In situ green synthesis of lysozyme/silver nanoparticles sol and their antimicrobial properties
Abstract
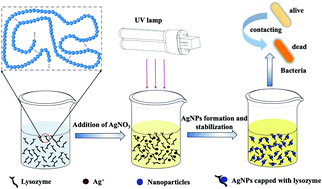
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have been widely considered an ideal antimicrobial material due to their superior efficacy. However, they are prone to introducing toxic chemical reductants and stabilizers in the preparation process of AgNPs, and nanoparticles tend to agglomerate, affecting the antibacterial properties and tremendously limiting further application in antibacterial fields. In this study, lysozyme/silver nanoparticles sol (LZM/AgNPs) was synthesized based on the green and controllable process by UV irradiation, with highly biocompatible lysozyme (LZM) as a reducing agent and stabilizer and silver nitrate as the metal precursor. The analysis results manifested that LZM effectively played the roles of dispersant and stabilizer, and LZM/AgNPs with uniform and stable dispersion were obtained. Besides, LZM/AgNPs integrate LZM and silver nanoparticles' antibacterial properties, and the antibacterial rate of LZM/AgNP-9 h against Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ranged from 97% to 99%. Moreover, the excellent biocompatibility of the lysozyme functionalized silver nanoparticles exhibited a high potential for use in asepsis and therapy in the future. Our present work provides a new, facile and eco-friendly strategy for controlling the shape of metal nanoparticles in photoreduction synthesis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...