Bioorthogonal chemistry for prodrug activation in vivo
Abstract
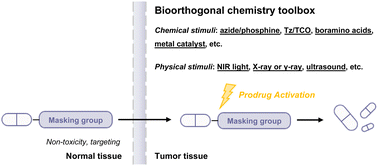
Prodrugs have emerged as a major strategy for addressing clinical challenges by improving drug pharmacokinetics, reducing toxicity, and enhancing treatment efficacy. The emergence of new bioorthogonal chemistry has greatly facilitated the development of prodrug strategies, enabling their activation through chemical and physical stimuli. This “on-demand” activation using bioorthogonal chemistry has revolutionized the research and development of prodrugs. Consequently, prodrug activation has garnered significant attention and emerged as an exciting field of translational research. This review summarizes the latest advancements in prodrug activation by utilizing bioorthogonal chemistry and mainly focuses on the activation of small-molecule prodrugs and antibody–drug conjugates. In addition, this review also discusses the opportunities and challenges of translating these advancements into clinical practice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...