In vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of novel half-sandwich ruthenium complexes containing quinoline derivative ligands†
Abstract
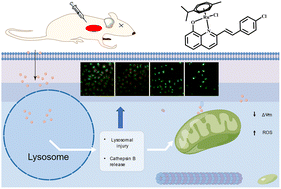
A series of half-sandwich ruthenium complexes containing quinoline derivative ligands was synthesized, which had excellent antitumor toxicity toward a variety of cell lines and could localize lysosomes. The damage of lysosomes promotes the release of cathepsin B and initiates downstream apoptotic cascade signals. The increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) caused by the decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) synergistically amplified the damage degree of lysosomes. In addition, the complex could inhibit cell transfer and clone formation. In vivo results showed that the complex had excellent biological effects in tested mouse samples as the body weight of mice did not change much during the treatment, and the mean tumor volume was significantly lower than the control group.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...