One-year nutrition counselling in the context of a Mediterranean diet reduced the dietary inflammatory index in women with breast cancer: a role for the dietary glycemic index†
Abstract
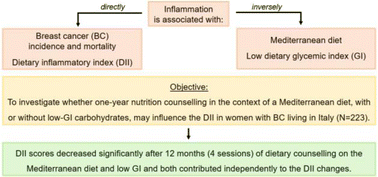
Background: the Mediterranean diet, the low dietary glycemic index (GI) and the dietary inflammation index (DII®) have been associated with lower risk of breast cancer (BC) incidence and mortality. Objective: to investigate whether one-year nutrition counselling in the context of a Mediterranean diet, with or without low-GI carbohydrates counselling, may influence the DII in women with BC. Methods: data were obtained from participants of DEDiCa trial randomized to a Mediterranean diet (MD, n = 112) or a Mediterranean diet with low-GI carbohydrates (MDLGI, n = 111). The diet-derived DII and GI were calculated from 7-day food records while Mediterranean diet adherence from PREDIMED questionnaire. Differences between study arms were evaluated through Fisher's exact test or Mann–Whitney test and associations with multivariable regression analyses. Results: Mediterranean diet adherence significantly increased by 15% in MD and 20% in MDLGI with no difference between arms (p < 0.326). Dietary GI significantly decreased from 55.5 to 52.4 in MD and 55.1 to 47.6 in MDLGI with significant difference between arms (p < 0.001). DII significantly decreased by 28% in MD and 49% in MDLGI with no difference between arms (p < 0.360). Adjusting for energy intake (E-DII) did not change the results. Higher Mediterranean diet adherence and lower dietary GI independently contributed to DII lowering (β-coefficient −0.203, p < 0.001; 0.046, p = 0.003, respectively). Conclusions: DII and E-DII scores decreased significantly after one-year with 4 nutrition counselling sessions on the Mediterranean diet and low GI. Increased adherence to the Mediterranean diet and low GI independently contributed to the DII changes. These results are relevant given that lowering the inflammatory potential of the diet may have implications in cancer prognosis and overall survival.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...