A {Zn4} cluster as a bi-functional luminescence sensor for highly sensitive detection of chloride ions and histidine in aqueous media†
Abstract
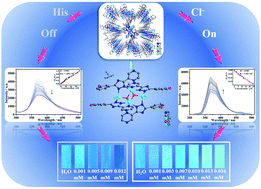
The luminescence sensor is one of the most effective devices for monitoring environmental pollution. By combining precise structures and defined functional sites, luminescent coordinated metal clusters (LCMCs) can allow mechanism-based luminescence sensing optimization. Here, a {Zn4} cluster has been fabricated by introducing uncoordinated N-, OH-dual hydrogen-bonding active sites as well as coordination of unsaturated ZnII sites. As expected, the {Zn4} cluster displays high selectivity and sensitivity for sensing Cl− with low detection limits (LODs) in pure water (0.94 μM), HEPES biological buffer (1.44 μM), and real river water media (1.36 μM) by luminescent enhancement which are much lower than the minimum standards of drinking water enacted by the World Health Organization (WHO) and U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (7.05 mM). Additionally, the {Zn4} cluster is also sensitive to histidine with low LODs in both pure water (0.83 μM), HEPES biological buffer (4.87 μM) and real river water samples (1.18 μM) through the luminescent quenching effect. Luminous test papers of the {Zn4} cluster are made to provide a convenient, quick and real-time naked eye detection effect for sensing Cl− and histidine. The luminescence sensing mechanism of Cl− is further revealed via integrating several experiments with density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The results indicate that the {Zn4} cluster is a promising material candidate for application in environmental monitoring.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...