Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Solvatomorphism with polar protic/aprotic and non-polar solvents in a series of complexes derived from the 5-phenylimidazole/tetrafluoroborate/copper(II) reaction system†
Maria-Ioanna
Delegkou
 a,
Nikos
Panagiotou
b,
Constantina
Papatriantafyllopoulou
a,
Nikos
Panagiotou
b,
Constantina
Papatriantafyllopoulou
 bc,
Anastasios
Tasiopoulos
bc,
Anastasios
Tasiopoulos
 b,
Dionissios
Papaioannou
a,
Spyros P.
Perlepes
b,
Dionissios
Papaioannou
a,
Spyros P.
Perlepes
 a and
Vassilios
Nastopoulos
a and
Vassilios
Nastopoulos
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Chemistry, University of Patras, 26504 Patras, Greece. E-mail: nastopoulos@upatras.gr
bDepartment of Chemistry, University of Cyprus, 1678 Nicosia, Cyprus
cNational University of Ireland Galway, H91 TK 33 Galway, Ireland
First published on 7th June 2024
Abstract
In a search to explore the structural landscape of possible copper(II) complexes with the 4-phenylimidazole/ tetrafluoroborate combination, considerable solvatomorphism has emerged. The utilization of a wide variety of crystallization solvents (polar protic, polar and non-polar aprotic) resulted in a series of seventeen crystalline solvatomorphs with the general formulae [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4]·x(solvent) [HL = 5-phenylimidazole, x(solvent) = 2(acetone)·2(water) (1), 2(methanol) (2), 2(ethanol) (3), 2(1-propanol) (4), 1.4(2-propanol) (5), 2(1-butanol) (6), 2(iso-butanol) (7), 1.33(tert-butanol) (8), 2(1-pentanol) (9), 2(dimethylformamide) (10), 1.2(acetone) (11), 2(tetrahydrofurane) (12), 1.85(1,4-dioxane) (13), 0.86(ethyl acetate) (14), 1(diethyl ether) (15), 0.7(diisopropyl ether) (16), 1(n-hexane) (17)]. A reaction using the CH2Cl2/MeCN solvent system produced crystals of the [Cu(HL)4(MeCN)(H2O)0.4](BF4)2 complex (18). Crystallization with nitromethane yielded [Cu{SiF2O(OMe)}2(HL)4]·0.8MeNO2 (19·0.8MeNO2), due to the in situ reaction of fluoride ions from BF4− ions with the glass surface of the vial used to grow crystals. The structures have been solved by single-crystal X-ray diffraction and the complexes were characterized by thermal analysis and infrared spectroscopy. The crystallization solvents are located in channels, with the exception of 1.33(tert-butanol) (8) and 1.2(acetone) (11) residing in lattice pockets. An analysis to understand the role of the solvents in the molecular self-assembly process is described. Depending on the hydrogen-bond functionalities of each solvent, three distinct cases emerge i) the solvents link neighboring [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] molecules via N–H⋯Osolvent–H⋯F intermolecular associations (polar protic solvents, compounds 1–9), ii) they are terminally connected to [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] molecules (polar aprotic solvents, compounds 10–13) and iii) they simply reside in channels without any involvement in supramolecular motifs (non-polar solvents, compounds 14–17). The final crystal packings result from the concerted action of robust N–H⋯F synthons and the above described interactions involving the solvent molecules.
Introduction
Two important crystallization parameters are the solvent used and the environmental conditions during storage of the reaction solution (e.g. temperature, relative humidity).1 Different solvents interact differently with a specific solute, affecting greatly the crystallization process.2 The presence of guest lattice solvent molecules within the crystal can affect the molecular conformation of the host molecule in the structure, as well as the type and strength of intermolecular interactions that characterize the crystal lattice, resulting in different physicochemical properties, such as thermodynamic stability, density, solubility, dissolution rate.Solvatomorphism, also named pseudopolymorphism, refers to the ability of a compound to yield crystal structures with unit cells that differ in their elemental composition through the inclusion of various amounts or types of solvent molecules,3 or shortly, the term solvatomorphism is used for designating solvate diversity of a particular host compound.4 There has been a long discussion and interesting arguments among experts in the field on the use of the terms solvatomorph and pseudopolymorph (or supramolecular isomer, co-crystal, solvate, or even false polymorph or quasipolymorph) that could describe, as clear and concise as possible, the above category of crystalline structures.5–13 Reaching consensus on this issue is important for scientific communication, and possibly also for intellectual property purposes.14 In the current study we opted for the term solvatomorphism, to point out that the crystalline structures [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4]·x(solvent) presented here, where HL is 5-phenylimidazole, differ in the type of solvent incorporated during crystallization of the molecule. Polymorphism (the phenomenon wherein the same substance exhibits different crystal packing arrangements15) and solvatomorphism have been interesting topics in crystal structure engineering in relation to the implications on the crystal packing (structural patterns, pre-desired topologies) and, ultimately, to the potential impact on the properties of crystalline solids (crystal property engineering).16–18 With respect to solvatomorphism in particular, the effect of the solvent on the organization of the supramolecular systems (based on solute-solvent specific interactions) is well-known and of great interest, both for academic studies and practical applications.19–21 For example, this has implications in pharmaceutical compounds (affecting their bioavailability, stability, purification process, among other factors, and hence the performance of the drug), in biological systems (where denaturation of proteins, by altering the protein solvent environment, results in significant changes in their biological activities), in the material sciences (e.g. in the self-assembly of MOFs,22,23 in organic and inorganic functional nanomaterials,24,25) to cite a few areas. It is noted that for some important compounds, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), solvatomorphs are the only kind of crystalline forms available for use in single-crystal X-ray diffraction studies.
Over the last years we have prepared and studied a series of 3d metal complexes with substituted imidazole ligands to identify the trends and patterns upon which their molecular and supramolecular assembly is organized, particularly with respect to intermolecular hydrogen-bond motifs and other weak interactions.26–31 With respect to this, we directed the present study to the use of the relatively small and flexible 4-phenylimidazole ligand (HL, Scheme 1) in combination with the tetrafluoroborate salt of copper(II). Copper(II) is an interesting and popular metal ion in coordination chemistry and has been named ‘chameleon’32 as it favours a variety of coordination numbers and geometries33 that can be realized by properly selecting the ligands and the reaction conditions. The 3d9 configuration makes copper(II) subject to Jahn–Teller distortion and this plays a predominant role in its stereochemistry. Thus, square planar or distorted tetrahedral (4-coordinate), square pyramidal or trigonal bipyramidal (5-coordinate), as well as distorted octahedral (6-coordinate) geometries dominate the coordination chemistry of copper(II). Imidazole and its derivatives34,35 are, among others, particularly interesting ligands in bioinorganic36,37 and metallosupramolecular chemistry, employed, for example, in the synthesis of clusters, coordination polymers and MOFs.38,39 4-phenylimidazole can coordinate to a metal ion via its pyridine-type N3-atom towards mononuclear species. At the supramolecular level, the ligand has a hydrogen-bond donor (the pyrrolic-type N1-atom) enabling the formation of strong motifs38,40–43 and is also capable of forming π⋯π stackings44–46 through its 5- and 6-membered aromatic rings.
The tetrafluoroborate ion usually acts as a counter-ion in coordination compounds. Due to its small size, non-nucleophilicity, resistance to coordination and stability, the BF4− ion finds extensive uses as the anion in ionic liquids, as a substitute for ClO4− ion that forms explosive salts, as a spectator for chelates of catalytic transition metals (e.g. Au, Pd, Pt) and as a counter-ion to highly reactive cations, such as nitrosonium, nitronium, pyrylium, aryldiazonium, triethoxonium (in Meerwein's salt) and iodonium (in Barluenga's reagent).47 During the last 40 years or so, there have been reports showing that the BF4− ion is not always stable, and that reaction with the ligand or the metal ion in coordination complexes may occur, often resulting in F−-containing compounds.48,49 Another interesting aspect of the chemistry of BF4− is that sometimes it can coordinate to metal ions in a terminal (monodentate) or bridging manner, but seldom coordination is strong.50–52 We have, therefore, chosen as a source of copper(II) the Cu(BF4)2·6H2O salt in order to study the tetrafluoroborate coordination ability and provide the copper(II) ion with the conditions to realize the optimal coordination geometry from the 5-phenylimidazole/tetrafluoroborate ligand system available.
Following this approach, we have prepared and characterized a total of nineteen new Cu(II) complexes (Scheme 1). Notable solvatomorphism was observed among them and, utilizing a variety of crystallization solvents, seventeen of these compounds (1–17) were found to be solvatomorphs with the general formula [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4]·x(solvent). Alongside, compounds [Cu(HL)4(MeCN)(H2O)0.4](BF4)2 (18) and [Cu{SiF2O(OMe)}2(HL)4]·0.8MeNO2 (19·0.8MeNO2) were also isolated and characterized (see below). All structures (molecular and supramolecular) have been studied and compared to explore the role of the solvent molecules (in terms of hydrogen-bonding capacity, size, shape) in the solvatomorph self-assembly process in the solid state.
Experimental
Materials and instruments
All reagents and starting materials were reagent grade, purchased from standard suppliers and used as received. All manipulations were performed under aerobic conditions. Microanalyses (C, H, N) were performed by the University of Patras microanalytical service. IR spectra (4000–400 cm−1) were recorded on a Perkin-Elmer PC 16 FT-IR spectrometer with the samples prepared as KBr pellets. Thermal decomposition measurements for selected complexes were performed using a Shimadzu TGA 50 analyzer under air; the rate of the temperature increase was 10 °C min−1.Preparation of complexes
X-ray crystallography
Suitable single-crystals of the compounds, covered with paratone-N oil, were mounted in cryo-loops at the end of a copper pin. Diffraction data were collected (ω-scans technique) on a SuperNova Rigaku diffractometer under a flow of nitrogen gas at 100(2) K using Mo Kα radiation (λ = 0.7107 Å), with the exception of compounds 5·1.4(2-PrOH) and 9·2(1-PeOH), for which Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å) was used. Crystallographic data are listed in Table 1. Data were collected and processed by the CRYSALIS CCD and RED software,53 respectively; the reflection intensities were corrected for absorption by the multiscan method. The structures were solved using direct methods (SIR92 (ref. 54) and SHELXT55) or the charge flipping algorithm (Superflip56,57) and the models were refined by full-matrix least-squares on F2 with SHELXL-2019/3.58 All non-H atoms were refined anisotropically; carbon-bound H-atoms were introduced at calculated positions and allowed to ride on their carrier atoms (riding model). The structure of 16 was refined as a non-merohedral twin with a 32![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 68 components ratio. All imidazole H-atoms on the pyrrolic-type N1 atom of the ligands, together with the hydroxyl H-atoms of the protic solvents in compounds 2–9 and the water H-atoms in compounds 1 and 18 were located in difference Fourier maps, and refined isotropically applying soft distance restraints (DFIX). Considerable disorder has been observed in most of the crystal structures. A two-part disorder model was applied to the BF4− ions in complexes 1, 2, 3, 7, 10, 11 and 13, while the highly disordered BF4− ion in complex 5 is best modelled over three sites (three-component model). Similar treatment has been applied for the analogous disordered {SiF2O(OMe)}− ion in compound 19. The HL ligands are also affected by positional disorder: this includes the phenyl ring in molecules 5 (triply disordered), 7, 13 and 15 (two sites) and the entire HL ligand in complex 11. Partial occupancies have been assigned after detailed refinement for the solvent molecules in compounds 5·1.4(2-PrOH), 11·1.2Me2CO, 13·1.85(1,4-dioxane), 14·0.86EtOAc, 16·0.7DIPE and 19·0.8MeNO2. The solvents in 3·2EtOH, 7·2(iso-BuOH), 9·2(1-PeOH), 12·2THF, 14·0.86EtOAc, 15·Et2O, 16·0.7DIPE and the coordinated MeCN in complex 18 have also been modelled over two sites; of these, the EtOAc, Et2O and DIPE solvents (in complexes 14, 15 and 16, respectively) are orientationally disordered about an inversion centre and the coordinated MeCN (in complex 18) about a two-fold axis.
68 components ratio. All imidazole H-atoms on the pyrrolic-type N1 atom of the ligands, together with the hydroxyl H-atoms of the protic solvents in compounds 2–9 and the water H-atoms in compounds 1 and 18 were located in difference Fourier maps, and refined isotropically applying soft distance restraints (DFIX). Considerable disorder has been observed in most of the crystal structures. A two-part disorder model was applied to the BF4− ions in complexes 1, 2, 3, 7, 10, 11 and 13, while the highly disordered BF4− ion in complex 5 is best modelled over three sites (three-component model). Similar treatment has been applied for the analogous disordered {SiF2O(OMe)}− ion in compound 19. The HL ligands are also affected by positional disorder: this includes the phenyl ring in molecules 5 (triply disordered), 7, 13 and 15 (two sites) and the entire HL ligand in complex 11. Partial occupancies have been assigned after detailed refinement for the solvent molecules in compounds 5·1.4(2-PrOH), 11·1.2Me2CO, 13·1.85(1,4-dioxane), 14·0.86EtOAc, 16·0.7DIPE and 19·0.8MeNO2. The solvents in 3·2EtOH, 7·2(iso-BuOH), 9·2(1-PeOH), 12·2THF, 14·0.86EtOAc, 15·Et2O, 16·0.7DIPE and the coordinated MeCN in complex 18 have also been modelled over two sites; of these, the EtOAc, Et2O and DIPE solvents (in complexes 14, 15 and 16, respectively) are orientationally disordered about an inversion centre and the coordinated MeCN (in complex 18) about a two-fold axis.
| Compound reference | 1·2Me2CO·2H2O | 2·2MeOH | 3·2EtOH | 4·2(1-PrOH) | 5·1.4(2-PrOH) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C36H32B2CuF8N8·2(C3H6O)·2(H2O) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·2(CH4O) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·2(C2H6O) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·2(C3H8O) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·1.4(C3H8O) |
| Formula mass/g mol−1 | 966.04 | 877.94 | 905.99 | 934.04 | 897.99 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Triclinic | Triclinic | Triclinic | Triclinic |
| Space group | P21/c |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
| a/Å | 8.8391(5) | 8.8582(4) | 8.9408(8) | 9.1101(3) | 9.0160(8) |
| b/Å | 26.4003(12) | 9.5536(7) | 9.5997(11) | 9.9335(4) | 9.6842(7) |
| c/Å | 9.9765(5) | 13.4305(9) | 13.2336(9) | 13.3316(6) | 13.7262(8) |
| α/° | 90 | 105.470(6) | 104.392(8) | 104.812(4) | 69.875(6) |
| β/° | 106.136(5) | 92.908(5) | 92.473(7) | 94.552(3) | 80.108(7) |
| γ/° | 90 | 107.642(5) | 106.907(9) | 104.842(4) | 72.626(7) |
| Unit cell volume/Å3 | 2236.3(2) | 1033.13(12) | 1044.43(18) | 1113.81(8) | 1070.77(15) |
| Z, Z′ | 2, 0.5 | 1, 0.5 | 1, 0.5 | 1, 0.5 | 1, 0.5 |
| Temperature/K | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) |
| Radiation type, μ/mm−1 | MoKα, 0.573 | MoKα, 0.609 | MoKα, 0.605 | MoKα, 0.569 | CuKα, 1.400 |
| No. of reflections measured | 14![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 738 738 |
7482 | 7679 | 9553 | 6493 |
| No. of independent reflections | 4369 | 4053 | 3665 | 4810 | 3806 |
| R int | 0.073 | 0.027 | 0.038 | 0.036 | 0.046 |
| Final R1 values (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.0442 | 0.0442 | 0.0667 | 0.0431 | 0.0845 |
| Final wR(F2) values (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.0839 | 0.0983 | 0.1458 | 0.0970 | 0.2183 |
| Final R1 values (all data) | 0.0715 | 0.0509 | 0.0867 | 0.0557 | 0.0962 |
| Final wR(F2) values (all data) | 0.0925 | 0.1036 | 0.1626 | 0.1051 | 0.2317 |
| Goodness of fit on F2 | 1.025 | 1.056 | 1.055 | 1.072 | 1.026 |
| Δρmax, Δρmin/e Å−3 | 0.369, −0.500 | 0.446, −0.518 | 0.812, −0.724 | 0.577, −0.504 | 0.781, −0.646 |
| CCDC number | 2342307 | 2342308 | 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 342 342![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 309 309 |
2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 342 342![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 310 310 |
2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 342 342![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 311 311 |
| Compound reference | 6·2(1-BuOH) | 7·2(iso-BuOH) | 8·1.33(tert-BuOH) | 9·2(1-PeOH) | 10·2DMF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C36H32B2CuF8N8·2(C4H10O) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·2(C4H10O) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·1.33(C4H10O) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·2(C5H12O) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·2(C3H7NO) |
| Formula mass/g mol−1 | 962.09 | 962.09 | 912.68 | 990.14 | 960.05 |
| Crystal system | Triclinic | Triclinic | Triclinic | Triclinic | Triclinic |
| Space group |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
| a/Å | 9.2340(6) | 9.2904(12) | 15.0482(5) | 9.3029(7) | 9.0724(7) |
| b/Å | 9.9950(8) | 9.9448(16) | 15.3209(5) | 9.9439(8) | 9.8173(7) |
| c/Å | 13.3246(9) | 14.0725(19) | 16.1054(7) | 14.3527(11) | 14.3397(9) |
| α/° | 105.451(6) | 110.200(13) | 103.710(3) | 73.234(7) | 75.963(6) |
| β/° | 94.995(5) | 94.866(11) | 110.373(4) | 73.473(7) | 71.693(6) |
| γ/° | 104.322(6) | 105.768(12) | 100.587(3) | 73.130(7) | 71.238(7) |
| Unit cell volume/Å3 | 1132.98(15) | 1151.1(3) | 3234.0(2) | 1187.02(17) | 1133.80(15) |
| Z, Z′ | 1, 0.5 | 1, 0.5 | 3, 1.5 | 1, 0.5 | 1, 0.5 |
| Temperature/K | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) |
| Radiation type, μ/mm−1 | MoKα, 0.562 | MoKα, 0.553 | MoKα, 0.585 | CuKα, 1.323 | MoKα, 0.563 |
| No. of reflections measured | 8034 | 8798 | 29![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 587 587 |
7751 | 9021 |
| No. of independent reflections | 3926 | 4261 | 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 042 042 |
4456 | 4665 |
| R int | 0.070 | 0.061 | 0.057 | 0.022 | 0.028 |
| Final R1 values (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.0634 | 0.0565 | 0.0573 | 0.0347 | 0.0401 |
| Final wR(F2) values (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.1504 | 0.1292 | 0.1353 | 0.0872 | 0.0911 |
| Final R1 values (all data) | 0.0861 | 0.0796 | 0.0867 | 0.0401 | 0.0496 |
| Final wR(F2) values (all data) | 0.1593 | 0.1503 | 0.1558 | 0.0922 | 0.1003 |
| Goodness of fit on F2 | 1.182 | 1.051 | 1.038 | 1.054 | 1.015 |
| Δρmax, Δρmin/e Å−3 | 0.491, −0.543 | 0.394, −1.008 | 1.081, −0.614 | 0.341, −0.373 | 0.482, −0.447 |
| CCDC number | 2342312 | 2342313 | 2342314 | 2342315 | 2342316 |
| Compound reference | 11·1.2Me2CO | 12·2THF | 13·1.85(1,4-dioxane) | 14·0.86EtOAc | 15·Et2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C36H32B2CuF8N8·1.2(C3H6O) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·2(C4H8O) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·1.85(C4H8O2) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·0.86(C4H8O2) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·C4H10O |
| Formula mass/g mol−1 | 883.55 | 958.06 | 976.85 | 889.62 | 887.97 |
| Crystal system | Triclinic | Triclinic | Triclinic | Triclinic | Triclinic |
| Space group |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
| a/Å | 8.950(3) | 9.4113(9) | 9.2398(7) | 8.6393(5) | 8.5831(9) |
| b/Å | 9.655(3) | 10.2218(12) | 9.9904(9) | 9.7696(6) | 9.7612(11) |
| c/Å | 13.284(4) | 12.8120(12) | 12.6976(12) | 12.8911(8) | 12.8928(11) |
| α/° | 73.31(3) | 87.054(9) | 78.043(8) | 99.164(5) | 98.221(8) |
| β/° | 87.75(2) | 75.179(9) | 85.634(7) | 93.555(5) | 93.854(8) |
| γ/° | 72.57(3) | 70.705(10) | 73.908(7) | 106.361(6) | 107.301(10) |
| Unit cell volume/Å3 | 1047.6(5) | 1123.8(2) | 1101.53(17) | 1024.08(11) | 1013.80(19) |
| Z, Z′ | 1, 0.5 | 1, 0.5 | 1, 0.5 | 1, 0.5 | 1, 0.5 |
| Temperature/K | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) |
| Radiation type, μ/mm−1 | MoKα, 0.600 | MoKα, 0.566 | MoKα, 0.582 | MoKα, 0.615 | MoKα, 0.620 |
| No. of reflections measured | 7907 | 9610 | 8689 | 6976 | 7573 |
| No. of independent reflections | 3654 | 4635 | 3848 | 3594 | 4186 |
| R int | 0.075 | 0.046 | 0.052 | 0.028 | 0.038 |
| Final R1 values (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.0891 | 0.0565 | 0.0898 | 0.0555 | 0.0466 |
| Final wR(F2) values (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.2167 | 0.1380 | 0.2293 | 0.1438 | 0.0922 |
| Final R1 values (all data) | 0.1478 | 0.0761 | 0.1355 | 0.0619 | 0.0703 |
| Final wR(F2) values (all data) | 0.2647 | 0.1537 | 0.2690 | 0.1500 | 0.1025 |
| Goodness of fit on F2 | 1.043 | 1.061 | 1.020 | 1.045 | 1.033 |
| Δρmax, Δρmin/e Å−3 | 0.773, −0.742 | 0.538, −0.541 | 0.895, −0.703 | 1.144, −1.149 | 0.524, −0.426 |
| CCDC number | 2342317 | 2342318 | 2342319 | 2342320 | 2342321 |
| Compound reference | 16·0.7DIPE | 17·(n-hexane) | 18 | 19·0.8MeNO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C36H32B2CuF8N8·0.70(C6H14O) | C36H32B2CuF8N8·C6H14 | C38H35.80CuN9O0.40(BF4)2 | C38H38CuF4N8O4Si2·0.8(CH3NO2) | |
| Formula mass/g mol−1 | 885.37 | 900.03 | 862.11 | 915.32 | |
| Crystal system | Triclinic | Triclinic | Orthorhombic | Monoclinic | |
| Space group |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) |
Pnn2 | P2/n | |
| a/Å | 8.7016(6) | 8.7411(10) | 11.1724(4) | 17.5681(7) | |
| b/Å | 9.8158(8) | 9.7698(14) | 12.3470(6) | 9.8878(3) | |
| c/Å | 12.9608(14) | 12.811(2) | 13.8235(6) | 24.2057(9) | |
| α/° | 96.464(8) | 97.513(13) | 90 | 90 | |
| β/° | 96.268(8) | 93.679(12) | 90 | 96.253(3) | |
| γ/° | 106.150(7) | 107.576(12) | 90 | 90 | |
| Unit cell volume/Å3 | 1045.07(16) | 1027.8(3) | 1906.89(14) | 4179.8(3) | |
| Z, Z′ | 1, 0.5 | 1, 0.5 | 2, 0.5 | 4, 1 | |
| Temperature/K | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) | |
| Radiation type, μ/mm−1 | MoKα, 0.600 | MoKα, 0.610 | MoKα, 0.656 | MoKα, 0.654 | |
| No. of reflections measured | 3674 | 7520 | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 413 413 |
37![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 126 126 |
|
| No. of independent reflections | 3674 | 4022 | 4140 | 37![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 126 126 |
|
| R int | — | 0.032 | 0.042 | 0.054 | |
| Final R1 values (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.0855 | 0.0508 | 0.0453 | 0.0610 | |
| Final wR(F2) values (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.2155 | 0.1155 | 0.1162 | 0.1546 | |
| Final R1 values (all data) | 0.1009 | 0.0640 | 0.0543 | 0.0778 | |
| Final wR(F2) values (all data) | 0.2269 | 0.1261 | 0.1259 | 0.1676 | |
| Goodness of fit on F2 | 1.101 | 1.060 | 1.021 | 1.061 | |
| Δρmax, Δρmin/e Å−3 | 1.339, −1.089 | 1.473, −0.997 | 0.636, −0.410 | 1.057, −0.693 | |
| CCDC number | 2342322 | 2342323 | 2342324 | 2342325 |
Geometric/crystallographic calculations were carried out using PLATON,59 OLEX2 (ref. 60) and WINGX61 packages; molecular/packing graphics were prepared with MERCURY.62 Photos of the crystals are shown in Fig. S1.†
Results and discussion
Synthetic comments
A variety of reactions were initially studied with the aim of preparing the largest possible number of complexes exploring the Cu(II)/HL/tetrafluoroborate system. Our trials included differing reactant ratios and concentrations, solvents, crystallization conditions and temperatures. It soon turned out that the reaction system yielded solvatomorphic compounds of the general formula [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4]·x(solvent). Utilizing a variety of crystallization solvents (polar protic, polar aprotic and non-polar) a series of seventeen crystalline solvatomorphs have been isolated. The general synthetic route with the individual formulae of the resulting complexes are illustrated in Scheme 1. A schematic illustration of the molecular structure of the solvatomorphs is shown in Scheme 2. Cu(II) is air stable and the synthetic work was thus conducted under aerobic conditions in the normal laboratory atmosphere. Attempts with iso-pentanol (15), MeNO2 (16) and tert-BuOH (17) as main reaction solvents did not produce exactly the anticipated solvatomorphs with respect to the included solvents; instead, the solvents used in the layering technique for crystal growth were found within the crystals, resulting in the 15·Et2O, 16·0.7DIPE and 17·(n-hexane) solvatomorphs, respectively. In the synthesis of compound 18, using CH2Cl2/MeCN as reaction solvents, the two tetrafluoroborato ligands in the anticipated [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] molecule have been replaced by a MeCN and a partially occupied water molecule (40%), producing crystals of the cationic [Cu(HL)4(MeCN)(H2O)0.4](BF4)2 complex (Fig. S2a†). The compounds were obtained by reactions with a metal-to-ligand ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2.5 or 1
2.5 or 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 and have an octahedral geometry at the metal centre; their colour is violet or mauve.
4 and have an octahedral geometry at the metal centre; their colour is violet or mauve.
 | ||
| Scheme 2 Schematic representation of the general molecular structure of 1–17 which have the same coordination entity. | ||
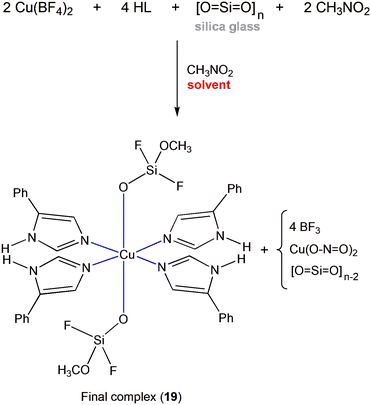
As in all reactions, Cu(BF4)2·6H2O was used as the metal source in the synthesis of 19·0.8MeNO2; however, the final crystalline product was identified as [Cu{SiF2O(OMe)}2(HL)4]·0.8MeNO2 (Schemes 3 and 4, Fig. S3a†). The coordinated {SiF2O(OMe)}− ions, which appear for the first time in coordination chemistry, were actually generated in situ by the reaction of fluoride anions from BF4− with the glass surface of the vial used to grow crystals of the complex. The proposed mechanism (Scheme 5) involves the following steps:
i) Initial formation of the complex I in which two molecules of nitromethane act as bidentate ligands and two molecules of 5-phenylimidazole as monodentate ligands. The complexation of nitromethane serves to facilitate the subsequent attack of its methyl group by the difluorosilicate anion.
ii) The difluorosilicate dianion (II), released from the glass surface upon attack of silicon atoms on the surface by tetrafluoroborate anions (Scheme 4), then partially displaces the nitromethane from the metal cation leading to the new complex III. The driving force for the liberation of the difluorosilicate dianion from the glass surface is the formation of the very strong Si–F bonds.47
iii) Facile intramolecular SN2 reaction of the complexed difluorosilicate anion on the neighbouring methyl group then leads to methylation of the difluorosilicate dianion with simultaneous formation of nitrite anion (complex IV). The latter is then displaced by a third molecule of 5-phenylimidazole to provide the new complex V.
iv) Steps 2 and 3 are then repeated with a second difluorosilicate dianion to give the final complex through the intermediate complexes VI and VII.
Four final remarks concerning our above mentioned mechanistic ideas are worthy of note at this point: (a) Further replacement in II by fluorides is not probable, because silicon bears a large number of electrons (totally 24!) around it, while O− is with +I (and +M) effects. Therefore, silicon cannot be attacked by other nucleophiles; moreover, O2− is an extremely bad leaving group, much worse than the already very bad HO− leaving group. (b) Recent theoretical studies63 have shown the possibility of gradual replacement of OH groups by F atoms in silicon dioxide until the formation of SiF4; in the theoretical study, however, the etchant was HF molecule, while in our experimental work the attacking species is F− (from BF4−). The glassware used in our laboratory is borosilicate glass. This has a more complicated structure compared to that of the simple silica glass used in the calculations, because it contains B atoms in the lattice and intermediate Na+ ions, but again the dominant species is SiO2. (c) It is well known in organic chemistry that the nitro group can play diverse roles that make several transformations;64 and (d) Reactions in which fluoride species attack to glassware to form silicon–fluoride compounds have been described in the literature.48
All attempts to employ chlorinated compounds (CH2Cl2, CHCl3) as crystallization solvents failed to give crystalline materials. Also attempts to prepare solvatomorphs [Cu(HL)4(BF4)2] using DMSO as the reaction solvent were in vain, probably due to the excellent donor capacity of this solvent which is readily coordinated to copper(II) hampering complexation with HL and BF4−.
All crystalline products were characterized by IR spectroscopy, microanalyses, single-crystal X-ray diffraction and TGA experiments (for selected compounds). Various trials to obtain crystals of the solvent-free forms, including triethyl orthoformate as a drying agent and several solvent mixtures, were in vain.
Description of the structures
To facilitate discussion and molecular comparison, the same numbering scheme has been assigned (where applicable) to the HL ligand atoms and the coordinated tetrafluoroborate ions for all compounds presented herein (Fig. 1).The X-ray structure determination of all compounds (1–19) revealed that the initially used 4-phenylimidazole ligand (HL) is present as its 5-phenylimidazole tautomeric form. This rearrangement, termed as annular tautomerism of 4(5)-phenylimidazole,65–67 is a result of the amphoteric character of the imidazole and involves the exchange of a proton from the pyrrole-type atom N1 to the pyridine-type atom N3. Tautomerism is accompanied by a significant change in ligand conformation and it is thus likely that the 5-phenyl form of the HL ligand is the most favourable one in terms of the formation of these complexes.
Compounds 1–17 crystallize in the P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) space group, with the exception of 1·2Me2CO·2H2O crystallizing in P21/c (Table 1). The asymmetric unit of these compounds, except for 8·1.33(tert-BuOH), contains half a [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] host molecule (Z′ = 1/2), with the copper(II) atom situated on an inversion centre. In 8·1.33(tert-BuOH) there are one and a half host molecules in the asymmetric unit (Z′ = 3/4), in which one of the two symmetry-independent copper(II) atoms is in a general position (Cu1) and the second one (Cu2) on an inversion centre. As previously mentioned, the isolated crystalline product 18, [Cu(HL)4(MeCN)(H2O)0.4](BF4)2, using CH2Cl2/MeCN as solvents, is not the expected solvatomorph; however it has been included in the study for comparison purposes. It has molecular symmetry, with a C2 axis passing through the NMeCN–Cu–OH2O direction of the complex (Z′ = 1/2) and crystallizes in the Pnn2 space group (Fig. S2a†). The replacement of the BF4− ligands with {SiF2O(OMe)}− coordinated ions in the solvatomorph 19·0.8MeNO2 has an impact on its molecular and crystal symmetry (Fig. S3†): the complex lacks molecular symmetry and crystallizes in the P2/n space group. The coordination geometry in all complexes (1–19) is distorted octahedral: this involves the pyridine-type nitrogen atom from the four ligands in the equatorial positions; in the axial positions there are two fluorine atoms from the terminal BF4− ions (1–17), or one OH2O and one NMeCN atom (18), or two O atoms from the monodentate {SiF2O(OMe)}− ions (19). The CuII − FBF4– bonds in 1–17 are weak (2.44–2.55 Å) and the metal centre is in an axially elongated octahedral environment (4 + 2); this is a consequence of the Jahn-Teller effect, typical for 3d9 systems. BF4− was traditionally considered as a typical example of a ‘noncoordinating ion’ 40 years ago or so. However, with the advent of single-crystal X-ray crystallography, it became evident that this anion can also be coordinated. To account for the coordination of this complex anion (and other anions such as CF3SO3−, ClO4−, AlX4−, MF6− with X = Cl, Br, I; M = P, As, Sb, etc.), the term ‘weakly coordinating anion’ (WCA) was coined.51 This expression allows for weak coordination, but also includes the potential of such complexes to serve as precursors of the ‘noncoordinated’ cation, for example, in catalytic processes. Thus, in complexes 1–17, the BF4− ion can be best described as WCA.
space group, with the exception of 1·2Me2CO·2H2O crystallizing in P21/c (Table 1). The asymmetric unit of these compounds, except for 8·1.33(tert-BuOH), contains half a [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] host molecule (Z′ = 1/2), with the copper(II) atom situated on an inversion centre. In 8·1.33(tert-BuOH) there are one and a half host molecules in the asymmetric unit (Z′ = 3/4), in which one of the two symmetry-independent copper(II) atoms is in a general position (Cu1) and the second one (Cu2) on an inversion centre. As previously mentioned, the isolated crystalline product 18, [Cu(HL)4(MeCN)(H2O)0.4](BF4)2, using CH2Cl2/MeCN as solvents, is not the expected solvatomorph; however it has been included in the study for comparison purposes. It has molecular symmetry, with a C2 axis passing through the NMeCN–Cu–OH2O direction of the complex (Z′ = 1/2) and crystallizes in the Pnn2 space group (Fig. S2a†). The replacement of the BF4− ligands with {SiF2O(OMe)}− coordinated ions in the solvatomorph 19·0.8MeNO2 has an impact on its molecular and crystal symmetry (Fig. S3†): the complex lacks molecular symmetry and crystallizes in the P2/n space group. The coordination geometry in all complexes (1–19) is distorted octahedral: this involves the pyridine-type nitrogen atom from the four ligands in the equatorial positions; in the axial positions there are two fluorine atoms from the terminal BF4− ions (1–17), or one OH2O and one NMeCN atom (18), or two O atoms from the monodentate {SiF2O(OMe)}− ions (19). The CuII − FBF4– bonds in 1–17 are weak (2.44–2.55 Å) and the metal centre is in an axially elongated octahedral environment (4 + 2); this is a consequence of the Jahn-Teller effect, typical for 3d9 systems. BF4− was traditionally considered as a typical example of a ‘noncoordinating ion’ 40 years ago or so. However, with the advent of single-crystal X-ray crystallography, it became evident that this anion can also be coordinated. To account for the coordination of this complex anion (and other anions such as CF3SO3−, ClO4−, AlX4−, MF6− with X = Cl, Br, I; M = P, As, Sb, etc.), the term ‘weakly coordinating anion’ (WCA) was coined.51 This expression allows for weak coordination, but also includes the potential of such complexes to serve as precursors of the ‘noncoordinated’ cation, for example, in catalytic processes. Thus, in complexes 1–17, the BF4− ion can be best described as WCA.
The bond lengths and angles observed for the current complexes are similar (e.g. the CuII–NHL bond lengths range from 1.99 to 2.02 Å). To compare the conformation of the [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] molecules in compounds 1–17, the relative orientation of the imidazole rings within each complex, as well as the orientation of the phenyl ring relative to the imidazole ring for each HL ligand are reported in Table 2. It appears that the conformation of the complexes is similar, with variations that presumably help to minimize steric hindrance, facilitate the effective formation of intermolecular synthons, and accommodate the included solvents. Considering the similarities in the unit-cell dimensions, the same space group (P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) ) and Z′ (= 1/2) and the similar internal arrangement in the related crystal lattices [in this instance, the conformation of the Cu(BF4)2(HL)4 host molecules], compounds 1–17 (with the exception of 1 and 8) could be described as isostructural solvatomorphs.68,69 However, the different hydrogen-bonding capabilities of the solvent molecules lead to variations in the networks of intermolecular interactions formed (see below).
) and Z′ (= 1/2) and the similar internal arrangement in the related crystal lattices [in this instance, the conformation of the Cu(BF4)2(HL)4 host molecules], compounds 1–17 (with the exception of 1 and 8) could be described as isostructural solvatomorphs.68,69 However, the different hydrogen-bonding capabilities of the solvent molecules lead to variations in the networks of intermolecular interactions formed (see below).
| Compound | ImA/ImB | ImA/PhRA | ImB/PhRB |
|---|---|---|---|
| a ImA: imidazole ring N1A–C2A–N3A–C4A–C5A; ImB: imidazole ring N1B–C2B–N3B–C4B–C5B; PhRA: phenyl ring C6A–C7A–C8A–C9A–C10A–C11A; PhRB: C6B–C7B–C8B–C9B–C10B–C11B. b Values for all orientations of the disordered phenyl ring PhRB. c For comparison with the HL ligands of the other structures, only the centrosymmetric [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] molecule of 8·1.33(tert-BuOH) is reported. d Values for the two orientations B and C of the disordered ligand B. | |||
| 1 | 66.1(1) | 8.0(1) | 26.4(1) |
| 2 | 81.0(1) | 12.0(2) | 23.4(1) |
| 3 | 80.6(2) | 13.9(2) | 27.8(2) |
| 4 | 88.3(1) | 16.7(1) | 14.3(1) |
| 5 | 79.5(2) | 4.1(3) | 4.4(3)/41.0(3)/34.3(3)b |
| 6 | 88.2(2) | 18.5(2) | 18.4(3) |
| 7 | 82.1(1) | 16.4(2) | 7.9(2)/26.7(2)b |
| 8 | 86.5(1) | 7.9(1) | 21.7(3) |
| 9 | 82.4(1) | 6.8(1) | 15.1(1) |
| 10 | 73.8(1) | 2.6(2) | 22.4(1) |
| 11 | 81.3(5)/79.9(5) | 11.6(4) | 29.5(7)/20.1(7) |
| 12 | 83.4(1) | 13.4(2) | 25.6(2) |
| 13 | 84.4(3) | 4.3(3) | 21.5(8)/48.9(8)b |
| 14 | 80.2(2) | 17.0(2) | 31.5(2) |
| 15 | 79.7(1) | 17.4(1) | 23.4(3)/44.2(3)b |
| 16 | 83.0(3) | 29.8(4) | 15.7(3) |
| 17 | 84.1(1) | 28.3(1) | 17.7(1) |
The geometrical parameters of the strong H-bonding motifs for all compounds are given in Table 3. The supramolecular structures of the compounds are sorted and studied into three groups based on the type of solvent they contain (polar protic, polar aprotic and non-polar) and the resulting hydrogen-bonding patterns (synthons).
| D–H⋯A | D–H | H⋯A | D⋯A | <(DHA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a For the disordered fluorine atoms of the BF4− ions, only the hydrogen-bonding of the major-occupancy disorder components is shown. Symmetry codes: (i) x, y, 1 + z; (ii) −1 + x, y, −1 + z; (iii) x, 1/2 − y, −1/2 + z; (iv) x, −1 + y, z; (v) 1 + x, y, 1 + z; (vi) x, y, −1 + z; (vii) 1 + x, y, z; (viii) x, 1 + y, z; (ix) 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z; (x) −x, −y, −z; (xi) 1− x, 2 − y, 1 − z; (xii) −1 + x, y, z; (xiii) −x, 1 − y, −z; (xiv) 1 + x, 1 + y, z; (xv) −x, −y, 1 − z; (xvi) x, −1 + y, −1 + z; (xvii) 2 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z; (xviii) 1 − x, −y, 1 − z; (xix) 1/2 − x, 1/2 + y, 1/2 − z; (xx) 1/2 + x, 3/2 − y, 1/2 − z; (xxi) 3/2 − x, y, 3/2 − z; (xxii) 5/2 − x, y, 3/2 − z. | ||||
| 1·2Me2CO·2H2O | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2Ai | 0.88(2) | 1.93(2) | 2.796(10) | 166(2) |
| N1B–H1B⋯O1i | 0.86(2) | 1.92(2) | 2.777(3) | 173(3) |
| O1–H1⋯F3Aii | 0.81(2) | 2.03(2) | 2.832(5) | 168(3) |
| O1–H2⋯O2iii | 0.84(2) | 1.94(2) | 2.776(3) | 174(3) |
| 2·2MeOH | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2Aiv | 0.85(2) | 1.91(2) | 2.683(4) | 152(3) |
| N1B–H1B⋯O1v | 0.85(2) | 1.95(2) | 2.804(3) | 177(3) |
| O1–H1⋯F3Avi | 0.85(2) | 1.90(3) | 2.705(9) | 158(4) |
| 3·2EtOH | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2Aiv | 0.86(2) | 1.93(3) | 2.722(6) | 151(5) |
| N1B–H1B⋯O1 | 0.86(2) | 1.96(3) | 2.798(6) | 165(6) |
| O1–H1⋯F3Avii | 0.86(2) | 1.90(1) | 2.671(8) | 148(4) |
| 4·2(1-PrOH) | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2iv | 0.85(2) | 1.91(2) | 2.749(2) | 168(3) |
| N1B–H1B⋯O1v | 0.86(2) | 1.96(2) | 2.812(2) | 173(3) |
| O1–H1⋯F3vi | 0.83(3) | 1.95(3) | 2.775(2) | 173(3) |
| 5·1.4(2-PrOH) | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2Aviii | 0.85(5) | 2.03(6) | 2.757(11) | 143(6) |
| N1B–H1B⋯O1vii | 0.86(4) | 1.86(5) | 2.721(11) | 176(9) |
| O1–H1⋯F3A | 0.82(5) | 1.79(5) | 2.586(12) | 163(5) |
| 6·2(1-BuOH) | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2ix | 0.85(2) | 1.93(3) | 2.754(5) | 161(5) |
| N1B–H1B⋯O1vii | 0.86(2) | 1.93(2) | 2.773(5) | 168(5) |
| O1–H1⋯F3 | 0.84(2) | 1.97(3) | 2.767(5) | 159(6) |
| 7·2(iso-BuOH) | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2Aiv | 0.84(2) | 1.97(2) | 2.812(7) | 176(3) |
| N1B–H1B⋯OA1vii | 0.83(2) | 2.10(2) | 2.925(10) | 172(4) |
| OA1–HA1⋯F3A | 0.84(2) | 1.99(4) | 2.790(9) | 160(9) |
| 8·1.33(tert-BuOH) | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F10x | 0.85(2) | 2.05(2) | 2.805(3) | 148(3) |
| N1B–H1B⋯F2xi | 0.85(2) | 2.00(2) | 2.820(3) | 163(3) |
| N1C–H1C⋯O1xii | 0.83(2) | 1.97(2) | 2.778(4) | 163(4) |
| N1D–H1D⋯O2 | 0.86(2) | 1.96(2) | 2.811(4) | 168(3) |
| N1E–H1E⋯F6 | 0.85(2) | 1.91(2) | 2.741(3) | 164(3) |
| N1F–H1F⋯F3xiii | 0.85(2) | 2.04(2) | 2.857(3) | 161(3) |
| O1–H1⋯F11xiv | 0.84(2) | 2.01(2) | 2.841(3) | 170(4) |
| O2–H2⋯F7ix | 0.84(2) | 2.08(3) | 2.844(3) | 150(4) |
| 9·2(1-PeOH) | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2viii | 0.85(2) | 2.01(2) | 2.818(2) | 159(2) |
| N1B–H1B⋯O1vii | 0.85(2) | 1.92(2) | 2.755(2) | 164(2) |
| O1–H1⋯F3 | 0.80(2) | 2.01(2) | 2.806(2) | 171(3) |
| 10·2DMF | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2Axi | 0.84(2) | 1.95(2) | 2.786(7) | 169(3) |
| N1B–H1B⋯O1xii | 0.84(2) | 1.96(2) | 2.776(3) | 164(2) |
| 11·1.2Me2CO | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2Axv | 0.85(2) | 2.07(5) | 2.832(7) | 149(7) |
| N1B–H1B⋯O1 | 0.86(2) | 2.03(1) | 2.839(2) | 157(6) |
| N1C–H1C⋯F3Bvii | 0.86(2) | 2.00(4) | 2.855(2) | 172(2) |
| 12·2THF | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2xii | 0.85(2) | 2.12(2) | 2.965(3) | 171(3) |
| N1B–H1B⋯OAxvi | 0.85(2) | 1.95(2) | 2.778(7) | 164(4) |
| 13·1.85(1,4-dioxane) | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2Aiv | 0.85(2) | 2.02(4) | 2.823(1) | 156(7) |
| N1B–H1B⋯O1 | 0.85(2) | 2.06(4) | 2.840(1) | 153(8) |
| 14·0.86EtOAc | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2ix | 0.84(2) | 1.97(2) | 2.768(4) | 157(4) |
| N1B–H1B⋯F3vii | 0.84(2) | 2.14(3) | 2.869(4) | 146(4) |
| 15·Et2O | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2xi | 0.84(2) | 1.96(2) | 2.754(3) | 157(3) |
| N1B–H1B⋯F3vii | 0.85(2) | 2.13(2) | 2.866(3) | 144(2) |
| 16·0.7DIPE | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2xii | 0.86(2) | 2.06(4) | 2.862(7) | 155(7) |
| N1B–H1B⋯F3viii | 0.86(2) | 2.00(4) | 2.782(6) | 150(7) |
| 17·(n-hexane) | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F2xvii | 0.85(2) | 2.11(2) | 2.876(3) | 149(3) |
| N1B–H1B⋯F3xviii | 0.84(2) | 1.98(2) | 2.770(3) | 155(3) |
| 18 | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F1xix | 0.87(3) | 1.99(3) | 2.825(6) | 161(6) |
| N1B–H1B⋯F2xx | 0.86(3) | 1.96(3) | 2.792(5) | 161(5) |
| O1–H1⋯F3 | 0.85(2) | 1.57(2) | 2.414(9) | 179(9) |
| 19·0.8MeNO2 | ||||
| N1A–H1A⋯F4xxi | 0.86(2) | 1.94(3) | 2.719(5) | 150(4) |
| N1B–H1B⋯F2xxii | 0.86(2) | 1.87(2) | 2.686(5) | 158(4) |
| N1C–H1C⋯F3Aiv | 0.86(2) | 1.98(2) | 2.828(5) | 168(4) |
| N1D–H1D⋯F1 | 0.86(2) | 1.98(2) | 2.828(4) | 169(4) |
The supramolecular patterns of a molecule in its crystalline environment are visualized by the 3D molecular Hirshfeld surface, defined by the molecule and the proximity of its nearest neighbours, and therefore encode information about all its intermolecular interactions.70–72 In addition, the accompanying 2D fingerprint plots provide information for the relative contribution of the various types of interactions on the Hirshfeld surfaces. Hirshfeld surfaces and associated fingerprints for three representative structures with different solvent type, 6·2(1-BuOH) with polar protic solvent, 10·2DMF with polar aprotic solvent and 17·(n-hexane) with non-polar solvent, along with detailed description, are given in Fig. S4.†
The molecular self-assembly in the hydrated compound 1·2Me2CO·2H2O (Fig. 1) is directed by the same type of hydrogen-bonding patterns as in compounds 2–7 and 9, forming 2D layers parallel to the ac plane of the unit cell (Table 3). In addition, the second H-atom of the water molecule, which is not involved in this pattern, forms a strong Ow–H⋯Oacetone interaction with a lattice acetone solvent molecule. It appears that the above presented P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) crystal lattice of the isostructural compounds 2–7 and 9 can no longer accommodate the additional acetone molecule, and eventually 1·2Me2CO·2H2O crystallizes in the P21/c space group.
crystal lattice of the isostructural compounds 2–7 and 9 can no longer accommodate the additional acetone molecule, and eventually 1·2Me2CO·2H2O crystallizes in the P21/c space group.
Compound 8·1.33(tert-BuOH), in P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) with 1.5 [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] molecules in the asymmetric unit, seems more complicated. Nevertheless, the molecules are similarly linked via N–H⋯F and N–H⋯Otert-BuOH−H⋯F patterns forming rigid 2D layers parallel to the (10
with 1.5 [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] molecules in the asymmetric unit, seems more complicated. Nevertheless, the molecules are similarly linked via N–H⋯F and N–H⋯Otert-BuOH−H⋯F patterns forming rigid 2D layers parallel to the (10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) ) plane of the unit cell with the solvents and two of the four ligands of each complex lying on either side of the layers.
) plane of the unit cell with the solvents and two of the four ligands of each complex lying on either side of the layers.
In all 1–9 structures, all hydrogen-bond donor and acceptor groups of the molecules and solvents are fully engaged in hydrogen-bonding motifs (see Table 3). When not hindered by steric effects or the prevailing stronger patterns, some weak π⋯π interactions between the aromatic rings of the ligands in the layers and between adjacent layers, along with a few non-classic C–H⋯F/O and C–H⋯π interactions, are also observed and help to stabilize the structures (Fig. S4†).
![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) ) plane. Some π⋯π interactions and other weak contacts between these layers organize the 3D assembly of the structure. The second 1,4-dioxane molecule (O2) is not involved in any major bonding pattern, except for two weak C–H⋯O interactions with the first dioxane molecule on either side.
) plane. Some π⋯π interactions and other weak contacts between these layers organize the 3D assembly of the structure. The second 1,4-dioxane molecule (O2) is not involved in any major bonding pattern, except for two weak C–H⋯O interactions with the first dioxane molecule on either side.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, contrary to 1
1, contrary to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 (or 1
2 (or 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1.33 in 8) observed in the preceding structures. The 1
1.33 in 8) observed in the preceding structures. The 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 ratios are dictated by the need to fully exploit all strong hydrogen-bond donor and acceptor groups, whereas in compounds 14–17 this is not necessary because the solvents are not engaged in any strong hydrogen-bonding pattern. In addition, the placement of the solvents on inversion centres helps to reduce the relative volume (%) they occupy within the unit cell and to accommodate them efficiently, considering they are large and elongated in shape. There is no solvent included in the crystal structure of 18 but only BF4− counterions located in lattice pockets (Fig. S7†); likewise, the nitromethane solvent in 19·0.8MeNO2 is also located in lattice pockets.
2 ratios are dictated by the need to fully exploit all strong hydrogen-bond donor and acceptor groups, whereas in compounds 14–17 this is not necessary because the solvents are not engaged in any strong hydrogen-bonding pattern. In addition, the placement of the solvents on inversion centres helps to reduce the relative volume (%) they occupy within the unit cell and to accommodate them efficiently, considering they are large and elongated in shape. There is no solvent included in the crystal structure of 18 but only BF4− counterions located in lattice pockets (Fig. S7†); likewise, the nitromethane solvent in 19·0.8MeNO2 is also located in lattice pockets.
| Compounda | V void/Vcell (%) | SGb (Z)c | Void space of solvents or counterions (for 18) |
|---|---|---|---|
| a 1 to 17: [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4]. b SG: space group. c Z: number of molecules in the unit cell. d Only the major-occupancy conformer of a disordered phenyl ring close to the solvent is used in the calculations. | |||
| 1·2Me2CO·2H2O | 25.4 | P21/c (2) | Channels along c |
| 2·2MeOH | 17.5 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along a |
| 3·2EtOH | 17.6 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along a |
| 4·2(1-PrOH) | 25.0 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along a |
| 5·1.4(2-PrOH)d | 20.9 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along [1![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0] 0] |
| 6·2(1-BuOH) | 26.2 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along a |
| 7·2(iso-BuOH)d | 25.3 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along a |
| 8·1.33(tert-BuOH) | 19.6 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (3) (3) |
Lattice pockets |
| 9·2(1-PeOH) | 30.1 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along a |
| 10·2DMF | 26.9 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along a |
| 11·1.2Me2COd | 16.3 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Lattice pockets |
| 12·2THF | 24.9 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along a |
| 13·1.85(1,4-dioxane) | 20.8 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along b |
| 14·0.86EtOAc | 19.1 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along a |
| 15·Et2O | 16.0 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along a |
| 16·0.7DIPE | 21.6 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along a |
| 17·(n-hexane) | 20.2 |
P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) (1) (1) |
Channels along a |
| 18 | 10.9 | Pnn2 (2) | Lattice pockets (BF4−) |
| 19·0.8MeNO2 | 9.5 | P2/n (4) | Lattice pockets |
IR study and TGA data in brief
The selected IR wavenumbers for the complexes cited in the Experimental Section refer to crushed, freshly isolated crystals; for this reason, the spectra exhibit bands of the lattice solvents. The presence of H-bonded H2O or alcohol lattice molecules in 1–9 is proven by the appearance of a medium-to-strong intensity band at ∼3400 cm−1 assigned to the ν(OH) mode; the broadness of the band is indicative of the participation of the –OH groups in H-bonds. This band is absent, as expected, from the spectra of 10–19, with the exception of 18; the spectrum of the latter shows a weak broad band assigned to ν(OH) of the coordinated H2O molecule.74 The bands at ∼1675 (1, 11), 1650 (10) and 1701 cm−1 (14) can be safely assigned to the characteristic ν(C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) mode of the carbonyl (1, 11), amide (10) and ester (14) functionalities that are present in the lattice solvents of the complexes. The ν(C
O) mode of the carbonyl (1, 11), amide (10) and ester (14) functionalities that are present in the lattice solvents of the complexes. The ν(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N) mode of the coordinated MeCN is hardly seen in the spectrum of 18, while the medium-intensity bands at 1561 and 1376 cm−1 in the spectrum of 19 are attributed to the νas(NO2) and νs(NO2), respectively, vibrations of the lattice MeNO2.75 A common weak to medium, broad feature in the spectra of all the complexes is due to the ν(NH) mode of the 5-phenylimidazole ligands, the broadness again indicating the participation of the N–H group in H bonds.
N) mode of the coordinated MeCN is hardly seen in the spectrum of 18, while the medium-intensity bands at 1561 and 1376 cm−1 in the spectrum of 19 are attributed to the νas(NO2) and νs(NO2), respectively, vibrations of the lattice MeNO2.75 A common weak to medium, broad feature in the spectra of all the complexes is due to the ν(NH) mode of the 5-phenylimidazole ligands, the broadness again indicating the participation of the N–H group in H bonds.
The band at 1026 cm−1 in the spectrum of 19 is assigned74 to the ν(Si–F) mode of the tetrahedral SiF2O(OMe)− ligand. The presence of tetrafluoroborato ligands (1–17) and BF4− counterions (18) is manifested by the appearance of the characteristic ν(BF) and δ(FBF) bands. The four normal modes of vibration of the ‘free’, i.e. uncoordinated (Td) BF4− ion are the ν1(A1) [νs(BF)], ν2(E) [δd(FBF)], ν3(F2) [vd(BF)] and ν4(F2) [δd(FBF)] ones;74 only ν3 and ν4 are IR-active. Monodentate coordination of the BF4− group (as in 1–17) lowers the symmetry from Td to C3v, splitting each of the triply degenerate modes, v3 and v4, into two components (F2 → A1 + E). The previously IR-inactive modes, v1 and v2, are activated in this process, i.e. monodentate coordination.74–76 Common bands due to the BF4− ligands in 1–17 appear at ∼1070, ∼1040, ∼760 and 515 cm−1, the first and the third ones probably overlapping with HL vibrations since they also appear in the spectrum of free 4-phenylimidazole. We tentatively assign the three high-wavenumber bands to the A1 + E components of v3 and to the activated v1 mode (exact assignments would be risky), and the band at ∼515 cm−1 arising from the splitting of v3 and/or from the activated v2 mode.77 All these spectral characteristics reveal a lower symmetry of the BF4− ion due to monodentate coordination. However, none of compounds 1–17 exhibits all six vibrations corresponding to the C3v symmetry. This is probably due to the masking of the additional expected bands by ligand's vibrations; however, this feature has also been explained52,77 in terms of the WCA behaviour of BF4−. Somewhat to our surprise, the four BF4− bands appear also in the spectrum of 18 although this complex contains purely ionic (Td) tetrafluoroborate counterions. This might be due to the involvement of the anions in H bonds, which makes BF4− to spectroscopically behave as ‘pseudocoordinated’.
Thermogravimetric (TG) data are available for complexes 2–5, 7, 10, 12, 15 and 17 (Fig. S8†). The samples were in the form of crushed (powdered) crystals and thus they were not completely dried, but contained various amounts of lattice solvents. For this reason, an in-depth discussion is not possible. The samples lose the lattice solvents at low temperatures, mainly dependent on their boiling point. Thus, the removal of MeOH in 2·2MeOH is complete at ∼70 °C, whereas that of DMF in 10·2DMF is complete at ∼190 °C. The observed experimental trend might be a coincidence since it is known that boiling point is a bulk property while this is not the case for single crystals that include lattice solvents. Thermally stable intermediates are clearly visible at temperatures above those of the complete loss of lattice solvents, corresponding to the unsolvated compounds. The main decomposition of the complexes occurs at ∼300 °C and is rather similar for most samples. For 3·2EtOH, 10·2DMF, 12·2THF and 15·Et2O decomposition gradually continues above 800 °C, the highest temperature limit of the instrument used. For the other complexes, a final plateau appears at slightly below or slightly above 600 °C and approximate mass loss calculations indicate that the final residue is CuO. For example, the final residue in 17·(n-hexane) is 10.1% of the original mass, while the theoretical value for CuO is 8.9%. The small discrepancies observed in most cases are presumably due to the assumption that the original samples at 20 °C contained all the amount of the lattice solvent found through crystallography.
Conclusions
The Cu(II)/HL/BF4− reaction system shows a remarkable competence to form solvatomorphs. The complexes are crystallized as solvated forms from a large number of polar protic, polar aprotic and non-polar solvents. The solvents included are H2O + Me2CO (1), MeOH (2), EtOH (3), 1-PrOH (4), 2-PrOH (5), 1-BuOH (6), iso-BuOH (7), tert-BuOH (8), 1-PeOH (9), DMF (10), Me2CO (11), THF (12), 1,4-dioxane (13), EtOAc (14), Et2O (15), DIPE (16) and n-hexane (17). They all crystallize in the P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) space group with Z = 1, except 1·2Me2CO·2H2O (in P21/c, Z = 2) and 8·1.33(tert-BuOH) (in P
space group with Z = 1, except 1·2Me2CO·2H2O (in P21/c, Z = 2) and 8·1.33(tert-BuOH) (in P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) , Z = 3). The initially used 4-phenylimidazole ligand is present in all complexes as its 5-phenylimidazole tautomeric form. There are two solvent molecules per [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] unit (with full or partial site occupancy due to disorder), except for solvatomorphs 1·2Me2CO·2H2O, 8·1.33(tert-BuOH) and 14–17 (in which the solvents are located on inversion centres, presumably to fit more efficiently in the unit cell since they are large and elongated). The [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] host molecules in the solvatomorphs have similar conformations with a few minor differences in the orientation of the aromatic rings, most likely to facilitate the formation of the H-bonding synthons and accommodate the included solvents. All solvent molecules reside in channels, except for compounds 8·1.33(tert-BuOH) and 11·1.2Me2CO (with a highly disordered HL ligand) in which the solvents are found in lattice pockets. The void space of the channels (or lattice pockets), calculated after the removal of the solvent molecules, ranges from 16.0% to 30.1% of the unit-cell volume. It follows that the [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] host framework of the seventeen structures can readily incorporate solvent molecules containing two to six light non-H atoms (C, O, N).
, Z = 3). The initially used 4-phenylimidazole ligand is present in all complexes as its 5-phenylimidazole tautomeric form. There are two solvent molecules per [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] unit (with full or partial site occupancy due to disorder), except for solvatomorphs 1·2Me2CO·2H2O, 8·1.33(tert-BuOH) and 14–17 (in which the solvents are located on inversion centres, presumably to fit more efficiently in the unit cell since they are large and elongated). The [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] host molecules in the solvatomorphs have similar conformations with a few minor differences in the orientation of the aromatic rings, most likely to facilitate the formation of the H-bonding synthons and accommodate the included solvents. All solvent molecules reside in channels, except for compounds 8·1.33(tert-BuOH) and 11·1.2Me2CO (with a highly disordered HL ligand) in which the solvents are found in lattice pockets. The void space of the channels (or lattice pockets), calculated after the removal of the solvent molecules, ranges from 16.0% to 30.1% of the unit-cell volume. It follows that the [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] host framework of the seventeen structures can readily incorporate solvent molecules containing two to six light non-H atoms (C, O, N).
At the supramolecular level, the large number of the solvatomorphs with a variety of solvents (with respect to their H-bond functionalities, size and shape) allows for interesting conclusions to be drawn. The molecular self-assembly is clearly directed by robust synthons formed by the N–H/BF4− donor/acceptor groups of the [Cu(BF4)2(HL)4] host molecules. Depending on the H-bond capabilities of the solvents included three distinct cases show up: i) the polar protic solvents (compounds 1–9) participate in the formation of N–H⋯Osolvent–H⋯F motifs and, together with the other N–H⋯F synthons, lead to compact 2D layers; ii) the polar aprotic solvents (compounds 10–13) are, perforce, only terminally linked through N–H⋯Osolvent interactions and, thus, the remaining N–H/BF4− groups can only form 1D tapes via N–H⋯F synthons; however, 1,4-dioxane (13), due to its centrosymmetrically-related oxygen atoms O and O*, is an exception participating in N–H⋯O–//–O1*⋯H–N motifs, which together with the other N–H··F interactions form 2D layers; and iii) the non-polar solvents (compounds 14–17) are not engaged in any strong H-bonding motif and the N–H/BF4− groups form directly 2D layers via N–H⋯F synthons. In all three cases the 1D or 2D constructions are further stabilized in 3D by means of weak interactions (e.g. π⋯π/C–H⋯π/C–H⋯O/C–H⋯F). All the N–H and O–H donor groups of the ligands and the solvents, respectively, and most of the fluorine acceptor atoms of the BF4− ions are engaged in synthon formation in the course of the crystallization process. Finally, the packing organization of the ‘failed’ structures 18 and 19·0.8MeNO2, corroborates the structure-directing role of the robust N–H⋯F synthon conserved among all seventeen solvatomorphs studied.
It seems that in the present series of solvatomorphs, the solvents have a distinct role in the formation of self-assembled structures, either by interfering with the otherwise expected synthon by forming alternative associations, or by connecting terminally to donor groups of the guest molecule, or by simply residing in channels participating only in structurally non-important weak interactions.
Work currently in progress in our laboratory involves the synthetic and structural study of the related Cu(II)/HL/ClO4−, Cu(II)/HL/PF6−, Cu(II)/HL/CF3SO3− and Cu(II)/HL/SiF62− systems in order to study the effect of solvatomorphism as a function of the weakly coordinating anion, and the extensions of this type of chemistry in other, non-Jahn–Teller distorted divalent metals, e.g. Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II).
Author contributions
MD: synthesis, X-ray structure analysis, IR/microanalyses, writing; NP, CP, AT: data collection/X-ray crystallography/TGA; DP: mechanistic studies, writing; VN, SPP: conceptualization, supervision, data curation, writing/draft preparation, project administration.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We thank Dr A. Kitos for some help with the crystallization experiments.Notes and references
- P. Klitou, C. M. Pask, L. Onoufriadi, I. Rosbottom and E. Simone, Cryst. Growth Des., 2020, 20, 6573 CrossRef CAS.
- U. J. Griesser, in Polymorphism in the Pharmaceutical Industry: The Importance of Solvates, ed. R. Hilfiker, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2006, pp. 211–233 Search PubMed.
- H. G. Brittain, J. Pharm. Sci., 2012, 101, 464 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. T. Ibragimov, CrystEngComm, 2007, 9, 111 RSC.
- T. L. Threlfall, Analyst, 1995, 120, 2435 RSC.
- A. Nangia and G. R. Desiraju, Chem. Commun., 1999, 605 RSC.
- K. R. Seddon, Cryst. Growth Des., 2004, 4, 1087 CrossRef CAS.
- G. R. Desiraju, Cryst. Growth Des., 2004, 4, 1089 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Bernstein, Cryst. Growth Des., 2005, 5, 1661 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Bernstein, Cryst. Growth Des., 2011, 11, 632 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Nangia, Cryst. Growth Des., 2006, 6, 2 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Stöger, P. Kautny, D. Lumpi, E. Zobetz and J. Fröhlich, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci., 2012, 68, 667 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. du Plessis and L. J. Barbour, Dalton Trans., 2012, 41, 3895 RSC.
- M. K. Stanton and A. Bak, Cryst. Growth Des., 2008, 8, 3856 CrossRef CAS.
- J. A. R. P. Sarma and G. R. Desiraju, in Crystal Engineering: The Design and Application of Functional Solids, ed. K. R. Seddon and M. J. Zaworotko, Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1999, vol. 539, pp. 325–356 Search PubMed.
- A. Nangia and G. R. Desiraju, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 4100 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Ranjan, R. Devarapalli, S. Kundu, S. Saha, S. Deolka, V. Vangala and C. Reddy, IUCrJ, 2020, 7, 173 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. R. Desiraju, IUCrJ, 2017, 4, 710 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. H. Görbitz and H.-P. Hersleth, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci., 2000, 56, 526 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Hao, S. Parkin and C. P. Brock, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci., 2005, B61, 689 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Mondal and J. A. K. Howard, CrystEngComm, 2005, 7, 462 RSC.
- M. Köppen, V. Meyer, J. Ångström, K. Inge and N. Stock, Cryst. Growth Des., 2018, 18, 4060 CrossRef.
- R. Seetharaj, P. V. Vandana, P. Arya and A. S. Mathew, Arabian J. Chem., 2019, 12, 295 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Yamada, Z. Shen and M. Miyake, Chem. Commun., 2006, 2569 RSC.
- A. Bernard, K. Zhang, D. Larson, K. Tabatabaei and S. M. Kauzlarich, Inorg. Chem., 2018, 57, 5299 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. A. Kounavi, C. Papatriantafyllopoulou, A. Tasiopoulos, S. P. Perlepes and V. Nastopoulos, Polyhedron, 2009, 28, 3349 CrossRef CAS.
- K. A. Kounavi, M. J. Manos, E. Moushi, C. Papatriantafyllopoulou, A. Tasiopoulos and V. Nastopoulos, Cryst. Growth Des., 2012, 12, 429 CrossRef CAS.
- K. A. Kounavi, E. Moushi, M. J. Manos, C. Papatriantafyllopoulou, A. Tasiopoulos and V. Nastopoulos, CrystEngComm, 2012, 14, 6492 RSC.
- K. A. Kounavi, A. Kitos, E. Moushi, M. J. Manos, C. Papatriantafyllopoulou, A. Tasiopoulos, S. P. Perlepes and V. Nastopoulos, CrystEngComm, 2015, 17, 7510 RSC.
- A. Kitos, E. Moushi, M. J. Manos, C. Papatriantafyllopoulou, A. Tasiopoulos, S. P. Perlepes and V. Nastopoulos, CrystEngComm, 2016, 18, 4733 RSC.
- V. Duros, C. Papatriantafyllopoulou, A. Kitos, A. Tasiopoulos and V. Nastopoulos, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci., Cryst. Eng. Mater., 2019, 75, 599 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Reinen, Comments Inorg. Chem., 1983, 2, 227 CrossRef CAS.
- F. A. Cotton, G. Wilkinson, C. A. Murillo and M. Bochmann, Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, Wiley, New York, 6th edn, 1999, pp. 865 Search PubMed.
- E. C. Constable, Metals and Ligand Reactivity: An Introduction to the Organic Chemistry of Metal Complexes, VCH, Weinheim, 1996, pp. 240–245 Search PubMed.
- S.-S. Chen, CrystEngComm, 2016, 18, 6543 RSC.
- S. J. Lippard and J. M. Berg, Principles of Bioinorganic Chemistry, University Science Books, Mill Valley, California, 1994 Search PubMed.
- R. M. Roat-Malone, Bioinorganic Chemistry, Wiley, New Jersey, 2002 Search PubMed.
- G. R. Desiraju, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1995, 34, 2311 CrossRef CAS.
- J. W. Steed and J. L. Atwood, Supramolecular Chemistry, Wiley, Chichester, 1st edn, 2009 Search PubMed.
- G. M. J. Schmidt, Pure Appl. Chem., 1971, 27, 647 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Steiner, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2002, 41, 48 CrossRef CAS.
- C. B. Aakeröy, N. R. Champness and C. Janiak, CrystEngComm, 2010, 12, 22 RSC.
- J. D. Dunitz and A. Gavezzotti, Cryst. Growth Des., 2012, 12, 5873 CrossRef CAS.
- C. A. Hunter and J. K. M. Sanders, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1990, 112, 5525 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Janiak, J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., 2000, 3885 RSC.
- M. Nishio, Y. Umezawa, H. Suezawa and S. Tsuboyama, in The importance of pi-Interactions in Crystal Engineering: Frontiers in Crystal Engineering, ed. E. R. T. Tiekink and J. Zukerman-Schpector, Wiley, Singapore, 2012, pp. 1–31 Search PubMed.
- J. Lozada, W. X. Lin, R. M. Cao-Shen, R. A. Tai and D. M. Perrin, Angew. Chem., 2023, 62, e202215371 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. I. Petrikat and S. Becker, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 2022, 648, e202200150 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Reedijk, Comments Inorg. Chem., 1982, 1, 379 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Beck and K. Sünkel, Chem. Rev., 1988, 88, 1405 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Krossing and I. Raabe, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2004, 43, 2066 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Burt, W. Grantham, W. Levason, M. E. Light and G. Reid, Polyhedron, 2015, 85, 530 CrossRef CAS.
- CrysAlis PRO (version 1.171.38.43), Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, UK, 2015 Search PubMed.
- A. Altomare, G. Cascarano, C. Giacovazzo, A. Guagliardi, M. C. Burla, G. Polidori and M. Camalli, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 1994, 27, 435 Search PubMed.
- G. M. Sheldrick, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A: Found. Adv., 2015, 71, 3 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Palatinus and G. Chapuis, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2007, 40, 786 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Palatinus, S. J. Prathapa and S. van Smaalen, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2012, 45, 575 CrossRef CAS.
- G. M. Sheldrick, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. C: Struct. Chem., 2015, 71, 3 Search PubMed.
- A. L. Spek, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. D: Biol. Crystallogr., 2009, 65, 148 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. V. Dolomanov, L. J. Bourhis, R. J. Gildea, J. A. K. Howard and H. Puschmann, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2009, 42, 339 CrossRef CAS.
- L. J. Farrugia, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2012, 45, 849 CrossRef CAS.
- C. F. Macrae, I. Sovago, S. J. Cottrell, P. T. A. Galek, P. McCabe, E. Pidcock, M. Platings, G. P. Shields, J. S. Stevens, M. Towler and P. A. Wood, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2020, 53, 226 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. H. Kim, S. J. Kwak, J. H. Jeong, S. You, S. K. Nam, Y. Kim and W. B. Lee, ACS Omega, 2021, 6, 16009 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Díaz-Salazar, J. C. Rodríguez-Colín, J. Vazquez-Chavez and M. Hernández-Rodríguez, J. Org. Chem., 2023, 88, 8150 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. M. Claramunt, M. D. Santa María, L. Infantes, F. H. Cano and J. Elguero, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 2002, 2, 564 RSC.
- M. Kubicki, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci., 2004, 60, 191 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. E. García-Rubiño, D. Choquesillo-Lazarte, M. C. Núñez and J. M. Campos, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. C: Cryst. Struct. Commun., 2011, 67, o484 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Bombicz, N. V. May, D. Fegyverneki, A. Saranchimega and L. Bereczki, CrystEngComm, 2020, 22, 7193 RSC.
- P. Bombicz, IUCrJ, 2024, 11, 3 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Spackman and J. J. McKinnon, CrystEngComm, 2002, 4, 378 RSC.
- M. A. Spackman and D. Jayatilaka, CrystEngComm, 2009, 11, 19 RSC.
- P. R. Spackman, M. J. Turner, J. J. McKinnon, S. K. Wolff, D. J. Grimwood, D. Jayatilaka and M. A. Spackman, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2021, 54, 1006 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. F. Gallagher and P. Mocilac, J. Mol. Struct., 2021, 1234, 130149 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Nakamoto, Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, Wiley, New York, 4th edn, 1986, pp. 130–141, 228–233, 280–282 Search PubMed.
- C. Stamou, W. Papawassiliou, J. P. Carvalho, K. F. Konidaris, V. Bekiari, P. Dechambenoit, A. J. Pell and S. P. Perlepes, Inorg. Chem., 2021, 60, 4889 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. P. Gaughan, Jr., Z. Dori and J. A. Ibers, Inorg. Chem., 1974, 13, 1657 CrossRef.
- A. N. Chebotarev, M. V. Shestakova and T. M. Shcherbakova, Russ. J. Coord. Chem., 2002, 28, 131 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: CCDC 2342307–2342325. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ce00304g |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |