CH4 storage in porous materials with adsorption-hydrate hybrid technology.
1. Introduction
With the rapid growth of the global economy and population, the demand for energy resources has increased consistently. Currently, natural gas (mainly CH4) is a heavily consumed energy resource and could meet this demand due to its abundance worldwide, high energy density, cleanliness and low cost. Nevertheless, efficient methods for storing and transporting natural gas are required to maximize the usage of this clean energy resource. One promising method is utilizing gas physisorption in porous materials. With readily tunable structures and pore sizes, metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are a very interesting class of porous materials for CH4 storage. In the past decade, tremendous efforts have been made to improve CH4 storage capacity in MOFs by optimizing their chemistry, structure and functionality. Recent experimental studies reported that pre-humidified MOFs could enhance CH4 storage capacity,1,2 especially at high pressure and moderate temperature.3 This interesting phenomenon is primarily attributed to the formation of CH4 hydrate in the presence of H2O in MOFs. Gas hydrates are one kind of ice-like solids with gas molecules entrapped into hydrogen-bonded water polyhedral cages. Similar to porous materials, CH4 hydrate itself has excellent storage capacity, i.e., one volume hydrate solid can contain approximately 170 volumes of CH4 at the standard temperature and pressure.4 Moreover, the unique self-preservation anomaly of gas hydrate5 can be leveraged for long-time preservation and transport of CH4 hydrate in MOFs at ambient pressure and low temperatures. Therefore, researchers have proposed to combine adsorption and hydrate formation to efficiently store CH4 in MOFs, i.e., the so-called adsorption-hydrate hybrid method.Toward this end, there have been increasing experimental and theoretical investigations to explore CH4 storage in MOFs via the adsorption-hydrate hybrid method.6,7 Liu and co-workers explored CH4 adsorption and hydrate formation in wet ZIF-8 with different water contents and observed that the storage capacity was raised by 56% with a water content of 35.1 wt%, which was conjectured to arise from hydrate formation in wet ZIF-8 pores.3 The experimental work by Casco et al. directly identified CH4 hydrate formation in pre-humidified MIL-100(Fe) and ZIF-8, and revealed that the surface chemistry, pore structure and water–framework interactions would significantly affect the amount and nature of gas hydrates formed in MOFs.8 Nevertheless, it was speculated that CH4 hydrate formation occurred primarily on the external surface or in the interparticle space due to the small cavities in most MOFs9,10e.g., the cavity sizes in ZIF-8, MIL-53 and HKUST-1 < 1 nm. A recent experimental study on CH4 hydrate formation in Cr-soc-MOF-1 and Y-shp-MOF-5 indicated that forming hydrate nanocrystals in MOF cavities would require a cavity size larger than the unit cell size of CH4 hydrate (1.2 nm); moreover, encapsulating CH4 hydrate nanocrystals inside Cr-soc-MOF-1 cavities could increase gas storage capacity by 50%.11 Chen and co-workers investigated the morphology and growth kinetics of CH4 hydrate in wetted ZIF-8 particles and quantified the effects of particle size, water content and pressure.12,13 Additionally, the phase behavior of gas hydrate has been reported to change in porous materials. Liu et al. revealed a pore-diameter dependent effect on CH4 hydrate equilibrium in wetted porous materials (ZIF-8, HKUST-1 and zeolite 13X) with a pore size ranging from 0.35 to 100 nm, i.e., strong inhibitory effect in nano-pores and marginal effect in macro-pores.14 The thermodynamic behavior of gas hydrates was observed to be relatively inhibited in the intergranular meso/macro pores of MIL-53.15 Certain MOFs have been reported to serve as effective promoters for CH4 hydrate formation for enhancing natural gas storage. Koh and co-workers drastically improved CH4 storage by over tenfold upon adding HKUST-1, ZIF-8 and ZIF-67, and these MOFs were found to significantly increase water-to-hydrate conversion and remarkably reduce the induction time for hydrate nucleation.9,10,16,17 Recent theoretical studies have been mainly focused on the formation kinetics of CH4 hydrate in MOFs. Our previous molecular dynamics (MD) simulation on CH4 storage in mesoporous MIL-101 revealed that though the pre-adsorbed water in MIL-101 cavities substantially reduces CH4 adsorption capacity, considerable CH4 hydrate preferentially forms in the intergranular space and significantly enhances the overall storage capacity.18 A two-way transport of CH4 and water in ZIF-8 was reported in MD simulation studies, and the synergist effect of physisorption and intergranular hydrates was found to promote CH4 storage in ZIF-8.19–21 Overall, the phase behavior and formation process of CH4 hydrate in MOFs are far more complex than in a bulk phase.
A fundamental understanding of CH4 hydrate formation in porous material is indispensable to manipulating natural gas hydrate, which exists abundantly in deep-sea porous sediments and is considered a new energy resource.22,23 Conceptually, CH4 hydrate formation is inhibited in marine sediments due to the reduced water activity and capillary effect of porous sediments.24 Several MD simulation studies explored the nucleation and growth of CH4 hydrate in the slit-nanopores of silica or clay to reveal the effects of geological factors on hydrate formation in marine sediments, including sediment solid surfaces, seawater ions, and organic matter.25–28 Recent experimental studies inferred that the crystal structure and stability of CH4 hydrate confined in sediments might be mainly affected by the hydrophilic/hydrophobic properties of sediment surfaces.29
Despite many achievements, the microscopic mechanism of hydrate formation in porous materials is still not fully elucidated. Low temperature near ice-points is often adopted in experimental and theoretical studies on CH4 storage in MOFs using adsorption-hydrate hybrid technology.3,8,11,18,19 Furthermore, high subcooling is commonly implemented in MD simulation studies on gas hydrate formation in a bulk phase.30,31 Subcooling is referred to as the difference between the melting temperature of gas hydrate and an applied temperature. It is worth mentioning that CH4 hydrate occurs at a moderate temperature in hydrate reservoirs due to the presence of a geothermal gradient therein. To the best of our knowledge, how moderate subcooling affects CH4 adsorption and hydrate formation in porous material has not been explored thus far. To address this issue, MD simulations have been conducted in this study to investigate CH4 hydrate formation at moderate subcooling in a mesoporous MOF namely MIL-101. The molecular insights obtained could provide a fundamental understanding of the formation process of natural gas hydrate in marine sediments, and bottom-up guidance on optimizing pressure-temperature conditions for CH4 storage in porous materials with adsorption-hydrate hybrid technology.
2. Simulation models and methods
In this study, MIL-101 was adopted as a porous material for CH4 hydrate formation due to its large pore volume. MIL-101 has a three-dimensional zeotype cubic structure with a lattice constant of 8.9 nm.32 Two kinds of spherical-like mesoporous cavities exist in MIL-101: a large cavity and a small cavity with a free diameter of 3.4 nm and 2.9 nm, respectively, which are sufficiently large to accommodate a unit cell of CH4 hydrate. MIL-101 is assembled from two building blocks of 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid (1,4-BDC) and the octahedral Cr3O trimer, which form corner-sharing supertetrahedra. Such a superhedron has 4 vertices and 6 edges and contains a free aperture of 0.86 nm, which is large enough for water and CH4 molecules to cross. The large cavity contains 28 supertetrahedra accessible through hexagonal and pentagonal windows with 1.6 × 1.5 nm2 aperture, while the small cavity consists of 20 supertetrahedra accessible through pentagonal windows with 1.2 × 1.2 nm2 aperture.The structure of MIL-101 was constructed based on experimental crystallographic data, and then a large cavity and a small cavity were cleaved with the cleaved bonds of Cr3O trimers terminated by methyl groups, following the methods in our previous study.33 The large and small cavities were placed into a simulation box with a size of 16.3 × 7.4 × 7.3 nm3, and the distance between the surfaces of the two cavity structures was 4.4 nm (Fig. 1). We used such a simplified MIL-101 model for two considerations. First, MOF samples in experimental studies often include intergranular mesopores among MOF particles, in addition to intrinsic cavities like the large and small MIL-101 cavities, thus, the outer space of the cavities can be regarded as intergranular mesopores. Second, the unit cell of MIL-101 is as large as 8.9 nm and direct simulation using a unit cell would be time-consuming. Thereafter, 2263 CH4 and 26![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 014 H2O molecules were randomly placed in the simulation box to form a homogeneous mixture with CH4 mole fraction xCH4 = 0.08. Such a homogeneous aqueous solution of CH4 containing MIL-101 cavities was taken as the initial configuration for simulation up to 900 ns to explore CH4 hydrate formation. It should be noted that the CH4 solution was moderately supersaturated with xCH4 = 0.08, much lower than that in sI crystalline hydrate (xCH4 = 0.148).
014 H2O molecules were randomly placed in the simulation box to form a homogeneous mixture with CH4 mole fraction xCH4 = 0.08. Such a homogeneous aqueous solution of CH4 containing MIL-101 cavities was taken as the initial configuration for simulation up to 900 ns to explore CH4 hydrate formation. It should be noted that the CH4 solution was moderately supersaturated with xCH4 = 0.08, much lower than that in sI crystalline hydrate (xCH4 = 0.148).
H2O and CH4 molecules were represented by TIP4P/Ice34 and OPLS-UA models,35 respectively. The Lennard–Jones parameters for MIL-101 were taken from the Universal Force Field (UFF),36 which can precisely describe the diffusion and adsorption behavior of gas molecules in MOFs. The cross-interaction parameters between unlike species were calculated using the Lorentz–Berthelot combination rule. The initial configurations of large and small cavities of MIL-101 were structurally optimized using density-functional theory (DFT) in DMol3, and the atomic charges of MIL-101 were taken from our previous study.18 Electrostatic interactions were calculated using the particle mesh Ewald method.37 Short-range nonbonded interactions were estimated with a cutoff of 1.0 nm. The pressure and temperature for the system were controlled with the Parrinello-Rahman barostat38 and the Nosé–Hoover thermostat,39 respectively. Trajectories were integrated using the leapfrog method with a time step of 2 fs and coordinates were saved every 40 ps. The MIL-101 cavities were position restrained with a moderate force constant of 1000 kJ mol−1 nm−2 during the simulation, thus, the cavities showed partial flexibility. The temperature and pressure for the system were set to 285 K and 50 MPa, corresponding to moderate subcooling of about 19 K. This is different from the high subcooling of 54 K (250 K and 50 MPa) usually adopted in previous MD simulation studies on CH4 hydrate formation from a gas/water two-phase system or a homogeneous CH4 solution system.30,31,40 The choice of moderate subcooling is based on the fact that there is relatively low subcooling in actual CH4 hydrate reservoirs under the sea floor, e.g., 283.15 K and 15 MPa for hydrate reservoirs in the South Sea of China.41 In addition, the conditions of 285 K and 15 MPa were also simulated to further examine the effect of lower subcooling of about 7 K on CH4 hydrate formation. To reveal the role of MIL-101 in CH4 hydrate formation and evolution, a control system without MIL-101 was simulated. Three repeated runs (Run1, Run2 and Run3) were performed using GROMACS-5.0.7 (ref. 42) for each condition, i.e., at 285 K and 50 MPa in the presence and absence of MIL-101, and at 285 K and 15 MPa in the presence of MIL-101. The corresponding subcooling temperatures were estimated based on the three-phase (water-hydrate-methane) coexistence curves of CH4 hydrate,43 which was simulated with the same potential models as used in this work (see Fig. S1†).
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Competition between CH4 hydrate formation and phase separation of CH4 in solution at moderate subcooling
To monitor the formation of CH4 hydrate in the system at moderate subcooling of 19 K (at 285 K and 50 MPa), a four-body structural order parameter (F4) for water molecules was analyzed. F4 is defined as ensemble averaged <cos(3θ)> and describes the torsion angle θ between the oxygen atoms of two water molecules within 0.35 nm and the outermost hydrogen atoms. It is often adopted to characterize the phase change of water by tracking the evolution of average value: 0.7, −0.04 and −0.4 for hydrate, liquid water and ice, respectively.44 The evolution of F4 during three repeated runs is shown in Fig. 2A. Additionally, the algorithm proposed by Jacobson et al. was used to recognize cage geometries45 and seven types of cages (512, 51262, 51263, 51264, 4151062, 4151063 and 4151064) were identified to be the most abundantly formed during CH4 hydrate formation. Fig. 2B displays the number of water molecules Nw in hydrate form (i.e., forming these seven types of cages). | ||
| Fig. 2 Evolution of (A) F4 order parameter and (B) number of water Nw in hydrate form during three repeated runs at 285 K and 50 MPa with subcooling of 19 K. | ||
As shown in Fig. 2A, F4 values in the three repeated runs increase from −0.04 at the beginning of the simulations, indicating that CH4 hydrate can easily nucleate in the supersaturated CH4 solution with xCH4 = 0.08. Afterwards, F4 values in Run1 and Run2 increase sharply to 0.16 and 0.05 within the initial 200 ns and 100 ns, and then increase gradually to 0.24 and 0.11 in the remaining simulation, respectively. This suggests two growth stages for CH4 hydrate: initial rapid growth and subsequent slow growth. In contrast, a different phenomenon is observed in Run3. The F4 value in Run3 increases quickly to a maximum of 0.05 at 75 ns and then drops slowly to −0.04 at 310 ns (Fig. 2A), indicating that the formed CH4 hydrate in Run3 decomposes gradually after the rapid hydrate growth stage. Furthermore, during the initial 50 ns, the F4 value in Run3 increases faster and is larger than those in Run1 and Run2, reflecting faster hydrate growth at the initial stage in Run3. The final F4 value in Run1 at 900 ns is much larger than that in Run2 (Fig. 2A) and more water molecules in Run1 are converted into hydrates (Fig. 2B), i.e., more hydrate solids are formed in Run1. It is noted that the final F4 values in Run1 and Run2 (0.24 and 0.11) are much smaller than that for hydrate (0.7), as the water in the system is excessive (the composition of CH4 in the system xCH4 = 0.08 is lower than xCH4 = 0.148 in sI crystalline hydrate) and there are still many water molecules in a liquid state. Such different formation behavior of CH4 hydrate in the three repeated runs is also reflected in the evolution of Nw in hydrate form (Fig. 2B). In Run1 and Run2, Nw increases quickly to 7500 and 3100 within 200 ns and 100 ns, and then gradually to 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500 and 5500 in the remaining simulation. In contrast, Nw in Run3 increases to 2500 at 75 ns and then decreases slowly to 0 at 310 ns. Further analysis will be performed below to elucidate the underlying mechanism in the formation kinetics of CH4 hydrate.
500 and 5500 in the remaining simulation. In contrast, Nw in Run3 increases to 2500 at 75 ns and then decreases slowly to 0 at 310 ns. Further analysis will be performed below to elucidate the underlying mechanism in the formation kinetics of CH4 hydrate.
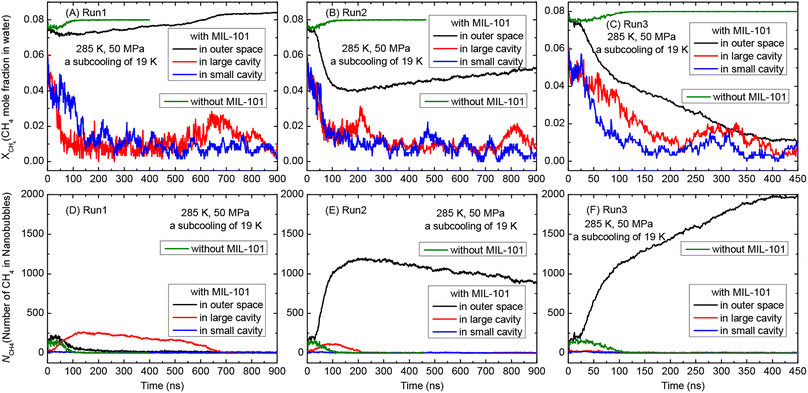
In addition to hydrate formation, phase separation of CH4 is also observed to occur in the supersaturated CH4 solution with initial xCH4 = 0.08 at moderate subcooling of 19 K (at 285 K and 50 MPa). It is noted that phase separation of CH4 reduces gas concentration in the solution, which has been demonstrated to play an important role in hydrate formation as hydrate grows faster at a higher gas concentration.31 Thus, the CH4 mole fraction in water (xCH4) and the number of CH4 molecules in nanobubbles (NCH4) in the small and large cavities of MIL-101 and their outer space were analyzed. As shown in Fig. 3D, in Run1, NCH4 in the outer space and in the large cavity of MIL-101 increase to a maximum of 230 and 260 at 50 ns and 120 ns, respectively, indicating the phase separation of CH4 in these regions. As a consequence, xCH4 in the outer space and in the large cavity decreases to 0.07 and 0.005 (Fig. 3A). In the subsequent simulation, with the sustained growth of CH4 hydrate, xCH4 in the outer space gradually increases to 0.085 and NCH4 in nanobubbles decreases to 0, i.e., the nanobubbles in the outer space completely decompose. In Run2, similar phase separation of CH4 in solution occurs. As shown in Fig. 3E, large nanobubbles containing up to 1200 CH4 molecules form in the outer space, while small nanobubbles with 120 CH4 molecules form in the large cavity of MIL-101. With the growth of CH4 hydrate, the small nanobubbles in the large cavity quickly decompose and the large nanobubbles gradually shrink to smaller ones with 850 CH4 molecules at 900 ns. Accordingly, xCH4 in the outer space decreases sharply to 0.04 and then increases slowly to 0.052 (Fig. 3B). In Run3, phase separation of CH4 occurs in the outer space of MIL-101 cavities and no obvious phase separation is observed in MIL-101 cavities. NCH4 in nanobubbles in the large and small cavities is close to 0, while most of the CH4 molecules (up to 2000) in the outer space gradually convert into nanobubbles (Fig. 3F). Thus, xCH4 in the outer space decreases continuously to 0.01 during the whole simulation (Fig. 3C).
It is observed that phase separation of CH4 in solution is a process of attracting and consuming aqueous CH4 molecules. During phase separation of CH4 in the large cavity of MIL-101 in Run1 (0–120 ns) and Run2 (0–80 ns), aqueous CH4 molecules therein are gradually depleted due to the formation of nanobubbles (Fig. 3D and E), and xCH4 in the large cavity is much lower than xCH4 in the outer space (Fig. 3A and B). Thus, a gas concentration gradient is established between these two regions and drives CH4 molecules to diffuse into the large cavity to further promote phase separation therein, as evidenced by the increase in the number of CH4 in the large cavity during 0–120 ns in Run1 and during 0–80 ns in Run2 (Fig. 4). By contrast, such CH4 transport from the outer space into MIL-101 cavities is not observed in the large cavity in Run3 and in the small cavity during the three repeated runs, as no obvious phase separation occurs therein. Interestingly, as shown in Fig. 4, the number of CH4 molecules in the large cavity decreases from a maximum during 120–900 ns in Run1 and during 80–300 ns in Run2, while the number of CH4 molecules in the large cavity in Run3 and in the small cavity during the three repeated runs decreases constantly from the beginning of the simulation. This indicates that CH4 molecules diffuse out from MIL-101 cavities into the outer space, probably to facilitate the formation of large nanobubbles and large hydrates in the outer space of cavities, as discussed below. Such two-way migration of CH4 molecules between the cavities and outer space was also observed in a recent experimental study on CH4 hydrate formation in activated carbons.46 As a result, in the late stage of simulation, xCH4 in the cavities of MIL-101 is low and no obvious nanobubble forms therein (Fig. 3A–C). In contrast, the finally formed large CH4 nanobubbles are always located in the outer space of MIL-101 cavities.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Evolution of the number of CH4 molecules in the large and small cavities of MIL-101 during three repeated runs at 285 K and 50 MPa with subcooling of 19 K. | ||
In order to directly inspect the processes of CH4 hydrate formation and phase separation of CH4 in the system at moderate subcooling of 19 K, we prepared the simulation snapshots of Run1, Run2 and Run3 (Fig. 5), which show the evolution of seven types of hydrate cages. For easy visualization, the periodic boundary of the simulation box was modified following the procedure in Fig. S2† to ensure the nucleation and growth of hydrate within the box (MIL-101 and CH4 nanobubbles may cross the box boundary). In the homogeneous CH4 solution in the presence of MIL-101 (Fig. 5A(I)–C(I)), hydrate cages uniformly form and generate several cage clusters (Fig. 5A(II)–C(II)). Most of these clusters grow to large hydrate (Fig. 5A(II)–(VII), B(II)–(VII), and C(II)–(IV)), while a few decompose (e.g., the two clusters on the left side in Run2, see Fig. 5B(II)–(IV)). As shown in Fig. 5A(II)–(VII), with the hydrate growth in Run1, CH4 molecules are gradually converted into hydrate and finally depleted in the solution (Fig. 5A(VII)). This indicates that CH4 hydrate formation is also a process of attracting and consuming many aqueous CH4 molecules. From Fig. 5, it is found that hydrate formation always occurs in the outer space, not in the MIL-101 cavities due to the low xCH4 therein (Fig. 3A–C). Under the moderate subcooling conditions, phase separation of CH4 to form nanobubbles occurs in the supersaturated CH4 solution and competes with the formation of CH4 hydrate for aqueous CH4 molecules. In Run1, phase separation of CH4 takes place in the large cavity of MIL-101 and forms a small nanobubble, which decomposes completely with the growth of large hydrate in the outer space (Fig. 5A(III)–(VI)). In Run2, during the phase separation of CH4, one small nanobubble and one large nanobubble form in the large cavity of MIL-101 and in the outer space (Fig. 5B(III)), respectively. Later, with the sustained growth of hydrate, the small nanobubble in the large cavity of MIL-101 completely disappears, while the large nanobubble in the outer space shrinks slowly (Fig. 5B(III)–(VII)). In Run3, one large nanobubble forms in the outer space of MIL-101 cavities during phase separation of CH4, while two cage clusters grow to two middle-sized hydrates (Fig. 5C(II)–(IV)). Interestingly, with the sustained growth of the large CH4 nanobubble, both middle-sized hydrates gradually decompose due to the accumulation of CH4 molecules in the nanobubble (Fig. 5C(IV)–(VII)). Such competition between hydrate formation and CH4 phase separation is also visualized in Videos S1–S3† for Run1, Run2 and Run3, respectively. The results for such competition can be summarized as follows: in Run1, almost all CH4 molecules in the system are converted into two hydrates (Fig. 5A(VII)); in Run2, about half of CH4 molecules in the system form a large nanobubble and the other CH4 molecules form a large hydrate (Fig. 5B(VII)); in Run3, almost all CH4 molecules in the system form a huge nanobubble (Fig. 5C(VII)). Additionally, the stability of CH4 nanobubbles and CH4 hydrate appears to be related to their sizes, i.e., the larger the size, the higher the stability. Thus, during the growth of large hydrate in Run2, the small nanobubble in the large cavity of MIL-101 decomposes more easily than the large nanobubble in the outer space (Fig. 5B(III)–(V)), whereas two middle-sized hydrates in Run3 (Fig. 5C(IV)) decompose more easily than the large hydrate in Run2 (Fig. 5B(IV)). Thus, the outcome of the competition between hydrate formation and phase separation is mainly determined by the relative stabilities of CH4 hydrate solids and CH4 nanobubbles.
3.2 Structures and crystallinity of incipient CH4 hydrate formed at moderate subcooling
It is found that moderate subcooling may facilitate the formation of crystalline CH4 hydrate. There are two types of crystalline forms for CH4 hydrate, namely, cubic structure I (sI), and cubic structure II (sII). sI hydrate is constructed from 51262 and 512 cages with a ratio of 6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2, while 51264 and 512 cages constitute sII hydrate with a ratio of 8
2, while 51264 and 512 cages constitute sII hydrate with a ratio of 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 16, i.e., the unit cell of sII hydrate has eight times more 512 cages than in sI hydrate.47 Moreover, 512 cages are arranged in different ways in sI and sII hydrates: in sI hydrate, 512 cages fill the interstices of 51262 cages but never share faces, whereas many 512 cages share faces in sII hydrate. It is observed that a large ordered incipient CH4 hydrate containing sI and sII domains forms on the right side of the system in Run1 (Fig. 5A) and in the middle of the system in Run2 (Fig. 5B), and the detailed formation process is displayed in Fig. 6A and B, respectively. A sII motif containing several 512 and 51264 cages forms in the outer space of MIL-101 cavities (Fig. 6A(I) and B(I)), which originated from an amorphous cluster of cages. This sII motif grows into a medium-sized sII domain, and a sI motif is observed to emerge on the lateral side of the sII domain (see the circles in Fig. 6A(II) and B(II)), which serves as a nucleus of the sI domain. Subsequently, the sII domain and the sI motif in the same hydrate co-grow simultaneously and rapidly (Fig. 6A(III) and B(III)). At the end of the simulation, a large hydrate with long-range order forms, which occupies almost the whole space between the large and small cavities of MIL-101. Moreover, crystalline sI and sII domains coexist in the ordered hydrate by connecting to each other with the linking cage 51263 (Fig. 6A(IV) and B(IV)). The dynamic formation process of the large ordered CH4 hydrate in Run1 and Run2 is also visualized in Videos S4 and S5.† The co-formation of sI and sII CH4 hydrate observed in this work is considered a kinetically favored process. It is well known that CH4 hydrate adopts sI as a thermodynamically stable phase. Nevertheless, at the nucleation and early growth stages of the ordered CH4 hydrate solids, the 512 cage is the most abundant and its growth is obviously earlier and faster than other cage types (Fig. 7C and D), and these abundantly formed face-sharing 512 cages (Fig. 6A(I) and B(I)) could facilitate the formation of sII hydrate. The reason why the 512 cage is kinetically favored over other cage types is because its size is most fitting for CH4, and more importantly, the angle in its pentagonal ring is quite close to the angle in water hydrogen bonding. Interestingly, such coexistence of sI and sII was also reported in a previous experimental study on CH4 hydrate formation at moderate subcooling.48 It is noted that stochasticity plays a role in the formation of these ordered incipient hydrates. The incipient large hydrate formed on the left side of the system in Run1 (Fig. 5A(VII)) and the two middle-sized hydrates formed in Run3 (Fig. 5C(IV)) are relatively amorphous with short-range order, only containing certain small sI or sII motifs (Fig. S3†).
16, i.e., the unit cell of sII hydrate has eight times more 512 cages than in sI hydrate.47 Moreover, 512 cages are arranged in different ways in sI and sII hydrates: in sI hydrate, 512 cages fill the interstices of 51262 cages but never share faces, whereas many 512 cages share faces in sII hydrate. It is observed that a large ordered incipient CH4 hydrate containing sI and sII domains forms on the right side of the system in Run1 (Fig. 5A) and in the middle of the system in Run2 (Fig. 5B), and the detailed formation process is displayed in Fig. 6A and B, respectively. A sII motif containing several 512 and 51264 cages forms in the outer space of MIL-101 cavities (Fig. 6A(I) and B(I)), which originated from an amorphous cluster of cages. This sII motif grows into a medium-sized sII domain, and a sI motif is observed to emerge on the lateral side of the sII domain (see the circles in Fig. 6A(II) and B(II)), which serves as a nucleus of the sI domain. Subsequently, the sII domain and the sI motif in the same hydrate co-grow simultaneously and rapidly (Fig. 6A(III) and B(III)). At the end of the simulation, a large hydrate with long-range order forms, which occupies almost the whole space between the large and small cavities of MIL-101. Moreover, crystalline sI and sII domains coexist in the ordered hydrate by connecting to each other with the linking cage 51263 (Fig. 6A(IV) and B(IV)). The dynamic formation process of the large ordered CH4 hydrate in Run1 and Run2 is also visualized in Videos S4 and S5.† The co-formation of sI and sII CH4 hydrate observed in this work is considered a kinetically favored process. It is well known that CH4 hydrate adopts sI as a thermodynamically stable phase. Nevertheless, at the nucleation and early growth stages of the ordered CH4 hydrate solids, the 512 cage is the most abundant and its growth is obviously earlier and faster than other cage types (Fig. 7C and D), and these abundantly formed face-sharing 512 cages (Fig. 6A(I) and B(I)) could facilitate the formation of sII hydrate. The reason why the 512 cage is kinetically favored over other cage types is because its size is most fitting for CH4, and more importantly, the angle in its pentagonal ring is quite close to the angle in water hydrogen bonding. Interestingly, such coexistence of sI and sII was also reported in a previous experimental study on CH4 hydrate formation at moderate subcooling.48 It is noted that stochasticity plays a role in the formation of these ordered incipient hydrates. The incipient large hydrate formed on the left side of the system in Run1 (Fig. 5A(VII)) and the two middle-sized hydrates formed in Run3 (Fig. 5C(IV)) are relatively amorphous with short-range order, only containing certain small sI or sII motifs (Fig. S3†).
 | ||
| Fig. 7 (A and B) Crystallinity and (C and D) number of seven types of cages for the large ordered hydrate formed on the right side of the system during Run1 (see Fig. 5A) and in the middle of the system during Run2 (see Fig. 5B) at 285 K and 50 MPa with subcooling of 19 K. | ||
To quantify the crystallinity degree of the large ordered CH4 hydrates formed in Run1 and Run2, crystallinity was calculated from the ratio of the number of characteristic cage links of a crystalline hydrate to the total number of cage links in the system.31 Crystallinity with a value 0 indicates a completely amorphous hydrate and a value of 1 means a perfect crystalline hydrate. Fig. 7A and B display the crystallinities of the ordered hydrates formed on the right side in Run1 and in the middle in Run2, respectively. Fig. 7C and D illustrate the corresponding evolution of seven types of cages. For the hydrate in Run 1 at 900 ns, its sI and sII crystallinities are about 0.4 and 0.5 (Fig. 7A), suggesting that the fractions of sI and sII structures are comparable. At the end of simulation (900 ns), as shown in Fig. 7B, the sI and sII crystallinities of the ordered hydrate in Run2 are about 0.2 and 0.55, respectively, indicating that most structures of the hydrate belong to sII and a small portion belongs to sI. Additionally, it is found that the evolution of sI and sII crystallinities is closely related to the growth of sI and sII domains in the ordered hydrate, i.e., the evolution of seven types of cages therein. For example, the number of sI-specific 51262 cages in the ordered hydrate in Run1 increases from 10 at 100 ns to 75 at 450 ns (Fig. 7C), indicating the growth of the sI domain, and makes the corresponding sI crystallinity in Run1 increase from 0.15 at 100 ns to 0.45 at 450 ns (Fig. 7A). Similarly, with increasing the number of sII-specific 51264 cages from 500 to 900 ns (Fig. 7C), the sII crystallinity in Run 1 is enhanced from 0.35 to 0.5 at 900 ns (Fig. 7A). Due to the coexistence of large sI and sII domains in the ordered hydrates in Run1 and Run2, 512, 51262 and 51264 cages are the most abundant cage type followed by the 51263 linking cage (Fig. 7C and D). Several meta-stable 4151062, 4151063 and 4151064 cages are observed in the incipient ordered hydrates, and most of them exist on the hydrate surfaces and convert into regular cages during hydrate growth.
3.3 Effects of lower subcooling and presence of MIL-101 on CH4 hydrate formation
To reveal the effect of low subcooling, such as in CH4 hydrate reservoirs in the South Sea of China, on CH4 hydrate formation, the condition of 285 K and 15 MPa with a corresponding lower subcooling of 7 K was chosen for further simulation. Fig. 8 shows the evolution of the simulation system under this condition during three repeated runs. It is found that at the low subcooling of 7 K, the process of phase separation of CH4 to form nanobubbles becomes dominant in a homogeneous CH4 solution with xCH4 = 0.08, while it becomes more difficult for CH4 hydrate formation. Only at the initial simulation stage (Fig. 8A(I)–(II) for Run1, Fig. 8B(I)–(III) for Run2, and Fig. 8C(I)–(IV) for Run3), several hydrate cages (no more than 10, see Fig. S4†) form and soon decompose. In contrast, phase separation of CH4 to form nanobubbles takes place easily in the solution. As a result, xCH4 in the small and large cavities of MIL-101 and their outer space decreases sharply to around 0.01 (Fig. S5A–C†), while NCH4 in nanobubbles in the outer space of MIL-101 increases rapidly (Fig. S5D–F†). Nevertheless, no obvious phase separation occurs in MIL-101 cavities, as NCH4 therein is close to 0. Additionally, migration of CH4 molecules from the MIL-101 cavities to the outer space is also observed (Fig. S6†), similar to the situation at 285 K and 50 MPa (Fig. 4). | ||
| Fig. 8 Phase separation of CH4 to form nanobubbles during Run1 (A(I)–(VII)), Run2 (B(I)–(VII)) and Run3 (C(I)–(VII)) at 285 K and 15 MPa with subcooling of 7 K. Hydrate cages are colored as in Fig. 5. MIL-101 cavities, CH4 and water molecules are shown as magenta sticks, green balls and light blue lines, respectively. The red arrows in the panels indicate the coalescence of CH4 nanobubbles. | ||
An interesting phenomenon is observed in the evolution of CH4 nanobubbles at a low subcooling of 7 K (at 285 K and 15 MPa). With the rapid phase separation of CH4 in solution, several small nanobubbles emerge in the system in the three repeated runs (Fig. 8A(III), B(II) and C(II)), and two small nanobubbles are observed to merge into a large nanobubble (Fig. 8A(III), (IV), B(II), B(III), C(II) and C(III)), and then only form two stable nanobubbles (Fig. 8A(V), B(IV) and C(IV)). Interestingly, as shown in Fig. 8A(V)–(VI) for Run1, and in Fig. 8B(IV)–B(V) for Run2, the large nanobubble gradually grows into a larger size, while the small nanobubble shrinks slowly until it completely disappears (Fig. 8A(VI)) or directly merges to the large nanobubble (Fig. 8B(VI)). Finally, the large nanobubble elongates in one direction to form an ellipsoid shape and develops into a stable cylindrical nanobuble crossing the simulation box (Fig. 8A(VII), B(VII) and S7†). Such evolution of CH4 nanobubbles also occurs in Run3 (Fig. 8C(IV)–(VII)), though it takes a much longer time as both nanobubbles have similar sizes and are very stable. The evolution of large and small nanobubbles in solution is similar to Ostwald ripening and is to minimize the surface energy of nanobubbles. Phase separation of CH4 in solution and coalescence of CH4 nanobubbles in the three repeated runs at 285 K and 15 MPa are visualized in Videos S6–S8.†
To unravel the role of MIL-101 in CH4 hydrate formation and evolution, we compare the results from three repeated runs in the presence and absence of MIL-101, respectively, under the same condition (285 K and 50 MPa with subcooling of 19 K). The main effect of MIL-101 is that its presence may promote phase separation of CH4 in solution to form nanobubbles, and then reduce the aqueous CH4 concentration and affect CH4 hydrate formation. In addition, the large and small cavity structures of MIL-101 provide two nanospaces with a diameter of 3.4 and 2.9 nm in solution. In the absence of MIL-101, xCH4 slightly decreases to 0.075 only at the initial simulation stage (Fig. 3), because a few CH4 molecules form small clusters in solution, and no phase separation and CH4 nanobubble formation are clearly observed in all three repeated runs (Fig. 9). In contrast, in the presence of MIL-101, phase separation of CH4 and formation of large nanobubbles occur in the large cavity of MIL-101 and the outer space (Fig. 3 and 5). The underlying mechanism for MIL-101 to promote phase separation of CH4 in solution may arise from two factors. The first factor is that the atoms of polar groups in MIL-101, including Cr and O in the Cr3O trimer, O in the carboxylate groups of 1,4-BDC and F, bind surrounding water molecules (as confirmed by the high peaks between these atoms and water oxygen in the g(r) curve, see Fig. 10A), thus weakening their ability to solvate CH4 molecules in solution. The second factor is that the methyl and benzene groups in MIL-101 adsorb CH4 molecules, as evidenced by the peaks at around 0.4 nm in the g(r) curve for CH4 and carbon atoms in these groups of MIL-101 (Fig. 10B), which may facilitate the formation of CH4 nanobubbles. It is noted that the presence of MIL-101 does not change the mode for hydrate formation in homogeneous CH4 solution, i.e., hydrate cages uniformly form at several sites in the system and develop into small clusters, which merge into one or two large hydrate clusters and then sustainedly grow to form large hydrate solids, as shown in Fig. 5 and 9. It is worth mentioning that CH4 hydrate solids formed in the absence of MIL-101 (Fig. 9A(VI), B(VI) and C(VI)) are quite amorphous with only certain sI and sII motifs (Fig. S3C and D†), further highlighting the important role of stochasticity in the formation of crystalline hydrate from a homogeneous CH4 solution at moderate subcooling of 19 K (at 285 K and 50 MPa). CH4 hydrate formation in the three repeated runs in the absence of MIL-101 is visualized in Videos S9–S11.†
 | ||
| Fig. 9 CH4 hydrate formation in CH4 solution in the absence of MIL-101 during Run1 (A(I)–(VI)), Run2 (B(I)–(VI)) and Run3 (C(I)–(VI)) at 285 K and 50 MPa with subcooling of 19 K. Hydrate cages are colored as in Fig. 5. CH4 and water molecules are shown as green balls and light blue lines, respectively. | ||
3.4 Implications for CH4 storage in porous materials via forming hydrates
When the adsorption-hydrate hybrid method is used for CH4 storage, it is expected to adsorb CH4 in the intrinsic nanopores of porous materials and form CH4 hydrates in the intergranular space, leading to a maximum gas storage capacity. In this study, a moderate temperature of 285 K and a pressure of 50 MPa (i.e., moderate subcooling of about 19 K) are implemented for CH4 hydrate formation in MIL-101. The main finding is that at such moderate subcooling, CH4 hydrate formation and phase separation of CH4 to form nanobubbles occur simultaneously in a homogeneous CH4 solution, and these two processes compete with each other. Nevertheless, the finally formed large CH4 nanobubbles always stay in the outer space rather than in the confined space of MIL-101 cavities. When the subcooling is lowered to 7 K (285 K and 15 MPa), the process of phase separation of CH4 to form nanobubbles becomes dominant over CH4 hydrate formation. In contrast, at higher subcooling of 29 K (275 K and 50 MPa), our previous study18 has shown that phase separation of CH4 to form nanobubbles is suppressed (Fig. S8†), while CH4 hydrate formation becomes dominant. These observations suggest that proper low subcooling (i.e., pressure-temperature conditions) should be adopted to facilitate CH4 hydrate formation and meanwhile suppress phase separation of CH4. Recent experimental studies also highlight the importance of proper pressure-temperature conditions for CH4 storage in porous materials with the adsorption-hydrate hybrid method. Chen et al. observed CH4 adsorption and hydrate formation in wetted ZIF-8 at 275.15 K and 7.0 MPa, however, no hydrate was formed at a higher temperature of 283.15 K.13 Koh et al. determined the dissociation temperatures of CH4 hydrate in HKUST-1, ZIF-8 and ZIF-67 at 8.0 MPa were 283.45–283.85 K, 281.15–281.65 K and 281.75–282.05 K, respectively.9,10 Natural gas hydrates in actual marine sediments may also form under moderate subcooling, e.g., 283.15 K and 15 MPa for hydrate reservoirs in the South Sea of China. Therefore, it is crucial to properly control operating conditions to achieve high-performance CH4 storage in porous materials. It is noted that to ensure CH4 hydrate formation within acceptable simulation time, this study has simulated a moderately supersaturated homogeneous CH4 solution with xCH4 = 0.08, i.e., CH4 molecules were directly dispersed in water; while in previous experimental studies,8,9,11 the cavities and intergranular space of pre-humidified MOFs were filled with water molecules. Thus, future MD studies should simulate the pre-humidified MOFs exposed to the CH4 gas phase, to elucidate how subcooling affects the diffusion and dissolution of CH4 into water and the subsequent nanobubble formation and hydrate formation processes in MOFs.4. Conclusions
Aiming to reveal the effect of moderate subcooling on CH4 hydrate formation, MD simulations have been performed to investigate CH4 hydrate formation from a homogeneous CH4 solution with xCH4 = 0.08 in the presence of MIL-101 at 285 K and 50 MPa (i.e., at subcooling of 19 K). The results show that at this moderate subcooling, CH4 hydrate formation and phase separation of CH4 to form nanobubbles occur simultaneously, and compete with each other for aqueous CH4 molecules. The outcome of the competition is primarily determined by the relative stabilities of CH4 hydrate solids and CH4 nanobubbles, which are closely related to their sizes. CH4 hydrate formation occurs exclusively in the outer space of MIL-101 cavities, whereas phase separation of CH4 to form nanobubbles takes place simultaneously in the MIL-101 cavities and their outer space. The small nanobubbles in the MIL-101 cavities gradually shrink and finally disappear, as CH4 molecules therein diffuse out to facilitate the growth of large nanobubbles and large hydrates in the outer space. Finally, the formed large CH4 nanobubbles and large CH4 hydrates always stay in the outer space rather than in the confined space of MIL-101 cavities. Moderate subcooling appears to facilitate the formation of large ordered CH4 hydrates containing sI and sII domains. Additionally, it is revealed that a lower subcooling of 7 K (at 285 K and 15 MPa) promotes the phase separation of CH4 to form nanobubbles and inhibits hydrate formation in a homogeneous CH4 solution. In the evolution of CH4 nanobubbles during phase separation, coalescence of CH4 nanobubbles to form large nanobubbles and an interesting phenomenon similar to Ostwald ripening are observed, i.e., the large nanobubble sustainedly grows to a larger size, while the small nanobubble shrinks gradually until completely disappears. The presence of MIL-101 can facilitate the phase separation of CH4 in solution. These molecular insights into the effects of the degree of subcooling on CH4 hydrate formation in MIL-101 could have important implications on optimizing pressure-temperature conditions for CH4 storage in porous materials with adsorption-hydrate hybrid technology.Author contributions
Zhongjin He: investigation, methodology, software, validation, visualization, formal analysis, data curation, writing – original draft, writing – review & editing, funding acquisition. Jianwen Jiang: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing – review and editing. Guosheng Jiang: resources, writing – review and editing. Fulong Ning: resources, writing – review and editing, project administration, funding acquisition.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42376202 and 41976203), and National Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (42225207).References
- A. S. Jalilov, Y. L. Li, C. Kittrell and J. M. Tour, Nat. Energy, 2017, 2, 932–938 CrossRef CAS
.
- E. Soubeyrand-Lenoir, C. Vagner, J. W. Yoon, P. Bazin, F. Ragon, Y. K. Hwang, C. Serre, J. S. Chang and P. L. Llewellyn, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 10174–10181 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- L. Mu, B. Liu, H. Liu, Y. T. Yang, C. Y. Sun and G. J. Chen, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 12246–12252 RSC
.
- E. D. Sloan, Nature, 2003, 426, 353–359 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- A. Falenty, W. F. Kuhs, M. Glockzin and G. Rehder, Energy Fuels, 2014, 28, 6275–6283 CrossRef CAS
.
- L. Borchardt, M. E. Casco and J. Silvestre-Albero, Chemphyschem, 2018, 19, 1298–1314 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Y. Wang, J. Duan, S. J. Chen, Y. Fu, X. F. Li, D. Wang, M. Zhang, Z. Q. Zhang, D. D. Liu and F. H. Wang, J. Energy Storage, 2022, 50, 104195 CrossRef
.
- M. E. Casco, F. Rey, J. L. Jordá, S. Rudic, F. Fauth, M. Martínez-Escandell, F. Rodríguez-Reinoso, E. V. Ramos-Fernández and J. Silvestre-Albero, Chem. Sci., 2016, 7, 3658–3666 RSC
.
- S. Denning, A. A. A. Majid, J. M. Lucero, J. M. Crawford, M. A. Carreon and C. A. Koh, ACS Appl. Mat. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 53510–53518 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Denning, A. A. A. Majid, J. M. Lucero, J. M. Crawford, M. A. Carreon and C. A. Koh, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2021, 9, 9001–9010 CrossRef CAS
.
- C. Cuadrado-Collados, G. Mouchaham, L. Daemen, Y. Q. Cheng, A. Ramirez-Cuesta, H. Aggarwal, A. Missyul, M. Eddaoudi, Y. Belmabkhout and J. Silvestre-Albero, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 13391–13397 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. Duan, Q. C. Li, Y. Fu, S. J. Chen, Y. X. Zhang and D. D. Liu, Fuel, 2022, 322, 124266 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. J. Chen, D. Wang, Z. Y. Wang, Y. Fu, Y. H. Xu and D. D. Liu, Energy, 2023, 283, 129013 CrossRef CAS
.
- H. Liu, S. Y. Zhan, P. Guo, S. S. Fan and S. L. Zhang, Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 349, 775–781 CrossRef CAS
.
- D. Kim, Y. H. Ahn and H. Lee, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2015, 60, 2178–2185 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Denning, J. M. Lucero, A. A. A. Majid, J. M. Crawford, M. A. Carreon and C. A. Koh, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2021, 125, 20512–20521 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Denning, A. A. A. Majid, J. M. Crawford, J. D. Wells, M. A. Carreon and C. A. Koh, Fuel, 2022, 325, 124920 CrossRef CAS
.
- Z. J. He, K. Zhang and J. W. Jiang, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2019, 10, 7002–7008 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Y. Wang, J. Duan, S. J. Chen, Y. Fu, Y. X. Zhang, D. Wang, J. L. Pei and D. D. Liu, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 430, 132901 CrossRef CAS
.
- J. Duan, X. Y. Jiang, Y. Fu, S. J. Chen and M. C. Zi, Fuel, 2023, 337, 126851 CrossRef CAS
.
- Z. Li, N. Li, J. Y. Kan, B. Liu and G. J. Chen, Fuel, 2023, 351, 129055 CrossRef CAS
.
- R. Boswell, Science, 2009, 325, 957–958 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. R. Chong, S. H. B. Yang, P. Babu, P. Linga and X.-S. Li, Appl. Energy, 2016, 162, 1633–1652 CrossRef
.
- M. B. Clennell, P. Henry, M. Hovland, J. S. Booth and M. Thomas, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 1999, 912, 887 CrossRef
.
- Z. J. He, P. Linga and J. W. Jiang, Langmuir, 2017, 33, 11956–11967 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. He, F. Mi and F. Ning, Energy, 2021, 234, 121260 CrossRef CAS
.
- Z. J. He, F. L. Ning, F. Y. Mi., B. Fang and G. S. Jiang, Energy Fuels, 2022, 36, 3628–3639 CrossRef CAS
.
- Z. Zhang, P. G. Kusalik, C. Liu and N. Wu, Energy, 2023, 285, 129414 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Takeya, H. Fujihisa, Y. Gotoh, V. Istomin, E. Chuvilin, H. Sakagami and A. Hachikubo, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117, 7081–7085 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. R. Walsh, C. A. Koh, E. D. Sloan, A. K. Sum and D. T. Wu, Science, 2009, 326, 1095–1098 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. J. He, K. M. Gupta, P. Linga and J. W. Jiang, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120, 25225–25236 CrossRef CAS
.
- G. Ferey, C. Mellot-Draznieks, C. Serre, F. Millange, J. Dutour, S. Surble and I. Margiolaki, Science, 2005, 309, 2040–2042 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Y. F. Chen, R. Babarao, S. I. Sandler and J. W. Jiang, Langmuir, 2010, 26, 8743–8750 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. L. F. Abascal, E. Sanz, R. G. Fernandez and C. Vega, J. Chem. Phys., 2005, 122, 234511 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- W. L. Jorgensen, J. D. Madura and C. J. Swenson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1984, 106, 6638–6646 CrossRef CAS
.
- A. K. Rappe, C. J. Casewit, K. S. Colwell, W. A. Goddard and W. M. Skiff, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, 114, 10024–10035 CrossRef CAS
.
- T. Darden, D. York and L. Pedersen, J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 10089–10092 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Parrinello and A. Rahman, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1980, 45, 1196–1199 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Nose, Mol. Phys., 1984, 52, 255–268 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Sarupria and P. G. Debenedetti, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2012, 3, 2942–2947 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- X. W. Qin, Q. Y. Liang, J. L. Ye, L. Yang, H. J. Qiu, W. W. Xie, J. Q. Liang, J. A. Lu, C. Lu, H. L. Lu, B. J. Ma, Z. G. Kuang, J. G. Wei, H. F. Lu and B. B. Kou, Appl. Energy, 2020, 278, 115649 CrossRef CAS
.
- B. Hess, C. Kutzner, D. van der Spoel and E. Lindahl, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2008, 4, 435–447 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. M. Conde and C. Vega, J. Chem. Phys., 2010, 133 Search PubMed
.
- L. A. Báez and P. Clancy, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 1994, 715, 177 CrossRef
.
- L. C. Jacobson, W. Hujo and V. Molinero, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2009, 113, 10298–10307 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- G. D. Zhang, M. T. Sun, B. J. Liu and F. Wang, Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 396, 125256 CrossRef CAS
.
-
E. D. Sloan and C. A. Koh, Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gases, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 3rd edn, 2008 Search PubMed
.
- J. M. Schicks and J. A. Ripmeester, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2004, 43, 3310–3313 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ta06952d |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |