Thgraphene: a novel two-dimensional carbon allotrope as a potential multifunctional material for electrochemical water splitting and potassium-ion batteries†
Abstract
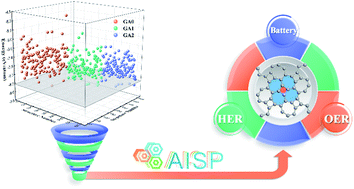
With crystal structure prediction using a genetic algorithm method, we propose a novel two-dimensional (2D) carbon allotrope with relatively low energy, which is composed of tetragonal and heptagonal carbon rings, named thgraphene. The robust thermodynamic, dynamic, and mechanic stability of thgraphene signify the high possibility for experimental synthesis. As a metallic 2D carbon material, thgraphene is proved to be an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions (HER and OER), with low overpotentials of 0.14 V and 0.46 V, respectively. Moreover, the HER/OER catalytic activities can be further tuned close to the ideal values by applying a certain amount of strain. Also, we find that thgraphene is a promising anode material for potassium-ion batteries due to its excellent ductility (Poisson’s ratio ∼ 0.39), ultra-low diffusion barrier (0.06 eV), high theoretical specific capacity (744 mA h g−1), and moderate average open-circuit voltage (0.30 V). Our findings highlight a new 2D carbon allotrope as a bifunctional HER/OER electrocatalyst and potassium-ion anode material.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...