DOI:
10.1039/D3CS90060F
(Correction)
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2023,
52, 5340-5342
Correction: Near-infrared metal agents assisting precision medicine: from strategic design to bioimaging and therapeutic applications
Received
5th July 2023
, Accepted 5th July 2023
First published on 12th July 2023
Abstract
Correction for ‘Near-infrared metal agents assisting precision medicine: from strategic design to bioimaging and therapeutic applications’ by Chonglu Li et al., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2023, 52, 4392–4442, https://doi.org/10.1039/D3CS00227F.
The authors regret that there were errors in some of the molecular structures in Fig. 5 (compound 19), Fig. 9 (compound 43), Fig. 11 (compounds 51 and 54), Fig. 12 (compound 56) and Fig. 15 (compounds 74 and 76) in the original article. The corrected figures are shown here. None of the conclusions in the paper are affected by these corrections.
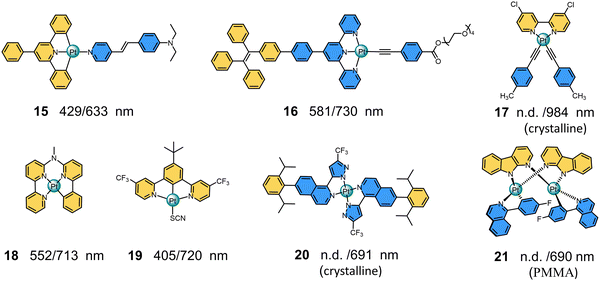 |
| | Fig. 5 Chemical structures and maximum absorption/emission wavelengths of NIR-I Pt(II) polypyridine complexes (15–21). | |
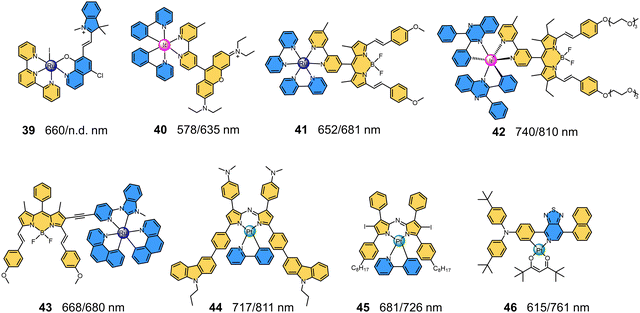 |
| | Fig. 9 Chemical structures and maximum absorption/emission wavelengths of NIR-I MMCs containing fluorophore ligands (39–46). | |
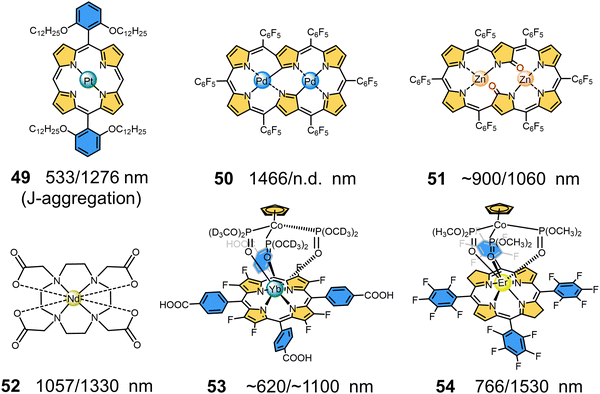 |
| | Fig. 11 Chemical structures and maximum absorption/emission wavelengths of NIR-II MMCs containing porphyrin ligands (49–54). | |
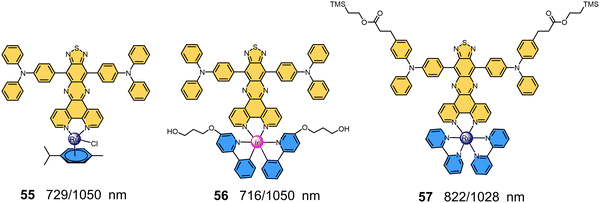 |
| | Fig. 12 Chemical structures and maximum absorption/emission wavelengths of NIR-II MMCs containing fluorophore ligands (55–57). | |
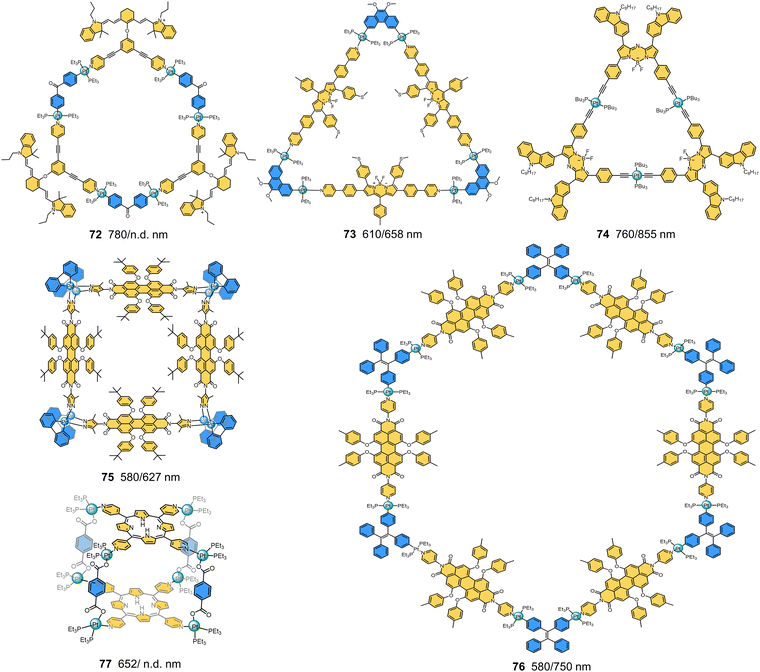 |
| | Fig. 15 Chemical structures and maximum absorption/emission wavelengths of NIR-I MOCs (72–77) containing fluorophores. | |
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
Footnote |
| † Equally contributed. |
|
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2023 |
Click here to see how this site uses Cookies. View our privacy policy here.  Open Access Article
Open Access Article




