Thermoelectric properties of an organoboron polymer n-doped with a N-heterocyclic carbene based dopant
Abstract
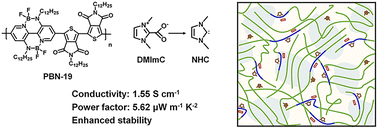
Organoboron polymers containing boron–nitrogen coordination bonds are a new class of n-type thermoelectric polymers. Their n-doping with a traditional hydride donor dopant suffers from low thermoelectric performance and unsatisfactory stability. In this manuscript, we report the n-doping of an organoboron polymer, PBN-19, with an N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) based dopant, 1,3-dimethylimidazolium-2-carboxylate (DMImC). The DMImC doped PBN-19 film exhibits an electrical conductivity of 1.55 S cm−1 and a power factor of 5.62 μW m−1 K−2, and maintains 80.0% of its initial electrical conductivity after 1 day storage at room temperature under a nitrogen atmosphere. Detailed examinations indicate that DMImC decomposed into NHC radicals upon thermal activation, which then reacted with the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O, C
O, C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C and C
C and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bonds on the PBN-19 skeleton realizing n-doping. The doping did not significantly disturb the π–π stacking and crystallization of PBN-19 and thus led to high thermoelectric performance. The covalent bonding of dopants on the polymer probably inhibited their diffusion out of the polymer matrix and thus slowed down the dedoping process. This work provides some new insights into the n-doping of organic thermoelectric materials.
N bonds on the PBN-19 skeleton realizing n-doping. The doping did not significantly disturb the π–π stacking and crystallization of PBN-19 and thus led to high thermoelectric performance. The covalent bonding of dopants on the polymer probably inhibited their diffusion out of the polymer matrix and thus slowed down the dedoping process. This work provides some new insights into the n-doping of organic thermoelectric materials.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2023 Journal of Materials Chemistry C HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...