Enhanced CO capture properties of Li2MnO3via inducing layered to spinel transition by cation doping with Fe, Co, Ni and Cu†
Abstract
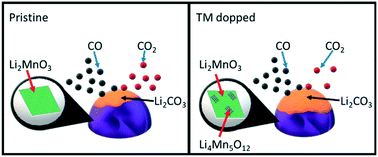
Lithium manganate (Li2MnO3) was the first alkaline ceramic to show selective CO chemisorption in non-oxidative atmospheres, which is of interest for gas separation processes, such as high purity H2 production. Thus, in the present study, the partial substitution of 10 mol% of the Mn ions in Li2MnO3 with Fe, Co, Ni or Cu ions to modify the CO oxidation–chemisorption properties was examined. All solid solutions were synthesized by a solid-state reaction and then characterized by XRD, Raman, EPR, XPS, SEM and EDS-mapping. Hence, it was evidenced that the addition of the different transition metal ions to the Li2MnO3 crystal structure induces several structural modifications, such as the formation of spinel Li1+xMn2−xO4 (0 < x < 0.33) and oxygen deficiencies at the particle surface. Also, in the copper case, partial integration of the Cu2+ ions due to CuO formation was identified. Afterwards, the CO oxidation–chemisorption processes were evaluated dynamically and isothermally through thermogravimetry. The kinetics were determined and fitted to the modified Jander–Zhang model for CO capture. These results showed that in all the solid solutions the CO oxidation–chemisorption surface and bulk processes were improved due to the easy lithium and oxygen diffusion. However, the lack of surface oxygens due to the different oxidation states of each transition metal limited the total CO capture in the Co-, Ni- and Cu-containing solid solutions. In fact, Fe–Li2MnO3 displayed the fastest kinetics due to the surface oxygen release as the oxygen deficient structure (Li2MnO3−δ) leads to faster lithium diffusion, increasing the CO capture efficiency in comparison to the pristine Li2MnO3. Thus, the Fe–Li2MnO3 solid solution may be of interest for further studies in gas separation applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...