On the application of hydrodynamic cavitation on a chip in cellular injury and drug delivery†
Abstract
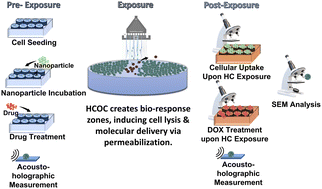
Hydrodynamic cavitation (HC) is a phase change phenomenon, where energy release in a fluid occurs upon the collapse of bubbles, which form due to the low local pressures. During recent years, due to advances in lab-on-a-chip technologies, HC-on-a-chip (HCOC) and its potential applications have attracted considerable interest. Microfluidic devices enable the performance of controlled experiments by enabling spatial control over the cavitation process and by precisely monitoring its evolution. In this study, we propose the adjunctive use of HC to induce distinct zones of cellular injury and enhance the anticancer efficacy of Doxorubicin (DOX). HC caused different regions (lysis, necrosis, permeabilization, and unaffected regions) upon exposure of different cancer and normal cells to HC. Moreover, HC was also applied to the confluent cell monolayer following the DOX treatment. Here, it was shown that the combination of DOX and HC exhibited a more pronounced anticancer activity on cancer cells than DOX alone. The effect of HC on cell permeabilization was also proven by using carbon dots (CDs). Finally, the cell stiffness parameter, which was associated with cell proliferation, migration and metastasis, was investigated with the use of cancer cells and normal cells under HC exposure. The HCOC offers the advantage of creating well-defined zones of bio-responses upon HC exposure simultaneously within minutes, achieving cell lysis and molecular delivery through permeabilization by providing spatial control. In conclusion, micro scale hydrodynamic cavitation proposes a promising alternative to be used to increase the therapeutic efficacy of anticancer drugs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...