Ionic guest in ionic host: ionosilica ionogel composites via ionic liquid confinement in ionosilica supports†
Abstract
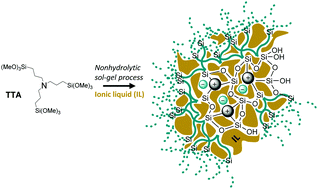
Ionosilica ionogels, i.e. composites consisting of an ionic liquid (IL) guest confined in an ionosilica host matrix, were synthesized via a non-hydrolytic sol–gel procedure from a tris-trialcoxysilylated amine precursor using the IL [BMIM]NTf2 as solvent. Various ionosilica ionogels were prepared starting from variable volumes of IL in the presence of formic acid. The resulting brittle and nearly colourless monoliths are composed of different amounts of IL guests confined in an ionosilica host as evidenced via thermogravimetric analysis, FT-IR, and 13C CP-MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy. In the following, we focused on confinement effects between the ionic host and guest. Special host–guest interactions between the IL guest and the ionosilica host were evidenced by 1H solid-state NMR, Raman spectroscopy, and broadband dielectric spectroscopy (BDS) measurements. The three techniques indicate a strongly reduced ion mobility in the ionosilica ionogel composites containing small volume fractions of confined IL, compared to conventional silica-based ionogels. We conclude that the ionic ionosilica host stabilizes an IL layer on the host surface; this then results in a strongly reduced ion mobility compared to conventional silica hosts. The ion mobility progressively increases for systems containing higher volume fractions of IL and finally reaches the values observed in conventional silica based ionogels. These results therefore point towards strong interactions and confinement effects between the ionic host and the ionic guest on the ionosilica surface. Furthermore, this approach allows confining high volume fractions of IL into self-standing monoliths while preserving high ionic conductivity. These effects may be of interest in domains where IL phases must be anchored on solid supports to avoid leaching or IL spilling, e.g., in catalysis, in gas separation/sequestration devices or for the elaboration of solid electrolytes for (lithium-ion) batteries and supercapacitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...