Janus monolayer HfSO with improved optical properties as a novel material for photovoltaic and photocatalyst applications
Abstract
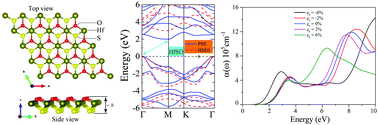
First principles calculations were performed to investigate the photocatalytic behavior of 2D Janus monolayer HfSO at equilibrium and under the influence of strains and external electric fields. A thorough investigation of the structural, electrical, and optical properties of HfS2, HfO2, and HfSO was also provided. In 1T configuration, the three 2D Janus monolayers were found to be dynamically and thermally stable. The phonon dispersion of strained HfSO demonstrates the material's dynamical stability. The Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio of 1T HfSO reveal isotropic elastic characteristics on the x–y plane as well as HfSO's tendency to expand transversally under compressive strains. The three monolayers HfS2, HfO2, and HfSO have appropriate band gaps for redox reaction activation, and the corresponding band gaps are 2.48 eV, 6.50 eV, and 2.98 eV. Furthermore, the extremely anisotropic mobility of electrons and holes on the x–y plane benefits the electron–hole separation process. The equilibrium HfSO has a moderate absorption rate of 5 × 105 cm−1 in the visible range, with the intensity increasing by around 20% with a −6% biaxial strain. Consequently, the absorption range is moved to a lower energy level, covering the majority of visible regions. The 2D Janus HfSO's asymmetric surface electrical characteristic is also discovered. As a result, HfSO is suggested to be a very promising material for application in optoelectronic devices, as well as photovoltaic and water-splitting catalysts, which can be greatly enhanced by appropriate stresses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...