Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleDimensionless evaluation and kinetics of rapid and ultradeep desulfurization of diesel fuel in an oscillatory baffled reactor†
Jasim I. Humadia,
Saba A. Gheni *b,
Safaa. M. R. Ahmedb and
Adam Harveyc
*b,
Safaa. M. R. Ahmedb and
Adam Harveyc
aPetroleum Processes Engineering, Tikrit University, Iraq
bChemical Engineering Department, Tikrit University, Iraq. E-mail: ghenis@tu.edu.iq
cProcess Intensification Group, School of Engineering, Newcastle University, UK
First published on 30th May 2022
Abstract
The oxidative desulfurization (ODS) of dibenzothiophene in diesel fuel cut using a homogeneous liquid catalytic system in a novel reactor is presented. Hydrogen peroxide was the oxidizing agent and acetic acid was the liquid catalyst. The oxidation process was conducted in a meso-oscillatory baffled reactor (“mesoOBR”) under mild operating conditions: atmospheric pressure, and 60 to 80 °C. The reactor was operated over a range of residence times (1–3 min), and frequencies and amplitudes of oscillation, leading to oscillatory Reynolds numbers in the range 64–383, and net flow Reynolds numbers in the range 5 to 16. The results showed that dibenzothiophene (DBT) removal in the OBR was significantly higher than in conventional processes under the same conditions (pressure of 1 atm and temperature near room temperature). The maximum DBT conversion was 94%, which was achieved in 3 min at 4 Hz and 6 mm amplitude. A significant improvement in the removal efficiency of DBT was achieved in OBR within only 3 minutes compared to previous studies, which required at least a half-hour reaction time to achieve the same or less removal efficiency. A reaction kinetic model was developed using the optimum experimental results achieved in the OBR. The apparent reaction order was 1, with significantly low apparent activation energies (24.7–29.0 kJ mol−1).
1. Introduction
Among the wide variety of contaminants in fossil fuels (e.g., crude oil, jet fuel, gasoline, diesel, etc.), naturally occurring organic sulfur compounds (OSCs) are the most abundant.1–3 The most common OSCs in fossil fuels are sulfides, disulfides, mercaptans, and thiophene (Th), and their derivatives. These types of OSCs release toxic SOx, upon combustion, leading to health and environmental problems.3–6 The most common technique for removing these compounds is hydrodesulfurization, however, the hydrodesulfurization (HDS) process requires severe operating conditions (high pressure and temperature), expensive hydrogen gas, and it is less useful in the removal of thiophene and its derivatives like DBT. Among the alternative desulfurization technologies to hydrodesulfurization, oxidative desulfurization (ODS) has received a great deal of attention in academia and industry.7,8 ODS involves organic sulfur compounds being oxidized to their corresponding sulfoxides and/or sulfones.9–11 Nawaf et al.12 investigated the ODS of DBT in light gas oil (LGO) using air as an oxidant under moderate operating conditions (atmospheric pressure, temperature range (130–200) oC) with MnO2/γ-Al2O3 as a catalyst in a trickle bed reactor under various operating conditions as follows: atmospheric pressure, temperature (403 K, 443 K, 473 K), initial sulfur content (600 ppm, 800 ppm, 500 ppm), and LHSV(1 h−1, 2 h−1, 3 h−1). They showed that the highest DBT conversion (81.2%) was achieved at 600 ppm, temperature = 473 K, and residence time = 1 h. Joskić et al.13 investigated the ODS of model gas oil using H2O2 as an oxidant and acetic acid as a catalyst in a batch reactor. The degree of sulfur removal increased to 90% at 90 °C, over 80 min. Numerous researchers studied the oxidative desulfurization process and suggested various kinetic models that describe the oxidation process, including first-order,14–17 second-order model,17,18 and nth-order models.19–22Various types of reactor designs have been used to oxidize sulfur compounds in diesel fuel in batch and flow processes. Li et al.23 studied oxidative desulfurization of model oil (BT or DBT in n-octane) with sulfur content 1000 ppm, using hydrogen peroxide as oxidant and tetra alkyl ortho-titanates (TAOTs) as catalysts in a batch reactor. The typical operating conditions required to reduce the sulfur content from 1000 to 10 ppm were: 10 min, molar ratio of O/S = 6, room temperature, and ambient pressure. Sobati et al.24 proposed a four-impinging-jets reactor (FIJR) for the ODS of kerosene. They examined the ODS at different operating and design parameters such as feed flow rate, inter nozzle distance, jet diameter, and jet Reynolds number. They found that the rate of ODS of kerosene increased because of the impinging process and shear forces exerted on the phases and the rate of ODS in the FIJR increased significantly compared to that obtained by a conventional reactor system such as continuous stirred-tank reactor because of decreasing the mass-transfer resistance due to high intensity mixing. Moreover, about 92% sulfur removal of kerosene has been obtained in FIJR. Various reactor designs have been used to oxidize sulfur compounds in fuel as shown in Table 1.
| Feedstock | System, catalyst/oxidant | Residence time | Type of reactor used | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model diesel fuel | tetra alkyl ortho-titanates (TAOTs)/H2O2 | 10 min | Batch reactor | 23 |
| Kerosene | Formic acid/H2O2 | 20 min | Four-impinging-jets reactor (FIJR) | 24 |
| Model diesel fuel | Isopropanol/H2O2 | 24 h | A film-shear reactor | 25 |
| Diesel fuel | Acetic acid/H2O2 | 3 min | OBR | Present study26 |
A new generation of near-plug flow reactors that can achieve plug flow under laminar flow conditions or flowing of large reactant molecules is OBR; it consists of a tubular device with baffles superimposed with fluid oscillation. OBR is considered in the present study for the first time in the desulfurization research field as an alternative for conventional plug flow reactors. In OBRs, uniform mixing and enhanced transport rates are achieved by the interaction of baffles with the oscillatory motion of the fluid, while maintaining flow conditions approximating plug flow27,28
The net Reynold's number (Ren) is defined as:
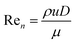 | (1) |
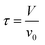 | (2) |
And the velocity of feed flow is;
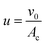 | (3) |
Three dimensionless numbers can describe the dynamic nature of OBRs. Firstly, the oscillatory Reo:
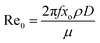 | (4) |
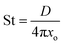 | (5) |
The Strouhal number relates the amplitude of oscillation (inversely proportional) to the baffle spacing (a multiple of D) and measures vortex propagation (degree of eddy propagation).29,31,32 Large St values are achieved at small amplitudes, giving poor vortex formation and vice versa. The previous studies in the literature showed that the tested range for St is 0.01–9;33,34 however, the range used most commonly is 0.15–4.35–37
The velocity ratio is described as the ratio of Reo to Ren, as shown in eqn (6).38
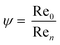 | (6) |
The most common scale-up methodology for commercial reactors that has been reported in the literature is based on matching the dimensionless groups. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the effect of conducting the ODS of diesel fuel at various oscillatory flow dimensionless groups at milder conditions, with significant 1-pass conversion and continuous reactors, thereby reducing time and efforts of scaling up process.
2. Experimental
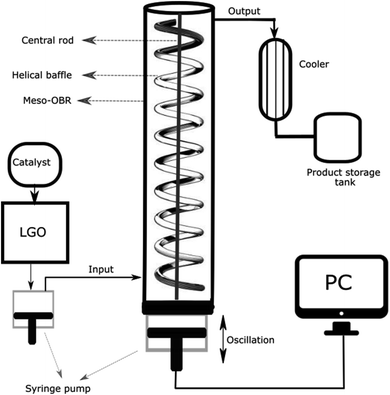
ODS was performed in the liquid phase using a homogeneous catalyst (acetic acid) and hydrogen peroxide oxidant. The experimental work can be summarized via the following steps:1. Designing, installation, and operation of an oscillatory baffled reactor using a helical baffle with a central rod.
2. Evaluating the performance of the OBR utilizing oxidation of sulfur compound in OBR at different mixing and operating conditions, which are temperature, residence time, the amplitude of oscillation, and the frequency of oscillation using acetic acid as a catalyst and H2O2 as an oxidant for DBT oxidation reaction.
2.1 Materials
The feedstock used was diesel fuel (total sulfur content 9 ppm), obtained from Pendik Company, Turkey. The physical properties of oil feedstock are given in Table S1,† below. Dibenzothiophene (DBT) was used as the model sulfur compound in the oil feedstock in this study. The DBT was obtained from Alfa Aesar Company, U.K. The specifications of the DBT used are summarized in Table S2.† Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was obtained from Merck Millipore Company, Germany. Its specifications are also summarized in Table S2.† Acetic acid (CH3COOH, 99% purity, J.T. Baker Company, USA) was used as a liquid catalyst in this work.2.2 Experimental setup
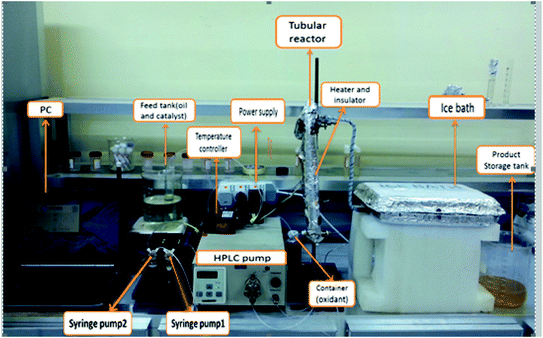
The continuous oxidation of DBT was carried out in an OBR unit. Fig. 1 is a diagram of the unit.The OBR unit consisted of an 8 mm inner diameter and 380 mm length fitted with 1.5 mm helical baffles with a 1.2 mm central insert, and a 12 mm pitch (Fig. 1), providing a volume of 19 mL. The OBR is connected to two Confluent PVM C-Series syringe pumps via PTFE tubing and a custom-built Swagelok union. Syringe pump 1 was used for feeding the diesel fuel and the catalyst from the feed tank to the reactor and syringe pump 2 was used for providing the fluid oscillation inside the reactor and for varying the frequency of oscillation from 0 to 4.34 Hz and the amplitude of oscillation from 0 to 12 mm. The pumps were made of 316 stainless steels, and were supplied by Eurodyne, Ltd, U.K. Both the oscillation amplitude and frequency were controlled by commands written in “Sapphire Commander” software. A liquid dosing pump made of 316 stainless steel type by CoMetro Technology, Ltd, U.K., was used for feeding the hydrogen peroxide solution to the tubular reactor Fig. 2.
2.3 Experimental runs
The first part of this study was conducted to evaluate the performance of OBR in the removal of the sulfur compounds (DBT) removal from diesel fuel via the ODS process using H2O2 as oxidant and acetic acid as catalyst under the operating conditions shown in Table 2. The volumetric ratio of diesel fuel to the oxidant (H2O2) and the ratio of the diesel fuel to the liquid catalyst (CH3COOH) were 25 and 10, respectively.39 To conduct the experimental runs, the temperature of the reactor was set to the desired temperature using the temperature controller. The liquid catalyst (acetic acid) was added to the feed tank and well mixed with the oil, then fed to the reactor as an emulsion. The desired flow rate was obtained by regulating the syringe pump using the software. Hydrogen peroxide was fed to the reactor at the desired flow rate by regulating the dosing pump. The fluid oscillation was achieved by oscillating the second syringe pump 2, which was set at the desired frequency and amplitude of oscillation by the Sapphire Commander software. When the system was at a steady state, the liquid samples were withdrawn from the liquid outlet of the cooling system and extraction process to remove the remnant of hydrogen peroxide (the oxidant), catalyst and the ODS products from the sweet fuel. Samples of the treated fuel were left to settle to allow for separation by extraction. The residue oil obtained from oxidation step subsequently then to be continued with the liquid–liquid extraction step by mixing the oxidized residue oil with solvent (ethanol) into the conical flask with the residue oil/solvent ratio (v/v) of 1/1. The mixture was heated to temperature of 30 °C accompanied by constant stirring for 60 min. Then the raffinate and extract phase was separated using separation funnel. Then, the samples were labeled for testing and analysis for the remaining sulfur content against the fresh sample. The reactor was left to cool to room temperature; then, it was removed and cleaned. Nitrogen was used to get rid of the by-product gases; then, ethanol was flown to wash the streams of the OBR unit.| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Temperature, °C | 60, 70, 80 |
| Residence time, min | 1, 2, 3 |
| Oscillation amplitude, mm | 2, 4, 6 |
| Oscillation frequency, Hz | 2, 3, 4 |
| Strouhal number, St | 0.3, 0.2, 0.1 |
| Oscillatory Reynolds number, Reo | 64–383 |
| Net flow Reynolds number, Ren | 5, 8, 16 |
| Velocity ratio, ψ = Reo/Ren | 4–72 |
2.4 Kinetic studies
The second part of this project dealt with investigating the kinetics of the oxidation reaction in the OBR. The kinetic parameters determined were the order of reaction (n), constant of reaction (k), pre-exponential factor (k0), and activation energy (E). The parameters were estimated at the optimal oscillation conditions obtained in the first part of this work. The kinetic runs were conducted at various times of reaction (0.5 min to 3 min) and at three different temperatures (60, 70, and 80 °C). DBT content in the feedstock and the desulfurized diesel fuel was tested in the HPLC system (EX-1600 FLD, Selon, China, C18 reverse-phase column (Philips, 5 μm × 0.4 cm), wavelength = 287). The mobile phase was n-hexane (HPLC grade, J.T. Baker, USA) flows at 1.0 mL min−1. The DBT percent conversion was calculated by eqn (6):
 | (7) |
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of the net flow on DBT conversion
The conversion of the DBT as a function of Ren (5, 8, and 16) and Reo (pressure, reaction temperature, the amplitude of oscillation, and frequency of oscillation) are shown in Fig. 3. It shows that the DBT conversion in OBR increased with increasing agitation. The conversion of DBT was increased when Ren was reduced as depicted in Fig. 4. This may be due to Ren being directly proportional to the diesel flow rate and inversely proportional to the residence time of reactants inside the OBR. So, the residence -time of reactants decreases with the increase of Rev. Hence DBT removal efficiency decreased. Also, laminar flow conditions were enhanced with a decrease in Ren. Thus, DBT removal efficiency was enhanced in OBR due to applying Ren ≤ 16 in the present study. The effect is more pronounced at higher Ren as the activity of the acetic acid catalyst decayed due to the high load of the reactant (feedstock) flown to the OBR.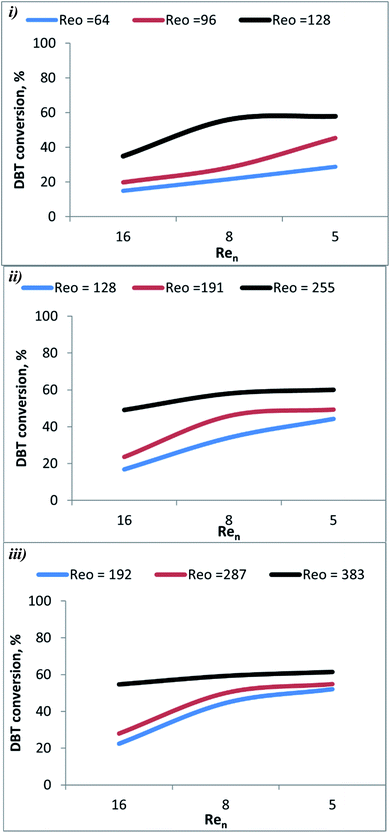 | ||
| Fig. 3 Effect of Ren on DBT conversion at different oscillation conditions and 60 °C (i) St = 0.3 (ii) 0.2 (iii) 0.1. | ||
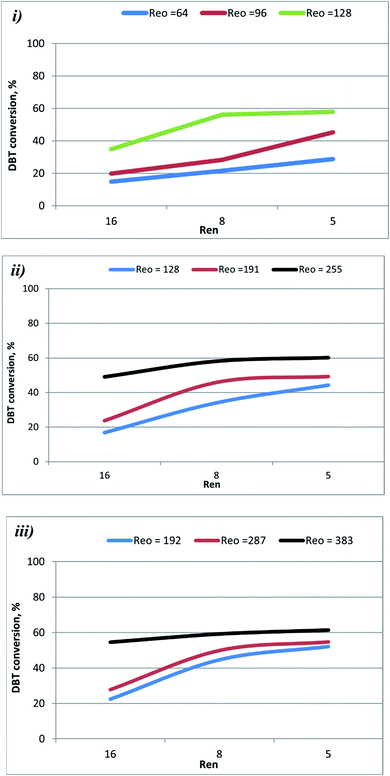 | ||
| Fig. 4 Effect of Ren on DBT conversion at different oscillation conditions and 70 °C.(i) St = 0.3 (ii) 0.2 (iii) 0.1. | ||
Fig. 5 shows that DBT conversion in the OBR was enhanced by decreasing flow rate (increasing residence time) and herby decreasing Ren. At T = 60 °C and xo = 2 mm, and f = 2 Hz, the conversion of the DBT increased from 15.0% to 22% as Ren decreased from 16 to 8. As the Ren was decreased to 5, the DBT conversion increased to 29.0%. At xo = 4 mm and f = 3 Hz, the increase to 70 °C with reducing the Ren from 16 to 5 resulted in raising the DBT conversion from 54.0% to 65.0%. At xo = 6 mm, f = 4 Hz, a significant increase in DBT conversion from 68.0% to 94.0% was observed as the temperature was raised to 80 °C, and the Ren was decreased from 8 to 5. In the present study, Ren was ≤ 16, suggesting that the flow was oscillating laminar. DBT conversion decreases as Ren increases as the residence time decreases. In a previous study,40 it was shown that good plug flow was obtained in a 350 mm length helically baffled meso-OBR at Ren = 2.55–7.2, Reo = 50–800 using a St = 0.1, and Reo = 50–300 using a St = 0.2. Their finding supports that the design of the reactor and the operating conditions in the present study are compatible with the requirements of achieving the plug flow conditions that resulted in the high conversion of DBT in the diesel fuel.
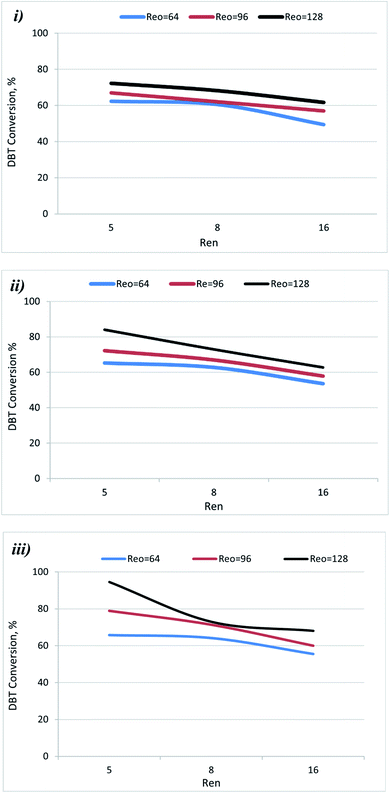 | ||
| Fig. 5 Effect of Ren on DBT conversion at different oscillation conditions and 80 °C. (i) St = 0.3 (ii) 0.2 (iii) 0.1. | ||
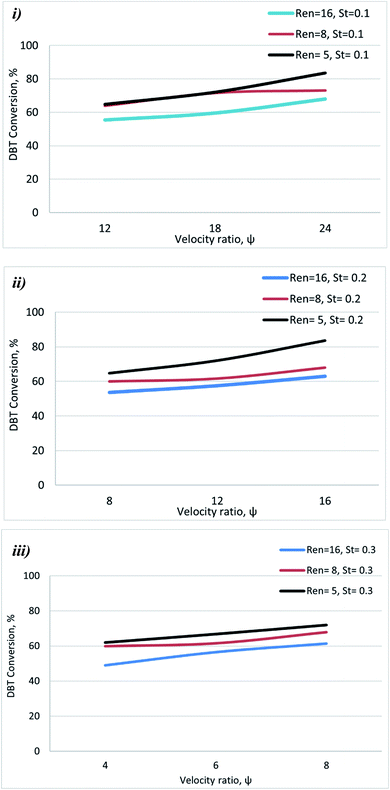
3.2 Effect of amplitude on DBT conversion
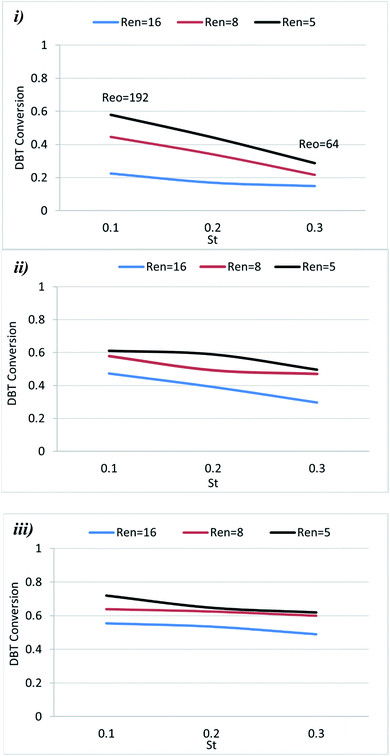
The Strouhal number (St) is the ratio of column diameter to stroke length, measuring the effective eddy propagation.28 The influence of St on DBT removal in the OBR was investigated at different St values (0.1, 0.2, and 0.3) and operation conditions. In general, the results showed that decreasing St led to enhancing the DBT removal.Fig. 6 shows that decreasing St led to enhancing DBT removal. The St is inversely proportional to the amplitude of oscillation and measures vortex propagation.29,31,32 The results showed that the oxidative desulfurization was enhanced by decreasing St due to increasing oscillation amplitude at constant tube diameter, which provides efficient mixing of reactants. As an emulsion reaction system oil (diesel fuel)-hydrogen peroxide), it appeared that the dispersion properties of the peroxide within the oil phase were not affected by the net flow rate, enabling dispersion-independent control of the residence time. Oscillation amplitudes and frequencies are the main parameters responsible for droplet breakage and initiation of the oxidation reaction. It has been reported that the mass transfer coefficient, kLa, decreases with increasing St (lowering the oscillation amplitude).41 The low value of the coefficient was due to the absence of the phase separation within the emulsion (oil containing DBT) and the hydrogen peroxide), which produced an extractive reaction effect.
 | ||
| Fig. 6 Effect of St on DBT conversion at (i) 60 °C, (ii) 70 °C, (iii) 80 °C, and different operation conditions. | ||
All these conditions caused a reduction in DBT conversion as St increases. The range of the St analyzed in the literature was in the range of 0.01–9. High St (St > 0.2) indicates that there is insufficient eddy generation to mix the baffle cavity effectively. In contrast, low St (St < 0.1) indicates intense eddy generation causing vortex propagation into adjacent baffle cavities.40
3.3 Effect of mixing (Reo) on DBT conversion
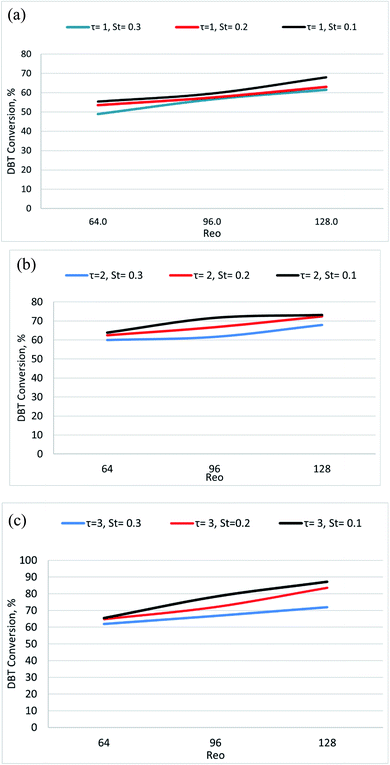
Different Oscillatory Reynolds Numbers (Reo) were examined in the present study to obtain the agitation rate that gives the highest DBT conversion in the OBR. The DBT removal efficiency was studied at the Reo range of 64–383, 80 °C, different residence times, and oscillation conditions. Generally, DBT removal increased with increasing Reo.Fig. 7 shows the profiles of desulfurization efficiency versus mixing intensity (Reo). As noted, an increase in Reo from 64 to 128 leads to increased desulfurization, from 66% to 94% at T = 80 °C and residence time of 3 min. Also, increasing the Reo from 64 to 128 leads to increasing desulfurization efficiency from 72% to 94% at T = 80 °C and a residence time = 3 min.
 | ||
| Fig. 7 Effect of Reo on DBT conversion at 80 °C at a different residence time (a) 1 min (b) 2 min (c) 3 min. | ||
The removal of DBT was increased by utilizing the oscillatory flow mixing (as measured by the Reo), due to enhanced mixing, as the Reo increased. As the ODS by hydrogen peroxide depends on the contact between the liquid–liquid reacting phases, therefore, mass transfer in the system becomes a crucial factor, and the contact between reacting phases increases the mixing quality of the liquid–liquid system in an OBR.42 Therefore, oscillatory mixing, which is governed by Reo, can be an effective method of removing mass transfer limitations in liquid systems. A dispersed flow regime is predicted at high Reo (high frequency and amplitude of oscillation) with droplet diameter small enough to limit interactions with the reactor walls. In this case, oscillation frequency was found to have a more significant impact than amplitude on the mass transfer coefficient.
The enhancement of Reo led to improved radial mixing as a result of the periodic vortices generated thereby enhanced plug flow conditions, and this enhancement led to raising the DBT conversion.43 The experiments showed that to achieve an efficient DBT removal conversion in the OBR and reach a very low sulfur content in the fuel, in compliance with the new environmental protection regulations, a combination of oscillation frequency 4 Hz and amplitude 6 mm was required. This is within the range required for high levels of plug flow.51
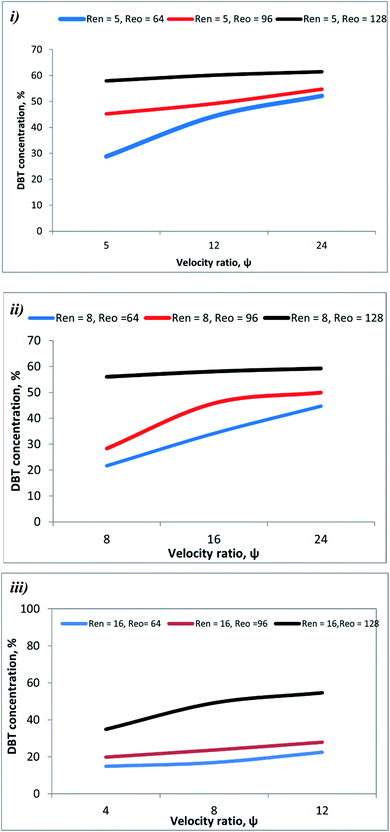
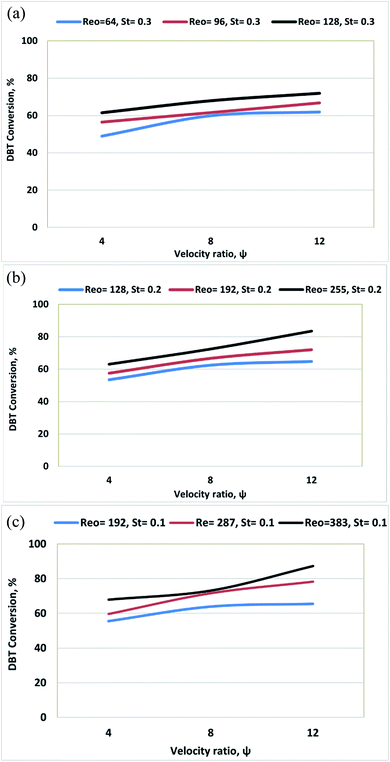
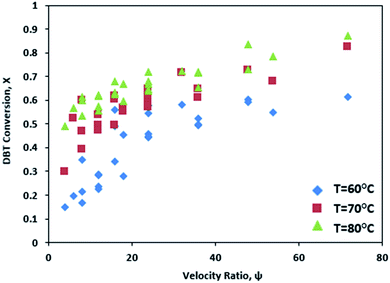
3.4 Effect of the velocity ratio (ψ) on DBT conversion
In this work, the oxidation reaction was conducted at various ψ (4–72). The experimental data showed that ψ significantly influences the DBT removal from diesel fuel. DBT conversion increases from 72% to 94% as ψ increases from 24 to 72 due to increasing Reo (oscillation amplitude) at T = 80 °C and Ren = 5 as shown in Fig. 8.Fig. 9 shows that DBT oxidation was enhanced from 66% to 94% with rising ψ from 36 to 72 due to increasing Reo (oscillation frequency) at T = 80 °C and Ren = 5.
As can be observed in Fig. 10, DBT removal efficiency increases from 68% to 94% with an increasing velocity ratio from 24 to 72 due to decreasing Ren at T = 80 °C and Reo = 383. Also, the DBT conversion due to the ODS process in the OBR is significantly enhanced by raising the ψ and increasing temperature, as shown in Fig. 11.
Phan et al.44 showed also that the plug flow behavior could be achieved in OBRs with a ratio of 2–10 or higher for mesoscale oscillatory helically baffled reactors.44 The present experimental work showed that the highest DBT removal efficiency was achieved at Ren = 5, Reo = 383, and ψ = 72.
3.5 The kinetic study of the ODS process in an OBR
The conditions for maximum DBT conversion were f = 4 Hz and xo = 6 mm at all temperatures (60, 70, and 80 °C). Hence, these conditions were used in the ODS kinetic experiments to obtain the kinetic parameters model towards these reaction variables (temperature and residence time). Fig. 12 shows the DBT conversion as a function of reaction time at different temperatures. The experiments showed that increasing the reaction time from 0.5 min to 3 min led to increasing DBT removal efficiency at the three oxidation temperatures.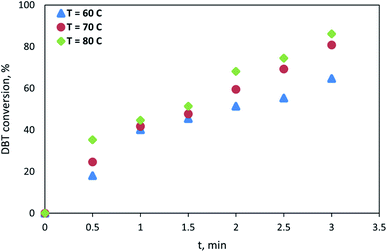 | ||
| Fig. 12 The kinetics profiles of the ODS of DBT in the OBR at = 4 Hz, xo = 6 mm, and different temperatures, conversion versus reaction time. | ||
The DBT conversion increased from 19% to 64% at 60 °C, 25% to 82% at 70 °C, and 36% to 86% at 80 °C as reaction time increases from 0.5 min to 3 min as shown in Fig. 12. It can be seen from Fig. 12 that the DBT removal efficiency increased with reaction time, and the time needed to achieve a high (94%) conversion was very short, at 3 min.
In this analysis, the integral method of kinetic data was used to determine the ODS of DBT kinetic parameters.
The rate law for DBT conversion is written as;
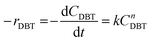 | (8) |
Assuming that the ODS of DBT in the diesel fuel obeys a first-order rate equation (n = 1);
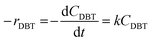 | (9) |
By separating and integrating eqn (9), we obtain:
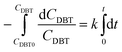 | (10) |
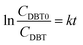 | (11) |
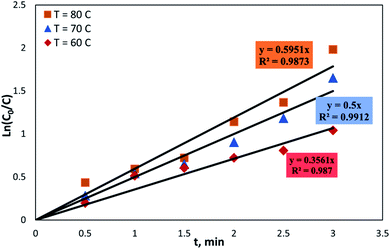
Fig. 13 shows the fitting of the kinetic data of the ODS of DBT in the OBR, according to eqn (11).
The reaction followed a first-order rate law at all temperatures (60, 70, and 80) with an R2 of 0.987, 0.973, and 0.96, respectively. The reaction rate constants were 0.3561 min−1 at 60 °C, 0.5 min−1 at 70 °C, and 0.5951 min−1 at 80 °C. It has been previously reported that the rate of oxidation reaction was well-represented by a first-order model [95, 207, 241].
The apparent activation energy for the oxidation of DBT can be obtained from the slope of the Arrhenius plot according to the linearized form of 1.1 as follow:
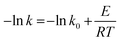 | (12) |
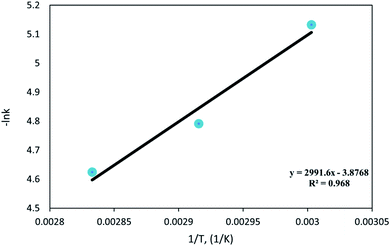
A plot of (−ln![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) k) vs. (1/T) is shown in Fig. 14 and fitted to a straight line. It is found that the activation energy (E) and the pre-exponential factor (k0) of DBT oxidation reaction in the OBR were 24.87 kJ mol−1 and 0.805 s−1, respectively.
k) vs. (1/T) is shown in Fig. 14 and fitted to a straight line. It is found that the activation energy (E) and the pre-exponential factor (k0) of DBT oxidation reaction in the OBR were 24.87 kJ mol−1 and 0.805 s−1, respectively.
The activation energy reveals that this catalytic OBR system could quickly oxidize DBT homologs compounds in OBR. The low pre-exponential factor of the oxidation reaction indicates the non-spontaneity of this reaction.45 Table 3 summarizes the activation energies of the ODS reaction with the first-order kinetics of the present study and previous studies.
The activation energy values reported by the previous studies were higher than the ones obtained in the present study in the OBR system. The oxidation reactivity of the sulfur-containing fuel increases with the increase in the electron density of the sulfur compound and leads to reducing the activation energy of the oxidation reaction.48,49 Therefore, this low activation energy can be attributed to the electrophilic addition of oxygen or the high electron density on S of the DBT.50
4. Conclusions
The oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene (DBT) in diesel fuel was conducted at a laboratory scale in a mesoscale oscillatory baffled reactor (meso-OBR). The parameters studied included: temperature (60–80 °C), residence time (1–3 min), Reynolds number (5–16), oscillatory Reynolds number (64–383), and Starhul number (0.1–0.3). The catalyst used was acetic acid (CH3COOH), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as the oxidant. The reaction was performed at atmospheric pressure. Within this parameter residence, the DBT conversion increased with temperature, residence time, oscillation frequency, and oscillation amplitude. The maximum single-pass conversion of DBT achieved was 94%. This was achieved at 80 °C, oscillatory Reynolds number of 382, and a net flow Reynolds number of 5. While other studies showed the use of other types of reactors, such as the batch, fixed, CSTR, and FIJR reactors, which achieved DBT removal efficiency similar to or less than those achieved in the present study but at a reaction time of not less than 30 min. The DBT conversion could not be increased further by increasing the temperature (more than 80 °C), as this would lead to H2O2 decomposition. However, the meso OBR design allowed a closer approach to the decomposition temperature, which is an advantage of using a tubular flow reactor for this application. The removal of the DBT from the diesel fuel via the homogeneous ODS reaction in the OBR was first order with respect to DBT concentration with lower apparent activation energy in comparison with the previous studies and higher frequency factor, of 24.9 kJ mol−1 and 0.805 s−1, respectively. The combination of the oscillatory motion and the helical baffle design provided sufficient mixing to accelerate the reaction. The operation of the mesoscale OBR at Ren between 5–8 along with Reo of 96–128 offered plug flow behavior. This enables the ODS to be upgraded in the OBR at a substantially short residence time. It was possible to achieve a high-performance continuous ODS process under milder operation conditions.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.References
- N. Li, X. Ma, Q. Zha and C. Song, Analysis and comparison of nitrogen compounds in different liquid hydrocarbon streams derived from petroleum and coal, Energy Fuels, 2010, 24(10), 5539–5547 CrossRef CAS.
- G. H. Prado, Y. Rao and A. de Klerk, Nitrogen removal from oil: a review, Energy Fuels, 2017, 31(1), 14–36 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Pawelec, R. M. Navarro, J. M. Campos-Martin and J. L. Fierro, Towards near zero-sulfur liquid fuels: a perspective review (vol 1, pg 23, 2011), Catal. Sci. Technol., 2013, 3(12), 3376 CAS.
- A. Liaquat, M. M. Kalam and M. Jayed, Potential emissions reduction in road transport sector using biofuel in developing countries, Atmos. Environ., 2010, 44(32), 3869–3877 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Jin, L. Lu, X. Ma, H. Liu, H. Chi and K. Yoshikawa, Effects of blending hydrothermally treated municipal solid waste with coal on co-combustion characteristics in a lab-scale fluidized bed reactor, Appl. Energy, 2013, 102, 563–570 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Colvile, H. Hutchinson, J. Mindell and R. Warrena, The transport sector as a source of air pollution, Atmos. Environ., 2001, 35(9), 1537–1565 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Abro, A. Abdeltawab, S. Al-Deyab, Y. Guangren, A. Qazi, S. Gao and X. Chen, A review of extractive desulfurization of fuel oils using ionic liquids, RSC Adv., 2014, 4(67), 35302–35317 RSC.
- X. Wang, W. Jiang, W. Zhu, H. Li, S. Yin, Y. Chang and H. Li, A simple and cost-effective extractive desulfurization process with novel deep eutectic solvents, RSC Adv., 2016, 6(36), 30345–30352 RSC.
- D. Zhao, Z. Sun, F. Li and H. Shan, Optimization of oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene using acidic ionic liquid as catalytic solvent, J. Fuel Chem. Technol., 2009, 37(2), 194–198 CrossRef CAS.
- X.-M. Yan, G.-s. Su and L. Xiong, Oxidative desulfurization of diesel oil over Ag-modified mesoporous HPW/SiO2 catalyst, J. Fuel Chem. Technol., 2009, 37(3), 318–323 CrossRef CAS.
- C.-f. Mao, R.-x. Zhao and X.-p. Li, Propionic acid-based deep eutectic solvents: synthesis and ultra-deep oxidative desulfurization activity, RSC Adv., 2017, 7(67), 42590–42596 RSC.
- A. Nawaf, A. Jarullah, S. Gheni and M. Iqbal, Development of kinetic and process models for the oxidative desulfurization of light fuel, using experiments and the parameter estimation technique, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2015, 54(50), 12503–12515 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Joskić, D. Margeta and K. S. Bionda, Oxidative desulfurization of model diesel fuel with hydrogen peroxide, Goriva Maziva, 2014, 53(1), 11–18 Search PubMed.
- M. Te, C. Fairbridge and Z. Ring, Oxidation reactivities of dibenzothiophenes in polyoxometalate/H2O2 and formic acid/H2O2 systems, Appl. Catal., A, 2001, 219(1–2), 267–280 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Deshpande, A. Bassi and A. Prakash, Ultrasound-assisted, base-catalyzed oxidation of 4, 6-dimethyl dibenzothiophene in a biphasic diesel–acetonitrile system, Energy Fuels, 2005, 19(1), 28–34 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Wang, E. Qian, H. Amano and K. Okata, Oxidative desulfurization of fuel oil: Part I. Oxidation of dibenzothiophenes using tert-butyl hydroperoxide, Appl. Catal., A, 2003, 253(1), 91–99 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Leitao and A. Rodrigues, Studies on the Merox process: kinetics of N-butyl mercaptan oxidation, Chem. Eng. Sci., 1989, 44(5), 1245–1253 CrossRef CAS.
- P. S. Tam, J. R. Kittrell and J. W. Eldridge, Desulfurization of fuel oil by oxidation and extraction. 2. Kinetic modeling of oxidation reaction, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 1990, 29(3), 324–329 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Zhao, H. Ren, J. Wang, Y. Yang and Y. Zhao, Kinetics and mechanism of quaternary ammonium salts as phase-transfer catalysts in the liquid–liquid phase for oxidation of thiophene, Energy Fuels, 2007, 21(5), 2543–2547 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Farshi and Z. Rabiei, Kinetic study for oxidation of existing mercaptans in kerosene using impregnated activated carbon with MEROX catalyst in alkaline solution, Pet. Coal, 2005, 47(1), 49–56 CAS.
- D. Huang, Y. Wang, Y. Cui and G. Luo, Direct synthesis of mesoporous TiO2 and its catalytic performance in DBT oxidative desulfurization, Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2008, 116(1–3), 378–385 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Wang, F. Yu, G. Zhang and H. Zhao, Performance evaluation of the carbon nanotubes supported CS2.5H0.5PW12O40 as efficient and recoverable catalyst for the oxidative removal of dibenzothiophene, Catal. Today, 2010, 150(1–2), 37–41 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Li, J. Zhang, F. Zhou, Y. Wang, X. Yuan and H. Wang, Oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene and diesel by hydrogen peroxide: Catalysis of H3PMo12O40 immobilized on the ionic liquid modified SiO2, Mol. Catal., 2018, 452, 93–99 CrossRef CAS.
- M. A. Sobati, A. Dehkordi, M. Shahrokhi and A. Ebrahimi, Novel type of four-impinging-jets reactor for oxidative desulfurization of light fuel oils, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2010, 49(19), 9339–9348 CrossRef CAS.
- B. R. Fox, B. Brinich, J. Male, R. Hubbard, M. Siddiqui, T. Saleh and D. Taylor, Enhanced oxidative desulfurization in a film-shear reactor, Fuel, 2015, 156, 142–147 CrossRef CAS.
- J. I. Hammade, et al., Fast, Non-Extractive, and Ultradeep Desulfurization of Diesel in an Oscillatory Baffled Reactor. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021 Search PubMed.
- A. N. Phan and A. Harvey, Development and evaluation of novel designs of continuous mesoscale oscillatory baffled reactors, Chem. Eng. J., 2010, 159(1–3), 212–219 CrossRef CAS.
- F. R. M. Rasdi, A. N. Phan and A. P. Harvey, Rapid determination of reaction order and rate constants of an imine synthesis reaction using a mesoscale oscillatory baffled reactor, Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 222, 282–291 CrossRef.
- X. Ni, M. R. Mackley, A. Harvey, P. Stonestreet, M. Baird and N. Rama Rao, Mixing through oscillations and pulsations—a guide to achieving process enhancements in the chemical and process industries, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 2003, 81(3), 373–383 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Harvey, M. Mackley and P. Stonestreet, Operation and optimization of an oscillatory flow continuous reactor, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2001, 40(23), 5371–5377 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Ni, G. Brogan, A. Struthers and D. Bennett, A systematic study of the effect of geometrical parameters on mixing time in oscillatory baffled columns, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 1998, 76(5), 635–642 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Ni and P. Gough, On the discussion of the dimensionless groups governing oscillatory flow in a baffled tube, Chem. Eng. Sci., 1997, 52(18), 3209–3212 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Brunold, J. Hunns, M. Mackley and J. Thompson, Experimental observations on flow patterns and energy losses for oscillatory flow in ducts containing sharp edges, Chem. Eng. Sci., 1989, 44(5), 1227–1244 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Dickens, M. Mackley and H. Williams, Experimental residence time distribution measurements for unsteady flow in baffled tubes, Chem. Eng. Sci., 1989, 44(7), 1471–1479 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Mackley and P. Stonestreet, Heat transfer and associated energy dissipation for oscillatory flow in baffled tubes, Chem. Eng. Sci., 1995, 50(14), 2211–2224 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Ni, S. Gao, R. Cumming and D. Pritchard, A comparative study of mass transfer in yeast for a batch pulsed baffled bioreactor and a stirred tank fermenter, Chem. Eng. Sci., 1995, 50(13), 2127–2136 CrossRef CAS.
- K. B. Smith, Scale-up of oscillatory flow mixing. 2000, University of Cambridge Search PubMed.
- M. Abbott, A. Harvey and G. Perezet, Biological processing in oscillatory baffled reactors: operation, advantages and potential, Interface Focus, 2013, 3(1), 20120036 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. F. Ali, A. Al-Malki, B. El-Ali, G. Martinie and M. Siddiqui, Deep desulphurization of gasoline and diesel fuels using non-hydrogen consuming techniques, Fuel, 2006, 85(10–11), 1354–1363 CrossRef CAS.
- J. McDonough, A. Phan and A. Harvey, Rapid process development using oscillatory baffled mesoreactors–A state-of-the-art review, Chem. Eng. J., 2015, 265, 110–121 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Hewgill, M. Mackley, M. Pandit and S. Pannu, Enhancement of gas-liquid mass transfer using oscillatory flow in a baffled tube, Chem. Eng. Sci., 1993, 48(4), 799–809 CrossRef CAS.
- E. López-Guajardo, E. Ortiz-Nadal, A. Montesinos-Castellanos and K. Nigam, Process intensification of biodiesel production using a tubular micro-reactor (TMR): experimental and numerical assessment, Chem. Eng. Commun., 2017, 204(4), 467–475 CrossRef.
- S. M. Ahmed, R. Law, A. Phan and A. Harvey, Thermal performance of meso-scale oscillatory baffled reactors, Chem. Eng. Process.: Process Intensif., 2018, 132, 25–33 CrossRef CAS.
- A. N. Phan and A. P. Harvey, Characterisation of mesoscale oscillatory helical baffled reactor—Experimental approach, Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 180, 229–236 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Borah, Desulfurization of organic sulfur from a sub-bituminous coal by electron-transfer process with K4[Fe(CN)6], Energy Fuels, 2006, 20(1), 287–294 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Ukkirapandian, V. Sadasivam and B. Sivasankar, Oxidation of dibenzothiophene and desulphurization of diesel, Pet. Sci. Technol., 2008, 26(4), 423–435 CrossRef CAS.
- F.-t. Li, R. Liu, J. Wen, D. Zhao, Z. Sun and Y. Liu, Desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by chemical oxidation and solvent extraction with Me3NCH2C6H5 Cl2ZnCl2 ionic liquid, Green Chem., 2009, 11(6), 883–888 RSC.
- W. Ahmad, I. Ahmad and M. Yaseen, Desulfurization of liquid fuels by air-assisted peracid oxidation system in the presence of Fe-ZSM-5 catalyst, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 2016, 33(9), 2530–2537 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Sachdeva and K. Pant, Deep desulfurization of diesel via peroxide oxidation using phosphotungstic acid as phase transfer catalyst, Fuel Process. Technol., 2010, 91(9), 1133–1138 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Hasan, J. Jeon and S. H. Jhung, Oxidative desulfurization of benzothiophene and thiophene with WOx/ZrO2 catalysts: effect of calcination temperature of catalysts, J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, 205, 216–221 CrossRef PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra01663j |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2022 |