A liposome-based combination strategy using doxorubicin and a PI3K inhibitor efficiently inhibits pre-metastatic initiation by acting on both tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages†
Abstract
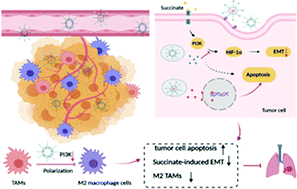
Pre-metastatic initiation is essential in tumor metastasis, and the inhibition of it could prevent the spread of cancers to distant organs. Both tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) play an important role in the pre-metastatic initiation stage. Herein, a liposome-based combination strategy which involves doxorubicin-loaded liposomes (Lip-Dox) and PI3K inhibitor-loaded liposomes (Lip-LY) was developed to simultaneously regulate tumor cells and TAMs for inhibiting pre-metastatic initiation. In tumor cells, Lip-LY sensitized cells to Lip-Dox treatment and inhibited the EMT process which was promoted by succinate, further mitigating succinate-induced migration and invasion of 4T1 cells. In TAMs, Lip-LY could efficiently inhibit the polarization of TAMs and reduce the percentage of M2 TAMs, so as to exhibit synergistic effects with Lip-Dox in TAM-induced metastasis. As a result, the combination treatment successfully reduced the lung metastasis of 4T1 bearing BALB/c mice by destroying metastatic tumor cells and inhibiting pre-metastatic initiation with decreased metastasis-associated protein expression. Overall, our work provided a simple and promising combination strategy for inhibiting pre-metastatic initiation in multiple ways to treat cancer metastasis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...