Copper(i) complexes with quinolone appended 1,8-naphthalimide conjugates: structural characterization, DNA and protein binding and cytotoxicity studies†
Abstract
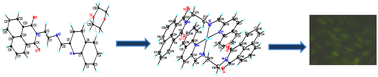
A novel 1,8-naphthalimide containing ligand (L) and its three mononuclear complexes with different anions, [Cu(L)2](NO3)·3(H2O) (1), [Cu(L)2]Cl·4(H2O) (2), [Cu(L)2]ClO4·DMF (3) was synthesized and characterized by NMR, infrared spectroscopy, elemental analysis, ESI-MS and single crystal X-ray crystallography. Single-crystal diffraction analysis of ligand L revealed the non-planar structure of the ligand with intermolecular π⋯π stacking interaction between naphthalimide moieties. Single-crystal X-ray studies of the complexes evidenced a seesaw geometry around the Cu(I) center. A competitive DNA binding and absorption titration study suggests an intercalative mode of DNA binding by complex 1. The fluorescence study of bovine serum albumin (BSA) with complex 1 revealed a dynamic quenching mechanism. A549 (adenocarcinoma human alveolar basal epithelial cells), MCF-7 (breast cancer cell line)) cell lines were used to assess the cytotoxicity of complex 1 using the MTT (3-[4,5-dimethylthiazole-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay. Complex 1 displayed improved cytotoxicity towards cancer cell lines in comparison with cis-platin. The cell accumulation study was investigated by fluorescence microscopy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...