Thermally stable proton conductivity from nanodiamond oxide†
Abstract
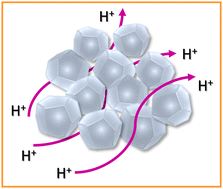
Herein, we report nanodiamond oxide (NDOx), obtained from modified Hummers’ oxidation of nanodiamond (ND), showing excellent proton conductivity and thermal stability. NDOx possesses hydrophilicity resulting in higher water adsorption and the retention of functional groups at elevated temperatures can be attributed to the high proton conductivity and thermal stability, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...