Effects of film thickness on electrochemical properties of nanoscale polyethylenedioxythiophene (PEDOT) thin films grown by oxidative molecular layer deposition (oMLD)
Abstract
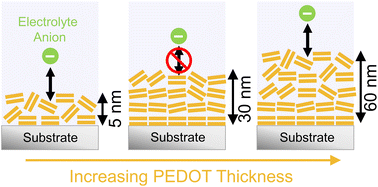
Poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene) (PEDOT) has a high theoretical charge storage capacity, making it of interest for electrochemical applications including energy storage and water desalination. Nanoscale thin films of PEDOT are particularly attractive for these applications to enable faster charging. Recent work has demonstrated that nanoscale thin films of PEDOT can be formed using sequential gas-phase exposures via oxidative molecular layer deposition, or oMLD, which provides advantages in conformality and uniformity on high aspect ratio substrates over other deposition techniques. But to date, the electrochemical properties of these oMLD PEDOT thin films have not been well-characterized. In this work, we examine the electrochemical properties of 5–100 nm thick PEDOT films formed using 20–175 oMLD deposition cycles. We find that film thickness of oMLD PEDOT films affects the orientation of ordered domains leading to a substantial change in charge storage capacity. Interestingly, we observe a minimum in charge storage capacity for an oMLD PEDOT film thickness of ∼30 nm (60 oMLD cycles at 150 °C), coinciding with the highest degree of face-on oriented PEDOT domains as measured using grazing incidence wide angle X-ray scattering (GIWAXS). Thinner and thicker oMLD PEDOT films exhibit higher fractions of oblique (off-angle) orientations and corresponding increases in charge capacity of up to 120 mA h g−1. Electrochemical measurements suggest that higher charge capacity in films with mixed domain orientation arise from the facile transport of ions from the liquid electrolyte into the PEDOT layer. Greater exposure of the electrolyte to PEDOT domain edges is posited to facilitate faster ion transport in these mixed domain films. These insights will inform future design of PEDOT coated high-aspect ratio structures for electrochemical energy storage and water treatment.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanoscale 2023 Emerging Investigators


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...