Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: Fluorescence resonance energy transfer enhanced photothermal and photodynamic antibacterial therapy post a single injection
Lei
Xue
a,
Qing
Shen
a,
Tian
Zhang
a,
Yibin
Fan
b,
Xiaogang
Xu
c,
Jinjun
Shao
*a,
Dongliang
Yang
a,
Wenli
Zhao
a,
Xiaochen
Dong
*a and
Xiaozhou
Mou
*d
aKey Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (KLOFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing Tech University (NanjingTech), Nanjing 211816, China. E-mail: iamjjshao@njtech.edu.cn; iamxcdong@njtech.edu.cn
bDepartment of Dermatology, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital, Affiliated People's Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou 310014, China
cDepartment of Geriatrics, Zhejiang Provincial Key Lab of Geriatrics & Geriatrics Institute of Zhejiang Province, Zhejiang Hospital, Hangzhou 310013, China
dClinical Research Institute, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital, Affiliated People's Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou 310014, China. E-mail: mouxz@zju.edu.cn
First published on 26th May 2023
Abstract
Correction for ‘Fluorescence resonance energy transfer enhanced photothermal and photodynamic antibacterial therapy post a single injection’ by Lei Xue et al., Mater. Chem. Front., 2021, 5, 6061–6070, https://doi.org/10.1039/D1QM00631B.
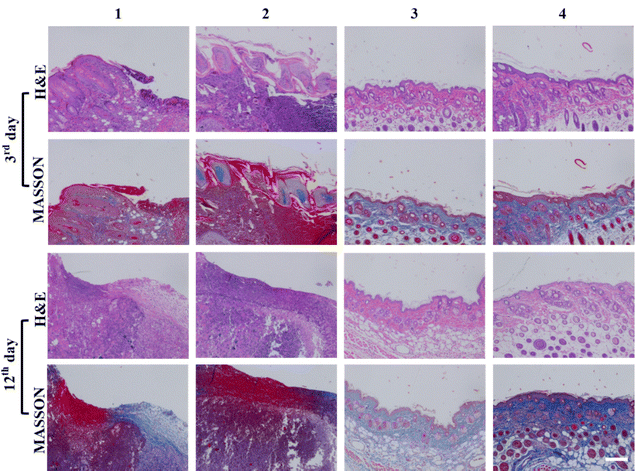
The authors regret that some errors have been identified in Fig. 4 and 7 of the original article.
Incorrect images were used for the bacterial viability of NDIA@PEG-Ce6/B at 808 nm, shown in Fig. 4(b) and in the agar plate photographs of MRSA treated with ‘NDIA@PEG-Ce6/B + 808 nm Laser’, shown in Fig. 4(d).
Incorrect images were used to demonstrate the H&E-stained image for group 4 (column 4: row 1 & row 2) and MASSON-stained image for group 3 (column 3: row 3 & row 4) in Fig. 7.
The correct versions of these figures are shown here. The data analysis and conclusions for this work remain unchanged.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2023 |