pH-Responsive nanomicelles for breast cancer near-infrared fluorescence imaging and chemo/photothermal therapy†
Abstract
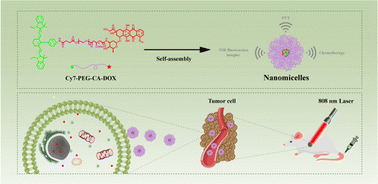
Chemotherapy, despite being the most common and effective cancer treatment, can cause several toxic adverse effects. Multimodal combined antitumor therapy, which accounts for the deficiency of monotherapy, has become an effective strategy for clinical cancer treatment. In this study, we describe the development of pH-sensitive Cy7-PEG-CA-DOX micelles with antitumor activity for controlled drug release, tumor imaging, and their synergy with photothermal therapy (PTT) and chemotherapy. The cyanine dye Cy7 was used as a near infrared (NIR) fluorophore and photosensitizer, and polyethylene glycol (PEG) served as a biocompatible carrier. The anticancer drug doxorubicin (DOX) was loaded onto PEG via aconitic anhydride bonds to increase pH sensitivity. Cy7-PEG-CA-DOX molecules initiated self-assembly to form nanomicelles (∼64.21 ± 0.49 nm) in aqueous solution. In vitro the DOX release rate reached 78% after 48 h at pH 5.5 due to the amide bond between DOX and aconitic anhydride becoming readily broken at low pH. Moreover, intracellular uptake images showed that Cy7-PEG-CA-DOX micelles effectively released DOX in 4T1 tumor cells. In vivo fluorescence imaging revealed that Cy7-PEG-CA-DOX micelles aggregated at tumor sites with optimal tumor imaging properties. More importantly, Cy7-PEG-CA-DOX micelles facilitated the favorable anti-breast cancer properties elicited by PTT and chemotherapy in vivo. This study provides a novel platform for constructing responsive multifunctional anticancer nanoparticles, which have significant potential applicability in controlled drug release and synergistic cancer therapy.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry C HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...