Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: Sodium doping for enhanced performance by highly efficient CsPbBr3 quantum dot-based electroluminescent light-emitting diodes
Yi
Huang
a,
Pengfei
Tang
a,
Wenxia
Zhang
*a,
Wensheng
Yan
a,
Bin Liu
b,
Xiaosheng
Tang
*ac,
Zhen
Wang
a,
Yue
Peng
a and
Weiwei
Chen
*a
aCollege of Optoelectronic Engineering, Chongqing University of Post and Telecommunications, Chongqing 400065, People's Republic of China. E-mail: zhangwx@cqupt.edu.cn; xstang@cqupt.edu.cn; chenww@cqupt.edu.cn
bSchool of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, People's Republic of China
cSchool of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, People's Republic of China
First published on 2nd March 2022
Abstract
Correction for ‘Sodium doping for enhanced performance by highly efficient CsPbBr3 quantum dot-based electroluminescent light-emitting diodes’ by Yi Huang et al., J. Mater. Chem. C, 2022, DOI: 10.1039/d1tc05997a.
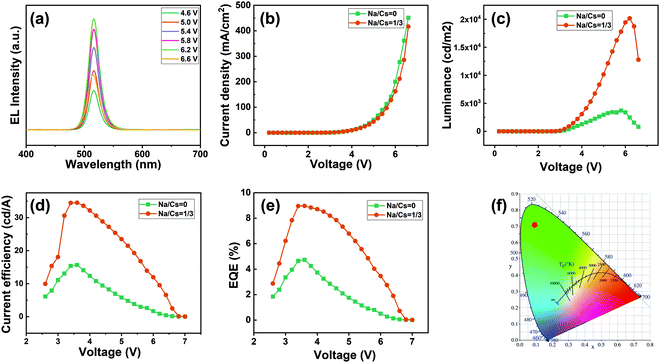
The authors regret an error in Fig. 7 in the published article, where Fig. 7b (current density–voltage plot) was accidentally replaced with a duplicate of Fig. 7d. The correct version of Fig. 7 is shown here.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2022 |