Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleAn improved stereodivergent and practical synthesis of α- and β-pseudouridines†
Viktor
Barát
 ,
Anqi
Chen
and
Yee Hwee
Lim
,
Anqi
Chen
and
Yee Hwee
Lim
 *
*
Green Chemistry and Biocatalysis, Institute of Sustainability for Chemicals, Energy and Environment, A*STAR, Singapore. E-mail: lim_yee_hwee@isce2.a-star.edu.sg
First published on 8th December 2022
Abstract
An improved stereodivergent and practical synthesis of both α- and β-pseudouridines has been achieved from a common intermediate. This practical approach features a highly diastereoselective Grignard reaction using inexpensive protected D-ribose under non-cryogenic conditions and a divergent one-pot, acid-mediated global deprotection–cyclisation and anomerization to give β-pseudouridine, or a Mitsunobu cyclisation followed by deprotection to provide α-pseudouridine. Detailed 1H NMR kinetic studies provide insight into the cyclisation and anomerization steps.
1. Introduction
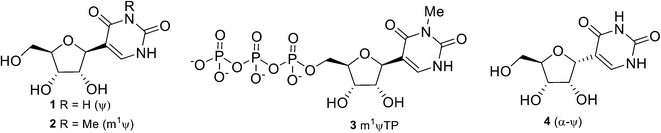
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules are typically made up of four ribonucleosides, adenosine (A), guanosine (G), cytidine (C), and uridine (U). However, with the advancement in characterization and sequencing technology, we now know that there exist numerous modified ribonucleosides in nature.1 These modified nucleosides serve important purposes due to their ability to regulate the function, stability, or structures of RNA.2 In particular, U isomer β-pseudouridine (ψ) 1 is formed post-translationally from U, catalysed by the enzyme ψ-synthase, and occurs naturally in all types of RNAs (tRNA, rRNA, snRNA, snoRNA, scaRNA, and mRNA).3 This transformation from U to ψ can help to increase the stability and rigidity of RNA due to an increase in hydrogen bonding from the nucleobase N1 of ψ. Recently, this well-known phenomenon has been most prominently featured in the application of the related hypermodified nucleoside, N1-methyl-β-pseudouridine (m1ψ) 2, in the form of N1-methyl-β-pseudouridine 5′-triphosphate (3) in the mRNA-based vaccine developed against the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which caused the COVID-19 pandemic.4,5 The need to manufacture billions of doses of vaccines has resulted in surged demand for 3 and its precursors, driving up prices of these materials.Synthetic methods to access such C-glycosyl nucleosides (Fig. 1) are known as early as the 1970s,6 and since then, there have been sporadic developments.7–11 The need to produce large quantities of modified nucleosides such as m1ψ spurred interest in the scientific community to develop better technologies to access C-glycosyl nucleotides in general,12,13 though none of the syntheses dealt with ψ or m1ψ directly. An in-depth survey of the literature7–11,14,15 found that the existing synthesis routes for 1 suffered from several industrial production limitations though there is one report on the synthesis of 2via the selective methylation of 1 in nearly quantitative yield.16 To overcome of the challenges and impracticality associated with the existing processes, we herein report the development of a streamlined and scalable synthesis of β-pseudouridine (1), which could contribute to ensuring the supply and affordability of vaccines. In addition, our route enables access to unnatural α-pseudouridine (4), which may be valuable for biological studies.
Generally, one of the key steps in the reported synthesis of pseudouridines features the condensation between either the protected ribose 5 or aldehyde 8 and the lithiated pyrimidine, prepared in situ under cryogenic conditions by n-BuLi and pyrimidine 6, to give typically a diastereomeric mixture that is chromatographically separated (Scheme 1A and B).6,7 The respective diastereomers 7 and 9 then undergo an acid-mediated cyclisation step to give either β- or α-pseudouridine, depending on the stereochemistry of the starting diastereomer. In more recent reports, however, of stereoselective syntheses9–11 of pseudouridines, there has been an increase in the number of synthetic steps from two to five involving multiple cryogenic steps (Scheme 1C).
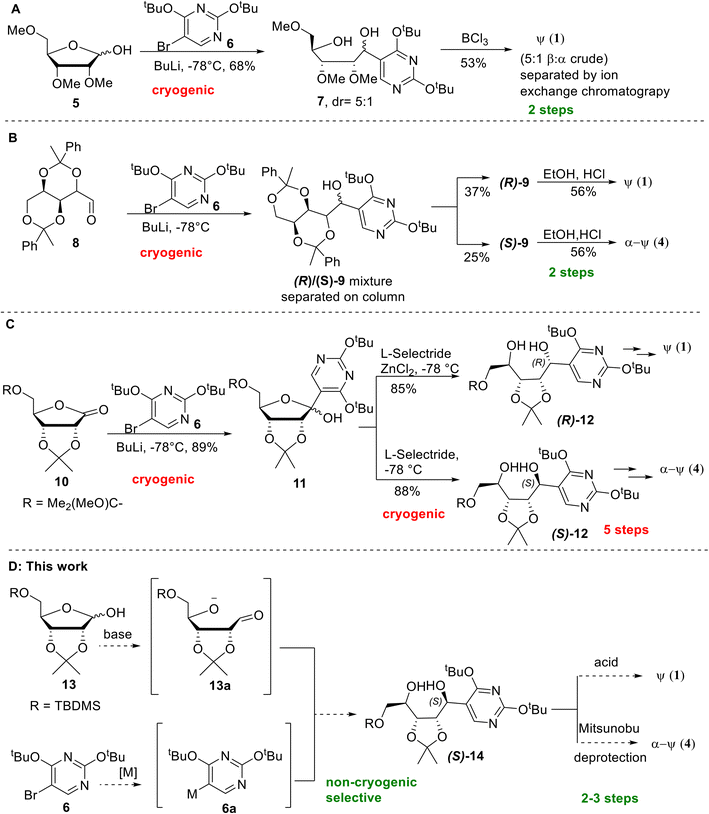 | ||
| Scheme 1 Existing and proposed approaches for the synthesis of pseudouridines. A: A two-step synthesis using protected ribose 5 followed by BCl3 mediated cyclisation of diol mixture.7 B: A two-step synthesis using protected aldehyde 8 followed by acidic cyclization of purified alcohols.6 C: A five-step stereoselective synthesis of diol 12 followed by Mitsunobu cyclisation.9 D: Proposed non-cryogenic, stereodivergent approach for the synthesis of both α- and β-pseudouridines. | ||
The stereoselective synthetic methods are based on the ability to achieve stereocontrol on the C1 stereochemistry of the ribose following the key condensation step. Nucleophilic addition of the pyrimidine building block 6 onto a protected ribonolactone 10 led to a diastereomeric mixture of alcohols 11, which upon exposure to reducing agent L-selectride gave C1-(S) diol (S)-12 as a single diastereomer. Alternatively, treatment of 11 with L-selectride in the presence of ZnCl2 allows the C1-(R) diol (R)-12 to be obtained diastereoselectively (Scheme 1C). Subsequent Mitsunobu cyclisation proceeds with the inversion of the C1 stereochemistry, and upon a 2-step deprotection, (R)-12 leads to β-pseudouridine 2, while (S)-12 leads to α-pseudouridine 3. Despite being a high-yielding step generally, the need to chromatographically separate diastereomers or the use of special reducing agents and cryogenic conditions typically would pose a significant challenge during scale-up.
2. Results and discussion
In our effort to improve and streamline the synthesis of β-pseudouridine, a reaction of the protected ribose 13,17 with the Grignard reagent of protected bromopyrimidine 6,18 for the synthesis of azasugars19 attracted our attention because 13 is inexpensive, and the reaction could be carried out at room temperature instead of using cryogenic conditions. Together with the acidic cyclisation reported by Moffatt et al.,6 we were prompted to investigate a potentially concise and scalable route for the synthesis of pseudouridines (Scheme 1D). Of note, the reported Grignard reagent had to be generated under ultrasonic irradiation with n-butylmagnesium chloride, and the reaction with 13 gave only a 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 R/S ratio of the Grignard addition product.19 In addition, the excess (3 equivalents) of the pyrimidine Grignard reagent had to be used, which is not cost-effective. Therefore, significant improvement will be needed to render this reaction more practical for pseudouridine synthesis.
1 R/S ratio of the Grignard addition product.19 In addition, the excess (3 equivalents) of the pyrimidine Grignard reagent had to be used, which is not cost-effective. Therefore, significant improvement will be needed to render this reaction more practical for pseudouridine synthesis.
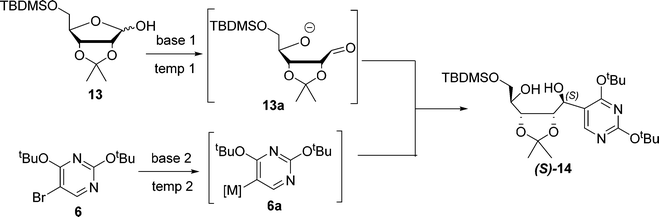
Diastereoselective synthesis of (S)-14
Our investigation commenced with the addition reaction of transmetalated pyrimidine 6a with the protected D-ribose 13. Extensive screening was carried out to identify the optimal reagent and conditions (Table 1), benchmarking against the reported conditions19 (entry 1). The reaction of the lithiated pyrimidine 6a (M = Li) with 13 produced comparable results in terms of yields and diastereoselectivity to the benchmark but had to be carried out under deep cryogenic conditions (entry 2). The pyrimidine Grignard reagent generated from both iPrMgCl (entry 3) and iPrMgCl × LiCl (Turbo Grignard, entry 4) provided similar yields, and surprisingly in >20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 diastereoselectivity of the diol (S)-14 at room temperature. In addition, the Turbo Grignard gave higher conversion at both small and larger scales (entries 4 and 10), demonstrating the scalability of this approach. As one equivalent of the metalated pyrimidine 6a is sacrificed for the deprotonation of the ribose hydroxyl group to form aldehyde intermediate 13a for the addition reaction, we sought to replace this with an inexpensive base for the deprotonation to reduce the needed amount of 6a, which is more costly. Initially, NaH and LiHMDS were tested, but no diol product was formed (entries 5 and 6). n-BuLi was effective at both −78 (entries 7–9) and 0 °C (entry 10). Better yields could be obtained when it was combined with two equivalents of 6a generated from Turbo Grignard (entries 8–10). Moreover, when the reaction was scaled up at the gram scale, and the best isolated yield of 67% was achieved while retaining high selectivity (entry 10). Interestingly, though the origin of the exclusive diastereoselectivity of the reaction between 6a and 13 under Grignard conditions is not clear at this stage, the excellent selectivity and elimination of cryogenic conditions make this Grignard reaction step practical and easily scalable.
1 diastereoselectivity of the diol (S)-14 at room temperature. In addition, the Turbo Grignard gave higher conversion at both small and larger scales (entries 4 and 10), demonstrating the scalability of this approach. As one equivalent of the metalated pyrimidine 6a is sacrificed for the deprotonation of the ribose hydroxyl group to form aldehyde intermediate 13a for the addition reaction, we sought to replace this with an inexpensive base for the deprotonation to reduce the needed amount of 6a, which is more costly. Initially, NaH and LiHMDS were tested, but no diol product was formed (entries 5 and 6). n-BuLi was effective at both −78 (entries 7–9) and 0 °C (entry 10). Better yields could be obtained when it was combined with two equivalents of 6a generated from Turbo Grignard (entries 8–10). Moreover, when the reaction was scaled up at the gram scale, and the best isolated yield of 67% was achieved while retaining high selectivity (entry 10). Interestingly, though the origin of the exclusive diastereoselectivity of the reaction between 6a and 13 under Grignard conditions is not clear at this stage, the excellent selectivity and elimination of cryogenic conditions make this Grignard reaction step practical and easily scalable.
| Entry | Base 1 | Temp 1 (°C) | Base 2 | 6a (equiv.) | Temp 2 (°C) | dr of (S)-14a | Yieldb (conversion) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Determined by 1HNMR from the crude product. b Conversion was determined by 1H NMR, and the yield refers to the isolated product. c Formation of the Grignard reagent and the reaction were carried out under sonication.19 | |||||||
| 1c | — | — | nBuMgCl | 3 | 25 | 70![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30 30 |
56% |
| 2 | — | — | nBuLi | 3 | −78 | 70![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30 30 |
54% (70%) |
| 3 | — | — | iPrMgCl | 3 | 25 | >20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
50% (66%) |
| 4 | — | — | iPrMgCl × LiCl | 3 | 25 | >20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
60% (88%) |
| 5 | NaH | 0 | iPrMgCl × LiCl | 2 | 25 | — | Conversion <10% |
| 6 | LiHMDS | 0 | iPrMgCl × LiCl | 2 | 25 | — | Conversion <10% |
| 7 | nBuLi | −78 | iPrMgCl | 2 | 25 | >20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
26% (68%) |
| 8 | nBuLi | −78 | iPrMgCl × LiCl | 2 | 25 | >20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
57% (68%) |
| 9 | nBuLi | −78 | iPrMgCl × LiCl | 2 | 25 | >20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
57% (70%, gram scale) |
| 10 | nBuLi | 0 | iPrMgCl × LiCl | 2 | 25 | >20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
67% (87%, gram scale) |
Synthesis of β-pseudouridine 1
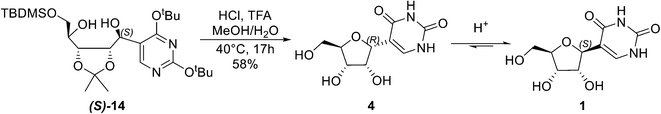
Having optimized the Grignard step, our attention was turned to the deprotection–cyclisation key step (Scheme 2). While the global deprotection of (S)-14 is straightforward,6 cyclisation of diol (S)-14 to form β-pseudouridine (1) is challenging, as previously reported cyclisation of alcohol (S)-9 (Scheme 1B) has shown a mixture of α- and β-pseudouridine in a ratio of 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2.6 Mechanistic studies revealed that the cyclisation proceeds via an SN2 mechanism, forming initially the α-pseudouridine (4), which then undergoes incomplete anomerization leading to an anomeric mixture favoring the α-pseudouridine.6 These results appeared to indicate that the acid-mediated cyclisation of (S)-14 is unlikely to be synthetically useful. However, considering that the β-anomer (1) is thermodynamically more stable, we envisioned that the identification of suitable conditions could drive the reaction in favour of 1 in a practical, one-pot fashion (Scheme 2).
2.6 Mechanistic studies revealed that the cyclisation proceeds via an SN2 mechanism, forming initially the α-pseudouridine (4), which then undergoes incomplete anomerization leading to an anomeric mixture favoring the α-pseudouridine.6 These results appeared to indicate that the acid-mediated cyclisation of (S)-14 is unlikely to be synthetically useful. However, considering that the β-anomer (1) is thermodynamically more stable, we envisioned that the identification of suitable conditions could drive the reaction in favour of 1 in a practical, one-pot fashion (Scheme 2).
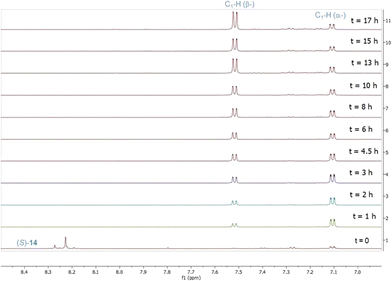
Extensive screening of conditions, including acids, solvents, temperature, and reaction time, for the deprotection–cyclisation of (S)-14 was carried out (see the ESI†). These factors were found to have synergetic effects, and the best conditions were identified to be 90% aq. methanol containing 1.25 M HCl and 0.26 M trifluoroacetic acid at 40 °C for 17 hours. In order to understand this one-pot deprotection–cyclisation better, NMR studies were carried out to follow the course of the reaction (Fig. 2). As expected, both deprotection and cyclisation had been completed within the first hour, giving an α-/β-mixture in a ratio of 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. As the reaction continued, the β-anomer increased, accompanied by the formation of a small amount of the by-product at 4.5 hours. By 6 hours, the ratio of α-/β-anomers had reached 1
1. As the reaction continued, the β-anomer increased, accompanied by the formation of a small amount of the by-product at 4.5 hours. By 6 hours, the ratio of α-/β-anomers had reached 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. At reaction termination, the α-/β-anomer ratio had reached 1
1. At reaction termination, the α-/β-anomer ratio had reached 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 and levelled off in a composition of 76% β-anomer, 15% α-anomer and 9% by-product as determined by 1H NMR. Applying the optimised conditions to the preparative scale provided a ratio of β-/α-anomers of 3
3 and levelled off in a composition of 76% β-anomer, 15% α-anomer and 9% by-product as determined by 1H NMR. Applying the optimised conditions to the preparative scale provided a ratio of β-/α-anomers of 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 in favour of β-anomer. β-pseudouridine 1 was isolated by recrystallisation of the crude mixture from EtOH in 58% yield with characterisation data identical to those reported in the literature.11 It is noteworthy that the product composition of the acid-mediated one-pot deprotection–cyclisation process is sensitive to the surface area–volume of the reactor vessels, suggesting that this step could benefit from a continuous process (see the ESI†). Nonetheless, the high diastereoselectivity of the Grignard reaction and the conciseness and practicality of the route would make this more amenable to scale-up, provided that the surface area–volume of the reactor vessels could be maintained.
2 in favour of β-anomer. β-pseudouridine 1 was isolated by recrystallisation of the crude mixture from EtOH in 58% yield with characterisation data identical to those reported in the literature.11 It is noteworthy that the product composition of the acid-mediated one-pot deprotection–cyclisation process is sensitive to the surface area–volume of the reactor vessels, suggesting that this step could benefit from a continuous process (see the ESI†). Nonetheless, the high diastereoselectivity of the Grignard reaction and the conciseness and practicality of the route would make this more amenable to scale-up, provided that the surface area–volume of the reactor vessels could be maintained.
Synthesis of α-pseudouridine 4
Having achieved a concise and practical synthesis of β-pseudouridine (1), we further sought to diversify the easily accessible diol (S)-14 for the synthesis of unnatural α-pseudouridine (4), which could be valuable for biological studies. Our initial efforts using an acid-mediated one-pot deprotection–cyclisation strategy provided a 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
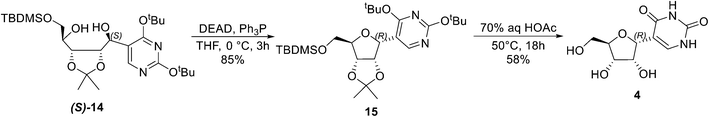
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 ratio of α- and β-pseudouridines at best after significant optimisation (see the ESI†). Attempted recrystallization under various conditions was unsuccessful to isolate pure 4. To this end, the reported Mitsunobu cyclisation9 was applied, and this easily led to the cyclised product (15). The final global deprotection provided α-pseudouridine (4) in 58% yield (Scheme 3).
2 ratio of α- and β-pseudouridines at best after significant optimisation (see the ESI†). Attempted recrystallization under various conditions was unsuccessful to isolate pure 4. To this end, the reported Mitsunobu cyclisation9 was applied, and this easily led to the cyclised product (15). The final global deprotection provided α-pseudouridine (4) in 58% yield (Scheme 3).
3. Conclusions
We have developed a divergent route that enables access to both α- and β-pseudouridines. Capitalising on the common intermediate (S)-14, a one-pot deprotection–cyclisation leads to β-pseudouridine (1), while a Mitsunobu cyclisation followed by deprotection provides α-pseudouridine (4). This improved route features a non-cryogenic, highly diastereoselective Grignard reaction that provides the key intermediate (S)-14 in a single diastereomer and the anomerization of α-pseudouridine to the thermodynamically favoured β-pseudouridine. We believe that this concise and practical route would have the potential to apply to the manufacturing of pseudouridine molecules that are critical to the production of nucleic acid therapeutics such as mRNA vaccines.4. Experimental
General
Reactions requiring inert conditions were performed using a standard Schenk technique under an argon atmosphere using oven dried glassware. All chemicals were used as received from Sigma-Aldrich and TCI. A commercial standard of β-pseudouridine was purchased from TCI (P2939: pseudouridine (Synthetic)). Anhydrous solvents were obtained from a laboratory solvent purification system. Water for the reactions was obtained from an ELGA PURELAB Ultra system (18.2 MΩ cm). Deuterated solvents were purchased from Cambridge Isotope or Sigma-Aldrich and used without further purification. Chromatographic purifications were performed on a CombiFlash NextGen 300 using standard silica columns and flow rates. NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance 400 MHz spectrometer equipped with a cryoprobe. Chemical shifts (δ) are reported in ppm and referenced to residual non-deuterated solvent peaks (CDCl3: 1H 7.26 ppm; 13C: 77.23 ppm; DMSO-d6: 1H: 2.50 ppm, 13C: 39.5 ppm; pyridine-d5: 1H: 7.58 ppm). Optical rotation data was collected on a Jasco P2000 polarimeter in a 10 mm cuvette.Synthesis of diol (S)-14
To a solution of 5-bromo-2,4-tert-butoxy-pyrimidine 6 (1.98 g, 6.58 mmol) in anhydrous THF (26 mL), a Turbo Grignard reagent (1.3 M in THF, 5.8 mL, 7.56 mmol) was added under argon and stirred at room temperature for 3 hours.In a separate flask, protected ribose 13 (1.0 g, 3.29 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous THF (13 mL) and cooled in an ice bath, and n-BuLi (2 M in cyclohexane, 1.64 mL, 3.28 mmol) was added, followed by stirring for 10 minutes. This solution was transferred slowly into the pyrimidine Grignard solution and stirred at room temperature for 22 hours. The reaction was quenched by the addition of sat. aq. NH4Cl and water, which were then extracted twice with EtOAc. The combined organics were washed with brine and then concentrated in vacuo. The crude mixture was purified on a CombiFlash using a 40 g silica column eluted with a hexane/EtOAc gradient of 10% to 25%. An off-white foam was obtained: 1.16 g (2.2 mmol), 67% yield. The diol was obtained as a single diastereomer and confirmed to have S configuration on ribose C1 by comparing the 1H NMR and optical rotation data to the literature.11 [α]22D = +16.49 (c 2.05 in DCM) [lit. [α]22D = +16.0 (c 2.05 in DCM)];111H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.22 (s, 1H), 4.96 (dd, J = 9.6, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 4.45 (dd, J = 9.6, 5.5 Hz, 1H), 4.22 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 4.17 (dd, J = 9.5, 5.5 Hz, 1H), 4.01–3.87 (m, 2H), 3.76–3.66 (m, 1H), 3.46 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 1.63 (s, 9H), 1.61 (s, 9H), 1.34 (s, 3H), 1.26 (s, 3H), 0.93 (s, 9H), 0.12 (s, 6H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 168.19, 163.19, 156.91, 115.77, 108.75, 82.17, 80.33, 77.30, 69.70, 65.73, 64.59, 28.65, 28.60, 28.11, 26.06, 25.38, 18.53, −5.18, −5.22.
Synthesis of β-psuedouridine (1)
A solution of diol (S)-14 (500 mg, 0.947 mmol) in MeOH (11.25 mL), cc. aq. HCl (1.25 mL) and TFA (0.25 mL) was heated to 40 °C for 17 hours and then evaporated to dryness. The residue was recrystallized from EtOH to give 1 as an off-white powder, 135 mg (0.55 mmol), 58% yield. The NMR data corresponds to the literature.11 [α]22D = −2.57 (c 0.51 in H2O) [commercial standard: [α]22D = −2.41 (c 0.51 in H2O)]; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.10 (s, 1H), 10.87 (s, 1H), 7.52 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 4.89 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 4.78 (dd, J = 6.4, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 4.68 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H), 4.46 (dd, J = 4.5, 0.9 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (m, 2H), 3.69 (dt, J = 6.0, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 3.59 (ddd, J = 11.9, 4.8, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 3.44 (ddd, J = 11.9, 6.5, 3.7 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 163.63, 151.10, 139.72, 111.10, 83.11, 78.83, 73.85, 70.34, 61.09.Synthesis of 15
A solution of (S)-14 (220 mg, 0.416 mmol) and triphenylphosphine (219 mg, 0.833 mmol) in anhydrous THF (33 mL) was cooled in an ice bath, and diethyl azodicarboxylate (DEAD, 130 μL, 0.833 mmol) was added and then stirred for 3 hours. The mixture was evaporated to dryness, and the residue was purified on a CombiFlash using a 12 g silica column eluted with a hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) EtOAc gradient of 1% to 50%. A colorless oil was obtained: 180 mg (0.353 mmol), 85% yield. The NMR data corresponds to the literature.11 [α]22D = −74.6 (c 2.46 in DCM) [lit. [α]22D = −72.1 (c 3.58 in DCM)];111H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.28 (d, J = 0.9 Hz, 1H), 5.22 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 1H), 4.95–4.80 (m, 2H), 4.21 (t, J = 3.1 Hz, 1H), 3.90–3.72 (m, 2H), 1.59 (s, 9H), 1.59 (s, 9H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.27 (s, 3H), 0.91 (s, 9H), 0.07 (s, 3H), 0.06 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.38, 163.31, 156.97, 112.20, 112.11, 83.94, 83.33, 81.90, 81.54, 79.95, 78.94, 65.78, 28.67, 28.53, 26.38, 26.03, 25.16, 18.23, −5.41, −5.60.
EtOAc gradient of 1% to 50%. A colorless oil was obtained: 180 mg (0.353 mmol), 85% yield. The NMR data corresponds to the literature.11 [α]22D = −74.6 (c 2.46 in DCM) [lit. [α]22D = −72.1 (c 3.58 in DCM)];111H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.28 (d, J = 0.9 Hz, 1H), 5.22 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 1H), 4.95–4.80 (m, 2H), 4.21 (t, J = 3.1 Hz, 1H), 3.90–3.72 (m, 2H), 1.59 (s, 9H), 1.59 (s, 9H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.27 (s, 3H), 0.91 (s, 9H), 0.07 (s, 3H), 0.06 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.38, 163.31, 156.97, 112.20, 112.11, 83.94, 83.33, 81.90, 81.54, 79.95, 78.94, 65.78, 28.67, 28.53, 26.38, 26.03, 25.16, 18.23, −5.41, −5.60.
Synthesis of α-pseudouridine 4
A solution of 15 (180 mg, 0.353 mmol) in 8 mL acetic acid and 3.5 mL water was heated to 50 °C for 18 hours and then evaporated to dryness. The residue was dissolved in EtOH and then evaporated until a thick white precipitate appeared, which was filtered and washed with EtOH to give 4 as a white powder: 50 mg (0.205 mmol), 58% yield. [α]22D = −101.1 (c 0.51 in H2O). The NMR spectrum in pyridine-d5 corresponds to the literature.61H NMR (400 MHz, Pyridine-d5) δ 13.02 (s, 1H), 12.50 (s, 1H), 8.01 (s, 1H), 6.90 (s, 1H), 6.54 (s, 1H), 5.67 (dd, J = 3.0, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 5.05 (s, 1H), 4.70 (ddd, J = 7.8, 4.6, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 4.39 (dd, J = 11.9, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 4.22 (dd, J = 11.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H); 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.91 (br, 2H), 7.12 (d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 4.81 (s, 1H), 4.71 (dd, J = 3.0, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (s, 1H), 4.02 (dd, J = 8.2, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 3.92 (t, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 3.71 (ddd, J = 8.0, 5.0, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 3.64–3.54 (m, 1H), 3.40 (d, J = 13.5 Hz, 1H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO) δ 163.46, 151.45, 139.36, 109.31, 81.69, 75.71, 72.51, 71.19, 61.68.Author contributions
VB, AC and YHL conceptualized the study. VB designed and performed the experiments. VB wrote the initial manuscript draft. AC and YHL reviewed, edited and wrote the manuscript.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Agency for Science, Research & Technology (A*STAR), Singapore and the A*STAR Institute of Sustainability for Chemicals, Energy and Environment (SC22/21-10474U) for this work.Notes and references
- P. J. McCrown, A. Ruszkowska, C. N. Kunkler, K. Breger, J. P. Hulewicz, M. C. Wang, N. A. Springer and J. A. Brown, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA, 2020, 11, e1595 Search PubMed.
- W. A. Cantara, P. F. Crain, J. Rozenski, J. A. McCloskey, K. A. Harris, X. Zhang, F. A. P. Vendeix, D. Fabris and P. F. Agris, Nucleic Acids Res., 2011, 39, D195 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. K. Borchardt, N. M. Martinez and W. V. Gilbert, Annu. Rev. Genet., 2020, 54, 309 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Q. Kim, B. D. Burgute, S. Tzeng, C. Jing, C. Jugers, J. Zhang, L. L. Yan, R. D. Vierstra, S. Djuranovic, B. S. Evans and H. S. Zaher, Cell Rep., 2022, 40, 111300 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Kis, C. Kontoravdi, R. Shattock and N. Shah, Vaccines, 2021, 3, 205 CrossRef PubMed.
- U. Lerch, M. G. Burdon and J. G. Moffatt, J. Org. Chem., 1971, 36, 1507 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. M. Brown and R. C. Ogden, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1981, 723 RSC.
- P. J. Gohar and C. S. Chow, Tetrahedron Lett., 1999, 40, 2049 CrossRef.
- S. Hanessian and R. Machaalani, Tetrahedron Lett., 2003, 44, 8321 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Chang, J. Herath, T. H. Wang and C. S. Chow, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2008, 16, 2676 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, Y. Jia, Y. Li and C. Yu, Org. Lett., 2022, 24, 511 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Wang, Q. Sun, Y. Jiang, H. Zhang, L. Yu, C. Tian, G. Chen and M. J. Koh, Nat. Synth., 2022, 1, 235 CrossRef.
- M. Pfeiffer and B. Nidetzky, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 6270 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Chang, J. Herath, T. H. Wang and S. Chow, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2008, 16, 2676 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Yu, H. Chang and T. Chien, New J. Chem., 2019, 43, 8796 RSC.
- A. Matsuda, C. K. Chu, U. Reichman, K. Pankiewicz, K. A. Watanabe and J. J. Fox, J. Org. Chem., 1981, 46, 3603 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. H. Jin, P. Liu, J. Wang, R. Baker, J. Huggins and C. K. Chu, J. Org. Chem., 2003, 68, 9012 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. C. Kofnik and P. Knochel, Org. Lett., 2006, 8, 4121 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Momotake, J. Miyo, K. Yamaguchi, H. Togo and M. Yokoyama, J. Org. Chem., 1998, 63, 7207 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d2re00381c |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2023 |