Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Advanced materials for micro/nanorobotics†
Jeonghyo
Kim‡
 a,
Paula
Mayorga-Burrezo‡
a,
Paula
Mayorga-Burrezo‡
 b,
Su-Jin
Song‡
b,
Su-Jin
Song‡
 a,
Carmen C.
Mayorga-Martinez
a,
Mariana
Medina-Sánchez
cdef,
Salvador
Pané
a,
Carmen C.
Mayorga-Martinez
a,
Mariana
Medina-Sánchez
cdef,
Salvador
Pané
 g and
Martin
Pumera
g and
Martin
Pumera
 *abhi
*abhi
aAdvanced Nanorobots & Multiscale Robotics Laboratory, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, VSB – Technical University of Ostrava, 17. listopadu 2172/15, Ostrava 70800, Czech Republic. E-mail: martin.pumera@vsb.cz; pumera.research@gmail.com
bFuture Energy and Innovation Laboratory, Central European Institute of Technology, Brno University of Technology, Purkyňova 123, Brno 61200, Czech Republic
cCIC nanoGUNE BRTA, Tolosa Hiribidea 76, San Sebastián, 20018, Spain
dIKERBASQUE, Basque Foundation for Science, Plaza Euskadi, 5, Bilbao, 48009, Spain
eMicro- and NanoBiomedical Engineering Group (MNBE), Institute for Emerging Electronic Technologies, Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research (IFW), 01069, Dresden, Germany
fChair of Micro- and Nano-Biosystems, Center for Molecular Bioengineering (B CUBE), Dresden University of Technology, 01062, Dresden, Germany
gMulti-Scale Robotics Lab, Institute of Robotics and Intelligent Systems, ETH Zürich, Tannenstrasse 3, CH-8092 Zürich, Switzerland
hDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Yonsei University, 50 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 03722, Republic of Korea
iDepartment of Medical Research, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University, No. 91 Hsueh-Shih Road, Taichung, Taiwan
First published on 14th August 2024
Abstract
Autonomous micro/nanorobots capable of performing programmed missions are at the forefront of next-generation micromachinery. These small robotic systems are predominantly constructed using functional components sourced from micro- and nanoscale materials; therefore, combining them with various advanced materials represents a pivotal direction toward achieving a higher level of intelligence and multifunctionality. This review provides a comprehensive overview of advanced materials for innovative micro/nanorobotics, focusing on the five families of materials that have witnessed the most rapid advancements over the last decade: two-dimensional materials, metal–organic frameworks, semiconductors, polymers, and biological cells. Their unique physicochemical, mechanical, optical, and biological properties have been integrated into micro/nanorobots to achieve greater maneuverability, programmability, intelligence, and multifunctionality in collective behaviors. The design and fabrication methods for hybrid robotic systems are discussed based on the material categories. In addition, their promising potential for powering motion and/or (multi-)functionality is described and the fundamental principles underlying them are explained. Finally, their extensive use in a variety of applications, including environmental remediation, (bio)sensing, therapeutics, etc., and remaining challenges and perspectives for future research are discussed.
1. Introduction
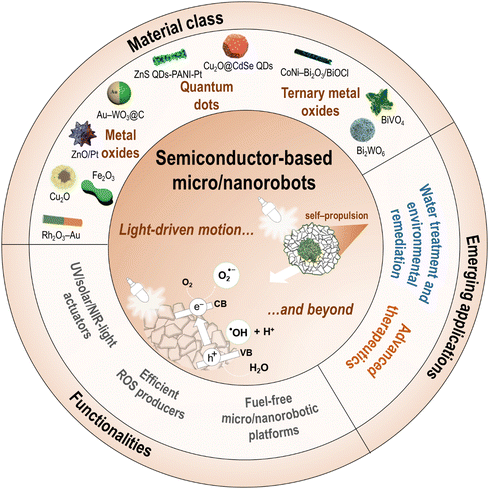
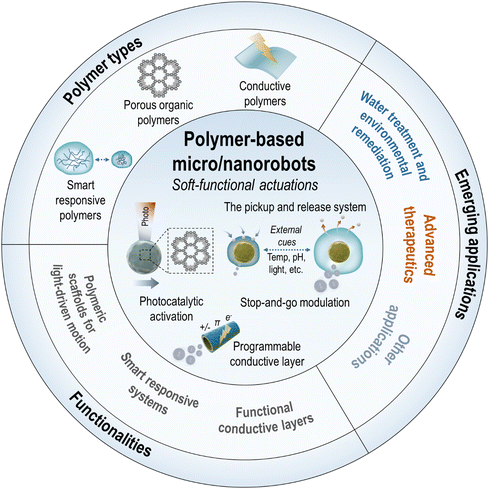
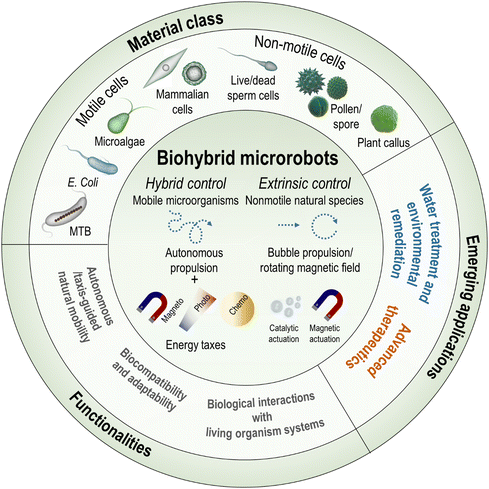
Micro/nanorobots are tiny robotic systems that are able to move precisely and perform specific tasks at a small scale by harvesting fuels or energy sources surrounding them. Their untethered and coordinated movements enable robust interaction and accurate manipulation in microenvironments, even for missions in hard-to-reach areas. The development of micro/nanorobots is a frontier area of interdisciplinary research and has evolved dynamically and rapidly in recent years. Because these small robots are primarily composed of functional components made of micro/nanoscale materials, combining advanced materials with micro/nanorobotic systems has been a key direction to achieve higher levels of maneuverability, programmability, intelligence, and multifunctionality. Among the plethora of materials being considered for micro/nanorobotics, this review focuses primarily on five emerging families of materials that have developed most rapidly in the last decade: two-dimensional materials, metal–organic frameworks, semiconductors, polymers, and biological cells. Their unique physicochemical, mechanical, optical, and biological properties have been incorporated into micro/nanorobots to achieve propulsion and actuation as they are, or to provide robotic systems with additional multifunctionalities, thus promoting their extensive use in a variety of innovative technologies.As a key requirement for next-generation micro/nanorobotics, advanced materials offer significant potential in various aspects: (i) two-dimensional (2D) materials that possess unique properties distinct from their 3D counterparts, enabling advances in nanotechnology.1–7 Emerging 2D materials such as transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), transition metal carbides (MXenes), 2D monoelemental materials (Xenes), 2D carbon nitrides (C3N4), and metal phosphorus trichalcogenides (MPX3) are now integral to micro/nanorobotics and offer novel functionalities such as light-driven microengines or bio-affinity/catalytic/photothermal interfaces;8–12 (ii) metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are highly porous crystalline materials known for their large surface area, stability, and versatile synthetic architectures.13,14 Families such as zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF), University of Oslo (UiO), or Materials Institute Lavoisier (MIL) are fascinating building blocks for micro/nanorobotic systems due to their capabilities for molecular adsorption, dynamic mass transport, and biocompatibility, etc., making them suitable for targeted drug delivery and enhanced catalytic performance;15–19 (iii) the interaction between active materials and light as a versatile and clean energy source is a highly appealing area of research in micro/nanorobotics, with semiconductors playing a crucial role in the creation of light-driven, photocatalytic micro/nanorobots.20–23 These systems act as actuators for ultraviolet (UV), visible (Vis), and/or near-infrared (NIR) light and efficiently generate motion, enabling the development of fuel-free micro/nanorobotic platforms with significant potential for environmental and biomedical applications;24–26 (iv) polymers, with their versatile properties and responsiveness to stimuli, are crucial for smart micro/nanorobotic systems, enabling controlled motion and manipulation at the micro- and nanoscale.27,28 Their programmability and adaptability, driven by multiple modulating factors such as temperature, pH, light, magnetic field, ultrasound, etc., enhance the unique soft functionalities to expand their applications in various research fields;29–33 and (v) biological cells hybridized with synthetic functional materials act as small-scale living robots in advanced therapeutic technologies, offering autonomous actuation and low toxicity.34,35 These cell-hybrid robots swim and navigate efficiently through various guidance mechanisms and can serve as biological templates for fabricating biocompatible microrobots that are attractive as next-generation medical microrobots.36–38
This review provides an up-to-date report on the progress and future prospects of micro/nanorobots as driven by advanced materials, with particular emphasis on the categorization of materials, designs, fabrication methods, motion mechanisms, specific functionalities, and advanced applications for intelligent micromachinery (Fig. 1). First, we will categorize the five fastest-growing material families and their advantageous properties that are uniquely implemented in micro/nanorobotics, including two-dimensional materials (TMDs, MXenes, Xenes, carbon nitrides, MPX3), metal–organic frameworks (ZIF types, UiO types, MIL types), semiconductors (metal oxides, ternary metal oxides, quantum dots), polymers (smart responsive polymers, porous organic polymers, conductive polymers), and biological cells (bacterial cells, mammalian cells, plant cells). Then, we will discuss the design rationales and fabrication methods for these hybrid material systems. Further, we will clarify their promising potential for powering motion and (multi)functionalities with fundamental principles behind them. Also, an overview of advanced applications will be provided, including environmental remediation, (bio)sensing, therapeutics, etc. Finally, we will give perspectives and the outlook for future research. Taken together, this review aims to provide a vast library of emerging materials for advanced micro/nanorobotics, offering to researchers in the field a comprehensive insight into the choice of materials, strategic designs, and next-generation applications.
2. Advanced micro/nanorobotic material systems
2.1. New materials for micro- and nanoscale robots
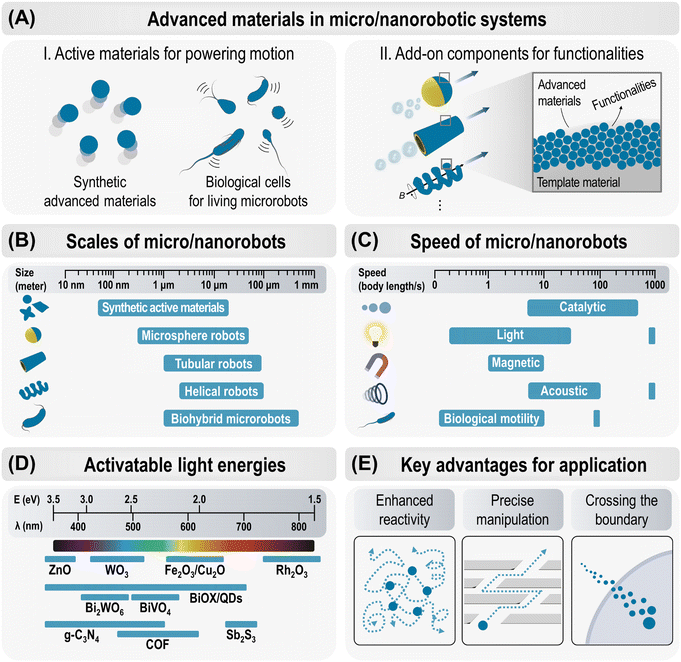
Small-scale robots capable of precise control and predefined tasks at the micro- and nanoscale were probably the first desired technologies from the early days of nanoscience and nanotechnology. The synergy between their active motion and unique physicochemical properties has led to groundbreaking innovations in micro- and nanoscale robots, significantly expanding their capabilities and applications.39–45 Micro/nanorobots are miniature machines with dimensions below 1000 μm that can convert various energy triggers into mechanical movement to perform specific functions.40,42,46 In nature, autonomous mobile systems exist at all scales, from biological molecular machines and living microorganisms to the collective movements of insects and animals.36,47 These natural systems inspire today's electronically controlled macro-robotic systems, such as the schooling of underwater robots,48 swarms of aerial flying robots,49 and many other examples currently being reported. However, the fabrication and operation of micro/nanorobotic systems is much more challenging because this scale is too small to integrate conventional electronic circuits and mechanical motor devices.40 In addition, the propulsion of micro- and nanoscale robots in liquid fluids fundamentally differs from macroscopic swimming due to the negligible effect of inertial forces compared to viscous forces.36,44,50 Therefore, the key breakthrough can be achieved through the consideration of advanced material systems that can be equipped as functional components to enable the desired maneuverability, programmability, intelligence, and multifunctionality in micro/nanorobots.Over the past decade, various new material systems have been extensively implemented in micro/nanorobots, leading to practical advances in the research and development of small-scale robotic technology. Fig. 2A illustrates the role of advanced materials in micro/nanorobotic systems in two main categories: (i) generating active movements in their inherent structures and (ii) being integrated as functional components in other microrobotic platforms to provide multifunctional capabilities. The first group includes various new (photo)catalytic materials and biological microorganisms that have active propulsion by themselves. The second group comprises advanced materials that can be assembled on the surface of microspheres, microtubes, or helical microrobotic platforms, enabling various functional enhancements. This review systematically classifies recent advances in micro/nanorobotics, focusing on five main families of advanced materials. These are summarized in Tables S1–S9 (ESI†) and will be further discussed in the following sections.
2.2. Design, fabrication, and sizes
Design and fabrication strategies have been crucial to the development of micro/nanorobots with effective propulsion and sophisticated functions. Significant progress has recently been made by actively adopting advanced bottom-up and top-down manufacturing techniques. The main consideration was on creating desired geometries such as asymmetrical spheres, multimetallic rods, microtubular or helical structures to achieve effective motion and control.The bottom-up approach initially constructs individual functional components in minimal size and gradually integrates intelligent micro/nanorobots.51 This method explores advanced nanotechnologies to continuously enhance capabilities at smaller scales. A variety of techniques have been investigated within the bottom-up approach, including physical (sputtering, evaporation, and atomic layer deposition), chemical (polymerization, hydrothermal reaction, precipitation, electrostatic assembly), electrochemical (template-assisted electrochemical deposition), and biological (bioconjugation, cell/bacterial culture) methods.42 In contrast, the top-down strategy manufactures micro/nanorobots by three-dimensional carving or printing to obtain the desired shape and geometry. The mainstream of this approach includes micro- and nanolithographic techniques such as direct laser writing (DLW), stereolithography (SLA), and digital light processing (DLP), which inherently offer high reproducibility, high throughput, and precise control of geometry.45 Among these, two-photon polymerization (2PP)-based 3D laser lithography offers the highest resolution in 3D printing technologies, enabling the creation of complex structures from various materials (organic, inorganic, passive, and active) with high reproducibility. Particularly, the fabrication of dynamic and reconfigurable materials (also known as 4D printing) is highly beneficial in medical microrobotics for sophisticated functions such as gentle biological interactions, adaptability in capillaries, and controlled cargo protection and release.45
Here, we categorize the representative designs of micro/nanorobots into three types and compare their scales, as shown in Fig. 2B and Table S10 (ESI†).
(i) Spherical microstructures offer a simple and versatile geometric design for the fabrication of micro/nanorobots. First, functional spherical particles with different material compositions can be directly used as robotic bodies. In these cases, the fabrication methods of the microrobots rely on the synthetic routes of micro- and nanomaterials, allowing the highly affordable and scalable production of micro/nanorobots. Alternatively, the microsphere robots can also be produced by depositing functional materials on the surface of template microparticles; in particular, an asymmetric morphology with Janus structure has been widely used and explored. A variety of techniques have been developed, including hydrothermal/annealing, oil–water emulsion, sputtering/chemical bonding, and electron beam (e-beam) evaporation.
(ii) Tubular robots are conical- or cylindrical-shaped microtubes that can propel like small-scale jets or rockets and are a commonly explored design in the fabrication of micro/nanorobots. Tubular robots can be propelled by the (photo)catalytic bubble propulsion mechanism, in which an inner (photo)catalytic layer deposition is essential. The (photo)catalytic reaction initiated by the addition of fuel (hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)) or light irradiation generates bubbles inside the tube. The bubble evolution and ejection provide thrust in the opposite direction, leading to the propulsion of the tubular robots.52,53 These microscale tubular structures are mainly fabricated by rolled-up nanotechnology, template-assisted electrodeposition, and 3D printing techniques.52,53 Template-assisted electrodeposition for fabricating tubular robots starts with the deposition of a polymer layer into a tubular- or conical-shaped porous membrane, e.g., polycarbonate (PC) membrane, which acts as a scaffold for subsequent deposition of the catalytic or magnetic layers. In the sequential electrodeposition, the applied electrical current reduces cations of the target material solution, resulting in the multilayer deposition of desired materials on the inner wall of a porous membrane.52 The final structure can be released by the following membrane dissolution process with methylene chloride. Template-assisted electrodeposition offers easy fabrication of microtubular structures in relatively high yield without sophisticated instrumentation.52,53 3D printing and solution-based chemical synthesis enable template-free tubular robot fabrication, allowing the potential for scalable fabrication of microrobots with systematic and consistent designs.
(iii) Helical robots often contain magnetic components that can achieve propulsion by rotating magnetic fields that convert rotational motion into translational motion, resulting in locomotion similar to that produced by bacterial flagella.36,50,54 Their controllable 3D movements in a narrow and confined area in an untethered fashion make them highly promising for various purposes such as biomedical applications.54 Helical micro/nanorobots can be fabricated by a variety of techniques such as self-scrolling, glancing angle deposition, template-assisted electrodeposition, direct laser writing, biotemplating, and microfluidic methods.36,54 These techniques enable the systematic fabrication of helical structures with different compositions and sizes ranging from nano- to micro-scales, depending on their application and working environment. Helical micro/nanomachines have been comprehensively reviewed elsewhere.36,50,54
2.3. Propulsion, navigation, and speed
Propulsion of micro/nanorobots in low Reynolds number environments is challenging due to dominant viscous forces over inertial forces, requiring asymmetric, non-reciprocal motion for effective propulsion.36,44,50 Several strategies have been developed to overcome this challenge and realize an effective propulsion. The representative energy sources and mechanisms are summarized in Fig. 2C and Table S11 (ESI†) and their propulsion speeds are compared.(i) Catalytically propelled micro/nanorobots convert chemical fuels into mechanical motion through catalytic reactions, where the asymmetric release of chemical products leads to propulsion via bubble ejection or self-phoresis.44 For example, tubular microrockets with an inner catalytic layer (e.g., Pt) in H2O2 generate O2 bubble jets that provide relatively strong thrust and mobility (ca. 50–375 body length per s) compared to other propulsion mechanisms, and further functionalization of the magnetic layer, e.g., Ni or Fe, can improve directional guidance.52,55 On the other hand, micro/nanorobots can move spontaneously in response to gradients, such as solute concentration (self-diffusiophoresis), electrical potential (self-electrophoresis), or temperature (self-thermophoresis). Enzymes, such as catalase, urease, and glucose oxidase, can propel the micro/nanorobots in their specific substrates (H2O2, urea, and glucose), which is particularly applicable in biomedical applications where natural substrates are present, such as in the bladder for urea.56 Catalytic micro/nanorobots are less controllable in their motion and have a limited lifetime as the materials degrade during the catalytic reaction.
(ii) Light-driven micro/nanorobots can be propelled through photocatalytic reactions or photothermal interactions (ca. 1–30 body length per s). Briefly, photons matching in energy with the semiconductor band gaps (Eg) generate electron–hole pairs that catalyze photochemical reactions, leading to motion via self-phoresis or bubble propulsion. Light is a versatile energy source, enabling both motion and catalytic degradation simultaneously, yet light-driven motion faces challenges such as imprecise control, limited penetration depth of light, and inefficiency in media with high ionic strength.42
(iii) Magnetically actuated micro/nanorobots can be operated at moderate speeds (ca. 1–5 body length per s) but offer several significant advantages, such as precise manipulation, non-invasive operation, and compatibility with various media, including biological environments.50,54 A variety of propulsion and navigation mechanisms, including translation, corkscrew motion, surface rolling, and ciliary motion, have been demonstrated using uniform magnetic field gradients and rotating or oscillating magnetic fields.44,50 For example, in a magnetic helical structure with magnetization along its short axis, a rotating magnetic field exerts a continuous torque to drive rotation around the long axis, resulting in a corkscrew motion that propels forward.50,57,58 In surface rolling motion, a rotating magnetic field along the vertical axis exerts a perpendicular torque on the micro/nanorobots, causing them to rotate in the x–z plane; this configuration generates different drag forces near the surface and on the other side, resulting in rolling and propulsion parallel to the horizontal (x–y) plane.33,59,60 Despite its advantages, magnetic manipulation is limited by the need for sophisticated electromagnetic devices, which may not be readily available in certain circumstances.
(iv) Acoustic field-driven micro/nanorobots are advantageous for biomedical applications due to the harmless, biocompatible, and versatile nature of ultrasound fields.61 The density and shape of material systems, often studied in multimetallic nanowires, are key to converting acoustic radiation into propulsion, and ultrasound also enables precise ON/OFF motion control by modulating bubble aggregation in microrockets.44,61,62 Acoustic fields can generate powerful motion (ca. 100 body length per s), which makes them even more attractive when combined with precise directional control methods.
(v) Biohybrid micro/nanorobots leverage living biological systems that move autonomously using local energies, achieving high propulsion speeds (ca. 1–10 body lengths per s), autonomy, and adaptability in biological environments. Cells and microorganisms have sophisticated motility systems driven by internal molecular motors, such as autonomous swimming with flagella or cilia, and energy taxes-guided movements.63 The living organisms offer an attractive biomimetic behavior with negligible toxicity, making them ideal for biomedical applications, including targeted drug delivery.
2.4. Activatable light energies
Advances in semiconductor materials have led to significant progress in light-driven micro/nanorobots that can operate without fuel and wirelessly. A variety of photoactive materials, responsive to UV, Vis, and/or NIR wavelengths, have been proposed with different propulsion mechanisms. The representative semiconducting materials employed in light-driven micro/nanorobots are summarized in Fig. 2D and Table S5–S7 (ESI†), considering key characteristics of their activatable wavelengths to drive propulsion. The classification of materials, motion mechanisms, functionalities, and applications are discussed in detail in Section 5, Semiconductors.2.5. Key advantages in practical applications
The active motion of micro/nanorobots, with their adaptive, collective, and programmable behaviors, provides unique capabilities and advantages for various practical applications (Fig. 2E). (i) Enhanced reactivity: active materials exhibit superior reactivity compared to passive (static) materials. Their continuous movement facilitates diffusion, mass transfer, and local fluid mixing, enabling ‘on-the-move’ target capture and sensing. This significantly boosts the efficiency of reaction in (bio)sensing, water purification, and therapeutic systems.42,56,64 (ii) Precise manipulation: precisely navigated micro/nanorobots are particularly significant in medical applications. Magnetic actuation is primarily utilized to enable versatile locomotion modes such as crawling, rolling, walking, swimming, and climbing in navigating challenging anatomical regions and biological barriers, while performing therapies with high precision and efficacy. More recently, artificial intelligence (AI) has been integrated with magnetic actuation systems to reinforce the manipulation of small-scale robots, enabling them to navigate complex biological environments with greater accuracy and efficiency.65 (iii) Crossing the boundary: micro/nanorobots actively cross the boundary between two systems and perform multiple tasks efficiently. This clearly distinguishes them from passive systems in catalysis and therapeutics. For example, therapeutic micro/nanorobots deployed at the target site facilitate rapid cell internalization, intracellular transport, and efficient drug delivery.66,67 On the other hand, antimicrobial micro/nanorobots penetrate biofilm matrices and synergistically disrupt bacteria through chemical and mechanical effects, improving the effectiveness of biofilm eradication.68,69 Their ability to effectively cross boundaries promises new strategies in unexplored areas of research.3. Two-dimensional materials
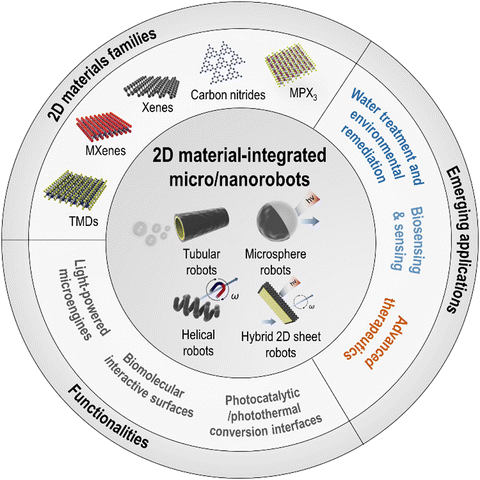
The impact of graphene has spurred rapid growth of 2D layered material families. In micro/nanorobotics, semiconducting TMDs, metallic MXenes, buckled 2D Xenes, polymeric 2D carbon nitrides, and MPX3 have demonstrated significant potential and outstanding properties, suggesting opportunities for new material systems in future technologies. Pumera's group has most extensively explored this approach. They have demonstrated the advantageous performances of the 2D materials-integrated micro/nanorobots based on a wide range of 2D families, e.g., TMDs (MoS2, WS2), MXenes (Ti3C2Tx), Xenes (black phosphorus (BP), arsenene (2D As), germanene (2D Ge)), carbon nitrides (C3N4), MPX3 (MnPS3), etc.70–74 Most of the reports were the first use of these 2D materials in micro/nanorobotics from the earliest time in 2015, which has ignited the following interests in the related research fields. Wang's group has presented the first concept of template electro-deposited tubular MoS2 microrobots for potential drug delivery carriers and biosensing platforms.9 Escarpa's group has developed various biosensing and food analysis platforms based on a variety of multicomponent 2D-based microrobots.10,64,75 Sitti's group has demonstrated the intriguing photocharging effects of carbon nitride-based microrobots.12,76 Pané's group has provided MoS2-implemented artificial bacterial flagellum (ABF)-type magnetic robots.77In this section, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of recent research in micro/nanorobotics using advanced layered 2D materials (Fig. 3). Table S1 (ESI†) summarizes the various motion mechanisms, the functionalities of 2D materials, and the applications for each type of 2D material-integrated micro/nanorobots. The major types of emerging 2D layered materials used in micro/nanorobotics can be classified into TMDs, MXenes, Xenes, carbon nitrides, and MPX3. These 2D materials are implemented in micro/nanorobots with various designs, which will be discussed after being categorized into tubular, microsphere, helical, and hybrid 2D sheet-type robots. The different kinds of fabrication methods are also summarized depending on the 2D robot designs. After that, the role of 2D materials in micro/nanorobotics will be discussed with two main categories: (i) 2D materials as microengines for powering motion and (ii) 2D materials as add-on components with specific functionalities. Furthermore, an overview of their emerging applications will be provided.
3.1. 2D materials families
3.2. Role of 2D materials in micro/nanorobotics
3.2.1.1. Tubular robots. 2D materials can be deposited in microtubular structures and provide various functionalities (Fig. 4A). Although there are some examples of rolled-up technique-based microrobots using GO, we will not discuss them here as graphene is not a material of interest in this review. Conductive 2D materials, such as TMDs, are directly used as the outer scaffold layer. Further deposition of catalytic Pt or Au on the inner layer leads to TMD-based tubular microrobots, e.g., MoS2/Pt, MoS2/Au, WS2/Pt, and WS2/Ni/Pt microtubes.9,10,82 Alternatively, 2D materials can be combined with the outer layer of the tubular robot by physical/chemical adsorption in a separate process.92,99,104 For example, fluorescent 2D Ge derivatives were attached to the GO/Pt microtubes, which can be done by physical adsorption using a simple incubation process.92 Effective adsorption of 2D Ge was evident by the different emission colors of fluorescent-labeled microrobots under UV irradiation. Another approach introduces the 3D-printed millimeter-scale tubular robots using a filament made of polylactic acid (PLA) and graphene.104 Their usability is demonstrated with further decoration of functional layers, such as aluminum/gallium (Al/Ga), Fe3O4, and C3N4, suggesting the concept of 3D printing-enabled milli-scale tubular robot fabrication with 2D materials. In a more recent report, melamine and ferric nitrate precursors were absorbed by kapok fiber (KF) microtubes. The dried KF samples were processed by sequential thermal treatment, resulting in the fabrication of g-C3N4 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles’ (NPs) inner and outer surfaces of the KF microtubes.99 One intriguing example is the g-C3N4-based tubular robot synthesized by hydrothermal reaction and calcination process, which can move by photocatalytic-induced bubble-propulsion under visible light irradiation without a metal/enzyme-based catalytic layer.8
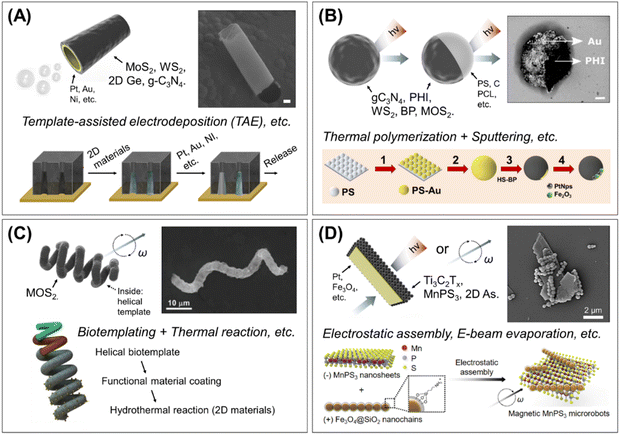 | ||
| Fig. 4 Major types of 2D material-integrated micro/nanorobots and fabrication methods. (A) Tubular robots. Multilayered microtubes with bubble-propelled movement and the representative fabrication process by template-assisted electrodeposition. Scale bar: 5 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 82. Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society, and permission from ref. 70. Copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH. (B) Microsphere robots. This type can be divided into two subcategories: 2D material-based microparticles (i.e., 2D in the core), or 2D wrapped Janus microspheres (i.e., 2D on the surface). The representative preparation steps of 2D wrapped Janus sphere robots by Au sputtering and thiol-modified 2D materials binding method. Scale bar: 400 nm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 76. Copyright 2020, National Academy of Sciences, and permission from ref. 105. Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society. (C) Helical robots. Biotemplated 2D material-based helical robots and the fabrication method with biotemplating and hydrothermal reaction. Reproduced with permission from ref. 77. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. (D) Hybrid 2D sheet robots. Functional components (Pt, Fe3O4, etc.) hybridized 2D sheet robots and example of preparation method based on electrostatic assembly. Reproduced with permission from ref. 74. Copyright 2022, Elsevier Inc. | ||
3.2.1.2. Microsphere robots. Several types of 2D microsphere robots have been introduced, which can be classified into two categories: 2D material-based microparticles (i.e., 2D in the core) and 2D wrapped Janus microspheres (i.e., 2D on the surface) (Fig. 4B).
First, microparticles composed of 2D materials, such as 2D MoS2 nanosheets or 2D carbon nitride species (e.g., C3N4, PHI, etc.), can be directly used as autonomous spherical robots. For example, sodium-intercalated 2D MoS2 particles were prepared by chemical intercalation by submerging MoS2 in tetrahydrofuran solutions of sodium naphthalenide.81 The 2D carbon nitride microparticles were mainly synthesized by thermal polymerization of precursors, e.g., melamine, urea, etc., at high temperatures (550 °C); then, those could be further functionalized with catalytic (i.e., Pt, Au, etc.) or magnetic (i.e., Fe3O4, etc.) components through chemical reduction, sputtering, solvo/hydrothermal, or colloidal assembly processes.12,76,95,98
An alternative design for microsphere robots involves wrapping 2D materials on the surface of template microparticles. In this approach asymmetric Janus particles have been widely explored. For example, the core–shell structure of g-C3N4/carbon (C) microspheres was fabricated by sequential thermal treatments. The C microspheres and g-C3N4 synthesized in an independent process were mixed and reacted in hydrothermal and annealing processes, which led to the formation of the g-C3N4 shell on template particles.97 In a different approach, WS2–polycaprolactone (PCL) polymeric microsphere robots were fabricated by the oil–water emulsion polymerization technique.64 In this method, organic droplets containing the WS2, PCL, Pt, and Fe3O4 were generated in an aqueous state. During the solvent evaporation, inorganic materials were not miscible with PCL and tended to accumulate on the droplet surface to be stabilized at the water/oil interface,106 resulting in the WS2 encapsulated PCL microspheres after solidification. One technique widely used for architecting Janus microspheres is physical vapor deposition, which involves sputtering and e-beam evaporation.107 The fabrication of an asymmetric Janus structure is based on the deposition of vaporized target materials onto the template microspheres that are drop-casted on a clean surface followed by their release and collection by sonication.107,108 These techniques are convenient and highly controllable to create homogeneous nanometer-level target material coating.107,108 One interesting approach with this technique is thiol (HS)-modified 2D materials wrapping on the gold-sputtered microspheres. In this method, Au/polystyrene (PS) Janus microspheres were first fabricated by sputtering and then incubated with sulfhydryl (HS)-modified BPs, allowing the specific attachment of BPs on the Au layer by gold–thiol bonding. Finally, the Janus 2D BP/PS microsphere robots were obtained.105,109 Otherwise, the source of 2D materials can be directly deposited by e-beam evaporation. In recent work, a thin Mo layer is asymmetrically deposited on the TiO2 hollow particles by e-beam evaporation and then reacted with thermal treatment for sulfurization.83 This sequential process resulted in uniform deposition of MoS2 on one side of the TiO2 particles, which were then used as MoS2/TiO2 Janus microsphere robots.
3.2.1.3. Helical robots. Helical robots, enabling magnetic propulsion and precise control, have been a promising template for 2D-integrated micro/nanorobots. In a recent study, the biotemplated 2D MoS2-based magnetic helical microrobots, so-called “MoSBOTs,” are introduced (Fig. 4C).77 The cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis (S. platensis) was used as a helical scaffold. The scaffold surface was modified with Fe3O4 NPs followed by the hydrothermal growth of MoS2 nanoflakes and the reduction of Au NPs. This work describes the potential of TMD-based helical robots in biomedical applications that can motivate the future development of various 2D material-engineered helical robots.
3.2.1.4. Hybrid 2D sheet robots. Most 2D materials are utilized after being incorporated/deposited on the backbone of micro-carriers as classified in the above subsections, e.g., 2D-deposited microtubes, 2D-wrapped microparticles, or 2D-grown helical templates. This is most probably due to the difficulty of providing asymmetric driving forces to 2D planar geometry and the lack of studies for the effective motion of 2D sheet objects.74 Some recent approaches are being pursued the individually acting 2D sheet robots that exploit inherent 2D materials as robot bodies without add-on carriers (Fig. 4D).11,72–74 These 2D sheet robots are capable of preserving their intrinsic 2D properties as well as maximizing reactive surface area, which could lead to higher robotic performances such as facilitated reactivity, enhanced properties, guided targeting, collective control, etc.
2D sheet robots have been fabricated by hybridizing 2D sheets with functional components that provide motion-driving forces, such as catalytic-, magnetic-, or photocatalytic materials. For example, Pt-deposited layered 2D As flakes were fabricated by e-beam evaporation, i.e., 2D As–Pt nanorobots, and demonstrated the H2O2-fueled fast circular propulsion.72 In another work, MXenes sheets were used as a 2D robot body, where a thin layer of Pt was asymmetrically deposited on the Ti3C2 nanoflakes and TiO2 was further decorated by the partial oxidation of Ti3C2 in liquid media.73 The resulting 2D TiO2–Ti3C2/Pt robots are capable of light-driven self-propulsion through the photocatalytic property of TiO2 on the 2D Ti3C2 flakes as well as catalytic propulsion by the Pt layer. The choice of motion driving can be variable depending on the end-use purpose. The follow-up study introduced MXene-based Pt/TiO2/γ-Fe2O3 hybrids, which were prepared by thermal annealing of Ti3C2Tx MXene, deposition of a Pt layer, and subsequent surface decoration with γ-Fe2O3 NPs.11 A thermal annealing process converted Ti3C2Tx into multi-layered TiO2, corresponding to the photocatalytic activity for light-driven motion. Further, γ-Fe2O3 decoration allowed the magnetic collection of 2D MXene–hybrid microrobots. Another recent work introduced magnetically actuated hybrid 2D MPX3 robots using MnPS3 and 1D magnetic nanochains.74 The magnetic 2D MnPS3 microrobots were fabricated by electrostatic assembly, where positively functionalized 1D Fe3O4 nanochains were adhered on the negatively charged surface of 2D MnPS3 sheets, resulting in 1D/2D hetero-dimensional hybrids. The use of anisotropic Fe3O4 nanochains affords sufficient magnetic responsiveness to layered 2D sheet structures with minimal immobilization, allowing the preservation of intrinsic 2D MnPS3 surfaces for chemical interaction. Because a variety of 2D materials, such as TMDs, MXenes, C3N4, etc., show charged characteristics, the electrostatic interaction-based solution process can provide a versatile strategy for the fabrication of hetero-structured 2D sheet robots with high potential for scalable production.
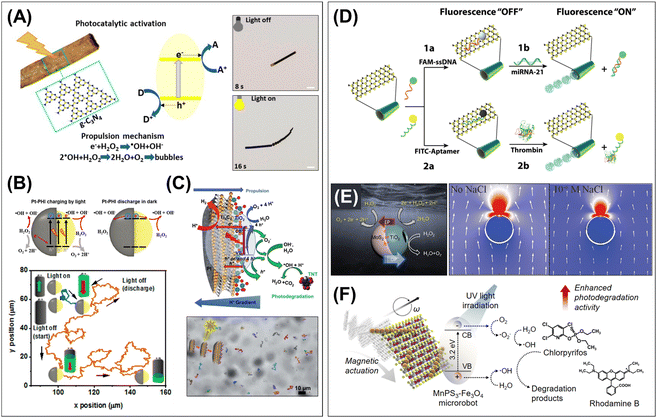 | ||
| Fig. 5 The role of 2D materials in micro/nanorobotics, by dividing into two main categories: (i) 2D materials as microengines for powering motion (left panel), and (ii) 2D materials as add-on components with specific functionalities (right panel). (A) Photocatalytic bubble-propulsion of the g-C3N4-based tubular robots and stop-and-go motion control by turning on/off the light illumination. Scale bars: 10 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 8. Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society. (B) Photocharging ability of the PHI-based Janus microsphere robots, proposed mechanism, and swimming performance in the dark condition after the light energy charging. Reproduced with permission from ref. 76. Copyright 2020, National Academy of Sciences. (C) Ti3C2 MXene-based 2D sheet robots and asymmetrical photocatalytic redox reaction-driven propulsion under UV light irradiation. Reproduced with permission from ref. 73. Copyright 2021, The Royal Society of Chemistry. (D) Biomolecular interactive surface of MoS2/metal tubular robots and fluorescence “Off–On” assay procedures. Reproduced with permission from ref. 9. Copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH. (E) Heterojunction in MoS2/TiO2 Janus microsphere robots and self-diffusiophoresis/self-electrophoresis competing propulsion mechanism that enable boosting speed with the addition of ionic solution. Reproduced with permission from ref. 83. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. (F) Photocatalytic conversion of 1D/2D hetero-dimensional MPX3 hybrid robots and magnetically actuated 2D photocatalysis under UV light irradiation. Reproduced with permission from ref. 74. Copyright 2022, Elsevier Inc. | ||
Despite their remarkable potential, there are very few examples of applying 2D materials as microengines. To date, there are only two classifications using light-driven and Marangoni effect-based propulsion mechanisms. Therefore, there is a great opportunity to search the types of 2D materials for catalytic-, magnetic-, ultrasound-, and electric-responsive powering sources for micro/nanorobotic applications.
3.2.3.1. Biomolecular interactive surfaces. 2D materials offer highly compatible bio/chemical molecular affinity interfaces. Their ultra-thin and layered structure significantly increases the active surface area and a rich surface chemistry with functional groups makes them highly advantageous for bio/chemical molecular interaction. Emerging 2D materials, such as MoS2, WS2, BP, and 2D-As, have demonstrated their promise in affinity interfaces as drug delivery carriers and mobile biosensing platforms. One example is the MoS2/metal tubular robots, where MoS2 serves as the backbone skeleton of microtubes as well as the outer bio-affinity interfaces.9 The MoS2 has a van der Waals stacked trilayer structure with a sandwiched layer of Mo atoms between sulfur layers in which the nonbonding molecular orbitals promote π–π stacking interaction with nucleotides and (poly)cyclic compounds. On the surface of MoS2-based tubular robots, chemotherapeutic drugs (DOX) can be loaded via π–π interaction and hydrophobic adsorption, and the release is triggered by the control of pH. Higher drug loading capacity is proved by comparison with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) tubular robots. 2D As–Pt Janus robots have also been explored for anticancer drug carriers.72 DOX-loaded 2D As–Pt Janus robots show high cellular uptake mainly due to the size effect (∼200 nm) and mechanical self-propelling. Furthermore, 2D MoS2, WS2, and BPs can act as powerful quenchers of fluorophores based on the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) effect, enabling on/off fluorescent biomolecules detection in the mobile micro/nanorobotic platform (Fig. 5D). For example, the dye-labeled oligonucleotides were rapidly immobilized on the MoS2 surface by π–π interactions.9 Alternatively, the negatively charged surface of MoS2 and WS2, due to the existence of sulfide groups, can have electrostatic adsorption for peptides containing positively charged amino acids, such as lysine and histidine, with a partial contribution of hydrophobic interactions.64,82 The interaction of peptides in BP surfaces can be achieved by a contribution of chemisorption and electrostatic effects.105 These fluorescent-tagged nucleotides/affinity peptides adsorbed on the surface of MoS2, WS2, and BP-based micro/nanorobots are in the FRET quenching state and can recover fluorescence signals through the release of the 2D materials from the surface.9,64,82,105
3.2.3.2. Catalytic boosters for acceleration. Emerging 2D materials and their heterostructures in micro/nanorobotic systems contain unique physicochemical/optoelectronic structures that can regulate electron charge transfer or catalytic pathways and thus accelerate microrobot propulsion. These systems have been designed by leveraging heterostructures of BPs, and MoS2 that are implemented in tubular, or Janus microsphere robots. For example, bubble-propelled BP–Pt tubular robots exhibit improved propulsion performance compared to bare Pt microtubes.71 The increase of the tubular robot's velocity was observed as threefold higher at the same H2O2 concentration. This phenomenon could be due to the faster electron transfer and enhanced catalytic effect, which result in more efficient bubble evolution at the BP–Pt heterostructures compared with bare Pt surface. In another study, the BP-wrapped PS microsphere robots exhibited an enhanced propulsion behavior in the bubble-light or bubble-magnetic-light combinatorial motion.109 In the heterogeneous structure of the BP/Pt or MnO2/Fe2O3, the 2D BP layer acts like an electron acceptor that facilitates electron transfer toward the asymmetric layers of Pt/Fe2O3 or MnO2/Fe2O3. The bubble propulsion speed is increased 1.5 times with light irradiation (bubble-light combinatorial mode) and further enhanced up to 3 times by the association of the magnetic field. The fluid dynamic simulations elucidated that the propulsive energy can be enhanced by a better distribution of the fuel by magnetic and/or light activation. More recent work describes the interesting motion behavior of MoS2/TiO2 Janus microsphere robots that results from their unique heterojunction structures (Fig. 5E).83 The combination of MoS2/TiO2 in the Janus sphere broadens the light absorption from the UV to the visible light range, which contributes to efficient visible light-powered locomotion. Furthermore, the MoS2/TiO2 Janus microsphere robots showed boosted speed with the addition of ionic solution (i.e., NaCl), which is elucidated by the light-powered competing propulsion method in both experimental and theoretical aspects. The unique type-II band gap alignment of MoS2/TiO2 heterojunction offers competing propulsion of light-powered self-diffusiophoresis (TiO2 hemisphere) and self-electrophoresis/osmosis (MoS2 hemisphere) in opposite directions. With the addition of an ionic solution, self-electrophoresis is quickly suppressed, whereas self-diffusiophoresis is barely affected by ions, resulting in a distinct speed increase in response to ions.
3.2.3.3. Photocatalytic/photothermal conversion interfaces. The use of emerging 2D materials to the outer surface facilitated advanced performances of “on-the-fly” photoactive micro/nanorobots. 2D semiconducting materials, such as MnPS3, C3N4, and WS2, were equipped in robotic bodies that can act as efficient moving photocatalysts. For example, 1D/2D hetero-dimensional MnPS3–Fe3O4 hybrid robots are capable of combining the intrinsic photocatalytic activity of 2D MnPS3 and magnetic response from Fe3O4 nanochains (Fig. 5F).74 These microrobots demonstrate magnetic-powered propulsion, guided collective navigation, and efficient photocatalytic activity in UV light wavelengths. The mechanically active 2D MnPS3 photocatalysts can promote local fluid convection and a self-stirring effect, which is experimentally corroborated by the enhanced photodegradation efficiency of organic compounds. In another approach, the photocatalytic chitosan–C3N4 hydrogel layer is coated on the surface of the 3D-printed millimeter-scale tubular robots.104 These robots can move by bubble propulsion via the water-splitting reaction while adsorbing and degrading organic compounds under visible light illumination. Another interesting example is the NIR-responsive photocatalytic activation of WS2/Ni/Pt tubular robots.10 The layered WS2 possesses inherent NIR photocatalytic activity due to its indirect band gap (1.20–1.39 eV) and high valence band; thus, it can be activated in wavelengths ranging from 700 to 1000 nm. These WS2/Ni/Pt tubular robots were used for “on-the-fly” NIR photodegradation of organic compounds, proving motion-enhanced photocatalytic activity. On the other hand, the high photothermal conversion efficiency of 2D MoS2 in the NIR range and their low toxicity make them promising for biomedical applications.77 The MoS2-based magnetic helical robots, combining magnetic navigation and high NIR photoabsorbent feature, are exploited for targeted photothermal ablation of cancer cells, which achieves similar efficiency to DOX without the cytotoxic effects associated with passive chemotherapies.
3.2.3.4. Other functionalities: capacitive enhancer and fluorescent labeling. A variety of intrinsic properties of 2D materials have high potential as actuating functional materials when integrated with micro/nanorobotics platforms. For example, 2D WS2 exhibits outstanding inherent electrochemical and capacitive properties in various electronic systems. Incorporating WS2 in robotic microdevices, i.e., WS2–PANI/Pt tubular robots, results in autonomous propulsion by catalytic fuel decomposition and navigating in the microchannel to enhance the capacitive behavior of the circuit after the attachment.70 This work showed the possible application of “on-the-fly” 2D supercapacitors for on-demand delivery and the adjustment of electric circuits. Meanwhile, highly stable fluorescent 2D-Ge derivatives were developed and modified on the surface of tubular robots.92 2D Ge–GO/Pt tubular robots have bright fluorescent emissions, i.e., red and blue, depending on the type of 2D-Ge derivatives, and exhibit the potential of 2D material-based labeling agents for fluorescent tracking and imaging.
3.3. Applications
One strategy widely used for this purpose is the integration of light-powered motion and photodegradation with 2D photocatalytic robots. For example, g-C3N4 and Ti3C2–TiO2 nanosheets can be propelled with light illumination and simultaneously perform light-triggered oxidation–reduction reactions, showing enhanced photodegradation efficiency for Rhodamine B (RhB) and trinitrotoluene (TNT), respectively.73,97 In addition, the incorporation of iron oxide components can impart extended functionalities, such as directed guidance, collective self-rotating motion, and facile recovery after reaction as well as increased light absorption and Fenton oxidation capacity.74,96,98,99,104 For the photodegradation of tetracycline, the Fe3O4/f-C3N4 microsphere robots showed a 13.4% increased degradation efficiency with the collective magnetic rotation (Fig. 6A).98 The selected area degradation was presented in two reservoir-connected channels with RhB decoloration, thus demonstrating the utility of magnetic mobility for targeted catalysis. The g-C3N4/Fe3O4/KF tubular robots exhibited 2.25 times improved photodegradation efficiency for RhB compared to the static mode.99 Also, a 6.8% increased efficiency is observed in comparison with the degradation using only g-C3N4, implying the higher performance of the Fenton reaction effect in the photocatalytic process. On the other hand, the MnPS3–Fe3O4 2D sheet robots present collective movement in a programmed fashion.74 These magnetically moving 2D sheet photocatalysts showed enhanced degradation efficiency of 10.3% and 8.8% for RhB and chlorpyrifos (CPS), respectively, compared with static hybrid materials.
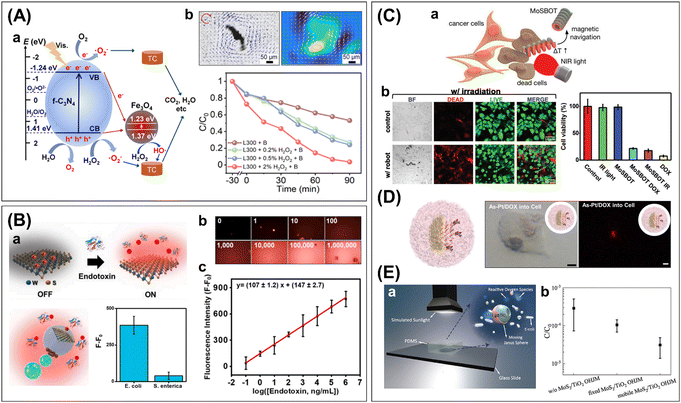 | ||
| Fig. 6 Applications of 2D-integrated micro/nanorobotic platforms in advanced nanotechnologies, including water treatment, biosensing/sensing, therapeutics, and pathogenic bacteria eradication. (A) Fe3O4/f-C3N4 microsphere robots for visible light photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline. (a) Proposed photodegradation mechanism. (b) Increased efficiency with the collective magnetic rotation. Reproduced with permission from ref. 98. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society. (B) WS2-based Janus sphere robots for sensitive E. Coli. endotoxin detection. (a) Schematics of sensing principle based on the fluorescence “Off–On” strategy and selectivity test in raw bacteria lysates. (b, c) Calibration curve for endotoxin detection and corresponding fluorescent microscopy images. Reproduced with permission from ref. 64. Copyright 2020, Elsevier Inc. (C) MoS2-based magnetic helical robots for targeted photothermal ablation of osteosarcoma MG-63 cells. (a) Schematic illustration of targeting cell ablation experiment. (b) Confocal fluorescence images and cell viabilities comparing the cell ablation effects. Reproduced with permission from ref. 77. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. (D) Cellular uptake of drug-loaded 2D As–Pt Janus robots for human lung carcinoma cells (A549) treatment. Scale bars: 5 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 72. Copyright 2020, Elsevier Inc. (E) MoS2/TiO2 Janus microsphere robots for sunlight-powered photocatalytic water disinfection of E. coli. (a) Schematic of water disinfection test. (b) Motion-driven enhancement of bacterial disinfection efficiency with the mobile MoS2/TiO2 Janus robots. Reproduced with permission from ref. 83. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. | ||
Another interesting approach is the use of the WS2/Ni/Pt tubular robots for the degradation of a model pollutant Remazol Brilliant Blue R.10 Due to the inherent NIR light photocatalytic activity of WS2, the catalytic degradation can be initiated in NIR light illumination (λ = 800 nm), which showed more than 2 times enhanced photodegradation efficiency with the addition of H2O2 and bubble propulsion. Meanwhile, the photocatalytic-driven bubble-propelled g-C3N4 tubular robots were used for the removal of heavy metal ions such as Cu, Cr, Ni, Co, Cd, and Pb.8 Such binding is achieved by the interaction between the metal ions and the g-C3N4 surface, i.e., the metal complex formation and acid–base interaction. Interestingly, the binding of heavy metal ions increased the speed of tubular robots in the presence of H2O2 fuel, which probably contributed to the fuel decomposition process. Moreover, Cu2+ ions showed a quenching effect for the strong blue fluorescence of g-C3N4 tubular robots. Thus, these 2D tubular robots can be exploited for the removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater and simultaneous monitoring by fluorescence quenching.
Several 2D based-micro/nanorobots have proved the practical usability of the fluorescence “off/on” assay for the detection of clinically relevant biomarkers, such as miRNA-21, thrombin, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and cholera toxin B.9,64,82,105 For the detection of miRNA-2 and thrombin, the MoS2/Pt, tubular robots were loaded with fluorescein amidine (FAM)-ssDNAs or fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-aptamers by π–π stacking interaction.9 After that, the continuous bubble-propelled movement of the probe-loaded tubular robots enhanced the recognition of target analytes as detected by fluorescence signals. In comparison with their static counterparts, the fluorescence recovery was increased from 6% (static) to 96% (mobile) for miRNA-21 detection, and from 10% (static) to 90% (mobile) for thrombin detection, suggesting the significant role of active movements for fast and efficient biomolecular recognition. For the detection of LPS, also known as “endotoxins,” tetramethylrhodamine (TMRho)-labeled affinity peptides were adsorbed on the surface of WS2/Pt tubular robots or PCL/Pt/Fe/WS2 microsphere robots through electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions (Fig. 6B).64,82 The affinity peptides can recognize LPSs with higher affinity and then release them, restoring the fluorescent marker. The assay based on the WS2/Pt tubular robots exhibited a limit of detection (LOD) of 1.9 ng mL−1 and 40% (shaking) and 50% (static) enhanced efficiency compared with control experiments in motion activation. Moreover, the spiked sample tests in tap water, serum, and saliva showed excellent recovery and the selective real condition assay was validated with bacterial culture media. In the case of the PCL/Pt/Fe/WS2 microsphere robots-based assay, an LOD of 120 pM was obtained, which is comparable to the result of the gold standard, i.e., the Limulus Amoebocyte lysate tests, yet requires a much shorter assay time (5 min vs. ∼1 h).105 The quantitative recovery rate in real sample experiments (human serum and bacterial culture) verified the applicability of the suggested assay. The PS/Au/BP microsphere robots also can be used for cholera toxin B detection. With the off/on fluorescence and competitive binding strategy, the assay exhibited a LOD of 0.015 μg mL−1 and excellent performance in complex samples (human serum) and bacteria culture media.
In another approach, the Ti3C2Tx–Pt/TiO2/γ-Fe2O3 2D sheet robots were used for the rapid preconcentration of nanoplastics and electrochemical detection.11 The Ti3C2Tx-based 2D sheet robots can electrostatically capture and magnetically separate the negatively charged PS beads (carboxylated, 50 nm), as a model nanoplastic. The collected samples were transferred to the screen-printed electrodes and the signals were measured using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). In the presence of the nanoplastic-captured robots, the charge transfer resistance (Rct) is increased because of their lower conductivity and the neutralized surface charges inducing the Coulomb repulsion of the redox probe ions. This work suggests a new concept of MXene-based microrobots for a fast nanoplastic trapping and screening method for wastewater treatment.
2D materials afford advantageous interfaces for sensing platforms. Also, the continuous movement allows the self-stirring effect and localized fluid convection as well as higher chances of molecular binding and enhanced binding kinetics. Hence, bio-assays with 2D-based micro/nanorobots can enhance the sensitivity (ng mL−1 level) and shorten the time to result (1.5–10 min),64,82,105 which are critical factors for practical applications in point-of-care diagnostics and on-site screening tools.
On the other hand, the MoS2-based magnetic helical robots are used for targeted photothermal ablation of osteosarcoma MG-63 cells.77 2D MoS2 can induce both photodynamic and photothermal therapy, i.e., the effect of photogenerated reactive oxygen species (ROS) and light-triggered heating, respectively. The experimental results revealed radical species production from the MoS2-helical robots is negligible, whereas the local temperature increase is significant and reaches a fast cell-killing level (>50 °C) in a short time (<30 min). Thus, cell ablation could be primarily ascribed to the photothermal effect. Consequently, the NIR-responsive MoS2-based magnetic helical robots achieved cell-killing efficiency up to 82% within 30 min, which is comparable to the effect of DOX yet avoiding side effects of chemotherapeutics. This work demonstrated an efficient non-invasive thermal ablation for cancer treatment, taking advantage of 2D MoS2 in an active platform.
4. Metal–organic frameworks
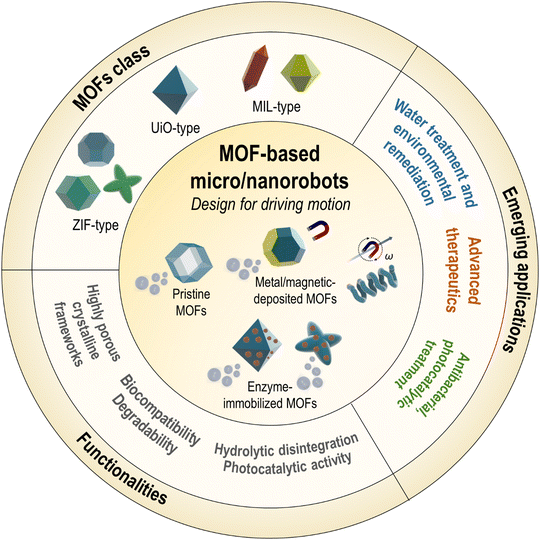
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are an emerging class of crystalline porous materials composed of metal nodes and organic linkers.13,14 These materials exhibit high porosity, exceptional surface area, physicochemical stability, and various accessible synthetic architectures; thus, they have been extensively explored for many applications including gas separation, chemical adsorption, nanomedicine, catalysis, and energy conversion.13–15 The families of MOFs, such as ZIF, UiO, or MIL, are fascinating building blocks for the fabrication of micro/nanorobotic systems. MOFs provide abundant surfaces for molecular adsorption and cargo loading along with well-ordered active sites within the hierarchical porosity.13,111 Their dynamic motion facilitates efficient mass transport and physical/chemical reactions, thereby enhancing adsorptive and catalytic performances.16,17 In addition, biocompatible and degradable MOFs are compelling candidates for targeted and controlled drug delivery.16,17 Other intriguing properties of MOFs, such as self-disintegration, photocatalytic activity, and the ability to be combined with biomolecules and functional components15,18,19 have further extended their potential as advanced platforms for micro/nanorobotics.This section will discuss recent advances in the use of MOFs for micro/nanorobotics (Fig. 7). This will cover the main types of MOFs, design, fabrication, motion mechanisms, functionalities, and applications (Tables S2–S4, ESI†). Several MOFs have been explored in micro/nanorobotic systems, which can be classified into three main types: zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF)-, University of Oslo (UiO)-, and Materials Institute Lavoisier (MIL)-type compounds. Depending on the motion-driving strategies, the design of MOF-based micro/nanorobots will be discussed after classifying them into active pristine MOFs and active component-hybridized MOF composites. Furthermore, their specific add-on functionalities and performances in applications will be summarized.
4.1. MOFs class
4.2. Role of MOFs in micro/nanorobotics
4.2.1.1. Active pristine MOFs. The pristine MOFs coordinating catalytic metal sites within the frameworks can be employed as a motion-generating microengine in micro/nanorobots. The cobalt-based MOF, ZIF-67, has been explored as a catalytic component in Janus microparticle systems, where cobalt(II) nodes act as a catalyst to decompose H2O2 fuel or for light-activated ionic self-diffusiophoresis.116,118 Chin and co-workers introduced Janus ZIF-8/ZIF-67 crystals, which are fabricated by epitaxial growth of the ZIF-67 layer on the ZIF-8 crystals that are partially embedded in a polymeric film (Fig. 8A).116 The Janus MOF crystals, propelled by bubble generation on the ZIF-67 side that contains redox-active Co(II), have demonstrated the potential of pristine MOFs to power effective motion at the microscale. In another work, light-activated self-propelling Janus ZIF-67 particles were reported.118 One side of the ZIF-67 crystals was covered with 3-trimethoxysilyl propyl methacrylate (TPM) oil through nucleation and polycondensation. The light exposure generates holes that oxidize H2O or decompose H2O2 to form hydroxyl radicals, protons, and oxygen as well as MOF particles to generate Co(II) ions while the activated electrons react with oxygen to form superoxide. A local electric field and chemopressure induced by an asymmetric distribution and diffusivity contrast of charged species lead to a self-propelled motion known as “ionic self-diffusiophoresis”. The ZIF-67/TPM Janus particles can be activated by UV or visible light, with a tuning of speed by light intensity or by the addition of H2O2 fuel.
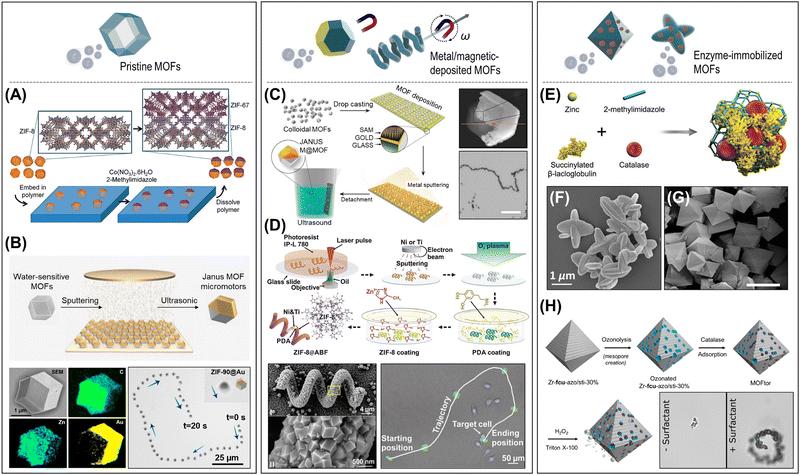 | ||
| Fig. 8 Design and fabrication of MOF-based micro/nanorobots depending on the driving-motion strategies. (A) and (B) Active pristine MOFs. (A) Catalytically propulsive Janus ZIF-8/ZIF-67 crystals fabricated by epitaxial growth of the ZIF-67 layer on the ZIF-8 crystals. Reproduced with permission from ref. 116. Copyright 2014, The Royal Society of Chemistry. (B) Janus ZIF-90 microparticle with an asymmetric covering layer of Au, and its swimming trajectory in water. Reproduced with permission from ref. 129. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society. (C) and (D) Metal/magnetic-deposited MOFs. (C) Fabrication of Janus MOF microcrystals (ZIF-8, UiO-66) with metallic layers (Au, Co, Pt) using the desymmetrization at interfaces approach, and motorized motion of Pt@ZIF-8 particles. Scale bar: 100 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 123. Copyright 2016, The Royal Society of Chemistry. (D) Two-photon polymerization stereolithography-based fabrication of ZIF-8/Ni/Ti microhelices, their morphology, and precise maneuvering along a complex trajectory. Reproduced with permission from ref. 58. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH. (E)–(H) Enzyme-immobilized MOFs. (E) and (F) ZIF-L particles co-entrapping CAT and succinylated β-lactoglobulin for pH-responsive motion control. Reproduced with permission from ref. 67. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH. (G) and (H) Multistep fabrication process for the UiO-CAT hybrid micromotors and the comparison of surfactant-dependent bubble propulsion. Scale bar: 10 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 125. Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society. | ||
Wang, Cohen, and co-workers reported the catalytic metal center-coordinated UiO-67 frameworks that enable chemically controllable bubble propulsion systems.126 First, the bipyridine-integrated UiO-67 scaffolds were synthesized and then processed to the metalation of the bipyridine sites with cobalt (Co) or manganese (Mn). The synthesized UiO-67-Co(bpy) or UiO-67-Mn(bpy) particles can be propelled by catalyzing the decomposition of H2O2 fuel, demonstrating catalytically active UiO-MOF micromotors.
More recently, interesting self-fueled Janus MOF micromotors that utilize the self-disintegration behavior of MOFs have been reported by Yan, Ma, and co-workers (Fig. 8B).129 The researchers synthesized five types of MOF particles (ZIF-90, ZIF-67, ZIF-8, MOF-5, UiO-66) and coated half the surface with an asymmetric covering layer (e.g., Au, Ag, Pt, Ni, or SiO2) using thermal evaporation. In an aqueous solution, the uncoated MOF surfaces (ZIF-90, ZIF-67, ZIF-8, MOF-5) were gradually disintegrated by spontaneous hydrolysis, leading to the continuous production of OH− ions and metal ions (Zn(II), Co(II)). This generates an asymmetric ionic gradient and a local diffusioelectric field, resulting in the propulsion of Janus MOF particles by ionic self-diffusiophoresis. In contrast, the UiO-66 Janus particles did not show self-propulsion, as the negligible release of Zr(IV) ions due to their high water stability. The results confirmed that structural asymmetry is a critical factor for driving motion rather than the type of coating materials. The mild and slow self-disintegrating allows excellent reusability and a long lifetime of motion capability.
4.2.1.2. Metal/magnetic-deposited MOFs. Catalytic metal-deposited MOFs are one of the most widely investigated architectures to generate effective propulsion through chemical reactions. The deposition of metal layers (Pt, Au, Ag, MnO2, etc.) on the MOFs is typically achieved by the physical sputtering or chemical reduction methods.123,124,130–132 The metal catalysts can react with chemical fuel sources in the surrounding fluid environment, such as H2O2 or other organic compounds, leading to a propulsive force by generating gas bubbles or other chemical species. Maspoch and co-workers have introduced Janus MOF microcrystals (ZIF-8, UiO-66) with metallic layers (Au, Co, Pt) that perform catalytic bubble propulsion (Fig. 8C).123 Several catalytically propulsive metal-deposited MOF-based micro/nanorobots have been reported, including, Ag/ZIF Janus particles,130 ZIF/Pt microrods,131 MnO2/ZIF-8 microtubes,132 and UiO-66/Pt colloidosomes.124
The magnetic integration with MOF-based micro/nanorobots can offer a higher level of controllability such as magnetic guidance and magnetic steering. The magnetic components (i.e., Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3, Co, Ni, etc.) can be imparted to the MOF architectures by physical/chemical attachment, simultaneous chemical reduction during MOF crystallization, or by sputtering.57,58,115,117,124,131,132 One strategy widely employed in earlier approaches is the use of catalytically propelled MOFs with magnetic directional guidance. Catalytically functionalized MOFs allow effective and fast propulsion by decomposing the chemical fuels while the direction of MOF-microjets can be guided by external magnetic fields.117,124,131,132 More advanced maneuverability of magnetic-driven MOF microrobots was demonstrated by Puigmarti, Pané, and co-workers. In a series of reports, the researchers introduced several microhelice structures combined with MOF (ZIF-8, MIL-100, MIL-125, or UiO-66) and magnetic (Ni, Fe3O4, etc.) components.57,58,115 For example, helical polymeric chassis (IP-L 780) were fabricated by two-photon polymerization (2PP) stereolithography and then coated with layers of Ni (magnetic) and Ti (biocompatibility) (Fig. 8D).58 Subsequently, the surface treatment with polydopamine enabled the nucleation and growth of ZIF-8. Similarly, gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA)-based biodegradable helical microchassis were also fabricated using 2PP stereolithography.115 The helical gelatin surface was further coated with organo-mineralized magnetic Fe/ZIF-8 particles, resulting in a helical hybrid system that possesses magnetic, biocompatible, and biodegradable characteristics. In another work, a universal biotemplating process was developed for the fabrication of magnetic helical MOF assemblies.57 The biotemplate used in this process was a filamentous cyanobacterium, S. platensis, which was first decorated with a magnetic layer by incubating it with Fe3O4 NPs. Afterward, a macromolecular binding layer of gelatin was coated onto the magnetic helices, which allows the anchoring of various types of MOF nanocrystals, such as MIL-100(Fe), MIL-125NH2, UiO-66, or ZIF-8, through electrostatic interaction. These magnetic MOF microhelices can be actuated by applying a rotational magnetic field and performing corkscrew locomotion with precise maneuvering along a user-designated pathway.
4.2.1.3. Enzyme-immobilized MOFs. The integration of enzymes with MOFs offers a promising platform that provides a microenvironment to protect enzymes from denaturation while enhancing enzymatic performance through controlled pore/surface properties and has shown great promise in various applications.18,133 In micro/nanorobotic systems, catalase (CAT) is widely used as a biocatalyst for powering micro/nanorobots through the generation of oxygen from H2O2 decomposition. An interesting example is the ZIF-L particles co-entrapping CAT and other pH-responsive materials, where the biomolecules induced the crystallization of ZIF-L and became embedded within the resulting porous framework (Fig. 8E and F).30,67 The CAT/ZIF-L particles demonstrate CAT-powered bubble propulsion and pH-responsive motion manipulations. In another work, dual enzyme functionalized ZIF-8 nanomotors loaded with upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) and photosensitizers have been introduced.134 Two enzymes, CAT and glucose oxidase (GOx), were covalently modified onto the ZIF-8 surface by employing the linker molecule glutaraldehyde. The propulsion of GOx/CAT/ZIF-8 nanomotors can be achieved by enzymatic cascade reactions. In this process, glucose, serving as the primary fuel, is decomposed by GOx to produce H2O2. Subsequently, CAT decomposes H2O2 into water (H2O) and oxygen (O2), leading to the generation of propulsive forces for the nanomotors. Another approach relies on the ozonolysis process-based micro- and mesoporous UiO-type Zr-MOF (Fig. 8G and H).125 Mesopores provide sufficient space to adsorb the CAT; thus, the fabricated CAT/UiO particles performed jet-like bubble propulsion powered by an enzymatic reaction.
Additionally, MOFs can also serve as host frameworks, immobilizing additional functional materials and allowing engineered performances in active interaction systems. For example, the incorporation of Co or Mn metals into the bipyridine-UiO-67 framework results in UiO-67-Co(bpy) or UiO-67-Mn(bpy) micromotors, which can be propelled by the metal-based catalytic decomposition of chemical fuels.126 Interestingly, the addition of chelating reagents such as iminodiacetic acid (IDA) or ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) can inhibit the catalytic reaction by removing the metal ions within the frameworks, leading to dramatically reduced propulsion speed. Therefore, the concept of a chemically controllable micromotor engine was proposed, exploiting the metalated-MOF system. On the other hand, the ZIF-L presents large cavities within its 2D layered pore structures, making it an efficient host material for encapsulating CAT and other pH-responsive materials.30,67 By combining CAT/ZIF-L particles with succinylated β-lactoglobulin (cat-β/ZIF), the pH-responsive speed regulating system was demonstrated (Fig. 9A).67 The succinylated β-lactoglobulin is soluble at neutral pH, allowing chemical fuel to permeate and access the CAT embedded within the ZIF-L frameworks, thereby enabling propulsive motion. In contrast, under mild acidic conditions, the succinylated β-lactoglobulin transforms into a gel-like conformation that blocks the access of chemical fuels, resulting in reduced motion.
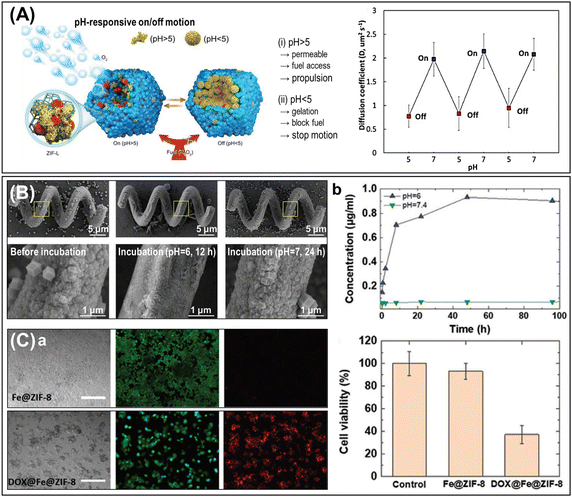 | ||
| Fig. 9 Specific functionalities of add-on MOF components in micro/nanorobotic platform. (A) Speed regulating and motion switching microrobotic systems. Succinylated β-lactoglobulin hybridized CAT/ZIF-L micromotors with pH-responsive on/off motion. Reproduced with permission from ref. 67. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH. (B) and (C) Biocompatibility and degradability of MOFs for therapeutic cargo delivery. (B) Morphological degradation of the ZIF-8 crystals coated on the polymeric microhelices when exposed to pH 6.0 solution for 12 h. Reproduced with permission from ref. 58. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH. (C) (a) LIVE/DEAD staining fluorescence images of MDA-MB-231 cells treated with Fe@ZIF-8 and DOX@Fe@ZIF-8. Scale bars: 200 μm. (b) pH-dependent release of DOX from Fe@ZIF-8 particles in different buffer solutions (i.e., release at pH = 6, and no release at pH = 7.4), and cell viability analysis showing the biocompatibility of Fe@ZIF-8 particles and the therapeutic efficacy of DOX@Fe@ZIF-8 particles. Reproduced with permission from ref. 115. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH. | ||
The biocompatibility and degradability of MOFs are important characteristics for their use in biomedical applications. MOFs, such as ZIF-8 or MIL-100, exhibit favorable biocompatibility, enabling their safe interaction in biological environments without inducing significant adverse effects.17,30,57,115 Cytotoxicity tests performed on MDA-MB-231 cells incubated with Fe/ZIF-8 particles for 72 h or MIL-100(Fe) for 24 h revealed their minimal toxic effect with a cell viability of ∼90% in both cases.57,115 Also, the treatment of MCF-7 cells with ZIF-L particles for 24 h showed no significant reduction in cell viability.30 MOFs are also degradable in specific conditions through various mechanisms, including hydrolysis. For example, ZIF-8 is stable at physiological pH (pH = 7.4) but decomposes under mild acidic conditions (pH 6.0).58,115 In SEM observations, the ZIF-8 crystals coated on the polymeric microhelices exhibited significant morphological degradation when exposed to a pH 6.0 solution for 12 h, whereas they maintained their structure in a pH 7.0 environment for 24 h (Fig. 9B).58 This degradability feature holds potential for pH-responsive drug release systems that specifically target the extracellular tumor matrix with similar acidic microenvironments. These MOFs exhibit remarkable compatibility with the cellular environment, posing no harmful responses. They not only enable the controlled breakdown of cargo but also facilitate precise release, making them exceptionally intriguing for integration into drug carriers alongside micro/nanorobotic platforms (Fig. 9C).115
4.3. Applications
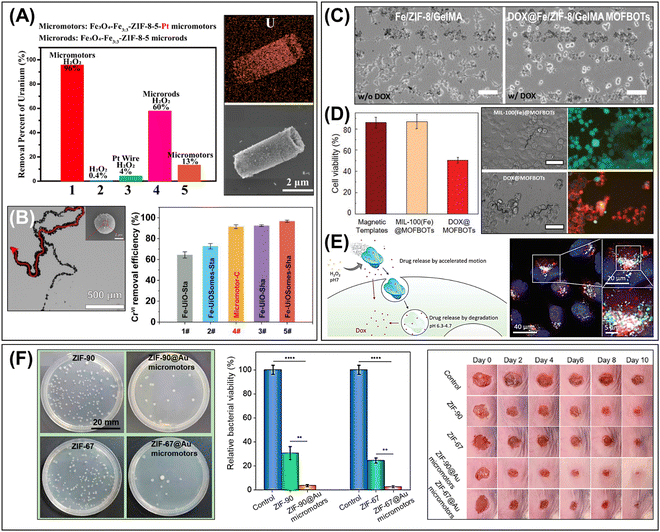 | ||
| Fig. 10 Advanced applications of MOF-based micro/nanorobots. (A) Enhanced removal efficiency of radioactive wastes (UO22+) using the self-propelled Fe3O4/Fe/ZIF-8/Pt tubular micromotors. SEM-EDS analysis shows the distribution of uranium on the surface of the tubular micromotors after the adsorptive reaction. Reproduced with permission from ref. 131. Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society. (B) Bubble-propelled Fe3O4/UiO-66/Pt colloidosomes for enhanced removal efficiency of heavy metal ions (Cr(VI)). Reproduced with permission from ref. 124. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. (C) Drug delivery of DOX@Fe/ZIF-8/GelMA helical microrobots to the MDA-MB-231 cancer cells. DOX drugs can be released after enzymatic degradation of GelMA core and pH-triggered dissolution of Fe/ZIF-8, leading to the effective local delivery and floated as dead cells. Scale bar: 100 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 115. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH. (D) Cell viability test and LIVE/DEAD staining fluorescence images showing the efficient targeted drug delivery of MIL-100(Fe) microhelices to the MDA-MB-231 cancer cells. Scale bar: 50 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 57. Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH. (E) Schematic representation of drug delivery by cat-β/ZIF micromotors and overlaid optical microscopy images showing internalization of Dox-loaded micromotors and release of drug in acidic compartments. Reproduced with permission from ref. 67. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH. (F) Self-fueled Janus ZIF-90/Au and ZIF-67/Au micromotors and enhanced antibacterial effects evaluated by in vitro bacteria E. coli test and in vivo mice dermal wound treatment. Reproduced with permission from ref. 129. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society. | ||
Chemically propelled ZIF-based micro/nanorobots have also been used for active drug delivery systems. One recent study shows that self-propelled ZIF-67 nanorobots loaded with DOX are capable of targeted drug delivery to mitochondria for cancer therapy.135 The doxorubicin-triphenylphosphonium (DOX-TPP)-encapsulated ZIF-67 nanorobots are driven by hydrogen peroxide, which is overexpressed in tumor cells. At the same time, encapsulated mitochondriotropic TPP+ leads to targeted movement into the mitochondria, resulting in the accumulation of DOX-loaded nanorobots at the mitochondria. The ZIF-67@DOX-TPP nanorobots showed enhanced anticancer effects against various types of cancer cells through mitochondria-mediated apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction, which was further validated by in vivo experiments using two animal models, including a subcutaneous tumor model and an orthotopic breast tumor model. Another approach involves the utilization of a pH-responsive CAT/ZIF-L microrobotic system, which demonstrates their potential as a carrier of drug delivery.115 The system employed succinylated β-lactoglobulin and CAT-entrapped ZIF-L (cat-β/ZIF) particles, which exhibited pH-dependent motion switching between the “on” state at pH 7 and the “off” state at pH 5.67 The large porosity of ZIF-L facilitated a higher loading capacity for DOX while the MOF structure significantly enhanced the embedded CAT activity, enabling responsiveness to biologically relevant H2O2 levels. The cat-β/ZIF particles exhibited accelerated motion and drug discharge within the tumor microenvironment, attributed to the presence of biological H2O2 at pH 7. Subsequently, they underwent degradation and drug release under acidic conditions after cellular uptake (Fig. 10E). A cell viability test performed with HeLa cells showed an enhanced cytotoxic effect by the activated movement and diffused DOX distribution throughout the cells after treatment.
MIL compounds, such as MIL-125NH2 and MIL-88B, exhibit intrinsic photocatalytic activity, making them highly promising for integration with micro/nanorobotic systems.57,128 For example, MIL-125NH2 is known for its visible light photocatalytic activity (550 nm) with a band gap of ∼2.6 eV.57 In this regard, the application of MIL-125NH2-based biotemplated microhelices has been introduced as a magnetically actuated photocatalyst for the degradation of an organic pollutant (RhB). The porous surface of MIL-125NH2 allows for the high absorption of RhB molecules, subsequently leading to effective degradation by photocatalytic redox reaction under UV-Vis light illumination (>90% within 60 min), confirming their potential for water treatment to remove organic pollutants through photocatalysis. On the other hand, MIL-88B/PPy/MB-based microrobots were investigated as agents for photo-induced anticancer therapy.128 The Vis/NIR light irradiation enables their targeted accumulation and penetration into human cervix carcinoma HeLa cells and induces the generation of H+ ions and ROS. Consequently, these phototoxic effects can initiate apoptosis and induce the mechanical destruction of cancer cells.
5. Semiconductors
Semiconductors interacting with light as a versatile and clean energy source represent one of the most attractive research directions within the micro/nanorobotics community.20–23,136–138 Considering light-powered navigation, several strategies can be pursued, although enhanced propulsion is provided by photocatalytic materials.139,140 Briefly, photons matching in energy with the semiconductor band gaps (Eg) generate electron–hole pairs that initiate photocatalytic reactions involving different driving forces. The fate of these charge defects (e.g., transfer or recombination) determines the efficiency of the photocatalytic motion. Moreover, the self-propulsion of photocatalytic microrobots can be easily regulated by switching on/off the external source as well as by modifying the wavelength or the intensity. Consequently, the great interest aroused by these highly responsive materials may not be of any surprise. UV-activated titanium-based microrobots led the first investigations on photochemical reactions to achieve autonomous movements.141–145 However, the promising use of solar light to power motion fostered the exploration of alternative candidates. Consequently, the list of photocatalytic materials for the preparation of microrobots has rapidly been enlarged with a plethora of semiconductors showing red-shifted absorption. In any case, light-triggered navigation is not the only context where photocatalysts have been explored. The development of advanced microrobots responding to several propulsion modes has paved the way to exploit the versatility of these materials on additional tasks from the biomedical to environmental fields.24–26 As a result, semiconductors are nowadays at the forefront of research, being one of the greatest evolutionary forces.This section presents a detailed discussion of the state-of-the-art of semiconductor-based micro/nanorobots, highlighting not only the novel materials explored but also the broad applicability they might have (Fig. 11). The key characteristics of semiconductor-based micro/nanorobots are summarized in Tables S5 to S7 (ESI†), comparing their material compositions, fabrication techniques, activatable light energies, functionalities, and applications. First, we will introduce the main types of semiconductors used in micro/nanorobotics (e.g., metal oxides, ternary metal oxides, quantum dots, organic semiconductors, etc.) and their advantageous properties and fabrication methods. Then, the role of semiconductors in micro/nanorobotics will be highlighted by dividing these into two main categories: (i) actuators for light-driven motion and (ii) add-on functional components. The underlying mechanisms of various light-driven motions, such as phototaxis, navigation, and swarming behavior, and their specific capabilities will be described. We will also explain the promise of semiconductor-based micro/nanorobots in a variety of applications, including molecular/solid pollutants degradation and ROS-based therapeutics.
5.1. Semiconductors class
5.1.1.1. Zinc oxide (ZnO, Eg: ∼3.2 eV). After an initial appearance as transient microrobots,147 Cai's group was the first to explore ZnO-based structures in a photocatalytic context.148 Highly reproducible template-assisted atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique was used to prepare the Pt-microrockets with a ZnO outer layer and responsible for enhanced speeds under UV light irradiation. The same methodology was followed by the group later on when they replaced the Pt inner layer with Ni instead, aiming at extra magnetic guidance of the photocatalytic microtubes.149 Nonetheless, not only microtubes have been reported: Pumera's group followed water-based chemical precipitation to obtain ZnO microspheres with a hierarchical structure.150 Interestingly, the synthesis temperature resulted to be a key parameter for size tuning and this, in turn, affected the mechanism for self-propulsion. The authors also carried out Pt asymmetric coating via physical vapor deposition (PVD) to minimize the recombination of the photogenerated electron–hole pairs in the resulting Janus structures. After that, members of the same group presented updated ZnO/Pt microrobots to gain further insights into key parameters affecting their light-driven motion.151 First, they played with the band energy levels of semiconductors to enhance the photocatalytic activity through efficient heterojunctions. They reported a ternary ZnO/TiO2/Pt Janus version, including an additional TiO2 interlayer. Moreover, non-porous ZnO microparticles were used to limit the electron trapping. To this end, previous hierarchical structures went through a sintering process. On a third attempt, they focused their attention on surface/interface morphologies.152 Two porous ZnO/Pt microrobots with different surface roughness were obtained by varying the concentration of an ionic precursor during the water-based chemical precipitation. In this sense, they were able to demonstrate how an intimate coupling of nanosheets may lead to the achievement of fuel-less light-triggered motion.
Without leaving the Janus concept, Zhang's group conceived an original morphology for alternative light-driven ZnO/Au microrobots.153 The hydrothermal method was used to get ZnO microrods with two well-differentiated segments according to their diameters. Subsequent Au sputtering guaranteed the final asymmetry needed to explore different motion modes further. Alternative ZnO/Pt Janus microrobots were presented by Hu's group with hollow ZnO microspheres instead of previously reported solid particles.154 An Ostwald ripening mechanism explained the transformation from solid to final hollow structures through yolk–shell intermediates after a calcination process was applied. Beyond Janus configuration, Simmchen's group proved that no metallic coating was needed to achieve light-driven motion.155 On the contrary, it was guaranteed by the self-asymmetry of their ZnO microrobots with yolk–shell structure in combination with the ZnO/ZnO2 heterojunction resulting from the partial passivation of ZnO in the presence of H2O2. In this line, Pumera's group reported the generation of diverse asymmetric star-shaped ZnO-based microrobots with light-driven motion just by including silver156 or gold157 precursors during the hydrothermal reaction or chemical precipitation method, respectively. On the contrary, an external source of asymmetry was used by Zhang's group to achieve self-propulsion.158 In particular, the surfaces of anisotropic ZnO microrods were chemically functionalized with a range of polysiloxane patches. Finally, ZnO microstructures have also been used as seeds for more complex designs for self-propelled micromotors. For instance, Pumera's group generated brush-shaped microrobots from ZnO microrods by preferential NH3 etching and glancing angle Pt deposition.159 Alternatively, Kienle's group grew a GaN layer on the surface of ZnO microneedles in a system for hydride vapor phase epitaxy. Simultaneously, a hydrothermal removal of ZnO was carried out to get the final hybrid GaN/ZnO microtubes. Moreover, the inner ZnO layer was also decorated with (Ga1–x·Znx) (N1–xOx) nanowires bearing AuGa-alloy nanodots at the terminal positions.160
5.1.1.2. Tungsten oxide (WO3, Eg: ∼2.7 eV). Khoshmanesh's group authored one of the earliest publications on light-driven motion based on the photocatalytic properties of WO3.161 They analyzed Galistan liquid spheres coated with WO3 NPs, proving their self-propulsion under UV light at different H2O2 concentrations. Years later, Ren's group produced hybrid WO3@C structures from the surface functionalization of carbon microspheres.162 The authors demonstrated efficient adsorption of WO3 nanocrystals, favoring enhanced photocatalytic activity of the semiconductor. Light-driven navigation in pure water was proved for the final Au–WO3@C Janus microrobots under UV-light. Interestingly, the authors observed motion directions toward the Au-coated side, in contrast to common TiO2/Au Janus microrobots. Moreover, they proved the acceleration of the Au–WO3@C Janus in the presence of low concentrations of dyes due to the enhanced diffusiophoretic effect. Finally, Pumera's group has recently reported a UV-light-driven single-component WO3 microrobot easily prepared by hydrothermal reaction and a subsequent calcination process.163
5.1.1.3. Iron oxides. Hematite and maghemite, α-Fe2O3 and γ-Fe2O3, respectively, are the two possible mineral forms for Fe(III) oxide. Despite their similar photoresponse (Eg: ∼1.9–2.2 eV),164 it is important to highlight a key difference between them in terms of their magnetic behavior. The cubic structural arrangement in maghemite, as in Fe3O4, results in a ferromagnetic material. On the contrary, an antiferromagnetic hematite arises from a rhombohedral geometry. In any case, the response of these iron oxides to an external magnetic field is guaranteed,165–167 providing magnetic guidance capability over catalytic propulsion.168,169 Moreover, enhanced speeds could also be achieved thanks to Fenton reactions.167,170
Great advances have been made since Palacci's group reported their pioneering works on UV/blue light-propelled Fe2O3 peanut-shaped colloids.166,171–173 For instance, He's group kept the peanut shape to gain further insights into the phototactic behavior of the colloidal microrobots obtained from chemical precipitation.174 Nonetheless, this is not the only exploited morphology. He's group described the preparation of complex colloidal α-Fe2O3-based structures with different shapes.175 The authors demonstrated the potential of curvature-controlled emulsion polymerization to generate asymmetric microparticles by growing additional polystyrene nanostructures. Later, Zhang's group prepared Fe2O3 microspheres through a sol–gel method and subsequently by an encapsulation/dewetting/polymerization process to obtain shape-tunable Janus microrobots.176 They studied the UV-light-driven motion of these asymmetric structures and demonstrated their controlled directionality under a magnetic field. On a second attempt, the group continued with the combination of Fe2O3–polymer to gain further insights into the fabrications of adaptive materials.177 They showed the ability of Fe2O3/polysiloxane hybrid colloids to undergo dynamically reconfigurable self-assembly. To this end, the authors demonstrated the relevance of the redox reactions triggered by Fe2O3 and chemical fuel under UV irradiation. Moreover, they reported self-assembled chains and flower structures that could be exchanged by decreasing the UV intensity or by the action of an external magnetic field. Alternatively, Pumera's group used Fe2O3 microspheres prepared by a hydrothermal method and obtained final Janus microrobots, exploring several metallic asymmetries.165 They studied the dynamics of these self-propelled microrobots under UV-light in different scenarios of chemical fuel and proved the magnetic steering. In subsequent work, they delved into the consequences that the thickness of the asymmetric metallic coating on Janus microrobots might have for their photocatalytic activity.178 Considering surface modifications, Sanchez's group prepared SiO2 microtubes with an MnO2 inner layer, combining the template-assisted sol–gel method and hydrothermal reactions.179 The authors then carried out a final surface functionalization to include γ-Fe2O3 NPs, implanting photocatalytic properties under visible irradiation and magnetic guidance to the catalytic motion. On the contrary, Miao's group prepared α-Fe2O3 NPs by hydrothermal method and used them for the external functionalization of the halloysite nanotubes through a two-step wet chemistry procedure.180 The catalytic propulsion provided by the Ag NPs inserted in the tubular inner layer was noticeably enhanced by the photocatalytic activity of the α-Fe2O3 NPs under visible light.
Iron oxyhydroxide (FeOOH) is an alternative Fe(III) derivative and one of the most earth-abundant materials. Up to four stable polymorphs have been reported depending on the geometrical arrangement of their ions. Thus, it offers different electronic band gap energies (Eg: ∼2.0–2.5 eV)181 to exploit its appealing photocatalytic activity in the visible wavelengths. Moreover, when compared with Fe2O3, FeOOH is the preferred option to enhance the photocatalytic activity of the widely used TiO2.182 Recently, Baraban's group studied the effect of β-FeOOH nanocrystals on the self-propulsion of Janus microrobots.183 They used polystyrene microspheres asymmetrically coated with Ag by PVD and partially converted to AgCl through a surface modification with FeCl3. This last step was responsible for the presence of β-FeOOH nanocrystals over the whole of the microspheres. Among other things, β-FeOOH acted as a cocatalyst under blue light, providing enhanced speeds, and was in charge of the light-driven motion when green light was used. The same design was used by the authors later on to evaluate ionic transport processes.184
5.1.1.4. Cuprous oxide (Cu2O, Eg: ∼2.1 eV). Mallouk's group was the first to report visible light-driven motion on Cu2O microrobots, taking full advantage of its narrow band gap.185 To this end, Janus structures were generated from Cu2O microspheres prepared by chemical precipitation and half-covered with an Au layer. Then, Gibbs’ group enlarged the photoactivity of Cu2O-based microrobots with the hybrid design resulting from the combination of TiO2 and Cu2O semiconductors.186 The authors used silica microspheres as nucleation centers for the sequential growth of photocatalytic arms by e-beam evaporation. They reported different self-propulsion under light irradiation, with several types of motion depending on the selected wavelength, from UV to blue light, and the chemical fuel. Going a step further, Cai's group devised a glucose-powered green light-photoactivated microrobot made of Cu2O microspheres with interspersed nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes.187 Doping with the carbonous materials resulted in enhanced photocatalytic activity due to the reduced charge recombination on the semiconductor. The importance of achieving successful performances in fully green environments pushed these authors to gain further insights into the photocatalytic activity of Cu2O. In a second work, they focused their attention on oxygen vacancy-based Cu2+1O microparticles (Eg: ∼1.54 eV), easily obtained by a one-pot chemical precipitation.188 The enhanced photoactivity ability enabled the propulsion in pure water or low concentration of tannic acid under blue to red light exposure. Liu’s group recently put their effort into shapes and crystal facets and the impact they may have on the photocatalytic activity of visible light-driven microrobots,189 similar to Pumera's group in the case of Ag3PO4 microrobots.190 To this end, the authors evaluated the motion abilities of Cu2O micro-octahedrons with tailored crystal morphologies obtained by chemical precipitation. Following this trend, the latest report on Cu2O-based microrobots to date has been authored by Tu's group.191 They have prepared hollow microparticles with particular active facets exposed by the hydrothermal method and evaluated a phototaxis reversal behavior. In addition to their light-driven mobility, these microrobots show the ability to detect local pH changes, adding an important dimension to their functionality. This ability to sense pH variations enhances the appeal of these microrobots and further expands their versatility and potential applications.
5.1.1.5. Rhodium oxide (Eg: ∼1.41 eV). Very recently, Wang's group has reported highly reproducible asymmetric nanorods made of Au and Rh2O3, and easily prepared by template-assisted electrodeposition and subsequent annealing in air.192 Fuel and fuel-free environments have been used to trigger the photocatalytic self-propulsions under different sources of light irradiation. Interestingly, the authors have proved that the motion of these microrobots could be activated by UV and the full spectrum of visible light (purple to red), although they noticed decreasing speeds as the wavelength shifted to lower energies.
5.1.2.1. Bismuth oxyhalides (BiOX, X = Cl, Br, I). In between oxides and halides, bismuth oxyhalides owe their excellent optical and electronic properties to the van der Waals and strong covalent interactions inside their layered structures.193 Moreover, different optical band gaps (Eg) distributed along the UV-Vis range can be found depending on the selected halogen element. Besides, BiOX are also indirect band gap semiconductors, meaning that photo-excited electrons and holes cannot be easily recombined.194 As a result, BiOX are nowadays considered as ideal candidates for photocatalysis under visible light. BiOCl was the pioneer member to be used in the field. Pané's group coupled BiOCl (Eg: ∼3.6 eV) with Bi2O3 (Eg: ∼2.8 eV) to form the photocatalytic segment of a 3D hybrid microstructure.195 To this end, pulse electrodeposition of Bi/BiOCl and subsequent in situ oxidation of Bi were carried out. The resulting Bi2O3/BiOCl heterojunction showed an enhanced photocatalytic activity (10–15 times higher) than individual components. More recently, Xu et al. also produced biohybrid microrobots by depositing BiOCl nanosheets and Fe3O4 NPs on Chlorella cells as biotemplates.196 Moving on to BiOBr (Eg: ∼2.99 eV), BiOBr-based Janus micromotors modified with Fe(III) were presented by Yang's group.197 They prepared Fe3+-doped BiOBr microspheres through the hydrothermal method to achieve an enhanced photo-Fenton activity under sunlight irradiation. Additional components, such as Fe3O4 NPs and Mn3O4 asymmetric coating, were included in these complex structures, aiming at easy retrieval and catalytic propulsion, respectively.
Finally, Cai's group pioneered the use of BiOI photocatalyst, the most attractive bismuth oxyhalide due to its narrow band gap (Eg: ∼1.7 eV). They reported revolutionary fuel-free visible light-driven navigation with their Au-coated BiOI-based Janus microspheres.198 Some years later, Yao's group described an updated version of these Janus micromotors, including two additional steps in their synthesis procedure.199 On the one hand, freshly prepared Fe3O4 NPs were added to the BiOI hydrothermal synthesis, aiming at an easy retrieval of the micromotors. On the other hand, a surface modification with sheet-like AgI microplates was carried out to improve the degradation performance of final BiOI/AgI/Fe3O4/Au microrobots. Nevertheless, it is important to note that increased exposure of the higher photocatalytic surface area corresponds to heightened efficiency in photodegradation. Therefore, Pumera's group recently published alternative Fe3O4@BiOI microroses, where tailored Fe3O4 NPs were used for the surface functionalization of BiOI microparticles.200 Thus, the Janus configuration and, in turn, light-triggered motion were sacrificed behind larger BiOI surface areas. In this sense, magnetic steering was used instead. The identical concept was pursued by Bakar's group, wherein they affixed Fe3O4 nanoparticles to BiOI surfaces.201 However, their one-pot solution synthesis led to the formation of irregular Fe3O4@BiOI micromotors characterized by flaky shapes and a broad particle size distribution. In all preceding instances, BiOI served as the predominant component in the architecture of the microrobots. Nevertheless, it is incorporated as an element in heterogeneous structures through template-assisted electrochemical deposition.202
5.1.2.2. Bismuth tungstate (Bi2WO6, Eg: ∼2.8 eV). Bismuth tungstate (Bi2WO6) is an alternative Bi-based visible light-responsive photocatalyst with limited photocatalytic activity. Despite its perovskite-like or laminated structure made of [Bi2O2]2+ and [WO4]2− layers, the electron–hole recombination rate is still very high. Consequently, material scientists usually carry out additional metal doping or combinations with other semiconductors to enhance its performance.203 Pumera's group has explored the ability of Bi2WO6 to induce visible light-driven motion.204 The authors carried out a wet chemical synthesis combined with self-aggregation and Ostwald ripening processes to achieve single-component microspheres with hierarchical structures. Interestingly, useful swarming ability under visible light illumination was demonstrated.
5.1.2.3. Bismuth vanadate (BiVO4, Eg: ∼2.4 eV). Bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) is one of the most promising Bi-based photocatalysts. Not only is it visible light-active with a large absorbance rate, it is also highly (photo)stable, non-toxic, and corrosion-resistant, among others.205 Well aware of its great potential, Pumera's group described the first visible light-driven BiVO4 microrobots.206 Homogeneous star-shaped microstructures are presented that resulted from a coprecipitation method and subsequent hydrothermal treatment. Besides the pioneering stars, several other morphologies have already been reported for single-component BiVO4 micromotors, such as layered squares207 or spheroids208 (Simmchen's group), spheres with concave defects (Pumera's group),209 and the most recent microrods by Dong's group.210 All these morphologies have resulted from the hydrothermal method by playing with the synthesis parameters (e.g., additives, pH, temperature, or time). Pumera's group has also conferred magnetic activity to the original microrobots when combined with Fe3O4 NPs through surface functionalization211–213 or as part of polyethylenimine clusters.214 Moreover, light-driven GO-doped BiVO4 microspheres have been recently prepared by Chen et al. that exhibit enhanced absorption capabilities and a narrower band gap (Eg: ∼2.2 eV).210
Escarpa's group published the first description of metal chalcogenide QDs in the field of micromotors for sensing applications215 and also pioneered the use of QDs for photocatalytic purposes.216 Particularly, they carried out the encapsulation of ZnS (Eg: ∼3.8 eV) or CdS (Eg: ∼2.9 eV) QDs in PANI-Pt tubular microrobots. Interestingly, the QDs were not added by surface functionalization but rather were grown in situ inside the polymeric outer layer during its electrodeposition. A few years later, they applied the same technique for the preparation of light-driven CdS QDs/C60 tubular microrockets.217 Escarpa's group has also explored commercially available QDs (CdSe@ZnS and CdTe@ZnS, Eg: ∼2.3 eV) in polymeric matrices218,219 to obtain Janus micromotors with asymmetrical functionalization with Fe3O4 NPs. On the other hand, Lu's group used in situ deposition of CdSe QDs on octahedral Cu2O micromotors by means of ultrasonic dispersion220 while Dong's group followed a hydrothermal reaction to obtain PbS QDs/Cu2O microrobots.221 Interestingly, the addition of PbS QDs allowed the authors to report the first NIR-I (808 nm) light-driven microrobots with NIR-II (1100 nm) fluorescence.
It is important to mention that besides QDs, alternative strategies have been reported for metal chalcogenides in the field of microrobots. For instance, Pumera's group applied a CdS/ZnO ion-exchange reaction to generate CdS-based microrods222 or a microwave reactor to produce Sb2S3 microrods.223 An alternative core–shell Sb2Se3/ZnO design was explored by Tang's group, who took advantage of the in-plane asymmetry of Sb2Se3 to evaluate the polarization state of light and its effect on the speed of the light-driven microrobots.224 To this end, Sb2Se3 nanowires were prepared by physical vapor deposition method while a ZnO shell was later added by atomic layer deposition. Further, Tang's group also studied an alloy made of ZnSe and CdSe (ZnxCd1−xSe) as an n-type semiconductor for core–shell visible-light-driven nanowires with variable band gaps (Eg: ∼1.7–2.7 eV).225 Considering spherical shapes, Wang's group used the hydrothermal method to produce hierarchical CuS microspheres (Eg: ∼2.1 eV) as seeds of further CuS@Fe3O4/Pt Janus micromotors.226 Finally, Wang's group obtained ZnIn2S4 (ZIS) microspheres through a modified hydrothermal method and further functionalized them with Pt NPs.227 Importantly, a noticeable reduction of the band gap (Eg: ∼2.48 to 2.08 eV) was calculated after the photochemical deposition of Pt NPs on pristine ZIS microspheres. Table S7 (ESI†) summarizes the details of the most relevant examples from this group.
To conclude, it is important to highlight that hydrophobic materials are not exempt from being exploited in the field despite water being the most common media for the applicability of microrobots. On the contrary, hydrophilic platforms can be used to encapsulated them, as proved by Ma's group in the case of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)porphyrin (TAPP, Eg: ∼1.7 eV).231
5.2. Role of semiconductors in micro/nanorobotics
Photocatalysts, as constituents of micro/nanorobots, can perform different functions depending on their involvement (or not) in the navigation of these small entities. With that in mind, two subsections have been conceived that will discuss actuators for light-driven motion and semiconductors as add-on components with specific functionalities.Great efforts have been devoted to address photocatalytic self-propulsion during these past years and, fortunately, there is now a deep knowledge of all the main aspects involving this topic. For instance, three mechanisms that explain the driving force of photocatalyst-based light-driven motion have been described. Self-diffusiophoresis occurs after an asymmetric release of redox products. In this sense, an unbalanced production of ROS, such as superoxide anion (O2˙−) or hydroxyl radicals (OH˙), must occur after the interaction of the photo-induced charge carriers on the photocatalysts’ surface with the surrounding media (H2O, H2O2, glucose, etc.). To name some recent examples, Pumera's group linked self-diffusiophoretic motion to the single-component photocatalytic BiVO4 microrobots and proved how asymmetric morphologies can lead to irregular ROS production (Fig. 12A.a).206 For instance, self-diffusiophoresis was associated with the light-driven motion of the BiVO4 microstars206 and Bi2WO6 microspheres,191 in good agreement with their heterogeneous hierarchical surfaces. Nonetheless, not only ROS can trigger this mechanism. Gao's group proved that the photogenerated holes on ZIF-67-based Janus microspheres were able to produce an asymmetric flow of Co2+ ions that together with H+ would induce an ionic self-diffusiophoresis.118 The motion of ZnO@PTPM Janus microrobots developed by Zhang's group was related to the release of Zn2+ and OH− ions originated from the photocorrosion of the ZnO microspheres.232 In the case of the Ag3PO4 microrobots presented by Pumera's group, the propulsion came from the asymmetric production of Ag+ ions in a fuel-free context under visible light.190 It is also important to mention that the authors also prepared up to three different morphologies to demonstrate the enhanced photocatalytic activity of {111}-exposed facets over the {100} ones.
 | ||
| Fig. 12 Role of photocatalysts in micro/nanorobots. (A)–(D): Self-propulsion. (A) Mechanisms. Schematic illustrations for: (a) Self-diffusiophoresis under visible light irradiation of star-shaped BiVO4 micromotors. Reproduced with permission from ref. 206. Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society. (b) Self-electrophoresis. Electron transfer at the ZnO/Pt smooth interface, schematic representation of propulsion mechanism for the light-driven motion of the microrobots and trajectories with and without UV exposure in pure water. Modified with permission from ref. 152. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH. (c) Bubble recoil. Schematic representation for TiO2 microtubes and their associated processes of O2 bubble generation and ejection under UV light exposure in a fuel-free environment. Reproduced with permission from ref. 143. Copyright 2015, Wiley-VCH. (B) Phototaxis. pH-dependent phototaxis behavior of hollow Cu2O micromotors. Reproduced with permission from ref. 191. Copyright 2022, Elsevier Inc. (C) Swimming trajectories. Schematic representation and time-lapse images of the effect that lighting orientation has on the modes of motion of ZnO/Au microrobots. Reproduced with permission from ref. 153. Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society. (D) Swarming. Schematic illustration and optical snapshots depicting the efficient cooperative transport of a passive polymeric particle by means of the collective motion of phototactic TiO2 microrobots. Reproduced with permission from ref. 233. Copyright 2021, The Royal Society of Chemistry. (E) and (F) Active matters. (E) Adsorption. Schematic illustration of the removal capability against heavy metal ions of the Janus microrobots made of ZIF-67. Reproduced with permission from ref. 118. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society. (F) Fluorescence. Schematic representation of the mechanism of fluorescence of PbS QDs/Cu2O microrobots with NIR light irradiation, thanks to the presence of PbS QDs as proved by the comparative images and emission spectra with bared Cu2O microparticles. Reproduced with permission from ref. 221. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society. | ||
Alternatively, the light-induced motion of photocatalytic microrobots can also be attributed to a self-electrophoresis mechanism when a photo-induced electric field results from the unbalanced production of electrons. Considering photocatalytic Janus structures, such as the one presented by Pumera's group for Fe2O3165 or TiO2 microspheres by Hu's group,234 the electric field required for the electrophoresis mechanism is originated by the proton depletion at the asymmetric metallic coatings. Interestingly, Pumera's group addressed a detailed analysis of the effect of porosity of the semiconductor material for the self-propulsion of the microrobots.152 They demonstrated that smoother ZnO surfaces in ZnO/Pt Janus microrobots guaranteed a stronger interaction with the Pt coating. Thus, the authors describe an enhanced charge transfer at the interfaces of smother ZnO surfaces, resulting in lower electron–hole recombination and more efficient electrophoresis motion in a fuel-free context (Fig. 12A.b).
Finally, bubble recoil refers to displacement based on the growth and ejection of O2 bubbles generated under light exposure. Although it is mostly linked to catalytic microrobots, some examples of bubble-propelled semiconductor-based microrobots, either as microtubes143,144 (Fig. 12A.c) or Janus structures,145 have been reported.
Photocatalytic microrobots are highly responsive to light inputs, including on/off switchability. From the original works reported about TiO2-based Janus microspheres145 to complex designs,160 this on/off capability enables precise external control of their light-driven motion on demand. Unfortunately, beyond their activation, the limited or lack of accurate control over their directionality has usually been considered as one of the main drawbacks for light-induced navigation. However, great advances have been made in this matter during the last years to leave these concerns behind.
Phototaxis, or phototactic response, is the ability of photocatalytic microrobots to be self-propelled toward or away from the source of irradiation, meaning positive or negative phototaxis, respectively. As a result, targeted self-propulsion in phototactic microrobots is possible only by changing the lighting direction. Hu's group used ZnO/Pt microspheres to capture the instantaneous alignment of Janus microrobots under UV light.154 After illumination, an electric dipole was originated by the unbalanced surface charge of the two sides, activating an electrophoretic rotation. When the light and the dipole reached a parallel disposition, the rotation became a directional displacement, exhibiting negative phototactic motion. Therefore, as in the case of magnetic microrobots, orientated light-driven navigation in a fuel-free context was proved. Moreover, the authors extended their study to alternative Janus microrobots such as TiO2/Pt or CdS/Pt. In the case of single-component microrobots, Tu's group showed predesignated trajectories for Cu2O microrobots in pure water by adjusting the direction of the light.191 Moreover, they demonstrated an autonomous phototactic reversal behavior without altering the irradiation source. These hollow microspheres showed an adaptative response to local pH gradients and switched between positive (pH < 4) and negative (pH > 4) phototaxis due to changes in their surface zeta potentials (Fig. 12B). However, when discussing surface charges it is worth mentioning that besides the directionality of the motion, electrostatic interactions with substrates may also hinder self-propulsion, as demonstrated by Baraban's group.183
Lighting orientation can dictate not on only the direction but also the swimming trajectories for photocatalytic microrobots. To prove this point, Zhang's group designed original Janus ZnO/Au microrods comprising twinned microrods and evaluated their electrophoretic navigation.153 They described a positive phototaxis motion highly dependent of the incident angle of irradiation (αz). A precise tuning of this parameter enabled an evolution from circular trajectories (αz = 0°) to straight-line type (αz = 90°). Importantly, helical motions, typical of magnetic microrobots, were found at intermediate angles and particularly at αz = 45° (Fig. 12C). Nonetheless, this is not the only aspect with a great influence on swimming trajectories. These authors also demonstrated that the asymmetric shape imparted by the dissimilar diameters of the twinned rods was solely responsible for the observation of circular motions. In fact, regular Janus ZnO/Au microrods only showed the ballistic type.153 In an additional example, the asymmetric morphology related to the concave defects and hierarchical structures on single-component BiVO4 microspheres allowed Pumera's group to obtain helical trajectories without the need of further light settings.209
In terms of speed of motion, light-driven navigation is greatly influenced by the intensity (I) of the irradiation source, following Equation (I) = Øhc/λ (Ø: incident photon flux; h: Planck's constant; c: speed of light; and λ: wavelength of incident light). Correspondingly, Escarpa's group demonstrated the easy modulation of the velocity of CdS QDs/C60 tubular microrockets.217 They observed a proportional dependence resulting in higher speeds with increasing intensity of the incident light. Thus, the more photons reaching the surface of the CdS QDs the more efficient the light-induced phoretic mechanism. Consequently, one may think that increasing the photocatalytic surface would also result in an enhanced photocatalytic activity. Nonetheless, there is an important limitation for this affirmation. Zhang's group prepared light-activated metal oxide (TiO2, ZnO, or Fe2O3)/polymer Janus microrobots with variable photoactive surface area, taking full advantage of the wetting properties of the polymeric coating.176 Considering a diffusiophoretic mechanism, they proved that faster navigation could be achieved by increasing the exposed active area as long as the asymmetry of the motors; in turn, the asymmetric distribution of the resulting products was maintained. Similar conclusions about shape tunability were also reached later on by the same group with their ZnO/polysiloxane Janus microrobots232 and by Gao's group in the case of ZIF-67-based Janus microspheres.118 All in all, many are the parameters that can be tuned on demand to achieve efficient navigation across complex media, like human serum or blood samples, as demonstrated by Escarpa's group.218
Finally, it is important to emphasize that light-driven navigation is not a phenomenon individually experienced by photocatalytic microrobots. On the contrary, different interactions may arise resulting in a collective motion or swarming, which would increase the chances to perform more sophisticated tasks.137 For instance, Guan's group proved a collective phototactic motion based on tunable interactions of amorphous TiO2 microspheres enriched with hydroxyl groups.233 On the one hand, the authors described the generation of a cluster by the electrolyte diffusiophoretic motor–motor attraction under a negative phototaxis. On the other hand, they proved its disassembling into scattered microrobots by the action of an additional UV light source superimposed at 45°. Moreover, the authors took advantage of the assembling/disassembling ability to demonstrate the efficient transport and release of different passive cargoes (Fig. 12D). Collective motions in photocatalytic microrobots also enable the reproduction of alternative interactions in nature, such as the chasing–escaping process predators and prey. Guan's group also reported the generation of these biomimetic interplays in terms of repulsive and attractive interactions among several photocatalytic systems, such as hydroxyl-rich ZnO–TiO2 or Ag3PO4–TiO2 microparticles, among others.235 The swarming phenomenon was produced by diffusiophoretic attractive microparticles, or “prey,” linked to the intraspecies attraction. Due to the strong diffusiophoretic attraction, the “predator” microparticles were also dragged, repelling the prey in close vicinity. More recently, Dong's group explored the predator-prey concept between light-powered BiVO4-based microrobots.210 They reported fuel-free diffusiophoretic motions for single-component BiVO4 microrods and GO–BiVO4 microspheres under visible light. When these microrobots were combined, the BiVO4 microrods acted as predators, swarming around the GO–BiVO4 microspheres while low-intensity light irradiation was maintained. If the light intensity was increased, then the convergent electro-osmotic flow that attracted the BiVO4 predators toward the GO/BiVO4 prey was replaced by self-diffusiophoresis, pushing the microrods away. It is important to mention that the authors used positively charged glass substrates during the experiments in order to favor electro-osmosis over diffusiophoresis at low energy.
Photoluminescence is another interesting characteristic associated with photocatalysts. For instance, Kienle's group recorded a blue fluorescence signal for their complex GaN/ZnO microrobots, generated at the nanoscale-thin ZnO layer and stabilized at the interface with the GaN outer layer.160 As pointed by Pumera's group, photoluminescence is a powerful tool to evaluate the fate of photo-induced charge carriers.152 Considering Janus ZnO/Pt microrobots, the authors detected fluorescence quenching after the asymmetric Pt coating. Knowing that the main band from the ZnO emission spectrum is mainly related to self-trapped electron–hole pairs, its disappearance revealed suppression of the surface defects. In this sense, enhanced performance of ZnO/Pt heterojunctions and photocatalytic activity could be achieved. Similarly, Wang's group observed fluorescence quenching after the metallic functionalization of ZIS microspheres with Pt NPs.227 The authors also compared the lifetime of the radiative and non-radiative processes in bare and functionalized ZIS microspheres, obtaining reduced values in the case of Pt-ZIS. As a result, they determined an efficient transfer of the photogenerated electrons from the photocatalyst to the Pt NPs, which acted as an electron reservoir. However, this is not the only field of application of photoluminiscence. On the contrary, advanced tasks can be exploited by photocatalytic microrobots thanks to this property. Pumera's group discussed the benefits of the intrinsic fluorescence of the different morphologies of Ag3PO4 microrobots for the visualization of their position.190 This easy tracking of photoluminescent microrobots could be of great help for precise diagnosis and treatment. In this regard, Dong's group has recently reported PbS QDs/Cu2O microrobots with prominent and stable fluorescence at NIR (1100 nm), making them ideal for in vivo investigations (Fig. 12F).221 However, a great contribution to the concept of “on-the-fly” fluorescence sensing probes must be attributed to Escarpa's group and their works on metal chalcogenide microrobots.216,218 For instance, they were the first to apply CdTe QDs for the rapid recognition of heavy metals ions, such as Hg+, through the cation exchange capacity of Cd-based QDs.215 Hence, they evaluated the performance of the microrobots in terms of fluorescence quenching. Interestingly, only catalytic reactions were used for the self-propulsion of these Pt-based microtubes and not light-driven motion. This design clearly illustrates how semiconductors can be used as active materials without being actively involved in the navigation of the microrobots. Nonetheless, it is important to emphasize that even when they are not the main driving force for self-propulsion, they can provide a clear contribution to the overall speed rates for catalytic microrobots.236 To give an example, Escarpa's group prepared catalytic microtubes made of Pt, Pd, or MnO2, with an outer layer of C60 functionalized with CdS QDs.217 They proved a notable acceleration to propulsion under different wavelengths, from UV and visible range, due to the transfer of additional photogenerated electrons to the catalytic layer.
As previously mentioned, continuous progress in materials science has allowed the preparation of increasingly complex photocatalyst-based microrobots resulting from the blending of semiconductors with compounds of different nature. Aiming at a fuel-free context, the addition of materials responding to alternative physical stimuli (e.g., magnetic field or ultrasound) has been extensively and intensively explored. However, magnetic activity provided by iron oxides (γ-Fe2O3 or Fe3O4)169,200,214 or Ni195 has traditionally attracted greater attention within the community. In fact, hybrid photocatalytic microrobots with magnetic steering are at the forefront of research in terms of applicability. More accurate directionality, higher speed and strength of motion, and easy retrieval are provided by this synergistic combination, despite the great advances made to improve the on-demand control of light-driven motion. In any case, photocatalytic materials will produce ROS when exposed to light irradiation, regardless of their involvement in self-propulsion tasks. Therefore, semiconductors have been included as active materials in magnetic microrobots lately, and due to the enhanced mass transport they provide, efficient photocatalytic performances have been demonstrated.
5.3. Applications
Given these advantages, the use of semiconductor-based micro/nanorobots for environmental applications has rapidly become one of the main targets for researchers in this field. Compared with passive or static photocatalytic microparticles, self-propelled photocatalysts offer enhanced mass transfer, which promises higher efficiencies in a photodegradation context. Moreover, great efforts have been devoted to progress on a greener approach by limiting the use of chemical fuels. In this sense, two main research lines have been investigated: the development of light-driven motion in pure water and the combination of these highly photoactive materials with alternative driving forces. Among them, hybrid photoactive and magnetic microrobots have always occupied a privileged position due to the additional microrobot retrieval options that the implementation of magnetic propulsion provides. In terms of pollutants, the photocatalytic performance of microrobots has been proved with great success in a broad variety of environmental threat scenarios.
5.3.1.1. Organic dyes and textile fibers. Wastewater discharged from textile plants is one of the most studied emissions due to the amount of hazardous chemicals it returns to nature. As a result, many examples devoted to the elimination of organic dyes, such as Methylene Blue,197,220,237,238 Methyl Orange,227 and Rhodamine B,195,196,199,202,210,230 can be found in the literature. More recent studies are demonstrating the practical applicability of semiconductor-based micro/nanorobots for the degradation of solid plastic wastes, such as commercial textile fibers. Pumera's group introduced the self-propulsion and ROS production of Bi2WO6 microrobots against commercial baby wipes, achieving structural damage of the fibers after 50 hours. They highlighted the relevance of the autonomous accumulation and attachment of the microrobots to the fibers for the enhanced efficiency of photodegradation (Fig. 13A).204 More recently, the same group has reported 1D magnetic photocatalytic (Fe3O4/Bi2O3/Ag) microrobots capable of accelerating the degradation of commercial single-use face masks.60 Magnetically boosted 1D microswarms enable an active interaction with the polypropylene microfiber network, allowing the efficient photocatalytic reaction for morphological and compositional degradation of polymeric fiber waste.
 | ||
| Fig. 13 Applicability of photocatalytic micro/nanorobots. (A)–(D): Decontamination. (A) Textile fibers. Schematic representation of (a) the photoactivity of Bi2WO6 microrobots and (b) their interplay with textile fibers under light irradiation. Additionally, optical images of the microrobots’ attachment are shown, being a key step for further photodegradation. Reproduced with permission from ref. 204. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH. (B) Heavy metals. Schematic representation of (a) the propulsion of CdTe QDs-based microrobots and (b) their fluorescence quenching by Hg2+ ions. Time-lapse images and high-resolution TEM images of the original CdTe QDs and the resulting HgTe QDs obtained after mercury exchange are also shown. Reproduced with permission from ref. 218. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH. (C) Microplastics. Removal of plastic pieces by light-driven BiVO4-based microrobots. Reproduced with permission from ref. 212. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society. (D) Microorganisms. Schematic representation of the preparation of hollow ZnO/Pt Janus microrobots and time-lapse images showing the interaction of the microrobots with yeast cells. Reproduced with permission from ref. 154. Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH. (E) and (F): Biomedical applications. (E) Bacterial eradication. (a) Schematic representation of the Fe3O4@PEI/BiVO4 microrobots and their oral antibiofilm activity. (b) Different LIVE/DEAD staining intensities under fluorescent microscopy depicting the activity of magnetic BiVO4-based microrobots against oral biofilm. Top panels are related to the treatment with H2O2 alone, and bottom panels refer to the microrobot performance under visible light illumination and transversal rotating magnetic field. Reproduced with permission from ref. 214. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society. (F) ROS-based photodynamic therapy. Schematic illustration of the disaggregation of mature protein fibrils by light-driven BiVO4 micromotors and comparison with the dynamic thioflavin T fluorescent assay. Reproduced with permission from ref. 209. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. | ||
5.3.1.2. Explosives. Environmental pollution must be included among the negative consequences of military conflicts. In this sense, water contamination can be provoked by damage to industrial facilities and the release of chemical hazardous materials. Hence, several authors have used picric acid as a model pollutant for explosives in aquatic resources. For instance, Pumera's group tested the performance of their porous ZnO/Pt Janus microrobots against this pollutant in terms of two different phenomena: adsorption and photodegradation.150 To achieve an enhanced adsorption capability of polar picric acid, two main features were analyzed by the authors: (i) the large surface areas of ZnO microspheres with high concentrations of hydroxyl groups and (ii) the fast catalytic propulsion provided by the Pt asymmetric coating. Moreover, UV and Vis light irradiation sources were used to estimate the adsorption/photodegradation percentage of the explosive. However, it is important to emphasize that under visible light, where a negligible effect of the H2O2 alone was proved, a decent performance (≈23%) of the fuel-propelled porous microrobots after one hour was observed. In a second approach, the same group reported a removal capacity of 70% for picric acid in a fuel-free context after a two-hour treatment with their ZnO-based microbrushes.159 The authors attributed these good results to the UV light-driven motion of the microrobots and the efficient ROS production carried out on ZnO surfaces. A beneficial effect of the Pt layer, which limited the charge recombination, was mentioned too. Beyond ZnO-based microrobots, Pumera's group also demonstrated a satisfactory photodegradation of picric acid (≈74%) for their light-driven TiO2/Fe3O4/CdS microtubes after a two-hour treatment.222 Considering the whole spectrum of light, the authors stressed the importance of the amorphous TiO2 layer in charge of the required hydroxyl radical generation under UV irradiation to enhance the catalytic performance. Regarding the effect of photo-Fenton reactions against picric acid, Pumera's group focused their attention on hematite-based Janus microrobots.178 Interestingly, the authors analyzed the influence of the asymmetric Pt coating on the final photocatalytic performance. They showed a photodegradation efficiency of 56% for the microrobots with a 30 nm Pt coating after two hours of UV light irradiation and decreasing efficiencies for higher thicknesses of the metallic layer (e.g., 60 or 90 nm). The authors explained these results in terms of H2O2 availability. Because thicker Pt layers lead to faster H2O2 consumptions, only lower ROS production by photo-Fenton reactions could be achieved.
5.3.1.3. Heavy metals and pesticides. The rapid growth of metal industries and the intensive use of chemicals for soil treatment have led to an increasing presence of toxic metallic elements in aquatic resources. Bearing in mind that this kind of pollutant cannot be disintegrated and is not biodegradable, their bioaccumulation can lead to dramatic health consequences. In the interest of remedying this environmental concern, several water cleaning treatments with semiconductor-based micro/nanorobots have been reported. To name some, Sanchez's group utilized the γ-Fe2O3 NPs adsorbed on the surfaces of SiO2–MnO2 microtubes for the removal of metal ions.179 On the other hand, Escarpa's group took advantage of the cation exchange capabilities of chalcogenide compounds for the efficient removal of mercury ions.218 The authors confirmed the success of their strategy through the fluorescence quenching of the CdSe@ZnS QDs encapsulated on their visible light-driven Janus microrobots (Fig. 13B).
5.3.1.4. Microplastics and related compounds. As a major contributor to plastics pollution and one of the most relevant current environmental threats, the microplastics category includes all plastic materials fragments with sizes up to 5 mm. Their small dimensions limit the efficiency of common plastic removal methods, leading to their ubiquitous presence and accumulation in aquatic resources. Besides their durability and low biodegradability, the situation is even worse when taking into account that they have already affected animal health after entering the marine food chain. Thus, real actions must be taken before reaching the point of no return. To the best of our knowledge, Simmchen's group pioneered the first incursion into the microplastic problem by means of photocatalytic microrobots.239 To this end, they selected passive polystyrene microparticles as a model pollutant and TiO2-based microrobots with asymmetric Au and magnetic (Ni, Fe) coatings. In addition to their UV light-driven navigation, the authors proved strong attractive phoretic interactions between passive microparticles and individual Janus microrobots, promoted by the photocatalytic activity of the former. Moreover, the researchers also took advantage of the microrobots' magnetic activity to generate motile assemblies capable of removing microplastics in a fuel-free context under a magnetic field, just by shoveling. Later, Pumera's group used magnetic BiVO4 microstars to go a step further, considering the photodegradation of the attached plastic pieces.212 As depicted in Fig. 13C, the authors first used the visible light-driven navigation of the microrobots to promote interaction between the pollutants and the magnetic microstars and, subsequently, to collect them by means of an external magnet. As expected, higher removal efficiencies were observed for the microplastics models with less hydrophobic surfaces, where the interactions with the microstars were favored. Then, photocatalytic experiments were carried out over several days, observing a progressive weight loss with time. The same group explored the electrostatic capture and subsequent photodegradation of polyethylene glycol chains with hematite-based Janus microrobots, revealing a total degradation to shorter polymer chains after 24 h of treatment under UV light.165 Additionally, Osman's group demonstrated the photocatalytic activity of flake-like BiOI–Fe3O4 microrobots against polystyrene microplastics.201 The authors reported a total degradation of micron-sized polystyrene latex beads under visible light in less than one day. A negligible mass loss of 0.03% was obtained in the case of bigger plastic pieces after 120 hours of treatment with the light-driven microrobots. In contrast to previous reports where representative polymeric materials were used, Pumera's group has recently targeted a real-life pollutant when they tested the removal capabilities of Fe3O4@BiVO4 microrobots against cellulose acetate microfilaments coming from an actual cigarette filter.213
It is important to stress that the microplastic threat is not limited to the actual pollution caused by plastic materials. On the contrary, microplastics have become a source of deeper concern considering the great variety of chemical compounds that they might involve. For instance, Escarpa's group focused their attention on bisphenol A, a common additive in plastic to improve its durability and strength.216 Nonetheless, it is also a documented endocrine-disrupting compound; thus, its ubiquitous presence in the environment must be reduced. The authors took advantage of CdS QDs encapsulated on the surface of Pt-based microtubes for the photocatalytic degradation of the pollutant. They observed a complete mineralization after a 10-min treatment due to photo-induced ROS production under solar light irradiation together with their effective bubble-propelled navigation. Alternatively, Pumera's group targeted UV-filter residues from sunscreen lotions, which have also been detected when adsorbed on microplastics.200 To this end, they evaluated the performance of BiOI-based magnetic microrobots under blue light. The authors reflected on the photocatalytic and adsorption capabilities of the BiOI semiconductor, the large surface area provided by the hierarchical shape of the microspheres, and the magnetic guidance provided by Fe3O4 NPs as triggering effects for the photocatalytic removal of the residue.
5.3.1.5. Microorganisms. Besides the interaction and transport of passive particles, photocatalytic microrobots can also interplay with living microorganisms as alternative sources of pollution in wastewater. Yeast cells are usually selected as a pollutant model to this end due to their appropriate size and easy visualization. Among other examples, Hu's group demonstrated the controlled swimming trajectories of their hollow ZnO/Pt microrobots toward targeted clustered yeast cells.154 Interestingly, the authors were able to guide the navigation of the Janus microspheres only by playing with the light direction due to their phototactic propulsion under UV light exposure. After the approach, successful collections and transports were also proved together with the final release once the UV light was switched off (Fig. 13D). Similarly, an efficient yeast cell transport was also reported by Pumera's group for their single-component BiVO4 microstars only assisted by their visible light-driven motion.206 It is worth mentioning that the same group also analyzed a real case of residual yeast contamination in the food industry when considering craft beer samples.211 On that occasion, the authors turned to the magnetic steering of BiVO4/Fe3O4 microstars for an efficient removal in such a complex media as beer. On the other hand, they demonstrated the key role of the photocatalytic activity of the BiVO4 microstars with the yeast removal evolution from 39% in dark to almost 100% under visible irradiation.
5.3.1.6. Antibiotics. The increased production/consumption of medical treatments against bacterial infections is directly responsible for the environmental contamination with antibiotics and antibiotic resistance elements. Thus, there is an urgent need to limit the accumulation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in aquatic systems. Motivated by this human health threat, several research groups have evaluated the potential of their photocatalytic microrobots against antibiotics. For instance, Wang's group analyzed the degradation of tetracycline by taking full advantage of enhanced Fenton reaction activity in CuS@Fe3O4/Pt Janus microrobots.226 The authors demonstrated, in presence of chemical fuel, a synergistic effect for ROS production between CuS microspheres and the Fe3O4 NPs decorating them, and improved it with an asymmetrical Pt coating. Moreover, higher activity was achieved under light exposure due to the photocatalytic decomposition of H2O2 by CuS. In fact, 81% and 89% degradation were achieved under Vis and UV light irradiation, respectively, after only 5 min of treatment. The same pollutant was used by Wang's group to test the performance of their Pt-ZIS microrobots under visible light irradiation.227 Following a three-hour treatment, they reported an increase of 30% on the photocatalytic activity of semiconductor after surface modification of the ZIS microsphere with Pt NPs. The authors attributed this finding to enhanced charge separation together with the H2O2-fueled bubble propulsion provided by the metallic decoration. Alternatively, Pumera's group recently targeted oxytetracycline, which is a veterinary antibiotic.157 The authors devised a surface functionalization with laccase enzyme for their ZnO-based microstars to promote a hybrid enzymatic/photocatalytic degradation. They reported a progression on the removal efficiency of the microrobots from 51% (dark) to 65% (UV light) after 12.5 min of treatment in presence of chemical fuel.
5.3.2.1. Biofilm eradication. The term “biofilm” is used to describe a collection of microorganisms, like bacteria, that grows on surfaces. Biofilm is a major biomedical challenge due to the different contexts where it can be found, from chronic wounds to implants214,240 or urinary conducts,241 producing severe infections. Consequently, several works from the field of microrobots have been devoted to this topic, considering the sterilization capabilities of the photocatalytic ROS generation. Ma's group addressed the ability of microrobots with hybrid enzymatic and magnetic propulsion for bacteria-killing.231 Therefore, the authors carried out a surface functionalization of the SiO2 scaffolds with urease to promote urea-driven phoretic motion, with Fe3O4 in charge of the magnetic steering. Moreover, a photosensitizer (i.e., TAPP) was also loaded to achieve efficient ROS production from O2 molecules. Compared to static assays, the authors demonstrated increased ROS generation under blue light for the mobile entities. Two main reasons were described to explain this result: (i) a higher accessibility to the O2 molecules triggering the redox reaction and (ii) a better diffusion of the produced ROS. Keeping the focus on urinary infections, Pumera's group used urea-propelled TiO2 nanotubes loaded with CdS QDs for efficient ROS generation.241 The same group also explored dental implants.214 To this end, the authors developed magnetic and photocatalytic microclusters, combining photocatalytic BiVO4 microspheres and magnetic Fe3O4 NPs through a poly(ethylenimine) linker. They were able to prove the synergistic effect of photocatalysis and magnetic actuation for an efficient disruption of a model supragingival plaque bacteria in dental implants (i.e., Gram-positive Streptococcus gordonii, Actinomyces naeslundii, and Veillonella parvula and Gram-negative F. nucleatum). In addition, a successful performance against oral biofilm colonizing real dental implants (i.e., osseointegrated implant and abutment) was proved (Fig. 13E).
Photocatalysis has also been combined with the antibacterial activity of Ag-based microrobots even when small percentages of this element where used. As an example, Pumera's group reported light-driven star-shaped ZnO/Ag microrobots against Gram-negative P. aeruginosa and Gram-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) biofilms.156 They also tested the antibiofilm capabilities of light-driven B-TiO2/Ag microtubes against three bacterial species frequently found in facial implants (i.e., Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (Gram-negative) and Streptococcus mutans and MRSA (Gram-positive)).240 Finally, the same group used Ag3PO4 microrobots against Gram-positive MRSA and Gram-negative P. aeruginosa.190 The authors discussed the impact of exposed crystal facets of three different single-component morphologies in a fuel-free environment.
5.3.2.2. Neurodegenerative diseases. It is known that many age-related diseases, such as neurological disorders, are originated by abnormal peptide buildups. The disaggregation of the resulting mature fibrils has traditionally been the main strategy from ROS-based medicine to face this medical issue. Being aware of this biomedical challenge, Pumera's group recently presented single-component BiVO4 microrobots as appealing therapeutics to this end (Fig. 13F).209 Particularly, they grew human serum albumin (HSA) protein fibrils as the target model and leveraged the intrinsic ROS production of the microrobots related to their light-driven motion to demonstrate an efficient disassembly. The authors also highlighted the relevance of the enhanced surface area derived from their hierarchical shapes for the promising photocatalytic activity of these self-propelled ROS generators.
6. Polymers
Polymers offer synthetic versatility, tailorable properties, flexibility, environmental and bio-compatibility, degradability, and responsiveness to various external stimuli and have thus contributed significantly to the development of advanced smart micro/nanorobotic systems.27,28 Semiconducting polymers, such as covalent organic frameworks (COFs) or conjugated organic polymers, are a fascinating class of light-driven micro/nanorobotic materials due to their unique photocatalytic properties without inorganic compartments.242–244 Furthermore, as soft functional components, polymers can create systems with programmability and responsiveness. They enable controlled and adaptive motion behavior as well as the pickup, transport, and release of molecules or biological cells in microscale operations.29–33 These polymer actuators are driven by the combination of multiple modulating factors, including temperature, pH, light, magnetic field, ultrasound, etc. Multifunctional smart micro/nanorobotic systems integrated with polymers are expanding their unique applications in the environmental and biomedical fields.This section will discuss recent advances in the use of polymers for intelligent micro/nanorobotic systems (Fig. 14). The representative polymer-based micro/nanorobots are summarized in Table S8 (ESI†), highlighting key aspects of polymer types, actuation modalities, functionalities, and applications. Emerging classes of soft functional polymeric materials are classified into three categories: smart responsive polymers, porous organic polymers, and conductive polymers. With their advantageous properties, these polymer families have been used as light-driven micro/nanorobots with photocatalytic activity or as functional components for interactive and responsive actuators. The promising aspects of polymers and their subcategories will be summarized with micro/nanorobotic designs, fabrication, multifunctionality, and their underlying physiochemical mechanisms. Furthermore, an overview of their performance in practical applications will be summarized, including recyclable and programmable smart environmental reagents, active targeted therapeutics, self-propelled micro-supercapacitors, and others.
6.1. Polymeric materials types
COFs are crystalline, porous polymers with well-defined structures at the molecular level, typically consisting of light elements such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and other elements. These frameworks offer tailorable morphologies and properties and thus can be designed to incorporate targeted functionalities, such as photocatalytic property, fluorescence, biocompatibility, regulated chemical affinity, etc.242,249 In recent studies, different types of COFs have been exploited as functional components in light/chemical-driven micro/nanorobots for therapeutic drug carriers,242 microsensors,249 photo-theranostics,66 or water remediation agents.250 Conjugated organic polymeric networks, such as sulfur- and nitrogen-containing donor–acceptor polymers, have also been used as visible light-driven micromotors.243,244 In the semiconducting polymeric network structure, effective charge carrier separation is enabled by the short distance between electron-donating and electron-accepting subunits, leading to the enhanced photocatalytic activity to propel the micromotors through the self-diffusiophoresis mechanism.
Tubular microrobots can be fabricated by electrochemical deposition of the outer conductive polymer layer and the inner catalytic metal surface in a cylindrical porous template (e.g., polycarbonate membranes). Various conductive polymer–metal combinations have been explored, including PPy, PANI, PEDOT, PANI, and Au, Ag, Pt, Ni–Pt, etc.28 In these tubular microrobots, the outer conductive polymers provide a high-affinity layer for recognizing chemical and biological molecules based on various surface functional groups and electrostatic and π–π interactions while an inner metallic layer is responsible for catalytic bubble propulsion or responding to other energy sources such as ultrasound.28,62,251 Their electroactive, redox, and ion exchange capabilities are also of interest for micro/nanorobotic applications. For example, PPy allows the programmable modulation of the surface charge by switching the protonated and deprotonated forms of the polymer chains, which enables a controllable affinity for hormone molecules or the accumulation of microrobots by focused light beams.128,252 The light-absorbing PPy NPs modified with glucose oxidase/Cat also demonstrated bubble-propelled motion and the capability for light- and glucose-accelerated pollutant degradation.253
6.2. Role of polymers in micro/nanorobotics
 | ||
| Fig. 15 Autonomous micro/nanorobotic systems in combination with soft polymeric functionalities. (A) and (B) Photoactive porous organic frameworks. (A) COF-based light-driven microswimmers, i.e., imine-linked TABP-PDA-COF and azo-linked TpAzo-COF, and their phototaxis behavior following directional light illumination in ionic media. Reproduced with permission from ref. 242. Copyright 2023, Wiley-VCH. (B) Self-diffusiophoresis of hybrid Tz–Th microrobots under visible light irradiation induced by their polymeric coating. Scale bars: 20 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 244. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society. (C)–(E) Smart responsive systems. (C) (a) PDPA-embedded ZIF-L/CAT micromotors and pH-responsive vertical motion switching through buoyancy effects. (b) Repeatability within four consecutive pH sweeps. Reproduced with permission from ref. 30. Copyright 2019, Elsevier Inc. (D) Dynamic microtubes based on a thermoresponsive polymer (PNIPAM-co-ABP-AAc) and temperature-controlled capture and release of a single bovine sperm cell. Reproduced with permission from ref. 31. Copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH. (E) 3D-microprinted hydrogel microrobots performing decoupled multiple tasks, including temperature-controlled spike revelation (outer shell of pNIPAM) and pH-responsive swelling (inner sphere of pNIPAM-AAc). The scale bar in the SEM image is 50 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 33. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. (F) and (G) Functional conductive supporting layers. (F) Ultrasound-modulated reversible stop-and-go motion switching of a bubble-propelled PEDOT/Ni/Pt microengines. Scale bar: 20 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 62. Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society. (G) PANI-supported WS2/Pt micromotors act as micro-supercapacitors for “on-the-fly” capacitive enhancement of the electronic circuit. Reproduced with permission from ref. 70. Copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH. | ||
Conjugated organic polymeric network-based photocatalytic microrobots have been described by Pumera's group. For instance, they devised a metal-free network made of an organic backbone with donor and acceptor units to generate electron–hole pairs, thereby triggering the visible-light-driven motion.243 To this end, they linked benzotrithiophene (donor) and triazine (acceptor) units by means of a Stille cross-coupling reaction. A size distribution of irregularly shaped microparticles (Eg: ∼2.57 eV) was obtained, as expected from this type of chemical synthesis. Aiming at a more defined morphology, a new approach was pursued by the authors during their second attempt.244 Following the same donor–acceptor strategy, thiophene (donor) and 1,3,5-triazine (acceptor) monomers were selected as building blocks (Eg: ∼1.5 eV). However, instead of microparticles, a polymeric coating was produced in situ on mesoporous silica microtubes; consequently, highly homogeneous organic–inorganic hybrids were achieved (Fig. 15B). The resulting tubular microrobots can be propelled by the diffusiophoretic motion under visible light irradiation, which is responsible for the asymmetric photogeneration of ionic species in the inner cavities.
6.2.2.1. Programmable speed and motion. Polymers have been extensively exploited for intelligent micro/nanorobotic systems capable of controlled and adaptive movement in response to specific triggering factors. Wilson's group, for example, has presented thermo-responsive stomatocyte nanomotors that can be switched on/off to control motion by molecularly assembled PNIPAM polymer brushes.29 Stomatocytes are bowl-shaped polymeric vesicles that encapsulate platinum (Pt) NPs inside the structure. At a temperature below the LCST of PNIPAM, the hydrophilic PNIPAM brushes open the narrow gap of the stomatocytes, resulting in self-propelled motion through the catalytic decomposition of the chemical fuel (hydrogen peroxide). In contrast, when the temperature increases above the LCST, the PNIPAM brushes turn into a hydrophobic layer on the narrow gap, which blocks access to the hydrogen peroxide so that the propelling movement comes to a stop. This work demonstrates the reversible locomotion and braking system controlled at the nanoscale by a temperature-sensitive polymer. Another approach involved the use of the hydrophilic/hydrophobic phase-shifting polymer, PDPA, to fabricate CAT-PDPA/ZIF-L micromotors (Fig. 15C).30 At neutral pH conditions, the hydrophobic PDPA captures the generated O2 bubbles and exhibits rapid upward motion propelled by buoyancy forces. Conversely, PDPA undergoes a hydrophilic transformation at a slightly acidic pH, facilitating competitive binding of H+ ions instead of O2 bubbles. This triggers the subsequent downward motion in a vertical direction. In both hybrid systems, the conformational changes are reversible, providing repeated switching of motion in response to a transition in temperature or pH conditions. On the other hand, conductive polymers can be used for acoustically regulated tubular intelligent systems. The ultrasound field can modulate the switching of stop-and-go motions in bubble-propelled PEDOT/Ni/Pt microrobots by disrupting bubble evolution and ejection (Fig. 15F).62 In addition, the ultra-fast assembly of bubble-carried PEDOT/MnO2 micromotors was demonstrated by the mutual force of the bubbles.251
6.2.2.2. Pickup and release system. Polymeric micro/nanorobotic systems offer the capability to selectively capture and transport target objects and then release them at specific locations in a controlled manner. Polymer-based hybrids enable microengineering to pick up molecules, chemicals, or biological cells and release payloads triggered by specific stimuli, facilitating applications such as precise manipulation of cells, recyclable pollutants treatment, targeted drug delivery, etc.
Schmidt's group, for example, demonstrated the remote-controlled capture, transport, and release of a single sperm cell using dynamic rolled-up polymeric microtubes.31 The tubular microstructures consisted of thermo-responsive polymer, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-co-acryloylbenzophenone-co-(acrylic acid) (PNIPAM-co-ABP-AAc) and thin layers of Ti (adhesive)/Fe (ferromagnetic). This design allows reversible folding and unfolding to entrap and release sperm cells in response to temperature changes while providing magnetic directional control (Fig. 15D). The temperature-controlled manipulation of sperm cells can offer the development of advanced assisted fertilization techniques.
As recyclable active reagents for water treatment, Pumera's group presented magnetic nanorobots with thermo-responsive micellar copolymers that can absorb and dispose of pollutants.32 A pluronic tri-block copolymer (PTBC), consisting of a hydrophobic poly(propylene oxide) core and thermo-responsive hydrophilic poly(ethylene oxide) shell, is assembled on the surface of magnetite NPs. Above their critical micelle temperature (CMT), ∼25 °C, dehydration and intermicellar aggregation lead to a contaminant trap within the polymeric matrix, which is further facilitated by magnetic actuation. Subsequently, the separated nanorobots can dispose of the pollutants at low temperature (∼5 °C), in which the PTBC matrix is completely expanded through interaction with water. Finally, the nanorobots can be easily retrieved by magnetic separation and are ready for reuse. The combination of magnetically actuated nanorobots with temperature-responsive polymers offers a recyclable route to efficient water treatment with model pollutants, such as arsenic and atrazine.
A more complex system, multifunctional hydrogel microrobots that can respond to multiple stimuli, was developed by Sitti's group (Fig. 15E).33 The pollen grain-inspired microrobot structure, which consists of three functional hydrogel components, was fabricated using a 2PP-based 3D microprinting technique. The core sphere is first printed with poly N-isopropylacrylamide acrylic acid (pNIPAM-AAc), which is responsible for the drug carrier and pH-responsive on-demand release. Subsequently, the spiky structure of FePt NPs-embedded pentaerythritol triacrylate (PETA) layer was printed, which is covered with an outer shell of poly N-isopropylacrylamide (pNIPAM). The pNIPAM shell enables on-demand exposure of the spikes by shrinking in response to a temperature increase. The anchoring performance study showed that the spiked shell can generate higher pull-off and frictional forces compared to the non-spiked shell, which could contribute to the controllable attachment to soft tissue surfaces. Moreover, the FePt NPs in the PETA layer enable magnetically controlled locomotion with a maximum speed of 532 μm s−1. Finally, the inner spherical pNIPAM-AAc networks showed a volumetric swelling/shrinkage of up to 300% in solutions with different pH values, resulting in efficient loading and pH-responsive release of fluorescent molecules.
6.2.2.3. Functional conductive supporting layers. Conductive polymers, including PPy, PANI, and PEDOT, provide a conductive support layer in tubular micro/nanorobots with various chemical, optical, or electrical functionalities due to their surface functional groups, electrostatic and π–π interactions, redox, and ion exchange capabilities, which promote the smart performance of micro/nanorobotic systems. For example, the surface charge properties of the PPy-based tubular microrobots can be modulated by the protonation states of the PPy layer depending on the pH value, which enables controllable electrostatic interaction with other molecules.128,252 In another approach, as micro-supercapacitors, the PANI-based microtubes with WS2 and Pt have demonstrated self-propelled navigation and adhere to the electrode surface to enhance the capacitive behavior of the electronic circuit (Fig. 15G).70 Also, PPy possesses high light absorption and photothermal conversion capabilities, allowing self-thermophoretic motion under focused light beams, photo-induced therapy, and synergetic photocatalytic reactions.66,128,253
6.3. Applications
For example, chemically programmable tubular microrobots based on PPy polymer and Pt/Fe3O4 layer have been presented that can weave a macroscopic network of hormonal pollutants, α-oestradiol, and then remove them efficiently.252 The surface charges of the PPy/Fe3O4/Pt microrobots are variable depending on the pH conditions due to the protonation and deprotonation of the PPy layer, allowing a programmable affinity to interact with hormonal molecules. Under combined movements with H2O2 and light illumination, the PPy/Fe3O4/Pt microrobots were able to form a fibrous network of α-oestradiol on the microrobotic interface, rapidly concentrating hormonal pollutant molecules. With this strategy, 70% of the pollutants are removed after only 10 min of reaction, reaching up to 80% after 2 h of exposure.
In another approach, magnetic- and thermo-responsive nanorobots have been used as reusable adsorbents for the efficient removal of arsenic and atrazine from contaminated water.32 The PTBC micellar polymer assembled on the surface of the magnetite NPs adsorbs the pollutants at ambient temperature (∼25 °C) by intermicellar aggregation and subsequently discards them through a simple cooling step (∼5 °C), allowing the nanorobots to be reused for further cleaning cycles. The magnetically actuated nanorobots (18.6 mg) were exposed to a contaminated solution containing arsenic or atrazine (5 mg L−1) at 25 °C for 100 min, resulting in a removal efficiency of 65.2% and 61.5%, respectively, followed by a disposal efficiency of 48% and 34.6% at 5 °C, respectively. After ten recycling cycles, the removal efficiency decreased to 38% and 31.8%, respectively. Furthermore, their practical applicability was investigated in real wastewater samples such as tap water and river water. For arsenic or atrazine, a removal efficiency of 60–70% was achieved compared to the performance in ultra-pure water media.
Semiconducting microrobots based on conjugated organic polymers can combine light-driven motion and photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants under light irradiation and provide a large surface area arising from a porous network.243,244 These polymeric microrobots can generate reactive radical species (˙OH, ˙O2−) under visible-light irradiation, which are responsible for the decomposition of organic compounds. The sulfur- and nitrogen-containing donor–acceptor polymer microrobots (0.2 g L−1) were able to decompose the organic dyes RhB, MB, and MO (10 μmol) with a degradation efficiency of 97.5%, 97.1%, and 87.8%, respectively, after 90 min.243 On the other hand, triazine–thiophene (Tz–Th)-based tubular microrobots have been used for the efficient capture and photodegradation of abused psychoactive drugs that are toxic to aquatic organisms and the environment.244 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) was tested as a model drug pollutant and quantitatively analyzed using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectroscopy (LC-MS/MS). Self-propelled Tz–Th microrobots (150 μg mL−1) were able to rapidly degrade MDMA (200 ng mL−1) after 20 min of illumination with visible light and achieved complete degradation of intermediates after 2 h (Fig. 16A).
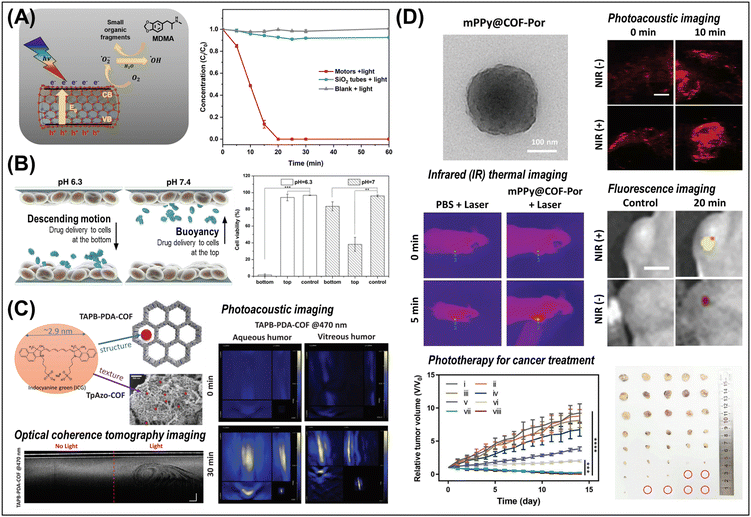 | ||
| Fig. 16 Soft polymeric micro/nanorobots for advanced applications. (A) Tubular microrobots coated with a semiconducting conjugated polymer (triazine-thiophene) for the photocatalytic degradation of MDMA. Time-dependent plot of MDMA degradation efficiency compared to control groups. Reproduced with permission from ref. 244. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society. (B) PDPA-embedded ZIF-L/CAT micromotors and pH-induced selective delivery of an anticancer drug (5-FU) in a 3D cell culture chamber. Cell viability of MCF-7 cells at the top and bottom of the culture chamber at different pH conditions. Reproduced with permission from ref. 30. Copyright 2019, Elsevier Inc. (C) ICG-loaded COF microswimmers and their real-time photoacoustic and optical coherence tomography imaging modalities. Reproduced with permission from ref. 242. Copyright 2023, Wiley-VCH. (D) PPy@COF-Por-based multimodal photo-theranostic nanomotor agents for cancer treatment. Real-time monitoring of tumor sites by trimodal in vivo imaging (infrared thermal/photoacoustic/fluorescence imaging). Time-dependent tumor growth curves and photographs confirming the enhancement of photo-therapeutic effects in the HCT116 xenograft mouse model. Scale bars are 2 mm (photoacoustic images) and 5 cm (fluorescence images). Reproduced with permission from ref. 66. Copyright 2023, Wiley-VCH. | ||
Crystalline organic porous materials, such as COFs, possess several advantages for therapeutic application, including porosity, tailorable properties, biocompatibility, and multimodal functionalities.242 For example, Sitti's group introduced two different types of COFs-based light-driven drug carriers (TAPB-PDA-COF, TpAzo-COF) that can be operated in intraocular fluids.242 The inherent large structural and textural porosities enable the efficient loading of drugs and dyes, such as DOX, insulin, or Indocyanine green (ICG). Cell viability tests on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) showed that the cytotoxic effect of both COF types is minimal, even at high concentrations, both with and without light illumination. The COF microswimmers can be propelled in different light wavelengths and simultaneously transport and release the pharmacological agents in a pH-dependent manner. In addition, the ICG-loaded COFs enable high-contrast photoacoustic imaging, optical coherence tomography, and hyperthermia inside the organs, demonstrating their potential for multimodal therapy and imaging microrobots for retinal diseases (Fig. 16C).
In another approach, COF-based hybrid nanomotors have been developed as multimodal photo-theranostic agents for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer (Fig. 16D).66 COF nanomotors (mPPY@COF-Por) consist of polypyrrole (PPy) core, porphyrin-COF shell (COF-Por), and cancer cell membrane coating, achieving directional motion through the self-thermophoretic force under NIR light irradiation. PPy core and COF-Por shell enable photothermal and photodynamic therapy by absorbing 808 nm (1.5 W cm−2) and 660 nm (50 mW cm−2) laser, respectively. Also, the photothermal conversion of PPy allows thermal imaging/photoacoustic imaging for real-time monitoring of cancer treatment. The De value of COF hybrid nanomotors in the biological medium was found to be 15.77 μm2 s−1 under NIR light irradiation (808 nm), facilitating target accumulation, cellular uptake, and tumor penetration, thus promoting subsequent phototherapeutic effects. The thermophoretic mobility of COF hybrid nanomotors led to a dramatic increase in tumor elimination rate in the HCT116 xenograft mouse model, suggesting integrated multimodal photo-theranostics for cancer treatment.
7. Biological cells
Biological cells hybridized with synthetic functional components have fascinating properties as living small-scale robots with autonomous cellular actuation and negligible toxicity, which has led to their intensive use in a variety of advanced therapeutic technologies.34,35 Cell-hybrid robots can efficiently swim by flagellar beating or by rolling onto a surface, and can be guided by different taxis mechanisms like chemotaxis and phototaxis, among others. Their motion can be also assisted by applying external physical fields like magnetic fields or ultrasound.63,254,255 Cells can also be used as templates for fabricating soft biocompatible/biodegradable microrobots.256 The underlying nature of biological entities possessing excellent biocompatibility and low toxicity, as well as various intriguing properties of each of the reported biohybrid microrobots, has been actively explored in their related fields.36–38This section offers the latest advancements and future outlook on emerging biological cells utilized in micro/nanorobotics. It uses a distinctive classification system to distinguish between motile and immotile/dead cells. The former leverage their inherent motion and functional capabilities while the latter serve as templates for crafting soft, biocompatible structures. These structures find applications in both environmental contexts and advanced therapeutic interventions (Fig. 17). Table S9 (ESI†) summarizes the characteristics of biohybrid micro/nanorobots, including cell types, propulsion and navigation strategies, functional components, and applications. Motion-driving strategies rely on the autonomous propulsion ability of biological components. Mobile microorganisms, e.g., bacteria, sperm, microalgae, etc., have active flagellar propulsion that can be engineered by an external motion guide to achieve collaborative performance. On the other hand, nonmotile biological species, such as pollen, spores, plant callus, and immotile cells can be exploited as biotemplates for functional material incorporation, capable of extrinsic source-powered motion guidance. Their advantageous properties, capabilities, and performances will be summarized with representative examples. Furthermore, we will provide an overview of advanced applications, including pollutant removal for environmental remediation and advanced therapeutics for drug delivery, cancer therapy, assisted fertilization, biofilm removal, etc.
7.1. Cells class
7.1.1.1. Bacteria-based biohybrids. Bacteria, which comprise prokaryotic microorganisms of diverse sizes (0.5–5.0 μm) and shapes, are ubiquitous and occupy every habitat on Earth.63,257 They can autonomously move, perceive external stimuli, and respond to the environment.258 Bacteria-based biohybrid robots at the micro/nanoscale (miniature size) can swim by their own power or integrate with external sources. In addition, their excellent biodegradability and biocompatibility are also merited.259 Therefore, the intrinsic characteristics of motile bacteria have attracted extensive interest as living small-scale robots, leading to a wide application in the field of micro/nanorobotics.260,261
Magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) are a unique species that naturally produce internal magnetic NPs, enabling the bacteria to move along the external magnetic field.262 Due to this unique property, MTB has gained great attention as a living microorganism for versatile uses in bacterial biohybrid research fields (Fig. 18A and B).263 In 2006, Martel introduced the possibility of controlling the direction of a living MTB through the integration of MTB and engineering systems.264 Pumera's group proposed living biohybrid robots to remove contaminants by controlling the movement of MTB under a magnetic field (Fig. 18A).265 Martel and co-workers developed bacteria-conjugated nanoliposomes by adding functional groups on the surface of Magnetococcus marinus MC-1 (MC-1) for drug-carrying.266 The results showed the improved biocompatibility of MTB and their capability of loading and delivering a large number of therapeutics by external magnetic fields without affecting bacterial motility in the same group (Fig. 18B). Additionally, control of the magnetic properties and motility of Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1 was demonstrated by depositing Fe3O4 nanoparticles on its surface, facilitating real-time tracking for cargo delivery systems.267 In the same vein, the accumulation of magnetite generated by M. magneticum AMB-1 was observed to enhance visualization in magnetic resonance imaging at tumor sites.268
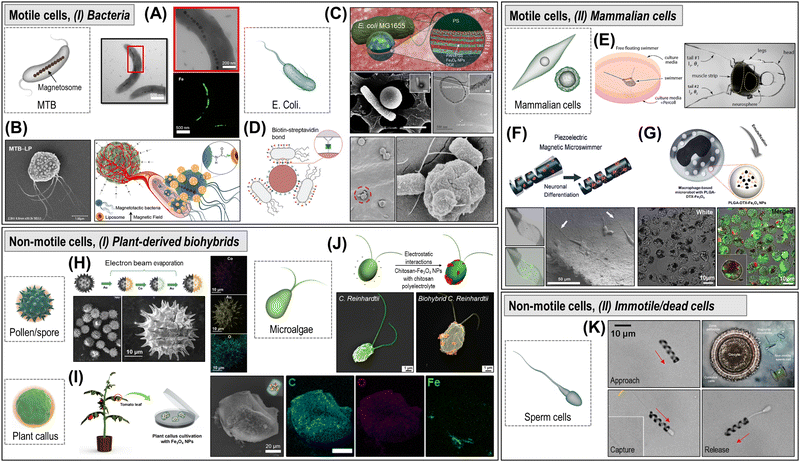 | ||
| Fig. 18 Motile/non-motile cell-based biohybrid robots. (A) and (B) MTB biohybrid robots. (A) TEM images and EDX elemental mapping of M. magneticum AMB-1 and inside magnetosome chains. Reproduced with permission from ref. 265. Copyright 2023, American Chemical Society. (B) MTB-liposome hybrids and magnetotactic cargo delivery. Reproduced with permission from ref. 266. Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society. (C) and (D) E. coli biohybrid robots. (C) PEM-MNP microparticles attached to E. coli MG1655 bacterium microswimmer. Reproduced with permission from ref. 269. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society. (D) Bacteriabot-microparticle binding by biotin–streptavidin conjugation and bioadhesive approach for active cell targeting. Reproduced with permission from ref. 270. Copyright 2017, Wiley-VCH. (E)–(G) Mammalian cell-based biohybrid robots. (E) Biohybrid robots for neuromuscular actuation. The swimmer for neuromuscular actuation consists of a free-standing soft scaffold, skeletal muscle tissue, and an optogenetic stem cell-derived neural cluster containing motor neurons. The swimmer propels itself by inducing flagellar dynamics, through cyclic muscle contraction induced by neural stimulation. Reproduced with permission from ref. 271. Copyright 2019, National Academy of Sciences. (F) Multifunctional soft microrobot with dispersed magnetic NPs and fusing a supple piezoelectric polymer matrix. Exposure to acoustic waves polarizes the piezoelectric of the microrobot, inducing the differentiation of neuronal cells. Reproduced with permission from ref. 272. Copyright 2019, The Royal Society of Chemistry. (G) Macrophage-based microrobot with PLGA–DTX–Fe3O4 theragnostic agents. Confocal microscopy images of PLGA–DTX–Fe3O4 NPs stained in red and macrophages stained in green. Reproduced with permission from ref. 273. Copyright 2016, Springer Nature. (H)–(J) Plant-derived biohybrid robots. (H) Pollen/spore biohybrid robots. Sunflower pollen-based BioBots fabricated by sequential metal deposition with electron beam evaporation. Reproduced with permission from ref. 274. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. (I) Plant callus biohybrid robots. Magnetic plant biobots fabricated by engineering plant callus with Fe3O4 NPs. Reproduced with permission from ref. 275. Copyright 2022, Springer Nature. (J) Microalgae biohybrid robots. Fabrication of magnetic/chitosan-microalgae (C. reinhardtii) biohybrid microswimmers by electrostatic interactions. Reproduced with permission from ref. 276. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH. (K) Artificially motorized sperm robots. Capture and transport of non-motile sperm with different functionalities using a magnetic helix. Reproduced with permission from ref. 277. Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. | ||
Escherichia coli can be an attractive microorganism for bacteria-based biohybrid micro/nanorobots (Fig. 18C and D). Sitti's group suggested bacteria-based microswimmers for targeted drug delivery using E. coli MG1655. For example, E. coli was attached to a multifunctional microparticle consisting of drug and magnetic NPs for targeted active drug delivery (Fig. 18C).269 The motility of such functionalized bacteria could be controlled by chemotactic and magnetic guiding, enabling accurate targeted drug delivery. To improve biocompatibility, biodegradability, and stability, Sitti's group used red blood cells (RBCs) as cargo carriers.259 They immobilized RBCs loaded with drugs and magnetic NPs on the bacteria, and remotely controlled by external magnetic fields. In addition, the bacteria population can be controlled by functionality RBCs using the on-demand light-activated hyperthermia after the process. The same group proposed a bioadhesive E. coli bacterial microswimmer that can be efficiently adhered to the surface of cells through mannose–lectin interactions for gastrointestinal and urinary delivery of therapeutics (Fig. 18D).270 They described the performance of bioadhesive E. coli biohybrid robots on the mannose-expressing cells and adhesion mechanism, which offers the promise of site-specific drug delivery for enhanced efficiency while suppressing side effects.
7.1.1.2. Mammalian cell-based biohybrids. These microrobots are tiny, biohybrid devices that integrate living mammalian cells with microscale robotic components, enabling them to exhibit dynamic behaviors, respond to environmental cues, and perform specific tasks. The integration of biological components, particularly mammalian cells, with synthetic materials allows researchers to harness the biological functionality and adaptability of cells while also benefiting from the precision and controllability of microscale robotics. These microrobots are designed to take advantage of the unique properties of mammalian cells, such as their ability to sense and respond to chemical gradients, adapt to changing environments, replicate, and interact with their surroundings. By combining these cellular capabilities with microfabrication techniques, scientists can create microrobots capable of performing tasks like targeted drug delivery, tissue repair, environmental monitoring, and even minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Among the most used mammalian cells in the field of microrobotics are muscle cells (myocytes), stem cells, immune cells, and sperm cells. Microrobots employing muscle cells as their foundation consist of a synthetic scaffold or framework, typically crafted using various microfabrication techniques. Subsequently, muscle cells sourced from entities such as skeletal or cardiac muscle are introduced through seeding. These cells hold immense appeal due to their inherent ability to contract in response to either electrical or chemical stimuli, resulting in the generation of mechanical motion. This capability for motion, when harnessed through meticulous design, can yield efficient movement on a small scale. An illustration of this concept is elucidated in the study by Sanchez and coworkers. In their research, a “Biobot” constructed from skeletal muscle cells was developed, featuring components molded from elastic materials and cells that were 3D-printed. Remarkably, the motion of this Biobot was not solely governed by chemical triggers; i.e., an electric field was also employed to dictate its movement. This strategic approach yielded impressive outcomes, achieving a peak velocity of three times its body length per second.278 This velocity was found to be comparable to previously documented biorobots founded on cardiac muscle, consequently surpassing those based on conventional muscle sources (Fig. 18E).271,279 Light can also be used to induce muscle contraction in order to vary either direction, speed, or movement duration of the resulting muscle-based microrobot.280
Similar to the above-mentioned biohybrid milli/microrobots, stem cell-based microrobots are also quite attractive as they have the ability to differentiate into various cell types and their function can be tuned with a certain stimulus, which is particularly appealing for tissue regeneration and replacement tasks. These cells are also incorporated into pre-patterned or microfabricated structures that serve as scaffolds to facilitate their seeding and sustainment. The cell differentiation process can be induced by chemical or physical cues. For example, Choi and coworkers developed a microrobot that accommodates mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), an electromagnetic actuation mechanism enabling precise three-dimensional guidance of the microrobot, and a magnet serving to affix the microrobot to the affected cartilage region. The use of these microrobots was for the cargo-release of stem cells which can regenerate cartilage tissue in situ. The conception and production of each constituent element took into account factors such as patient and medical staff accessibility as well as stringent clinical safety considerations.281 Subsequent to its development, the microrobot system's performance was evaluated using a rabbit knee model featuring cartilage defects. The primary objective of this assessment was to secure approval for clinical trials, underscoring the potential clinical utility of the microrobot system in addressing cartilage-related concerns.
Pané's group suggested a versatile micro- and nanorobot system, wireless in nature, for potential application in precise minimally invasive medical interventions. This multifunctional soft microrobot is adept at targeted cell therapy, encompassing both cell transportation and triggered cell differentiation. These micromachines were constructed from composite materials, fusing a supple piezoelectric polymer matrix with dispersed magnetic nanoparticles. The magnetic nanoparticles orchestrate the device's magnetic manipulation while the piezoelectric polymer serves a dual role, functioning as both a navigable framework and a cell electrostimulation platform responsive to acoustic cues. By employing a rotating magnetic field, the microrobots exhibit corkscrew-like movement within diverse fluid environments mimicking bodily fluids. Furthermore, exposure to acoustic waves polarizes the piezoelectric body of the microrobots, resulting in the induction of cell differentiation in neuron-like PC12 cells adhered to the surface of the microrobots. This synergistic approach holds promise for localized bioelectronic therapies (Fig. 18F).272
Microrobots can also be used to target stem cells and induce their differentiation in situ. This was the case of the reported biodegradable Spirulina plantensis (S. platensis) microrobots. These microrobots were embedded with Fe3O4 and piezoelectric BaTiO3 nanoparticles. The formerfirst ones to guide them toward the stem cells niche using external magnetic fields, and the second is to induce a local electric potential upon ultrasound stimulation, to induce cell differentiation.
Immunological cells are another type of widely used cells for building biohybrid microrobots. They are crucial components of the body's defense system, they are responsible for detecting foreign substances, infections, and diseases. The incorporation of these cells into microrobotics could lead to very interesting functionalities. They can serve for diagnosis, targeted and combined therapies, and disease monitoring. T cells, B cells, or macrophages have been first isolated from the patient's own body or from compatible donors and integrated into various synthetic microstructures. By doing so, it has been proven that the cells retain their ability to recognize specific antigens and respond to them. One direct advantage of using microrobots or synthetic microstructures is that they can be functionalized or loaded with specific antigens or markers that upon a local or external stimulus can trigger the function of the immune cells.
These innovative systems based on immune cells take advantage of the distinctive attributes and functions inherent to immune cells. These attributes include their presence in the bloodstream and various tissues, intricate intercellular communication capabilities, strong affinity for different self and foreign markers, unique capacity for responsive navigation and activity, production of diverse chemokines and cytokines, and selective cytotoxicity under specific conditions. These advancements have shown promise in mitigating conditions such as cancer, inflammatory disorders, autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative ailments, cardiovascular complications, and infectious diseases.282
A more specific example is the use of cancer theragnostic microrobots using recruited macrophages to transport therapeutic agents to tumor sites. These microrobots are engineered with docetaxel-loaded poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) NPs for chemotherapy and Fe3O4 magnetic NPs for active targeting using an electromagnetic actuation system. The microrobots are created by having macrophages phagocytize these drug-loaded NPs and magnetic NPs. Through in vitro tests on tumor cell lines, the microrobots demonstrate significant cytotoxic effects with a survival rate of less than 50%. Additionally, experiments on three-dimensional tumor spheroids highlighted the microrobots’ dual action: active tumor targeting through the electromagnetic actuation system and infiltration into the tumor by recruiting macrophages, leading to tumor cell death from the delivered antitumor drug. This work indicates that these active and transportable macrophage-based theragnostic microrobots could serve as biocompatible vectors for cancer therapy (Fig. 18G).273
Finally, highly motile cells like sperm cells have been suggested as propulsion sources of small-scale robots.283,284 Sperm's natural motility and swimming capabilities enable them to move within very intricate channels and swim against strong flow. Sperm-hybrid microrobots have been shown as potential drug delivery vehicles, especially to treat gynecological diseases.285–287 Their natural function of oocyte fertilization is particularly interesting in cases of infertility, particularly when sperm count is low, called “oligospermia”. Sperm can also be used to carry biosensors, for detecting specific molecules and biomarkers in biological fluids, and to elucidate parameters of the sperm and oocyte microenvironment. These capabilities can help solve some questions related to the event of oocyte fertilization and embryo development.
Schmidt's group demonstrated the coupling of motile sperm cells to artificial microstructures.288 Bimetallic nanomembranes were rolled into microtubes to capture single sperm cells. The cells’ flagellar motion propelled the biohybrid micromotors forward with the presence of iron enabling magnetic control. The micromotors were controlled magnetically, leading to separation from uncoupled structures and cells. Capturing sperm reduced their speed by 90%, attributed to structural load and constrained flagellar motion. Shortening microtubes from 50 μm to 20 μm tripled their speed to 33.3 μm s−1 but lowered coupling efficiency. Fibronectin functionalization improved coupling.289 New fabrication methods use maskless photolithography, yielding precise structures and improved coupling. These micromotors reached a speed of 49.8 ± 8.5 μm s−1 and featured magnetic control. Their speed was reduced at higher viscosity such as oviduct fluid; however, adaptability was constrained, limiting movement efficiency.290
Two-photon polymerization (2PP) was explored for complex microstructure fabrication. Streamlined shapes enhanced swimming in biological fluids. 2PP allowed precise positioning and rotational freedom of captured sperm cells. While 2PP offers design freedom, it also poses scalability challenges. Coupling inefficiency necessitates numerous microstructures for viable applications.286,287 A protein-based microflake was developed for efficient sperm transport but it also requires additional structures for propulsion.286 Binding magnetic particles to sperm heads yields magnetotactic sperm cells controlled by magnets and achieve high speeds. Scaling and efficiency have become central in micromotor design and critical for in vivo experiments, tissue imaging, and targeted delivery.291
The development of micromotors for immotile sperm cell transport is trending toward simpler structures. These micromotors are often propelled by rotating magnetic fields and could aid in delivering immotile sperm cells to oocytes in cases of strong asthenospermia.277 An early design consisted of a helical structure with a closed ring, enabling forward propulsion and sperm cell capture. Electrostatic binding of magnetic nanoparticles to sperm membranes has been explored for actuation. Iron oxide nanoparticles have been employed, enhancing imaging and allowing efficient manipulation.284
Sperm cell release from supporting microstructures at the target site presents challenges. Mechanical, enzymatic, and temperature-triggered release mechanisms have been investigated.286,292 A tetrapod micromotor, fabricated by 2PP, employed a mechanical release mechanism upon contact with a cancer spheroid. Enzymatic release was used in a protein-based microflake for multi-cell transport. Thermoresponsive polymers trigger sperm release, offering better control. Magnetic microparticles facilitate spermatozoa release during in vitro fertilization, binding to the cumulus layer surrounding the oocyte.
7.1.2.1. Plant-derived biohybrids. Plant-derived natural products are recent emerging building blocks for the fabrication of biohybrid robots. Plant-based micro/nanorobots that utilize unique structures and physiological systems of plant products are eco-friendly, biocompatible, and biodegradable.293 In this context, various approaches have been introduced to implement plant-derived biotemplates, such as microalgae, pollen, spores, and plant callus in the hybrid micro/nanorobotic systems (Fig. 18H–J).
As obtained from a natural product, pollen and spores have the benefits of biocompatibility, structural stability, and interesting architectures, such as hollow internal shells, and some have spiked rough surfaces.293,294 These characteristics can be leveraged as catalytic/magnetic biohybrid robots for specific applications.293,294 Pumera's group introduced several intriguing pollen-based biohybrid robots (Fig. 18H). For example, sporopollenin exine capsules (SECs) extracted from sunflower pollen grains possess many advantages as biotemplates for hybrid robots, such as physical robustness, uniform size distribution, internal cavities, and spiky morphologies.295 The surface of SECs was partially deposited with Pt layers, thus they can be propelled by bubble-propulsion with fuel decomposition. Moreover, bovine serum albumin was loaded in the internal cavity, demonstrating the capability for molecular encapsulation and transportation. In the following work, nine different pollen grains (dandelion, pine, lotus, sunflower, poppy, camellia, lycopodium, cattail, and galla) were used to fabricate the Pt-pollen hybrid microrobots, proving that the fabrication method is universal to apply in a variety of pollen sizes, shapes, and surface structures.296 In addition, the bubble-propelled Pt-pollen hybrid microrobots showed enhanced performance in heavy metals removal and anticancer drug transport by leveraging the surface properties. More recently, sunflower pollen-based robots were fabricated by asymmetric deposition of thin metal layers (Au, Co, and Au).274 Zhang's group introduced sunflower pollen-based magnetic urchin-like capsule robots and their swarming capabilities.297 The microswarm generated by external magnetic fields and their inherent spiky morphology allow active destruction of the extracellular polymeric substances, which is demonstrated in the biliary stents environment. The same group developed a biosensing technology to detect pathogenic bacteria and toxins by fabricating fluorescent magnetic spore-based microrobots.298 The incorporation of Fe3O4 NPs and carbon dots (CDs) in spore biotemplates, i.e., spore@Fe3O4@CDs, provides excellent magnetic motility in different media and real-time tracking through fluorescence emission, respectively. The final form of spore-based biohybrid robots effectively detects toxins secreted by Clostridium difficile (C. diff) bacteria, suggesting a new concept of biosensing platform using spore–biohybrid robots.
The technology of in vitro culture of cali derived from individual plant organs is one of the main techniques for obtaining a large number of new plants from a few cells due to the totipotency of plant cells. Recently, tomato callus-based magnetic biohybrid robots have been introduced using Fe3O4 NPs, i.e., tomato–biobots, which are capable of magnetic propulsion under a rotating magnetic field (Fig. 18I).275,299 During the callus culture period, Fe3O4 NPs did not affect cell viability. In addition, they demonstrated that L-ascorbic acid-loaded tomato–biobots can generate clones of tomato cells. The tomato–biobots were driven by transverse rotating magnetic fields, which suggests the possibility of delivery and sustained release of conventional pesticides or nutrients.299
Algae are plant-like organisms with characteristics of active locomotion in various environments, long life spans, facile surface functionalization, and are suitable for large-scale production. Among them, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (C. reinhardtii) has attracted significant interest in the use of microalgae-based biohybrid robots (Fig. 18J). C. reinhardtii is unicellular microalgae with a spherical shape that presents many advantages, such as high propulsion (100–200 μm s−1), autofluorescence that can be used for fluorescent tracking, and phototactic capabilities for perceiving the light direction.276,300 Sitti's group reported the effective propulsion of microalga-powered microswimmers as a cargo carrier in living cells.300 The microswimmer was prepared by depositing magnetic PS particles on C. reinhardtii by noncovalent interactions. The resulting microalgae-based hybrid robots exhibit active motility in diverse environments, cytocompatibility via co-culture with cells, and cargo delivery capability, and are thus proposed as a biohybrid targeted drug delivery platform. More recently, Wang's group proposed the microalgae-NP hybrid microrobots consisting of C. reinhardtii and antibiotic-loaded neutrophil membrane-coated NPs.301 The conjugation of NPs on the algal surface was achieved by click chemistry, and the resulting C. reinhardtii biohybrid robots showed high swimming speed (>110 μm s−1), homogeneous distribution, low clearance, and superb tissue retention time (>2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) days), resulting in an effective decrease of animal mortality. This work demonstrates the high potential of microalgae-based biohybrid robots for active therapeutic delivery in the in vivo environment, which is a continued challenge in the relevant research fields. In the following work, the same group introduced the microalgae-biohybrid robots embedded in a pH-sensitive capsule for efficient delivery into the gastrointestinal tract.302 Drugs and fluorescent dye are loaded on algae-based microrobots. The oral administration to mice showed enhanced chemotherapeutic effects compared to control groups and the long-lasting active motion of microalgae-based hybrid robots, suggesting in vivo drug delivery platforms for practical biomedical application.
days), resulting in an effective decrease of animal mortality. This work demonstrates the high potential of microalgae-based biohybrid robots for active therapeutic delivery in the in vivo environment, which is a continued challenge in the relevant research fields. In the following work, the same group introduced the microalgae-biohybrid robots embedded in a pH-sensitive capsule for efficient delivery into the gastrointestinal tract.302 Drugs and fluorescent dye are loaded on algae-based microrobots. The oral administration to mice showed enhanced chemotherapeutic effects compared to control groups and the long-lasting active motion of microalgae-based hybrid robots, suggesting in vivo drug delivery platforms for practical biomedical application.
7.1.2.2. Immotile/dead cells-based microrobots. Bovine sperm cells that lack mobility but are not alive have been employed as templates for soft microrobots. The initial concept was conceived within Medina-Sánchez's laboratory. The primary objective was to augment the functionality of these immotile but functional sperm cells by attaching magnetic micro- or nanoparticles to their tails by identifying some sperm tail proteins. This attachment would take advantage of the elasticity of sperm cells to facilitate sperm motion toward the oocyte, thus assisting in fertilization for cases of low sperm motility, called “asthenospermia”.277,283 This idea progressed from earlier work that employed helical microstructures to propel such inert sperm cells as discussed above (Fig. 18K).
Initial attempts at realizing this concept were outlined in various commentary articles,283,284,303 some including preliminary results. Subsequently, a similar notion was proposed, but this time leveraging non-living sperm cells and utilizing electrostatic interactions between sperm and particles. The aim was to craft soft robots with diverse capabilities. To achieve this, bovine sperm cells were coated with ferrite nanoparticles.256 Through the application of external oscillating fields, these templated-based microrobots exhibited effective propulsion. Furthermore, an initial proof of concept was demonstrated in the context of drug delivery. Notably, advancements were made to enhance the clustering and visualization of these microrobots using ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging, envisioning their use in living organisms in the future.291,292,304
7.2. Role of cells in the micro/nanorobotics
On the other hand, microorganisms’ awareness in detecting external energy gradients has been used for the steerable thrusting of biohybrid robots. These cells or microorganisms have intrinsic characteristics of responding to external stimuli and moving toward favorable environments, i.e., energy taxes, which can be categorized into magnetotaxis (magnetic fields), chemotaxis (chemical gradients), phototaxis (light), and so on.23,305–307 All these strategies enable active locomotive microorganisms with controllable collective behaviors, providing higher working efficiency and adaptability in complex environments due to the engineered cooperative performances.
The representative self-propelled living organism is MTB, which can naturally produce magnetic crystals within its intracellular matrix, i.e., the magnetosome, and thus moves along with the direction of Earth's magnetic field.308,309 The flagellated movement of MTB has been combined with magnetic guidance through the response of magnetosome chains or by further decoration of magnetic components (Fig. 19A). The innate magnetism of M. magneticum AMB-1 allows the swarm to be manipulated in one direction through a programmed clockwise magnetic field, and in precise directions using an external control device such as a joystick (Fig. 19B).265 The magnetotaxis of MTB was controlled by depositing Fe3O4 NPs on the surface of MTB. They demonstrated that the magnetic moment and sensitivity could be modulated by varying the concentration, size, and surface charge of magnetic NPs. Also, the development of MTB with tunable magnetic properties provides an interesting approach that breaks away from the conventional monotonous on/off concept.267 Cai and coworkers reported a biohybrid AI microrobot in which Indocyanine Green NPs were covalently attached on the surface of motile M. magneticum (AMB-1), leading to the sequential magnetic/optical conduction capability.310 These biohybrid AI microrobots can manipulate the direction under an external magnetic field and real-time tracking is possible due to the signal from the Indocyanine Green NPs. These abilities are used for precise target delivery through the micromanipulation of autonomous propulsion. Schuerle's group demonstrated the collective swarming of MTB and M. magneticum (AMB-1) by applying rotating magnetic fields.311 The motion of MTB swarms induced by the generated magnetic torque expanded volumetric convective flow, resulting in enhanced NPs extravasation and tissue penetration. More recently, a follow-up study presented a hybrid control strategy for enhanced transport of MTB through physiological barriers.312 A magnetic torque-driven cell surface exploration enabled four-fold enhanced translocation in the vascular endothelium model, demonstrating the feasibility of clinical use of MTB hybrid robots. Recently, Medina-Sanchez's laboratory presented a magnetotactic sperm micromotor.291 They assembled a biohybrid micromotor by using magnetic microparticles to enhance the stability of the microstructure-sperm coupling. These magnetotactic sperm cells have high motility and swimming speed. Additionally, the magnetically assembling micromotor clusters can be visualized using dual ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging. Finally, it is proposed as a tool that could enable minimally invasive sperm delivery to oocytes within the body for infertility treatment (Fig. 19C).
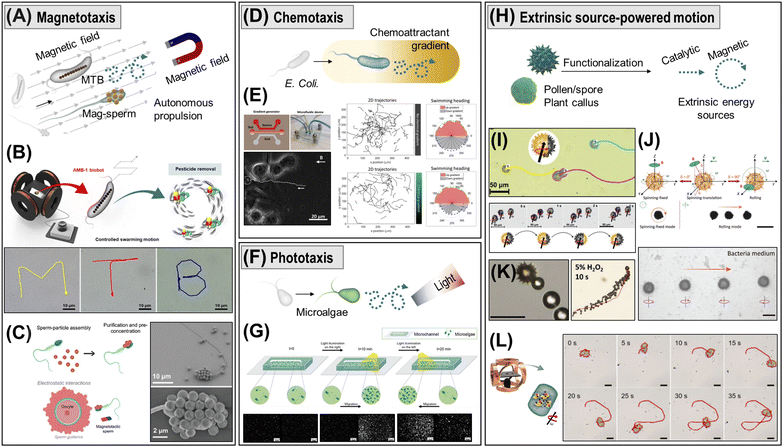 | ||
| Fig. 19 Propulsion and navigation strategies of biological cell hybrid robots. (A) Magnetotactic hybrid strategy. (B) Precisely controlled MTB biobots under the magnetic field with an external direction control device. Reproduced with permission from ref. 265. Copyright 2023, American Chemical Society. (C) Sperm-based magnetotactic biohybrid micromotor. SEM images of sperm cells bound to magnetic NPs through electrostatic interaction. Reproduced with permission from ref. 291. Copyright 2023, Wiley-VCH. (D) Chemotactic hybrid strategy. (E) Chemical gradient generating microfluidic device and comparison of the chemoattractant gradient-dependent mobility of E. coli biohybrid robots. Reproduced with permission from ref. 269. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society. (F) Phototactic hybrid strategy. (G) Visible light-driven phototaxis of C. reinhardtii. biohybrid robots in the microchannel. Reproduced with permission from ref. 276. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH. (H) Extrinsic source-powered strategies. (I) Magnetic actuation and motion mechanism of sunflower pollen-based magnetic BioBots. Reproduced with permission from ref. 274. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. (J) Dual operation modes of magnetic pollen biohybrid robots (spinning-fixed and rolling mode). Scale bar: 30 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 297. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. (K) Bubble-propelled motion of sporopollenin exine capsule biohybrid robots. Scale bar: 50 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 295. Copyright 2017, Wiley-VCH. (L) Magnetic manipulation of plant hybrid biobots and motion trajectories. Scale bar: 10 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 275. Copyright 2022, Springer Nature. | ||
Chemotaxis behavior describes the movement of bacteria or microorganisms in response to a concentration gradient of chemicals (signaling molecules) present in the environment. Biohybrid robots that exploit the sensory system of bioorganisms enable chemotaxis-based autonomous propulsion through the detection of attractant chemical gradients (Fig. 19D). For instance, Sitti's group demonstrated biohybrid microswimmers based on multiple Serratia marcescens bacteria and that exhibit collective chemotaxis behavior toward a chemoattractant (L-serine) gradient (Fig. 19E).313 In the following work, they also introduced biohybrid robots made of E. coli bacterium and polyelectrolyte microparticles.269 These biohybrid robots exhibited a chemotactic response to the chemoattractant (α-methyl-DL-aspartate). Further, Fe3O4 NPs embedded in the polyelectrolyte microparticles allowed magnetic directional guidance, demonstrating targeted drug delivery capability. The magneto-aerotactic bacterium Magnetococcus marinus strain MC-1 migrated to low oxygen concentrations under local magnetic field guidance, which is used for drug delivery to hypoxic tumor regions (i.e., toward O2 deficiency).314 In addition, Salmonella typhimurium (to L-aspartic acid) and neutrophil (to chemoattractant secreted by E.coli) have been also explored to create chemotaxis biohybrid robots.315,316
Phototaxis refers to the controlling motion or reorientation of bioorganisms responding to the direction or intensity of light (Fig. 19F and G).276,307 For example, C. reinhardtii, a biflagellated single-cell green alga, swims toward visible light due to its optical receptor. The C. reinhardtii hybrid robots exhibited fast and linear phototaxis responses with high swimming speeds, enabling a photocleavable drug delivery system.259 In another work, Volvox carteri, which possess positive phototaxis properties, are exploited as light-responsive microrobots and demonstrate unidirectional cargo transport in a microchannel system.317
Flagellated microorganisms have been used for biohybrid robots in combination with magnetic navigation. For example, the flagellated bacterium E. coli MG1655 was hybridized with RBCs containing DOX and magnetic NPs, which demonstrates flagellar propulsion and magnetic guidance for cargo delivery.259 In another work, biohybrid algal microrobots composed of C. reinhardtii were attached to polyelectrolyte magnetic particles and demonstrated autonomous 2D and 3D mobility that can be guided by an x-directional magnetic field.300
7.3. Applications
7.3.1.1. Heavy metals removal. Heavy metals, such as arsenic (As), zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), and lead (Pb), are discharged into water through industrial activities, causing toxic water pollution. Therefore, developing a technology that can promptly and efficiently remove heavy metals from contaminated areas is essential. Micro/nanorobots have been broadly developed with the realization of various functionalizations and their potential for environmental remediation by applying technologies of specific target detection and removal. In the same vein, nature-inspired biohybrid microrobots, such as algae, bacteria, etc., are attractive candidates for the efficient removal of heavy metals through biosorption and bioaccumulation mechanisms (Fig. 20A and B).63
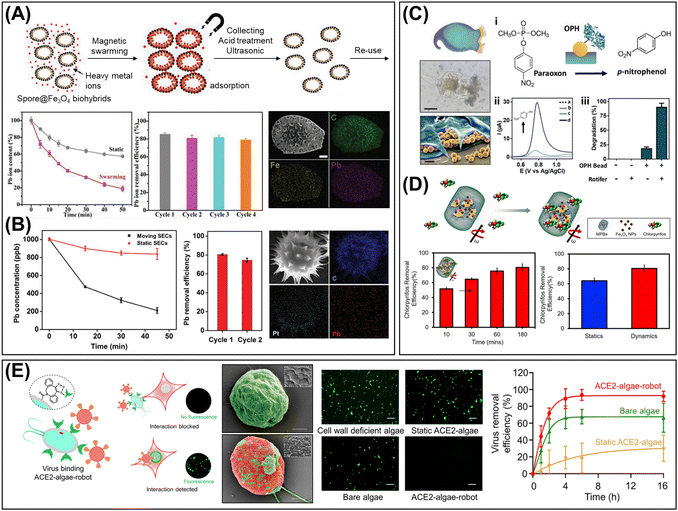 | ||
| Fig. 20 Environmental applications of biological cell hybrid micro/nanorobots. (A) and (B) Heavy metal removal. (A) Spore@Fe3O4 biohybrid adsorbents for efficient removal of heavy metal ions. The efficiency test for lead (Pb) removal, reusability, and SEM-EDX mapping images after decontamination. Scale bar: 1 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 322. Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH. (B) Decontamination of Pb (II) ions using bubble-propelled sporopollenin exine capsule biohybrid robots. Removal efficiency, reusability, and SEM-EDX mapping images after adsorption of Pb (II) ions. Reproduced with permission from ref. 295. Copyright 2017, Wiley-VCH. (C) and (D) Organic compound removal. (C) Microscopy and SEM images of rotifer accumulating particles within the inner lips. Example of nerve agent (methyl paraoxon) decontamination with organophosphorus hydrolase–microbeads modified rotifer biohybrid robots. Scale bars in microscopy and SEM images are 50 μm and 5 μm, respectively. Reproduced with permission from ref. 323. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH. (D) Removal of nerve agent (chlorpyrifos) by magnetic plant biobots. Time-dependent removal performances and efficiency comparison of static and dynamic biobots. Reproduced with permission from ref. 275. Copyright 2022, Springer Nature. (E) Pathogen removal. ACE2-algae-robot for the viral removal (SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus) in wastewater. SEM images of the ACE2-algae-robot before and after conjugated with SARS-CoV-2. Scale bar: 2 μm. Removal efficiency and corresponding fluorescent images. Scale bar: 100 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 324. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society. | ||
Many studies have reported MTB for heavy metal removal using their biosorption capability.325,326 The removal of hexavalent chromium (Cr6+) by MTB cultivated from a novel culture method was reported. They demonstrated that Cr6+ was successfully removed using MTB by controlling the different variables, such as temperature, pH, and microorganism concentration under electric and magnetic fields.327 Moreover, MTB successfully absorbed Cd2+ by improving the adsorption capability of bacterial surfaces.328
Plant-based biohybrid robots are also reported in environmental purification applications. For example, Pumera's group proposed plant-based biohybrid robots for environmental remediation such as heavy metal removal. They implemented a fruit tissue cell-derived microrobot deposited with Pt film and affordable for mass production.329 Moreover, SECs with spiky surface morphology extracted from sunflower pollen grains were introduced. SECs can be bubble-propelled by a surface coated with Pt and demonstrate heavy metals removal by this motion.295 Zhang's group presented the removal of pollutants using spore-based hybrid robots. The spore-based biohybrid adsorbent was prepared by fungi spores grown with Fe3O4 NPs. They confirmed the rapid removal of heavy metals (Pb ions) through a porous structure and a highly adsorbing component.322
7.3.1.2. Organic compound removal. Various biohybrid microrobots have been used for the decontamination of organic compounds (Fig. 20C and D). MTB has biosorption properties and can remove organic compounds in an aquatic environment.330,331 Based on the characteristics of pollutant adsorption and separation, removal of organophosphate (OP) pesticide was demonstrated using the magnetosomes extracted from MTB.325 Furthermore, the advent of microcleaners (“Rotibots”) with functionalized microbeads attached to marine rotifers demonstrated not only the adsorption of heavy metals but also the removal of bacteria and OP nerve agents in aqueous environments.323 Pumera's group proposed magnetic plant biobots (MPBs) for the removal of chlorpyrifos, one of the most widely used OP pesticides in agriculture and known to have serious effects on the human nervous system. The final form of MPBs was obtained from tomato leaves-derived plant tissue cells cultivated with ferromagnetic NPs. The 80% removal efficiency of chlorpyrifos by MPBs under a rotating magnetic field suggests that fuel-free plant-based biobots can be efficiently used to remove hazardous materials.275
7.3.1.3. Pathogen removal. Waterborne disease and infection caused by pathogens (e.g., bacteria, viruses, and helminths) are directly related to biosphere; thus, research on the rapid detection and removal of pathogens using biological cell hybrid robots has attracted great interest (Fig. 20E).332,333 The importance of this connection re-emerged during the recent coronavirus disease outbreak. For example, algae-based hybrid robots reported by Wang and coworkers demonstrated the effective removal of SARS-CoV-2 in contaminated aquatic media by angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor immobilized algae-based robots (ACE2-algae-robot). The ACE2-algae-robots were fabricated by attaching the ACE2 receptor to the surface of algae via a click chemistry reaction. Self-propelled ACE2-algae-robots can swim for long periods without external fuels and quickly and effectively remove target materials in diverse aquatic media.324
7.3.2.1. Drug delivery. Biological cell hybrid micro/nanorobots provide a strategy for targeting and efficient delivery of therapeutic agents. These biological microswimmers are integrated with various synthesis materials to enhance their functionality, enabling transportation and targeted drug delivery to hard-to-reach areas through self-propulsion and external power sources.
For example, engineered MTB-LPs were proposed for effective targeted drug delivery and fabricated through bioconjugation based on the covalent binding between amine groups on the surface of MC-1 MTB and carboxylated liposomes. Their results showed that a significant number of nanoliposomes were efficiently attached to MTB without impairing functionality or mobility while also improving biocompatibility.266 Therefore, it was emphasized that this MTB-LP system can effectively deliver therapeutic agents to hypoxic regions of hard-to-reach tumors by penetrating them.266 The multifunctional bacteria-driven microswimmers introduced by Sitti's group were fabricated for targeted drug delivery by attaching E. coli with polyelectrolyte multilayer (PEM) microparticles composed of doxorubicin and magnetite NPs (Fig. 21A). The microswimmers were shown to be more efficient and effective in targeted drug delivery compared to passive PEM microparticles in vitro, suggesting that the microswimmers can soon be utilized as an active drug delivery system in vivo.269 Further interesting research into two techniques suggests the ability to improve the transportation of NPs through the utilization of convective flow created by magnetically controlled micropropellers, inspired by bacterial flagella. Driven under the rotating magnetic field, the artificial bacterial flagellum and MTB confirmed the improved transport of NPs in a microfluidic model of blood outflow and tissue infiltration through microchannels. Consequently, the living MTB-based ferrofluid suggests that enhanced transport of NPs may be possible within the tumor microenvironment by increasing nanoparticle accumulation and extending penetration depth, and the convective effect of the artificial bacterial flagellum can be integrated with stents to induce drug release.311 Sperm, which are naturally adapted for optimal navigation within the female reproductive system, emerge as promising candidates for the treatment of cervical cancer and gynecological diseases as compared to other cellular-based drug delivery systems. The sperm-driven micromotor developed by Schmidt's group is employed as a drug carrier for potential cancer treatment in the female reproductive system. They fabricated a tetrapod microstructure to facilitate local guidance and release, establishing an effective drug delivery system (Fig. 21B and C).286,334
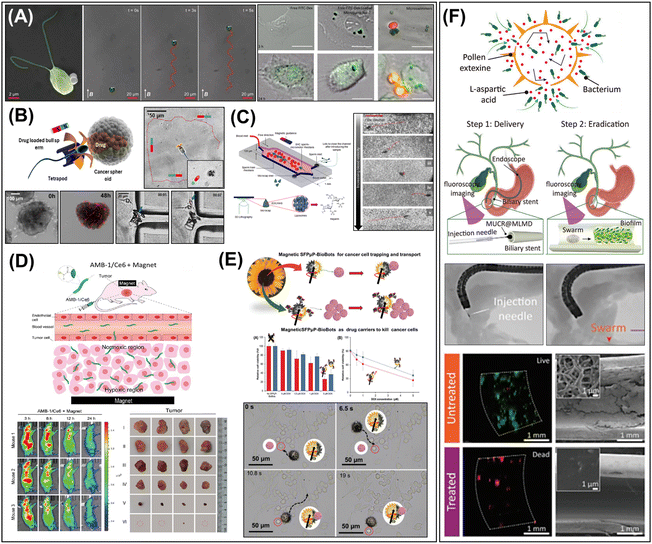 | ||
| Fig. 21 Bioinspired micro/nanorobots for advanced therapeutic applications. (A)–(C) Drug delivery. (A) SEM images of algal microswimmer and their propulsion trajectories under the 26 mT magnetic field. The drug-loaded PE-functionalized magnetic PS microparticles cultured with algal microswimmers were effectively delivered to HeLa cells. Scale bars: 20 μm. Reproduced with permission from ref. 300. Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH. (B) Sperm-driven micromotor-based system for targeted drug delivery to treat diseases in the female reproductive tract. Magnetic tetrapods guided the drug-loaded motile sperm cells to tumor spheroids and released them upon hitting tumor walls for localized drug delivery. Reproduced with permission from ref. 285. Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society. (C) Hybrid sperm micromotors equipped with a synthetic magnetic cap that efficiently and controllably swims against flowing blood in response to an external magnetic field. Reproduced with permission from ref. 286. Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society. (D) and (E) Cancer therapy. (D) Accumulation of AMB-1/Ce6 in mouse tumors by biological and magnetic dual mode. Fluorescence images and photographs showing the abilities of AMB-1/Ce6 to target and inhibit the tumor in vivo. Reproduced with permission from ref. 335. Copyright 2023, American Chemical Society. (E) Schematic illustration of magnetic sunflower pollen-based BioBot (SFPμP-BioBots) used as a drug carrier for killing the cancer cell. Time-lapse images of SFPμP-BioBots interacting with cancer cells manipulated under a magnetic field and cytotoxicity evaluation by loaded doxorubicin in SFPμP-BioBots. Reproduced with permission from ref. 274. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. (F) Biofilm eradication. Magnetic pollen biohybrid swarms for biofilm eradication in the biliary stents. Fluoroscopy-imaging-guided microswarm injection and navigation. Comparison of biliary stents with and without treatment of magnetic pollen biohybrid swarms. Reproduced with permission from ref. 297. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. | ||
Microalgae with an easy cultivation process are attractive candidates for other biohybrid robots. Microswimmers, powered by microalgae (C. reinhandtii), introduced by Sitti's group, are based on the natural biological swimmer's innate propulsion mechanism and physical properties. Biohybrid algal microswimmers consist of polyelectrolyte-functionalized magnetic spherical cargos attached to microalgae via noncovalent interactions; hence, they demonstrate excellent motility under various biological conditions. Furthermore, the microswimmer loaded with FITC-dextran (a model drug that mimics high molecular weight therapeutics) showed a higher cellular uptake compared to passive delivery. This suggests that the biohybrid microswimmer can be effectively used for targeted delivery applications.300 Recently, a microalgae-based motor platform was reported by Wang's group for oral drug delivery. To improve delivery to the small intestines, the functionalized algae motors were embedded inside a pH-sensitive capsule. The functionalized natural algae-based motor suggests practical biomedical applications used for drug delivery due to its efficient movement and long lifespan.302 In addition, they created algae-NP-robots loaded with antibiotics via click chemistry and these hybrid microrobots can actively deliver antibiotics to the lungs in vivo.301 Zhang's group reported the production of Spirulina microalgae coated with magnetite for in vivo fluorescence imaging and remote diagnosis.319 In addition, the MSP (magnetically engineered multicellular Spirulina) microswimmers were functionalized by utilizing the dehydration and rehydration capabilities of Spirulina cells, and their ability to transport and release molecular cargos was evaluated. These MSP microswimmers can be used to deliver molecular agents to the gastrointestinal tract.336
7.3.2.2. Cancer therapy. Biohybrid micro/nanorobots proved a strategy for targeting and efficient delivery of therapeutic agents. For example, MTB grown under microaerobic conditions can reach the hypoxic areas of tumors314 and their Fe content can be used as a positive contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging in vivo.268 Furthermore, enhanced microalgae-based biohybrid micro/nanorobots can also be used as targeted therapeutic agents through imaging.319 The excellent target/delivery capability of functionalized biohybrid micro/nanorobots based on diverse natural organisms, proven by various studies, has enabled cancer therapy to reach inaccessible tumor sites.
For example, Martel's group developed biohybrid microrobots to target hypoxic regions in solid tumors. They created biohybrid microrobots by attaching drug-loaded nanoliposomes onto the cell membranes of magnetotactic bacteria. Then, the innate magnetotaxis and aerotaxis mechanisms of MTB guided the microrobots to the hypoxic regions of the tumors. The results demonstrated that up to 55% of the biohybrid microrobots were able to penetrate and accumulate in the hypoxic regions of the tumors due to the unique biological properties of the microrobots’ actuators.314 A micromotor integrated with M. magneticum strain AMB-1 and photosensitizer Ce6 was developed by Chu's group (Fig. 21D). The chemically conjugated AMB-1/Ce6 micromotor exhibited active movement in high drug-loading capacity and hypoxic regions. Under laser irradiation, AMB-1/Ce6 demonstrated a higher level of ROS generation and efficiency in eliminating cancer cells compared to AMB-1. After treatment with AMB-1/Ce6, the mouse tumors disappeared, suggesting that AMB-1/Ce6 could be used for clinical therapy.335 Schuerle's group presented a hybrid control strategy that utilizes magnetic torque to initiate motion and autonomous taxis for navigation.312 They developed the M. magneticum strain AMB-1 via covalently coupled liposomes for a magnetically responsive model organism and carrier. In vivo, this microrobot demonstrated a 2.16-fold improvement in penetration, leading to an enhanced therapeutic effect on the tumors.
Pumera's group utilized sunflower pollen to attract and transport cancer cells. These biohybrid robots enabled magnetic-powered motion under rotating magnetic fields and exhibited capabilities for strong attraction for cancer cells due to the opposite surface charges, demonstrating enclosed drug delivery efficiency to the ovarian cancer cells (Fig. 21E).274
7.3.2.3. Biofilm eradication. Biohybrid micro/nanorobots, inspired by biological swarm behavior, have attracted significant attention due to their ability to achieve precise target delivery through cargo transportation, perform therapies, and execute predefined tasks using external sources as described earlier. Furthermore, their swarm-like movement has demonstrated the ability to efficiently load large amounts of cargo and exhibit strong convective forces.337,338 This motion provides significant advantages in the eradication of biofilm, which is a microorganism community embedded within an extracellular polymeric substances matrix.156,339
Sanchez and coworkers proposed that the magnetotactic bacteria MSR-1 can be used to deliver antibiotics to a specific infectious biofilm. They fabricated the MRS-1-DFX-MSM biohybrid system by combining living bacteria with mesoporous silica microtubes loaded with drugs and used the magnetotaxis mechanisms of the bacteria to penetrate into the biofilm and release the drugs. The results showed the promising advantages of addressing biofilm formation through targeting and drug delivery to local areas due to the capability of the biohybrid microswimmer to move to defined locations.340 The sunflower pollen-based urchin-like robots and their magnetic swarming were used for biofilm eradication (Fig. 21F).297 The spiky morphology and collective behavior enhanced the physical disrupting effect of the extracellular polymeric substances barrier. Subsequent antibacterial agent release and penetration achieved a synergistic effect for biofilm destruction. Their effective removal of biofilm and usability at the hard-to-reach area is demonstrated within the biliary stent, suggesting the great potential for the treatment of bacterial biofilm on medical implants. In another study, fast-moving aqua sperm micromotors obtained from African catfish were used to destroy bacterial biofilms.341 The ultrafast mobility of aqua sperm micromotors, driven by the water-induced adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consumption of ATPase, can generate strong mechanical forces that enable the destruction of the biofilm matrix within a short treatment time (less than one minute). Their practical applicability has been demonstrated by the efficient destruction of biofilms that had colonized medical catheters.
7.3.2.4. Assisted fertilization. Different sperm carriers have been suggested to treat some of the most common male infertility problems, such as low sperm count (oligospermia) and low sperm motility (asthenospermia) (Fig. 22).283 These carriers are designed either to guide or to propel sperm cells, respectively, with the purpose of moving them efficiently toward the fertilization site to meet the released oocyte and perform their intended function of fertilization.
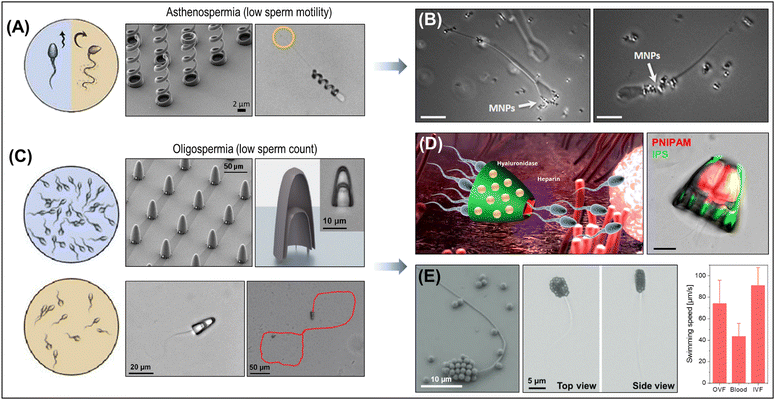 | ||
| Fig. 22 Sperm hybrid microrobots for assisted fertilization. (A) and (B) Strategies to improve sperm motility in the treatment of asthenospermia. (A) SEM image of polymeric helices fabricates by 3D laser lithography and optical image of morphological change after helix coupling. Reproduced with permission from ref. 277. Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. (B) A hybrid sperm micromotor combined with a magnetic microhelix enhances low sperm motility (asthenospermia). The functionalized sperm cell is captured, transported, and released by a rotating magnetic field. Moreover, the engineered hybrid sperm micromotor flocks can be magnetically guided, enhancing the success rate of fertilization. Reproduced with permission from ref. 284. Copyright 2020, Bioscientifica Ltd. (C)–(E) Strategies to assist the sperm transport in the treatment of oligospermia. (C) SEM image of a streamlined cap and bright field image of a sperm cell captured in a streamlined cap. The velocity of sperm-driven microrobots is enhanced in the intended operating environment by optimizing specially designed artificial microstructures. Reproduced with permission from ref. 290. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH. (D) Development of a 4D-printed multifunctional microcarrier capable of transporting and delivering multiple sperm cells. These sperm-microcarriers promote the interaction between sperm and oocytes for assisted fertilization through the heparin and hyaluronidase-loaded polymersomes. Reproduced with permission from ref. 292. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. (E) SEM and optical images of a magnetotactic sperm cell with integrated magnetic NPs on the sperm head. Swimming speed graph of micromotors in various environments bovine oviduct fluid (OVF), blood, and in vitro fertilization (IVF) medium. Reproduced with permission from ref. 291. Copyright 2023, Wiley-VCH. | ||
Typically, these male infertility problems are treated by conventional in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmatic sperm injection procedures, where the gametes are retrieved from the body and prepared in vitro to produce an embryo. Once the embryo is at the blastocyst stage or at an early stage, it is transferred back to the female uterus for further implantation and embryo development.284 The main drawback is that applying hormone stimulation and retrieving the gametes from their natural environment, etc., lead to very low embryo implantation rates due to excessive manipulation steps and oxidative stress. Scientists working in this field believe that by performing part of the infertility treatment process in vivo would improve significantly the outcome of the resulting pregnancies.
Various designs have been proposed to transport single and multiple sperm cells, ranging from rolled-up microtubes,342 2.5D- (Fig. 22C)290 and 3D-printed structures (Fig. 22A and B),277 and more recently, 4D carriers that respond to temperature and pH stimuli and, hence, realize the triggered released of sperm cells. Other functional components prepare sperm cells for oocyte fertilization and help overcome some of the biological barriers present in the female reproductive tract, e.g., the viscoelastic fluid in the oviduct and the cumulus cell complex surrounding the oocyte (Fig. 22D).292
Recent developments in this field have yielded improved protocols for the production of a high number of sperm-coupled microcarriers, efficient transfer between different microenvironments, and incorporation of functional components to enhance their function in complex environments and enable their visualization using imaging modalities like ultrasound and photoacoustics. Such developments bring these concepts closer to their intended application (Fig. 22E). Initial results in vivo reveal promising results and open the path toward their function demonstration in relevant scenarios.292,343,344
8. Future perspectives and outlook
Recent advances in materials and understanding of chemical principles have significantly advanced the field of micro/nanorobotics. In this trend, a comprehensive insight into the properties of emerging materials and their combination with active actuating systems is imperative to translate micro/nanorobotics into industrial and clinical practise and eventually solve the unmet challenges in the field. This review provided an overview of the recent progress in micro/nanorobotics driven by advanced materials, focusing on material types, designs, motion mechanisms, functionalities, and advanced applications to provide a broader perspective and stimulate progress in the field. The following section summarizes the three perspectives for next-generation micro/nanorobotics research based on advanced materials.First, it is crucial to consider an appropriate material system to ensure a longer operational lifetime, stable (photo)catalytic efficiency, and reusability. Micro/nanorobots made of (photo)catalytic materials, including 2D materials and semiconductors, are generally considered stable in the air. However, they tend to self-degrade during (photo)catalytic motion or when exposed to various environments (e.g., biological media), resulting in reduced structural stability and photochemical efficiency upon repeated use. Additionally, the (photo)catalytic reactions and their derived products may further compromise their structure or chemical composition. Therefore, the stability of (photo)catalytic micro/nanorobots can be varied depending on material systems, applied external energies, and reaction environments. Several studies have investigated their stability and reusability by analyzing the reaction efficiency and structural integrity of the materials after multiple reactions. For example, in the photocatalytic reaction, the speed of visible-light-driven Cu2O@CdSe microrobots decreased after 10 minutes, due to the transformation of the crystal structure of Cu2O into CuO, as well as the reduction of the photocatalytic reaction sites by the on-the-fly adsorption of pollutants.220 The authors admitted that the inevitable photocorrosion would result in a failure of the self-propulsion in the long term, but they proved a good recycling capability of the microrobots and an adsorption ratio of almost 90% after 5 times treatment. In another work, the photocorrosion resistance of Au–WO3@C Janus microrobots was discussed through 30 cycles of “stop/go” propulsion behavior by switching UV irradiation on and off, demonstrating high repeatability.162 On the other hand, the reusability of TiO2–Au Janus microrobots was explored and compared with alternative magnetic derivatives containing an additional Ni layer between the outer Au layer and the TiO2 core.345 As expected, the magnetic activity facilitated, among other things, the collection and reusability of the microrobots, faced through a centrifugation method otherwise. The reused magnetic microrobots presented comparable maximum velocities to the TiO2–Au microrobots in the same solution and stable photodegradation rates over 3 repeated tests, highlighting the great potential of these magnetic direction-controlled and recyclable microrobots. Similarly, the reusability of TiO2–Fe Janus microrobots was investigated, where the magnetic Fe layer was used not only to collect microrobots but also to enhance the degradation efficiency of pollutants through a photo-Fenton process.346 This system showed a degradation efficiency of up to 75%, even after being recycled for the fifth time, and associated the decrease in degradation with the Fe losses caused by the acidic pH required for the photo-Fenton reaction. Nonetheless, it was demonstrated that the microrobots maintained excellent photocatalytic propulsion over five cycles with negligible impact on their speed, explaining their efficient performance over time. In other examples, such as the foam-like C3N4/Fe3O4, MnPS3–Fe3O4, and triazine–thiophene (Tz–Th) microrobots, the degradation efficiency decreased only slightly (∼10%) over several consecutive cycles.74,98,244 The morphological and compositional stability of the microrobots before and after the reaction was confirmed by TEM-EDX or SEM analyses, demonstrating their durability during their photocatalytic activity.74,244 In contrast, the degradation efficiency of TiO2@Ti3C2/Pt micromotors decreased by ∼40% after three repeated reaction cycles.73 In the photothermal reaction, WS2 micromotors exhibited effective photophoretic motion by light-induced local heating and convection flow. However, the local temperature increase is diminished during four consecutive light irradiation cycles, plausibly due to the low thermal stability of WS2, resulting in structural deformation and reduced photoconversion capability.75
Second, the main challenge in manufacturing advanced micro/nanorobots is to assemble micro- and nanoscale elements in specific geometries to enable effective movement and functionality. To address this challenge, various “top-down” and “bottom-up” techniques have been developed to fabricate asymmetric structures, such as Janus particles, multimetallic nanorods, rolled tubes, and microhelices. These techniques are advancing in recent research, resulting in increasingly intricate and intelligent structures. Therefore, future manufacturing techniques are required to create complex 3D structures by processing advanced materials in a precise, reproducible, and scalable fashion. This will enable higher capabilities and intelligence, including adaptability, encodability, programmability, and reconfigurability. In this regard, light-based 3D microfabrication techniques such as two-photon photopolymerization show promise for scaling down 3D and 4D micro/nanorobotic systems through fast, reliable, and high-throughput manufacturing. In addition, 3D bioprinting holds significant potential for designing future micro/nanorobots combined with various bioconjugation and biomedical technologies.43
Finally, this review discusses numerous materials as components of advanced micro/nanorobots, each offering distinct advantages and perspectives. Together with this, it is important to emphasize that both stimuli-responsive materials and actuation mechanisms significantly influence the intelligence of micro/nanorobotic systems. Magnetic steering is currently leading the field in biomedical applications due to its exceptional maneuverability, while acoustic- or light-driven motion enable wireless control over a broader area. Efforts to integrate these characteristics of driving forces into responsive materials are paving the way for programmable and reconfigurable actuation systems, such as micro-scale origami,347 shape-morphing soft microrobots,348 which exhibit high complexity and intelligent actuation capabilities. The micro/nanorobotics community recognizes this strategy as the most promising path forward, fostering anticipation of future advances and overcoming current limitations for practical implementation.
The following part summarizes the individual sections and highlights unexplored future research directions, as well as opportunities and prospects for the development of next-generation intelligent micro/nanorobots based on advanced materials (Fig. 23).
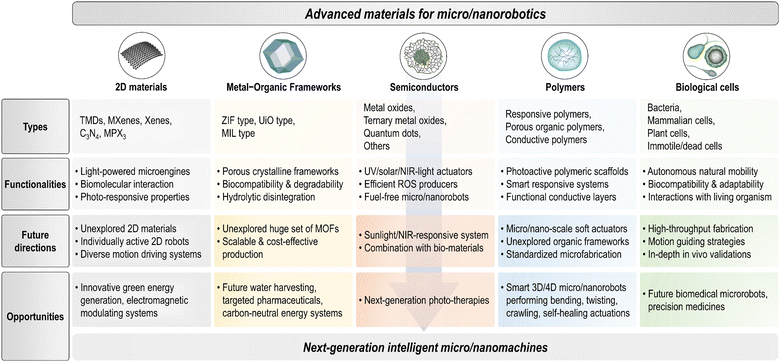 | ||
| Fig. 23 Summary of advanced materials for next-generation intelligent micro/nanomachines, including material types, functionalities, future research directions, and potential opportunities. | ||
Novel functionalities arising from layered 2D materials have shown more powerful performances in combination with macro/nanorobotic platforms, offering a plethora of opportunities and 2D-based active matters will continue to be a fascinating topic. Despite the great progress and promise witnessed in the recent few years, there are still some challenges that should be addressed in future research. First, the superb properties of 2D materials are numerous, but the examples used in micro/nanorobotic platforms are very limited. Thus, searching for unexplored properties of 2D materials in micro/nanorobotic systems and conceiving their integration would be the foremost issue. Another important point is the need for expanded study for the individually active 2D-sheet micro/nanorobots not equipped with template materials, such as microtubes or spheres. Exploiting the inherent 2D layered structure allows for preserving their intrinsic unique properties, thus paving the way for the full potential of 2D micro/nanorobotics. Apart from that, most 2D materials used for microengines are based on a light-driven photocatalytic propulsion mechanism. Therefore, possible propulsion mechanisms powered by 2D materials, such as catalytic, magnetic, acoustic, and electrically driven motion, need to be explored. These efforts will expand the applicability of 2D materials as active platforms for innovative green energy generation, electromagnetic modulation, and other applications.
The MOF families exhibit continuous growth due to their unique features and the extraordinary degree of variability, providing plenty of opportunities for creating a variety of active micro/nanorobotic systems. The future development of MOF-based micro/nanorobotics will have a greater impact by addressing the following challenges. First, despite an exceptionally huge set of MOF materials reported so far, a limited number of MOF types (e.g., ZIF-, UiO-, and MIL-types) have been exploited as active matter and micro/nanorobotic systems. Thus, it will be very promising to investigate the incorporation of newly developed porous framework materials in active platforms. Second, the availability of cost-effective and scalable synthesis for MOFs can enable the industrial-scale development of active MOF-derived functional materials. The intriguing concept of MOF-based active platforms holds significant advantages for emerging research areas such as water harvesting, targeted pharmaceuticals, carbon-neutral energy systems, etc. Therefore, further research is needed to drive the translation of these techniques into industrially relevant applications.
New venues for the exploitation of semiconductors were opened in the last decade within the emerging field of microrobots. Aware of the great potential of these hand-made entities, achieving efficient fuel-free self-propulsion in complex media when exposed to uniform illumination was the main goal. As a result, a plethora of photocatalytic materials was tested during those years for the preparation of light-responsive microrobots, exploring different shapes, morphologies, and compositions. Significant advances in light-induced motion mechanisms and alternative phenomena such as swarming and phototaxis faced limitations due to inaccurate control, but new strategies with hybrid microrobots using multiple driving forces are overcoming these challenges, extending the use of semiconductors beyond just powering motion. On the contrary, light-responsive materials have found a new gold mine as add-on components are exploited for additional applications due to their luminescent or adsorptive capabilities, among others. However, the most useful ability for the applicability of photocatalytic microrobots is undoubtedly the photogeneration of ROS. The growing impact of their performance as ROS producers is supported by the amount of new works regularly appearing either in water remediation or nanomedicine. Thus, aiming at a sunlight-based technology, the implementation of semiconductors must evolve toward light-responsive materials with efficient photocatalytic activities at lower frequencies and thus reducing dependency on UV wavelengths. Because deeper penetrations could be achieved with lower frequencies, this concept would also be valid in the case of photodynamic therapies, allowing the use of these microrobots beyond superficial diseases. On the other hand, there is still a lot to discuss about biohybrid microrobots. The combination of photocatalytic and non-photocatalytic components with biological materials would offer highly biocompatible self-propelled microdevices with optimal ROS production.
Polymers exhibit great potential for intelligent actuation systems in the micro- and nanoscale. The most remarkable feature is the possibility of a higher level of operations in response to multiple energy sources and triggering factors combining light, magnetic field, ultrasound, temperature, pH, etc., allowing them to actively move in aqueous environments and perform complicated tasks. In addition, their versatile synthesis, tailorable properties, and relatively high compatibility with the environment and biological systems open up many possibilities for practical applications. Despite the promising progress, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed in future research. First, most soft robotic systems have been extensively explored at the millimeter scale but have not yet been effectively miniaturized into micro/nanoscale actuators. Small-scale robotic systems that can perform various “soft” actuations, such as bending, twisting, crawling, self-healing, or 4D actuations, are not yet well defined and can therefore accelerate innovation in the relevant fields. Second, of great promise is the incorporation of other porous organic polymers (POPs) such as porous aromatic frameworks (PAFs), etc. Each class of porous organic materials possesses different characteristics and advantages, thereby offering new perspectives for the development of micro/nanorobotic systems in various engineering applications. Lastly, microfabrication and polymerization processes need to be well standardized to ensure the homogeneity and reproducibility of polymeric hybrids with other inorganic and biological materials.
In the past decade, there have been great advances and breakthroughs in biohybrid micro/nanorobots leveraging various highly promising biological cells and microorganisms. A number of impressive biohybrid robots have been developed based on motile cells or non-motile biological species. Moreover, the study of energy taxes-based and extrinsic powering source-based collective guidance has utilized efficient collaborative work for enhanced performances. However, there remain challenges to fully exploiting biohybrid robots for practical applications. One of the main problems is the difficulty in establishing reliable and high-throughput fabrication techniques. Most bioorganisms or natural products can be obtained by biological processes such as bacterial/cell cultures etc.; these have a limited production yield and are not suitable for mass production. This could be a significant drawback compared to inorganic or organic materials-based micro/nanorobots for actual applications. In addition, further study of different adaptable motion-driving methods is also required. Most extrinsic guidance strategies rely on magnetic and light sources. Magnetic manipulation has several advantages, but there remain limitations from the needs of electromagnetic devices. These are highly sophisticated and often less affordable or unsuitable for various applications. Guidance with light source is also attractive but it has depth limitations in water-containing environments. In this regard, an electric source based on electrophoresis or an ultrasound energy source could be possible options, but those have not been extensively studied for the guidance of biohybrid robots. Lastly, since the concept of biohybrid microrobot-based therapeutics has been proven, it is necessary to explore further in-depth in vivo studies to validate their practical usefulness in animal models and ultimately in humans. Overall, the approach with a variety of fascinating biological cells and organisms would accelerate the development of biohybrid micro/nanorobots for practical use in future biomedical devices, precision medicine, and other fields.
Data availability
No primary research results, software or code have been included and no new data were generated or analysed as part of this review.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The work was supported by ERDF/ESF project TECHSCALE (No. CZ.02.01.01/00/22_008/0004587). This research was co-funded by the European Union under the REFRESH-Research Excellence For REgion Sustainability and High-tech Industries project number CZ.10.03.01/00/22_003/0000048 via the Operational Programme Just Transition. M. M. S. gratefully acknowledges the financial support received from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (ERC Starting Grant Nr. 853609) and HORIZON-MSCA-2022-COFUND-101126600-SmartBRAIN3. S. P. acknowledges ETH under grant number 22-2 ETH-040.References
- K. Novoselov, A. Mishchenko, A. Carvalho and A. Castro Neto, Science, 2016, 353, aac9439 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Tan, X. Cao, X.-J. Wu, Q. He, J. Yang, X. Zhang, J. Chen, W. Zhao, S. Han, G.-H. Nam, M. Sindoro and H. Zhang, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 6225–6331 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Tao, N. Kong, X. Ji, Y. Zhang, A. Sharma, J. Ouyang, B. Qi, J. Wang, N. Xie, C. Kang, H. Zhang, O. C. Farokhzad and J. S. Kim, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 2891–2912 RSC.
- A. VahidMohammadi, J. Rosen and Y. Gogotsi, Science, 2021, 372, eabf1581 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W.-J. Ong, L.-L. Tan, Y. H. Ng, S.-T. Yong and S.-P. Chai, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 7159–7329 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Wang, T. A. Shifa, P. Yu, P. He, Y. Liu, F. Wang, Z. Wang, X. Zhan, X. Lou, F. Xia and J. He, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1802151 CrossRef.
- X. Chia and M. Pumera, Nat. Catal., 2018, 1, 909–921 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Villa, C. L. Manzanares Palenzuela, Z. Sofer, S. Matějková and M. Pumera, ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 12482–12491 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. V. Singh, K. Kaufmann, B. E. F. de Ávila, E. Karshalev and J. Wang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26, 6270–6278 CrossRef CAS.
- V. de la Asunción-Nadal, B. Jurado-Sánchez, L. Vázquez and A. Escarpa, Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 132–140 RSC.
- M. Urso, M. Ussia, F. Novotný and M. Pumera, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 3573 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Sridhar, F. Podjaski, Y. Alapan, J. Kröger, L. Grunenberg, V. Kishore, B. V. Lotsch and M. Sitti, Sci. Rob., 2022, 7, eabm1421 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Furukawa, K. E. Cordova, M. O’Keeffe and O. M. Yaghi, Science, 2013, 341, 1230444 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. J. Howarth, Y. Liu, P. Li, Z. Li, T. C. Wang, J. T. Hupp and O. K. Farha, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2016, 1, 1–15 Search PubMed.
- S. Dang, Q.-L. Zhu and Q. Xu, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2017, 3, 1–14 Search PubMed.
- B. Khezri and M. Pumera, Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, 1806530 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Terzopoulou, J. D. Nicholas, X.-Z. Chen, B. J. Nelson, S. Pané and J. Puigmarti-Luis, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 11175–11193 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Lian, Y. Fang, E. Joseph, Q. Wang, J. Li, S. Banerjee, C. Lollar, X. Wang and H.-C. Zhou, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46, 3386–3401 RSC.
- S. Yang, X. Li, G. Zeng, M. Cheng, D. Huang, Y. Liu, C. Zhou, W. Xiong, Y. Yang, W. Wang and G. Zhang, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2021, 438, 213874 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Eskandarloo, A. Kierulf and A. Abbaspourrad, Nanoscale, 2017, 9, 12218–12230 RSC.
- S. Palagi, D. P. Singh and P. Fischer, Adv. Opt. Mater., 2019, 7, 1900370 CrossRef.
- K. Villa and M. Pumera, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 4966–4978 RSC.
- L. Xu, F. Mou, H. Gong, M. Luo and J. Guan, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46, 6905–6926 RSC.
- J. Wang, Z. Xiong, J. Zheng, X. Zhan and J. Tang, Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51, 1957–1965 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Liu, J. Huang, T. Xu and X. Zhang, Microchim. Acta, 2022, 189, 116 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Safdar, J. Simmchen and J. Jänis, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2017, 4, 1602–1616 RSC.
- M. Ussia and M. Pumera, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2022, 51, 1558–1572 RSC.
- S. Hermanová and M. Pumera, Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 7332–7342 RSC.
- Y. Tu, F. Peng, X. Sui, Y. Men, P. B. White, J. C. van Hest and D. A. Wilson, Nat. Chem., 2017, 9, 480–486 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Guo, T. Wang, A. Rawal, J. Hou, Z. Cao, H. Zhang, J. Xu, Z. Gu, V. Chen and K. Liang, Mater. Today, 2019, 28, 10–16 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Magdanz, M. Guix, F. Hebenstreit and O. G. Schmidt, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 4084–4089 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. V. Vaghasiya, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, S. Matějková and M. Pumera, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 1026 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. W. Lee, J. K. Kim, U. Bozuyuk, N. O. Dogan, M. T. A. Khan, A. Shiva, A. M. Wild and M. Sitti, Adv. Mater., 2023, 35, 2209812 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Mazzolai and C. Laschi, Sci. Rob., 2020, 5, eaba6893 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Soto, J. Wang, R. Ahmed and U. Demirci, Adv. Sci., 2020, 7, 2002203 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Palagi and P. Fischer, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2018, 3, 113–124 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Ricotti, B. Trimmer, A. W. Feinberg, R. Raman, K. K. Parker, R. Bashir, M. Sitti, S. Martel, P. Dario and A. Menciassi, Sci. Rob., 2017, 2, eaaq0495 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Xu, H. Qin, H. Tian, L. Liu, J. Gao, F. Peng and Y. Tu, Appl. Mater. Today, 2022, 27, 101482 CrossRef.
- J. Llacer-Wintle, A. Rivas-Dapena, X. Z. Chen, E. Pellicer, B. J. Nelson, J. Puigmartí-Luis and S. Pané, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2102049 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Soto, E. Karshalev, F. Zhang, B. Esteban Fernandez de Avila, A. Nourhani and J. Wang, Chem. Rev., 2021, 122, 5365–5403 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Parmar, D. Vilela, K. Villa, J. Wang and S. Sánchez, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 9317–9331 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Urso, M. Ussia and M. Pumera, Nat. Rev. Bioeng., 2023, 1, 236–251 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Wang, Y. Wu, E. Yildiz, S. Kanyas and M. Sitti, Nat. Rev. Bioeng., 2024, 2, 470–485 CrossRef.
- C. Chen, S. Ding and J. Wang, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2024, 9, 159–172 CrossRef.
- F. Rajabasadi, L. Schwarz, M. Medina-Sánchez and O. G. Schmidt, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2021, 120, 100808 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Kim, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, J. Vyskočil, D. Ruzek and M. Pumera, Appl. Mater. Today, 2022, 27, 101402 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Jin and L. Zhang, Acc. Chem. Res., 2021, 55, 98–109 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Berlinger, M. Gauci and R. Nagpal, Sci. Rob., 2021, 6, eabd8668 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Zhou, X. Wen, Z. Wang, Y. Gao, H. Li, Q. Wang, T. Yang, H. Lu, Y. Cao, C. Xu and F. Gao, Sci. Rob., 2022, 7, eabm5954 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Zhou, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, S. Pané, L. Zhang and M. Pumera, Chem. Rev., 2021, 121, 4999–5041 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T.-Y. Huang, H. Gu and B. J. Nelson, Annu. Rev. Control Rob. Auton. Syst., 2022, 5, 279–310 CrossRef.
- V. Magdanz, M. Guix and O. G. Schmidt, Rob. Biomimetics, 2014, 1, 1–10 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Xu, B. Zhang, L. Wang, G. Huang and Y. Mei, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1705872 CrossRef.
- Y. Dong, L. Wang, V. Iacovacci, X. Wang, L. Zhang and B. J. Nelson, Matter, 2022, 5, 77–109 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Zha, T. Wang, M. Luo and J. Guan, Micromachines, 2018, 9, 78 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. Simó, M. Serra-Casablancas, A. C. Hortelao, V. Di Carlo, S. Guallar-Garrido, S. Plaza-García, R. M. Rabanal, P. Ramos-Cabrer, B. Yagüe, L. Aguado, L. Bardia, S. Tosi, V. Gómez-Vallejo, A. Martín, T. Patiño, E. Julián, J. Colombelli, J. Llop and S. Sánchez, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2024, 19, 554–564 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Terzopoulou, M. Palacios-Corella, C. Franco, S. Sevim, T. Dysli, F. Mushtaq, M. Romero-Angel, C. Martí-Gastaldo, D. Gong, J. Cai, X.-Z. Chen, M. Pumera, A. J. de Mello, B. J. Nelson, S. Pané and J. Puigmartí-Luis, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2107421 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, X. Z. Chen, C. C. Alcântara, S. Sevim, M. Hoop, A. Terzopoulou, C. De Marco, C. Hu, A. J. de Mello, P. Falcaro, S. Furukawa, B. J. Nelson, J. Puigmartí-Luis and S. Pané, Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, 1901592 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Zhang, T. Petit, Y. Lu, B. E. Kratochvil, K. E. Peyer, R. Pei, J. Lou and B. J. Nelson, ACS Nano, 2010, 4, 6228–6234 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Kim, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez and M. Pumera, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 935 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Li, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, C. D. Ohl and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2102265 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Xu, F. Soto, W. Gao, V. Garcia-Gradilla, J. Li, X. Zhang and J. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 8552–8555 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Alapan, O. Yasa, B. Yigit, I. C. Yasa, P. Erkoc and M. Sitti, Annu. Rev. Control Rob. Auton. Syst., 2019, 2, 205–230 CrossRef.
- M. Pacheco, V. de la Asunción-Nadal, B. Jurado-Sánchez and A. Escarpa, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2020, 165, 112286 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. A. Abbasi, A. Ahmed, S. Noh, N. L. Gharamaleki, S. Kim, A. M. B. Chowdhury, J.-Y. Kim, S. Pané, B. J. Nelson and H. Choi, Nat. Mach. Intell., 2024, 6, 92–105 CrossRef.
- J. Feng, S. P. Yang, Y. Q. Shao, Y. Y. Sun, Z. L. He, Y. Wang, Y. N. Zhai and Y. B. Dong, Adv. Healthcare Mater., 2023, 12, 2301645 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Gao, J. Hou, J. Zeng, J. J. Richardson, Z. Gu, X. Gao, D. Li, M. Gao, D. W. Wang, P. Chen, V. Chen, K. Liang, D. Zhao and B. Kong, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1808900 CrossRef.
- B. Sun, S. Kjelleberg, J. J. Sung and L. Zhang, Nat. Rev. Bioeng., 2024, 2, 367–369 CrossRef.
- C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, L. Zhang and M. Pumera, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2024, 53, 2284–2299 RSC.
- C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, J. G. S. Moo, B. Khezri, P. Song, A. C. Fisher, Z. Sofer and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26, 6662–6667 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Maric, J. G. S. Moo, B. Khezri, Z. Sofer and M. Pumera, Appl. Mater. Today, 2017, 9, 289–291 CrossRef.
- N. F. Rosli, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, A. C. Fisher, O. Alduhaish, R. D. Webster and M. Pumera, Appl. Mater. Today, 2020, 21, 100819 CrossRef.
- C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, J. Vyskočil, F. Novotný and M. Pumera, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9, 14904–14910 RSC.
- J. Kim, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez and M. Pumera, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 446, 137342 CrossRef CAS.
- V. de la Asunción-Nadal, D. Rojas, B. Jurado-Sánchez and A. Escarpa, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11, 1239–1245 RSC.
- V. Sridhar, F. Podjaski, J. Kröger, A. Jiménez-Solano, B.-W. Park, B. V. Lotsch and M. Sitti, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2020, 117, 24748–24756 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. de la Asunción-Nadal, C. Franco, A. Veciana, S. Ning, A. Terzopoulou, S. Sevim, X. Z. Chen, D. Gong, J. Cai, P. D. Wendel-Garcia, B. Jurado-Sánchez, A. Escarpa, J. Puigmartí-Luis and S. Pané, Small, 2022, 18, 2203821 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Manzeli, D. Ovchinnikov, D. Pasquier, O. V. Yazyev and A. Kis, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2017, 2, 1–15 Search PubMed.
- Q. H. Wang, K. Kalantar-Zadeh, A. Kis, J. N. Coleman and M. S. Strano, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2012, 7, 699–712 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Liu and Z. Liu, Adv. Healthcare Mater., 2018, 7, 1701158 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Wang, Z. Sofer, J. G. S. Moo and M. Pumera, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 9899–9902 RSC.
- V. C. D. la Asunción-Nadal, M. Pacheco, B. Jurado-Sanchez and A. Escarpa, Anal. Chem., 2020, 92, 9188–9193 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Huang, J. Guo, Y. Li, H. Li and D. E. Fan, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, 2203082 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Anasori, M. R. Lukatskaya and Y. Gogotsi, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2017, 2, 1–17 Search PubMed.
- M. Naguib, M. W. Barsoum and Y. Gogotsi, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2103393 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Xu, F. Xue, H. Zheng, Q. Ji, C. Qiu, Z. Chen, X. Zhao, P. Li, Y. Hu, Q. Peng and X. He, Nano Energy, 2022, 103, 107848 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Cai, J.-H. Ciou, Y. Liu, Y. Jiang and P. S. Lee, Sci. Adv., 2019, 5, eaaw7956 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Pumera and Z. Sofer, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1605299 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. R. Fan, R. Wang, H. Zhang and W. Wu, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50, 10983–11031 RSC.
- N. F. Rosli, N. Rohaizad, J. Sturala, A. C. Fisher, R. D. Webster and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 1910186 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Molle, J. Goldberger, M. Houssa, Y. Xu, S.-C. Zhang and D. Akinwande, Nat. Mater., 2017, 16, 163–169 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Maric, S. M. Beladi-Mousavi, B. Khezri, J. Sturala, M. Z. M. Nasir, R. D. Webster, Z. Sofer and M. Pumera, Small, 2020, 16, 1902365 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, K. Maeda, A. Thomas, K. Takanabe, G. Xin, J. M. Carlsson, K. Domen and M. Antonietti, Nat. Mater., 2009, 8, 76–80 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liu, Y. Liu, N. Liu, Y. Han, X. Zhang, H. Huang, Y. Lifshitz, S.-T. Lee, J. Zhong and Z. Kang, Science, 2015, 347, 970–974 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Ye, Y. Sun, H. Zhang, B. Song and B. Dong, Nanoscale, 2017, 9, 18516–18522 RSC.
- M. P. Rayaroth, D. Oh, C.-S. Lee, N. Kumari, I. S. Lee and Y.-S. Chang, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2021, 597, 94–103 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Song, Y. Tao, J. Liu, J. Lin, P. Dai, Q. Wang, W. Li, W. Chen and C. Zheng, RSC Adv., 2022, 12, 13116–13126 RSC.
- K. Feng, J. Gong, J. Qu and R. Niu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14, 44271–44281 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Zheng, X. Song, Q. Gan and J. Lin, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2023, 630, 121–133 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Gusmão, Z. Sofer and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1805975 CrossRef.
- R. Gusmão, Z. Sofer and M. Pumera, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 9326–9337 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, Z. Sofer, D. Sedmidubsky, S. Huber, A. Y. S. Eng and M. Pumera, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 12563–12573 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Rao, H. Wang, Y. J. Zeng, Z. Guo, H. Zhang and W. Liao, Adv. Sci., 2021, 8, 2002284 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Khezri, K. Villa, F. Novotný, Z. Sofer and M. Pumera, Small, 2020, 16, 2002111 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Yuan, M. Á. López, B. Jurado-Sánchez and A. Escarpa, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 46588–46597 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Pacheco, B. Jurado-Sánchez and A. Escarpa, Chem. Sci., 2018, 9, 8056–8064 RSC.
- H. Wang and M. Pumera, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 8704–8735 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Jurado-Sanchez, M. Pacheco, R. Maria-Hormigos and A. Escarpa, Appl. Mater. Today, 2017, 9, 407–418 CrossRef.
- K. Yuan, V. de la Asuncion-Nadal, B. Jurado-Sánchez and A. Escarpa, Chem. Mater., 2020, 32, 1983–1992 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Gao and J. Wang, ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 3170–3180 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Li, H. M. Wen, Y. Cui, W. Zhou, G. Qian and B. Chen, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 8819–8860 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Chen, Z. Yang, Y. Zhu and Y. Xia, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 16811–16831 RSC.
- K. S. Park, Z. Ni, A. P. Côté, J. Y. Choi, R. Huang, F. J. Uribe-Romo, H. K. Chae, M. O’Keeffe and O. M. Yaghi, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2006, 103, 10186–10191 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Yao and H. Wang, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 4470–4493 RSC.
- A. Terzopoulou, X. Wang, X. Z. Chen, M. Palacios-Corella, C. Pujante, J. Herrero-Martín, X. H. Qin, J. Sort, A. J. deMello, B. J. Nelson, J. Puigmartí-Luis and S. Pané, Adv. Healthcare Mater., 2020, 9, 2001031 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. T. Tan, J. T. Cham, M. R. Reithofer, T. A. Hor and J. M. Chin, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 15175–15178 RSC.
- L. Wang, H. Zhu, Y. Shi, Y. Ge, X. Feng, R. Liu, Y. Li, Y. Ma and L. Wang, Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 11384–11391 RSC.
- M. Ikram, F. Hu, G. Peng, M. Basharat, N. Jabeen, K. Pan and Y. Gao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 51799–51806 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zhong, J. Yao, R. Chen, Z. Low, M. He, J. Z. Liu and H. Wang, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 15715–15722 RSC.
- J. H. Cavka, S. Jakobsen, U. Olsbye, N. Guillou, C. Lamberti, S. Bordiga and K. P. Lillerud, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 13850–13851 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Winarta, B. Shan, S. M. Mcintyre, L. Ye, C. Wang, J. Liu and B. Mu, Cryst. Growth Des., 2019, 20, 1347–1362 CrossRef.
- F. Ahmadijokani, H. Molavi, M. Rezakazemi, S. Tajahmadi, A. Bahi, F. Ko, T. M. Aminabhavi, J.-R. Li and M. Arjmand, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2022, 125, 100904 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Ayala, C. Carbonell, I. Imaz and D. Maspoch, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 5096–5099 RSC.
- H. Huang, J. Li, M. Yuan, H. Yang, Y. Zhao, Y. Ying and S. Wang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61, e202211163 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Yang, X. Arqué, T. Patiño, V. Guillerm, P.-R. Blersch, J. Pérez-Carvajal, I. Imaz, D. Maspoch and S. Sánchez, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 20962–20967 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Li, X. Yu, M. Xu, W. Liu, E. Sandraz, H. Lan, J. Wang and S. M. Cohen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 611–614 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhang, X. Hu, T. Li, Y. Zhang, H. Xu, Y. Sun, X. Gu, C. Gu, J. Luo and B. Gao, J. Hazard. Mater., 2022, 429, 128271 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Dekanovsky, Y. Ying, J. Zelenka, J. Plutnar, S. M. Beladi-Mousavi, I. Křížová, F. Novotný, T. Ruml and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2205062 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Liu, X. Sun, Y. Peng, Y. Wang, D. Xu, W. Chen, W. Wang, X. Yan and X. Ma, ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 14666–14678 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Wang, W. Guo, X. Li, Z. Liu, H. Liu and S. Ding, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 42462–42467 RSC.
- Y. Ying, A. M. Pourrahimi, Z. Sofer, S. Matějková and M. Pumera, ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 11477–11487 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liu, J. Li, G. Wang, W. Yang, J. Yang and Y. Liu, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2019, 555, 234–244 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, P. C. Lan and S. Ma, ACS Cent. Sci., 2020, 6, 1497–1506 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. You, D. Xu, X. Pan and X. Ma, Appl. Mater. Today, 2019, 16, 508–517 CrossRef.
- X. Peng, S. Tang, D. Tang, D. Zhou, Y. Li, Q. Chen, F. Wan, H. Lukas, H. Han, X. Zhang, W. Gao and S. Wu, Sci. Adv., 2023, 9, eadh1736 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Chen, Q. Zhao and X. Du, Micromachines, 2018, 9, 41 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Wang, Z. Xiong and J. Tang, Adv. Intell. Syst., 2021, 3, 2000170 CrossRef.
- A. I. Bunea, D. Martella, S. Nocentini, C. Parmeggiani, R. Taboryski and D. S. Wiersma, Adv. Intell. Syst., 2021, 3, 2000256 CrossRef.
- R. Dong, Y. Cai, Y. Yang, W. Gao and B. Ren, Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51, 1940–1947 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Kong, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, J. Guan and M. Pumera, Small, 2020, 16, 1903179 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Hong, M. Diaz, U. M. Córdova-Figueroa and A. Sen, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2010, 20, 1568–1576 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Giudicatti, S. M. Marz, L. Soler, A. Madani, M. R. Jorgensen, S. Sanchez and O. G. Schmidt, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2014, 2, 5892–5901 RSC.
- F. Mou, Y. Li, C. Chen, W. Li, Y. Yin, H. Ma and J. Guan, Small, 2015, 11, 2564–2570 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Enachi, M. Guix, V. Postolache, V. Ciobanu, V. M. Fomin, O. G. Schmidt and I. Tiginyanu, Small, 2016, 12, 5497–5505 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, F. Mou, C. Chen, M. You, Y. Yin, L. Xu and J. Guan, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 10697–10703 RSC.
- W. Liu, X. Chen, X. Lu, J. Wang, Y. Zhang and Z. Gu, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 2003195 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Chen, E. Karshalev, J. Li, F. Soto, R. Castillo, I. Campos, F. Mou, J. Guan and J. Wang, ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 10389–10396 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Dong, C. Wang, Q. Wang, A. Pei, X. She, Y. Zhang and Y. Cai, Nanoscale, 2017, 9, 15027–15032 RSC.
- C. Wang, R. Dong, Q. Wang, C. Zhang, X. She, J. Wang and Y. Cai, Chem. – Asian J., 2019, 14, 2485–2490 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. M. Pourrahimi, K. Villa, Y. Ying, Z. Sofer and M. Pumera, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 42688–42697 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. M. Pourrahimi, K. Villa, Z. Sofer and M. Pumera, Small Methods, 2019, 3, 1900258 CrossRef CAS.
- A. M. Pourrahimi, K. Villa, C. L. Manzanares Palenzuela, Y. Ying, Z. Sofer and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1808678 CrossRef.
- S. Du, H. Wang, C. Zhou, W. Wang and Z. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 2213–2217 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. He, H. Jiang, J. Li, Y. Ma, B. Fu and C. Hu, Small, 2021, 17, 2101388 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Wang, M. Borrelli and J. Simmchen, ChemPhotoChem, 2021, 5, 933–939 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Ussia, M. Urso, K. Dolezelikova, H. Michalkova, V. Adam and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2101178 CrossRef CAS.
- C. M. Oral, M. Ussia and M. Pumera, Small, 2022, 18, 2202600 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhang, W. Xie, S. Du, H. Wang and Z. Zhang, Langmuir, 2022, 38, 4389–4395 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Ying, A. M. Pourrahimi, C. L. Manzanares-Palenzuela, F. Novotny, Z. Sofer and M. Pumera, Small, 2020, 16, 1902944 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Wolff, V. Ciobanu, M. Enachi, M. Kamp, T. Braniste, V. Duppel, S. Shree, S. Raevschi, M. Medina-Sanchez, R. Adelung, O. G. Schmidt, L. Kienle and I. Tiginyanu, Small, 2020, 16, e1905141 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Tang, S.-Y. Tang, V. Sivan, W. Zhang, A. Mitchell, K. Kalantar-Zadeh and K. Khoshmanesh, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, 103, 174104 CrossRef.
- Q. Zhang, R. Dong, Y. Wu, W. Gao, Z. He and B. Ren, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 4674–4683 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Peng, M. Urso and M. Pumera, npj Clean Water, 2023, 6, 21 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Aslam, M. T. Qamar, A. U. Rehman, M. T. Soomro, S. Ali, I. M. I. Ismail and A. Hameed, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 451, 128–140 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Urso, M. Ussia and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2101510 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Palacci, S. Sacanna, A. Vatchinsky, P. M. Chaikin and D. J. Pine, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 15978–15981 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Maria-Hormigos, M. Pacheco, B. Jurado-Sánchez and A. Escarpa, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2018, 5, 2993–3003 RSC.
- H. Ye, Y. Wang, X. J. Liu, D. D. Xu, H. Yuan, H. Q. Sun, S. B. Wang and X. Ma, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2021, 588, 510–521 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Yang, Y. Liu, J. Li, M. Zuo, W. Li, N. Xing, C. Wang and T. Li, Appl. Mater. Today, 2021, 25, 101190 CrossRef.
- R. Mestre, N. Cadefau, A. C. Hortelao, J. Grzelak, M. Gich, A. Roig and S. Sánchez, ChemNanoMat, 2021, 7, 134–140 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Palacci, S. Sacanna, A. P. Steinberg, D. J. Pine and P. M. Chaikin, Science, 2013, 339, 936–940 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Palacci, S. Sacanna, S.-H. Kim, G.-R. Yi, D. J. Pine and P. M. Chaikin, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., A, 2014, 372, 20130372 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Palacci, S. Sacanna, A. Abramian, J. Barral, K. Hanson, A. Y. Grosberg, D. J. Pine and P. M. Chaikin, Sci. Adv., 2015, 1, e1400214 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. H. Lin, T. Y. Si, Z. G. Wu, C. Y. Gao, X. K. Lin and Q. He, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 13517–13520 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. R. Li, Y. Y. Yu, L. W. Wang, S. M. Zhang, J. R. Liu, J. P. Zhang, A. B. Xu, Z. Y. Wu, J. T. Tong, S. H. Wang, M. Q. Xiao, Y. S. Fang, J. Yao, A. A. Solovev, B. Dong and L. He, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 9513–9521 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhu, H. G. Wang and Z. X. Zhang, Langmuir, 2021, 37, 4964–4970 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Kang, J. Zhu, X. L. Zhang, H. G. Wang and Z. X. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 4754–4758 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Peng, M. Urso and M. Pumera, Small Methods, 2021, 5, 2100617 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Villa, J. Parmar, D. Vilela and S. Sánchez, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 20478–20486 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wang, J. W. Si, Y. Z. Hao, J. Y. Li, P. P. Zhang, C. X. Zuo, B. Jin, Y. Wang, W. Zhang, W. Q. Li, R. F. Guo and S. D. Miao, Langmuir, 2022, 38, 1231–1242 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. A. Jelle, M. Hmadeh, P. G. O'Brien, D. D. Perovic and G. A. Ozin, ChemNanoMat, 2016, 2, 1047–1054 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Shoneye and J. Tang, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 511, 145479 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Huang, B. Ibarlucea, A. Caspari, A. Synytska, G. Cuniberti, J. de Graaf and L. Baraban, Eur. Phys. J. E: Soft Matter Biol. Phys., 2021, 44, 1–11 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Huang, V. Misko, A. Caspari, A. Synytska, B. Ibarlucea, F. Nori, J. Fassbender, G. Cuniberti, D. Makarov and L. Baraban, Commun. Mater., 2022, 3, 60 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Zhou, Y. C. Li, P. Xu, N. S. McCool, L. Li, W. Wang and T. E. Mallouk, Nanoscale, 2017, 9, 75–78 RSC.
- É. O’Néel-Judy, D. Nicholls, J. Castañeda and J. G. Gibbs, Small, 2018, 14, 1801860 CrossRef PubMed.
- Q. L. Wang, R. F. Dong, C. Wang, S. Y. Xu, D. C. Chen, Y. Y. Liang, B. Y. Ren, W. Gao and Y. P. Cai, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 6201–6207 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. L. Wang, R. F. Dong, Q. X. Yang, J. J. Wang, S. Y. Xu and Y. P. Cai, Nanoscale Horiz., 2020, 5, 325–330 RSC.
- W. J. Liu, X. Chen, X. Y. Ding, Q. Long, X. L. Lu, Q. Wang and Z. W. Gu, Nanoscale Horiz., 2021, 6, 238–244 RSC.
- D. Rojas, M. Kuthanova, K. Dolezelikova and M. Pumera, NPG Asia Mater., 2022, 14, 63 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Tan, B. Chen, M. Liu, J. Jiang, J. Ou, L. Liu, F. Wang, Y. Ye, J. Gao and J. Sun, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 448, 137689 CrossRef CAS.
- D. H. Cui, X. L. Lyu, S. F. Duan, Y. X. Peng and W. Wang, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2022, 5, 14235–14240 CrossRef CAS.
- X. J. Wei, M. U. Akbar, A. Raza and G. Li, Nanoscale Adv., 2021, 3, 3353–3372 RSC.
- W. L. Huang, J. Comput. Chem., 2009, 30, 1882–1891 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Mushtaq, M. Guerrero, M. S. Sakar, M. Hoop, A. M. Lindo, J. Sort, X. Chen, B. J. Nelson, E. Pellicer and S. Pané, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 23670–23676 RSC.
- L. Xu, D. Gong, N. Celi, J. Xu, D. Zhang and J. Cai, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2022, 579, 152165 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, J. Li, J. Li, X. Yan, F. Wang, W. Yang, D. H. Ng and J. Yang, J. Cleaner Prod., 2020, 252, 119573 CrossRef CAS.
- R. F. Dong, Y. Hu, Y. F. Wu, W. Gao, B. Y. Ren, Q. L. Wang and Y. P. Cai, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 1722–1725 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zhan, F. Wei, J. Zheng, C. Yin, W. Yang, L. Yao, S. Tang and D. Liu, Mater. Lett., 2020, 258, 126825 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Mayorga-Burrezo, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, J. Kim and M. Pumera, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 446, 137139 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Khairudin, N. F. A. Bakar and M. S. Osman, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2022, 10, 108275 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhou, B. Wu, L. Dekanovsky, S. Wei, B. Khezri, T. Hartman, J. Li and Z. Sofer, Flatchem, 2021, 30, 100294 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Chen, L. Z. Liu, C. Hu and H. W. Huang, Chin. J. Catal., 2021, 42, 1413–1438 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Villa, L. Děkanovský, J. Plutnar, J. Kosina and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 2007073 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Lotfi, M. E. Ouardi, H. A. Ahsaine and A. Assani, Catal. Rev., 2024, 66, 214–258 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Villa, F. Novotny, J. Zelenka, M. P. Browne, T. Ruml and M. Pumera, ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 8135–8145 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Heckel and J. Simmchen, Adv. Intell. Syst., 2019, 1, 1900093 CrossRef.
- S. Heckel, J. Grauer, M. Semmler, T. Gemming, H. Löwen, B. Liebchen and J. Simmchen, Langmuir, 2020, 36, 12473–12480 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Mayorga-Burrezo, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2106699 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. C. Chen, J. W. Jiang, X. Wang, H. Zhang, B. Song and B. Dong, J. Mater. Sci., 2022, 57, 4092–4103 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Villa, J. Vyskocil, Y. L. Ying, J. Zelenka and M. Pumera, Chem. – Eur. J., 2020, 26, 3039–3043 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Beladi-Mousavi, S. Hermanová, Y. L. Ying, J. Plutnar and M. Pumera, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 25102–25110 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Mayorga-Burrezo, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez and M. Pumera, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2023, 643, 447–454 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, J. Zelenka, K. Klima, P. Mayorga-Burrezo, L. Hoang, T. Ruml and M. Pumera, ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 8694–8703 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Jurado-Sánchez, A. Escarpa and J. Wang, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 14088–14091 RSC.
- B. Jurado-Sánchez, J. Wang and A. Escarpa, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 19618–19625 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. M. Hormigos, B. J. Sánchez and A. Escarpa, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 3128–3132 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Pacheco, B. Jurado-Sánchez and A. Escarpa, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 18017–18024 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Pacheco, B. Jurado-Sánchez and A. Escarpa, Nanoscale, 2021, 13, 17106–17115 RSC.
- X. Chen, X. Ding, Y. Liu, J. Li, W. Liu, X. Lu and Z. Gu, Appl. Mater. Today, 2021, 25, 101200 CrossRef.
- J. Wang, L. Li, R. Wei and R. Dong, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14, 48967–48975 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Ying, J. Plutnar and M. Pumera, Small, 2021, 17, 2100294 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Jancik-Prochazkova and M. Pumera, Nanoscale, 2023, 15, 5726–5734 RSC.
- X. Zhan, J. Zheng, Y. Zhao, B. Zhu, R. Cheng, J. Wang, J. Liu, J. Tang and J. Tang, Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, 1903329 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zheng, J. Wang, Z. Xiong, Z. Wan, X. Zhan, S. Yang, J. Chen, J. Dai and J. Tang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1901768 CrossRef.
- E. H. Ma, K. Wang, Z. Q. Hu and H. Wang, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2021, 603, 685–694 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. G. Yuan, M. Q. Gong, H. Huang, Y. Zhao, Y. L. Ying and S. Wang, Inorg. Chem. Front., 2022, 9, 5725–5734 RSC.
- J. Wang, Z. Xiong, X. Zhan, B. Dai, J. Zheng, J. Liu and J. Tang, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1701451 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. K. Zhou, Y. C. G. Li, P. T. Xu, L. Q. Ren, G. Y. Zhang, T. E. Mallouk and L. Q. Li, Nanoscale, 2017, 9, 11434–11438 RSC.
- L. Chen, M. J. Zhang, S. Y. Zhang, L. Shi, Y. M. Yang, Z. Liu, X. J. Ju, R. Xie, W. Wang and L. Y. Chu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 35120–35131 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Xu, C. Zhou, C. Zhan, Y. Wang, Y. You, X. Pan, J. Jiao, R. Zhang, Z. Dong, W. Wang and X. Ma, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1807727 CrossRef.
- W. Q. Xie, C. Zhou, X. L. Zhang, S. N. Du, W. Wang, H. G. Wang and Z. X. Zhang, ChemNanoMat, 2020, 6, 1749–1753 CrossRef CAS.
- J. H. Zhang, F. Z. Mou, Z. Wu, J. Q. Song, J. E. Kauffman, A. Sen and J. G. Guan, Nanoscale Adv., 2021, 3, 6157–6163 RSC.
- J. J. Li, X. L. He, H. D. Jiang, Y. Xing, B. Fu and C. Z. Hu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14, 36027–36037 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Z. Mou, X. F. Li, Q. Xie, J. H. Zhang, K. Xiong, L. L. Xu and J. G. Guan, ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 406–414 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. de la Asuncion-Nadal, R. Maria-Hormigos, B. Jurado-Sanchez and A. Escarpa, Appl. Mater. Today, 2022, 29, 101664 CrossRef.
- X. L. Cui, J. Li, D. H. L. Ng, J. Liu, Y. Liu and W. N. Yang, Carbon, 2020, 158, 738–748 CrossRef CAS.
- J. R. Liu, H. Chen, X. J. Shi, S. Nawar, J. G. Werner, G. S. Huang, M. M. Ye, D. A. A. Weitz, A. A. A. Solovev and Y. F. Mei, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2020, 7, 656–664 RSC.
- L. Wang, A. Kaeppler, D. Fischer and J. Simmchen, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 32937–32944 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Ussia, M. Urso, S. Kment, T. Fialova, K. Klima, K. Dolezelikova and M. Pumera, Small, 2022, 18, e2200708 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Villa, H. Sopha, J. Zelenka, M. Motola, L. Dekanovsky, D. C. Beketova, J. M. Macak, T. Ruml and M. Pumera, Small, 2022, 18, e2106612 CrossRef PubMed.
- V. Sridhar, E. Yildiz, A. Rodríguez-Camargo, X. Lyu, L. Yao, P. Wrede, A. Aghakhani, B. M. Akolpoglu, F. Podjaski, B. V. Lotsch and M. Sitti, Adv. Mater., 2023, 35, 2301126 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. S. Kochergin, K. Villa, F. Novotný, J. Plutnar, M. J. Bojdys and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 2002701 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. S. Kochergin, K. Villa, A. Nemeskalova, M. Kuchař and M. Pumera, ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 18458–18468 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Wei, Y. Gao, X. Li and M. J. Serpe, Polym. Chem., 2017, 8, 127–143 RSC.
- Y. Zhao, M. Hua, Y. Yan, S. Wu, Y. Alsaid and X. He, Annu. Rev. Control Rob. Auton. Syst., 2022, 5, 515–545 CrossRef.
- S. Palagi, A. G. Mark, S. Y. Reigh, K. Melde, T. Qiu, H. Zeng, C. Parmeggiani, D. Martella, A. Sanchez-Castillo, N. Kapernaum, F. Giesselmann, D. S. Wiersma, E. Lauga and P. Fischer, Nat. Mater., 2016, 15, 647–653 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Zhang, G. Xing, W. Chen and L. Chen, Mater. Chem. Front., 2020, 4, 332–353 RSC.
- K. Wang, W. Wang, S. Pan, Y. Fu, B. Dong and H. Wang, Appl. Mater. Today, 2020, 19, 100550 CrossRef.
- J. Xue, M. Zhang, J. Yong, Q. Chen, J. Wang, J. Xu and K. Liang, Nano Lett., 2023, 23, 11243–11251 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Lu, H. Shen, Y. Wei, H. Ge, J. Wang, H. Peng and W. Liu, Small, 2020, 16, 2003678 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Dekanovsky, B. Khezri, Z. Rottnerova, F. Novotny, J. Plutnar and M. Pumera, Nat. Mach. Intell., 2020, 2, 711–718 CrossRef.
- E. M. Kutorglo, R. Elashnikov, S. Rimpelova, P. Ulbrich, J. Říhová Ambrožová, V. Svorcik and O. Lyutakov, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 16173–16181 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Schwarz, M. Medina-Sánchez and O. G. Schmidt, Appl. Phys. Rev., 2017, 4, 031301 Search PubMed.
- J. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Kim, T. Yu and R. Bashir, APL Bioeng., 2022, 6, 036103 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Magdanz, I. S. Khalil, J. Simmchen, G. P. Furtado, S. Mohanty, J. Gebauer, H. Xu, A. Klingner, A. Aziz, M. Medina-Sánchez, O. G. Schmidt and S. Misra, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, eaba5855 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. C. Yang, K. M. Blair and N. R. Salama, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2016, 80, 187–203 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Stark, Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51, 2681–2688 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Alapan, O. Yasa, O. Schauer, J. Giltinan, A. F. Tabak, V. Sourjik and M. Sitti, Sci. Rob., 2018, 3, eaar4423 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. R. Edwards, R. W. Carlsen, J. Zhuang and M. Sitti, J. Microbio. Robot., 2014, 9, 47–60 CrossRef.
- E. Steager, C.-B. Kim, J. Patel, S. Bith, C. Naik, L. Reber and M. J. Kim, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, 90, 263901 CrossRef.
- A. Tay, H. McCausland, A. Komeili and D. Di Carlo, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1904178 CrossRef.
- L. Yan, S. Zhang, P. Chen, H. Liu, H. Yin and H. Li, Microbiol. Res., 2012, 167, 507–519 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Martel, 2006. in International Conference on Microtechnologies in Medicine and Biology. pp. 89-92 (IEEE).
- S.-J. Song, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, J. Vyskočil, M. Castoralova, T. S. Ruml and M. Pumera, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15, 7023–7029 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Taherkhani, M. Mohammadi, J. Daoud, S. Martel and M. Tabrizian, ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 5049–5060 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Li, H. Chen, X. Feng, C. Yu, F. Feng, Y. Chai, P. Lu, T. Song, X. Wang and L. Yao, Small, 2019, 15, 1900427 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. R. Benoit, D. Mayer, Y. Barak, I. Y. Chen, W. Hu, Z. Cheng, S. X. Wang, D. M. Spielman, S. S. Gambhir and A. Matin, Clin. Cancer Res., 2009, 15, 5170–5177 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B.-W. Park, J. Zhuang, O. Yasa and M. Sitti, ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 8910–8923 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Mostaghaci, O. Yasa, J. Zhuang and M. Sitti, Adv. Sci., 2017, 4, 1700058 CrossRef PubMed.
- O. Aydin, X. T. Zhang, S. Nuethong, G. J. Pagan-Diaz, R. Bashir, M. Gazzola and M. T. A. Saif, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2019, 116, 19841–19847 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Z. Chen, J. H. Liu, M. Dong, L. Müller, G. Chatzipirpiridis, C. Z. Hu, A. Terzopoulou, H. Torlakcik, X. P. Wang, F. Mushtaq, J. Puigmartí-Luis, Q. D. Shen, B. J. Nelson and S. Pané, Mater. Horiz., 2019, 6, 1512–1516 RSC.
- J. Han, J. Zhen, V. Du Nguyen, G. Go, Y. Choi, S. Y. Ko, J.-O. Park and S. Park, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 28717 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, M. Fojtů, J. Vyskočil, N. J. Cho and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2207272 CrossRef CAS.
- S.-J. Song, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, D. Huska and M. Pumera, NPG Asia Mater., 2022, 14, 79 CrossRef CAS.
- M. B. Akolpoglu, N. O. Dogan, U. Bozuyuk, H. Ceylan, S. Kizilel and M. Sitti, Adv. Sci., 2020, 7, 2001256 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Medina-Sánchez, L. Schwarz, A. K. Meyer, F. Hebenstreit and O. G. Schmidt, Nano Lett., 2016, 16, 555–561 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Guix, R. Mestre, T. Patiño, M. De Corato, J. Fuentes, G. Zarpellon and S. Sánchez, Sci. Rob., 2021, 6, eabe7577 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Xi, J. J. Schmidt and C. D. Montemagno, Nat. Mater., 2005, 4, 180–184 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Raman, C. Cvetkovic, S. G. M. Uzel, R. J. Platt, P. Sengupta, R. D. Kamm and R. Bashir, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2016, 113, 3497–3502 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Go, S.-G. Jeong, A. Yoo, J. Han, B. Kang, S. Kim, K. T. Nguyen, Z. Jin, C.-S. Kim, Y. R. Seo, J. Y. Kang, J. Y. Na, E. K. Song, Y. Jeong, J. K. Seon, J.-O. Park and E. Choi, Sci. Rob., 2020, 5, eaay6626 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. P. Jahromi, M. A. Shahbazi, A. Maleki, A. Azadi and H. A. Santos, Adv. Sci., 2021, 8, 2002499 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Magdanz, M. Medina-Sánchez, L. Schwarz, H. Xu, J. Elgeti and O. G. Schmidt, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1606301 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Schwarz, M. Medina-Sánchez and O. G. Schmidt, Reproduction, 2020, 159, R83–R96 CAS.
- H. Xu, M. Medina-Sánchez, V. Magdanz, L. Schwarz, F. Hebenstreit and O. G. Schmidt, ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 327–337 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Xu, M. Medina-Sánchez, M. F. Maitz, C. Werner and O. G. Schmidt, ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 2982–2993 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. F. Xu, M. Medina-Sánchez, W. N. Zhang, M. P. H. Seaton, D. R. Brison, R. J. Edmondson, S. S. Taylor, L. Nelson, K. Zeng, S. Bagley, C. Ribeiro, L. P. Restrepo, E. Lucena, C. K. Schmidt and O. G. Schmidt, Nanoscale, 2020, 12, 20467–20481 RSC.
- V. Magdanz, S. Sanchez and O. G. Schmidt, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25, 6581–6588 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Magdanz, M. Medina-Sánchez, Y. Chen, M. Guix and O. G. Schmidt, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25, 2763–2770 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Striggow, M. Medina-Sánchez, G. K. Auernhammer, V. Magdanz, B. M. Friedrich and O. G. Schmidt, Small, 2020, 16, 2000213 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Striggow, C. Ribeiro, A. Aziz, R. Nauber, F. Hebenstreit, O. G. Schmidt and M. Medina-Sánchez, Small, 2024, 20, 2310288 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Rajabasadi, S. Moreno, K. Fichna, A. Aziz, D. Appelhans, O. G. Schmidt and M. Medina-Sánchez, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, 2204257 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Luthfikasari, T. V. Patil, D. K. Patel, S. D. Dutta, K. Ganguly, M. M. Espinal and K. T. Lim, Small, 2022, 18, 2201417 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Ariizumi and K. Toriyama, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2011, 62, 437–460 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Wang, M. G. Potroz, J. A. Jackman, B. Khezri, T. Marić, N. J. Cho and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27, 1702338 CrossRef.
- T. Maric, M. Z. M. Nasir, N. F. Rosli, M. Budanović, R. D. Webster, N. J. Cho and M. Pumera, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 2000112 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Sun, K. F. Chan, Z. Zhang, L. Wang, Q. Wang, S. Yang, S. M. Chan, P. W. Y. Chiu, J. J. Y. Sung and L. Zhang, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, 2201888 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhang, L. Zhang, L. Yang, C. I. Vong, K. F. Chan, W. K. K. Wu, T. N. Y. Kwong, N. W. S. Lo, M. Ip, S. H. Wong, J. J. Y. Sung, P. W. Y. Chiu and L. Zhang, Sci. Adv., 2019, 5, eaau9650 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Huska, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, R. Zelinka and M. Pumera, Small, 2022, 18, 2200208 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Yasa, P. Erkoc, Y. Alapan and M. Sitti, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1804130 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Zhang, J. Zhuang, Z. Li, H. Gong, B. E.-F. de Ávila, Y. Duan, Q. Zhang, J. Zhou, L. Yin, E. Karshalev, W. Gao, V. Nizet, R. H. Fang, L. Zhang and J. Wang, Nat. Mater., 2022, 21, 1324–1332 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Zhang, Z. Li, Y. Duan, A. Abbas, R. Mundaca-Uribe, L. Yin, H. Luan, W. Gao, R. H. Fang, L. Zhang and J. Wang, Sci. Rob., 2022, 7, eabo4160 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Medina-Sánchez, V. Magdanz, L. Schwarz, H. Xu and O. G. Schmidt, Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems, Springer, 2017, pp. 579–588 Search PubMed.
- K. I. Middelhoek, V. Magdanz, L. Abelmann and I. S. Khalil, Biomed. Mater., 2022, 17, 065001 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Zhong, W. Li, Y. Qi, J. He and M. Zhou, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 1910395 CrossRef CAS.
- V. M. Moreno, E. Álvarez, I. Izquierdo-Barba, A. Baeza, J. Serrano-López and M. Vallet-Regí, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 7, 1901942 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Ji, Y. Wu, M. Pumera and L. Zhang, Adv. Mater., 2023, 35, 2203959 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Komeili, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2012, 36, 232–255 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Rismani Yazdi, R. Nosrati, C. A. Stevens, D. Vogel, P. L. Davies and C. Escobedo, Small, 2018, 14, 1702982 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Xing, T. Yin, S. Li, T. Xu, A. Ma, Z. Chen, Y. Luo, Z. Lai, Y. Lv, H. Pan, R. Liang, X. Wu, M. Zheng and L. Cai, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2008262 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Schuerle, A. P. Soleimany, T. Yeh, G. Anand, M. Häberli, H. Fleming, N. Mirkhani, F. Qiu, S. Hauert, X. Wang, B. J. Nelson and S. N. Bhatia, Sci. Adv., 2019, 5, eaav4803 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Gwisai, N. Mirkhani, M. G. Christiansen, T. T. Nguyen, V. Ling and S. Schuerle, Sci. Rob., 2022, 7, eabo0665 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhuang and M. Sitti, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 32135 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Felfoul, M. Mohammadi, S. Taherkhani, D. De Lanauze, Y. Zhong Xu, D. Loghin, S. Essa, S. Jancik, D. Houle, M. Lafleur, L. Gaboury, M. Tabrizian, N. Kaou, M. Atkin, T. Vuong, G. Batist, N. Beauchemin, D. Radzioch and S. Martel, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2016, 11, 941–947 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Park, S. J. Park, S. Cho, Y. Lee, Y. K. Lee, J. J. Min, B. J. Park, S. Y. Ko, J. O. Park and S. Park, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2014, 111, 134–143 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Shao, M. Xuan, H. Zhang, X. Lin, Z. Wu and Q. He, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 129, 13115–13119 CrossRef.
- M. Nagai, T. Hirano and T. Shibata, Micromachines, 2019, 10, 130 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. W. Carlsen, M. R. Edwards, J. Zhuang, C. Pacoret and M. Sitti, Lab Chip, 2014, 14, 3850–3859 RSC.
- X. Yan, Q. Zhou, M. Vincent, Y. Deng, J. Yu, J. Xu, T. Xu, T. Tang, L. Bian, Y.-X. J. Wang, K. Kostarelos and L. Zhang, Sci. Rob., 2017, 2, eaaq1155 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Maria-Hormigos, C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, T. Kinčl and M. Pumera, ACS Nano, 2023, 17, 7595–7603 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Jurado-Sánchez and J. Wang, Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2018, 5, 1530–1544 RSC.
- Y. Zhang, K. Yan, F. Ji and L. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1806340 CrossRef.
- F. Soto, M. A. Lopez-Ramirez, I. Jeerapan, B. Esteban-Fernandez de Avila, R. K. Mishra, X. Lu, I. Chai, C. Chen, D. Kupor, A. Nourhani and J. Wang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1900658 CrossRef.
- F. Zhang, Z. Li, L. Yin, Q. Zhang, N. Askarinam, R. Mundaca-Uribe, F. Tehrani, E. Karshalev, W. Gao, L. Zhang and J. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 12194–12201 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Ginet, R. Pardoux, G. Adryanczyk, D. Garcia, C. Brutesco and D. Pignol, PLoS One, 2011, 6, e21442 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, Y. Li, J. Zhao, H. Yao, S. Chu, Z. Song, Z. He and W. Zhang, Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2020, 14, 1–14 CrossRef.
- Y. Qu, X. Zhang, J. Xu, W. Zhang and Y. Guo, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2014, 136, 10–17 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Tanaka, Y. Nakata, T. Mori, Y. Okamura, H. Miyasaka, H. Takeyama and T. Matsunaga, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2008, 74, 3342–3348 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Wang, J. G. S. Moo and M. Pumera, Nanoscale, 2014, 6, 11359–11363 RSC.
- R. D. Ambashta and M. Sillanpää, J. Hazard. Mater., 2010, 180, 38–49 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Bahaj, P. James and F. Moeschler, Sep. Sci. Technol., 2002, 37, 3661–3671 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Troeger, B. F. Blacker, I. A. Khalil, P. C. Rao, S. Cao, S. R. Zimsen, S. B. Albertson, J. D. Stanaway, A. Deshpande and Z. Abebe, Lancet Infect. Dis., 2018, 18, 1211–1228 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Cacciò and R. Chalmers, Clin. Microbiol. Infect., 2016, 22, 471–480 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. F. Xu, M. Medina-Sánchez, V. Magdanz, L. Schwarz, F. Hebenstreit and O. G. Schmidt, ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 327–337 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Wang, Y. Qin, J. Liu, Z. Zhang, W. Li, G. Pu, Z. Yuanhe, X. Gui and M. Chu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15, 2747–2759 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Yan, J. Xu, Q. Zhou, D. Jin, C. I. Vong, Q. Feng, D. H. Ng, L. Bian and L. Zhang, Appl. Mater. Today, 2019, 15, 242–251 CrossRef.
- Y. Dong, L. Wang, K. Yuan, F. Ji, J. Gao, Z. Zhang, X. Du, Y. Tian, Q. Wang and L. Zhang, ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 5056–5067 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Ji, D. Jin, B. Wang and L. Zhang, ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 6990–6998 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Karygianni, Z. Ren, H. Koo and T. Thurnheer, Trends Microbiol., 2020, 28, 668–681 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. M. Stanton, B.-W. Park, D. Vilela, K. Bente, D. Faivre, M. Sitti and S. Sánchez, ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 9968–9978 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. C. Mayorga-Martinez, J. Zelenka, J. Grmela, H. Michalkova, T. Ruml, J. Mareš and M. Pumera, Adv. Sci., 2021, 8, 2101301 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Magdanz, S. Sanchez and O. G. Schmidt, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25, 6581–6588 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Aziz, J. Holthof, S. Meyer, O. G. Schmidt and M. Medina-Sánchez, Adv. Healthcare Mater., 2021, 10, 2101077 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Nauber, S. R. Goudu, M. Goeckenjan, M. Bornhäuser, C. Ribeiro and M. Medina-Sánchez, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 728 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wu, R. Dong, Q. Zhang and B. Ren, Nano-Micro Lett., 2017, 9, 1–12 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Wang, R. Dong, Q. Yang, H. Wu, Z. Bi, Q. Liang, Q. Wang, C. Wang, Y. Mei and Y. Cai, Nanoscale, 2019, 11, 16592–16598 RSC.
- J. Cui, T.-Y. Huang, Z. Luo, P. Testa, H. Gu, X.-Z. Chen, B. J. Nelson and L. J. Heyderman, Nature, 2019, 575, 164–168 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-W. Huang, M. S. Sakar, A. J. Petruska, S. Pané and B. J. Nelson, Nat. Commun., 2016, 7, 12263 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3cs00777d |
| ‡ These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |