Structure–activity relationships of hydrophobic alkyl acrylamides as tissue transglutaminase inhibitors†
Alana M. M.
Rangaswamy
,
Pauline
Navals
,
Eric W. J.
Gates
 ,
Sammir
Shad
,
Sarah K. I.
Watt
and
Jeffrey W.
Keillor
,
Sammir
Shad
,
Sarah K. I.
Watt
and
Jeffrey W.
Keillor
 *
*
Department of Chemistry and Biomolecular Sciences, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario K1N 6N5, Canada. E-mail: jkeillor@uottawa.ca
First published on 26th January 2022
Abstract
Tissue transglutaminase (TG2) is a multifunctional protein that plays biological roles based on its ability to catalyse protein cross-linking and to function as a non-canonical G-protein known as Ghα. The non-regulated activity of TG2 has been implicated in fibrosis, celiac disease and the survival of cancer stem cells, underpinning the therapeutic potential of cell permeable small molecule inhibitors of TG2. In the current study, we designed a small library of inhibitors to explore the importance of a terminal hydrophobic moiety, as well as the length of the tether to the irreversible acrylamide warhead. Subsequent kinetic evaluation using an in vitro activity assay provided values for the kinact and KI parameters for each of these irreversible inhibitors. The resulting structure–activity relationship (SAR) clearly indicated the affinity conferred by dansyl and adamantyl moieties, as well as the efficiency provided by the shortest warhead tether. We also provide the first direct evidence of the capability of these inhibitors to suppress the GTP binding ability of TG2, at least partially. However, it is intriguing to note that the SAR trends observed herein are opposite to those predicted by molecular modelling – namely that longer tether groups should improve binding affinity by allowing for deeper insertion of the hydrophobic moiety into a hydrophobic pocket on the enzyme. This discrepancy leads us to question whether the existing crystallographic structures of TG2 are appropriate for docking non-peptidic inhibitors. In the absence of a more relevant crystallographic structure, the data from rigorous kinetic studies, such as those provided herein, are critically important for the development of future small molecule TG2 inhibitors.
Introduction
Transglutaminases are a family of calcium-dependent enzymes known for their ability to cross-link proteins through formation of an Nε(γ-glutaminyl)lysine bond.1–3 These enzymes catalyze the formation of this covalent bond by mediating an acyl transfer mechanism through their active site cysteine residue.4,5 Transglutaminase 2 (TG2) is the most intensively studied isozyme of the transglutaminase family and has been implicated in fibrosis,6–8 celiac disease,9,10 and cancer metastasis.11–13 TG2 distinguishes itself from the other transglutaminases in that it also plays the role of an intracellular G-protein, in which it is known as Ghα.14 The TG2 protein undergoes a dramatic conformational change allowing its mutually exclusive function as either a G-protein, or as a cross-linking enzyme.15 When it adopts an open, linear, conformation that is stabilized by the binding of calcium ions, the transamidase binding site is formed, where substrates can bind before being crosslinked, isopeptidically cleaved, or hydrolysed.16 However, TG2 can also adopt a more compact, closed, form where its two C-terminal β-barrels fold in to cover the catalytic core, abolishing the transamidase binding site, and forming a GTP binding site that allows its G-protein activity.14 These two activities are mutually exclusive, with each conformation lacking the binding site for the opposing substrate.14,16–18Extensive work has gone in to validating TG2 as a therapeutic target in the treatment of celiac disease, cancer, and kidney fibrosis.19 Inhibitors of TG2 are extremely diverse, ranging from small molecules20–22 to peptides.23,24 Many of these inhibitors are designed to inactivate TG2's transamidase activity irreversibly, while some are also designed to suppress GTP binding by locking the enzyme in its open conformation.25 Since the first structure of the open conformation of TG2 was determined through X-ray crystallography,16 a hydrophobic pocket has been identified in the transamidase binding site on the α/β-catalytic core. This pocket, sometimes referred to as the ‘D-site’, is very appealing for the design of high affinity inhibitors. The scaffolds of many inhibitors have been designed to allow binding in the D-site, while presenting an electrophilic group that can react with the catalytic cysteine in the active site tunnel. These warhead groups include acrylamides,21,22,26,27 epoxides,28 6-diazo-5-oxo-norleucine (DON),10 and other α,β-unsaturated carbonyl groups.24,29 Very recently, peptidomimetic inhibitors designed to inhibit intestinal TG2 have progressed through phase II clinical trials for the treatment of celiac disease.30 However, there still remains a need for inhibitors of intracellular TG2, particularly in the context of its role in cancer, for which cell permeability is a critical hurdle.
In our previous work, we designed targeted covalent inhibitors of TG2 that were originally designed to mimic the structure of the glutamine substrate Cbz-Gln-Gly.24,26,28,29,31–33 These peptidomimetic inhibitors were subsequently optimized through multiple structure activity relationship (SAR) studies, resulting in inhibitors that are highly efficient and selective for TG2. The latest generations bear an acrylamide warhead that reacts with the active site cysteine, while filling the D-site pocket with a naphthoyl group (e.g., AA9) or a dansyl group (e.g. VA4) attached to a piperazine linker (Fig. 1).26
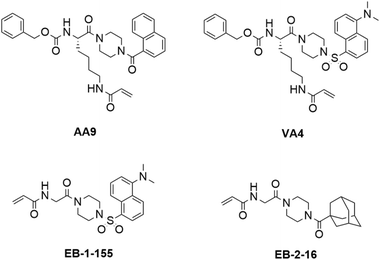 | ||
| Fig. 1 Structures of previously disclosed TG2 targeted covalent inhibitors. Peptidomimetic inhibitors AA9 and VA4 from the Keillor group26 and small molecule inhibitors EB-2-16 and EB-1-155 from the Griffin group.21,34 | ||
Taking an alternative approach, both the Cure Huntington's Disease Initiative Foundation (CHDI) and the Griffin group have developed small molecule inhibitors of TG2 through structure-based design.21,22,34,35 It is noteworthy that some of the most efficient inhibitors originating from this structure-based design also include piperazine-linked hydrophobic groups. This suggests that three research groups independently converged on a structural feature that confers affinity and favours binding, potentially by directing a hydrophobic group to the TG2 D-site. We were particularly intrigued by the lead compound developed by Badarau et al., featuring a dansyl fluorophore, piperazine bridge, and glycine linker to the acrylamide warhead, referred to as 3h in the original article,21 but also known as EB-1-155 (ref. 34) (Fig. 1). This inhibitor bears the same piperazine-dansyl motif as our inhibitor VA4; however, it is striking to note that although EB-1-155 lacks all of the structural elements of the N-terminus of VA4, this is not detrimental to potency, selectivity, or GTP binding suppression. This led us to hypothesize that directing a hydrophobic group to the D-site is of primary importance in the design of TG2 inhibitors and inspired us to design a simple SAR study to test this hypothesis. In the current work we varied both the hydrophobic moiety on the piperazine, and the length of the chain bearing the acrylamide warhead, seeking to find the ideal arrangement for optimizing D-site binding affinity. We evaluated the efficiency of these novel inhibitors36 and their ability to suppress GTP binding,37 and compare these data to the binding modes predicted by molecular modelling.
Results and discussion
Design
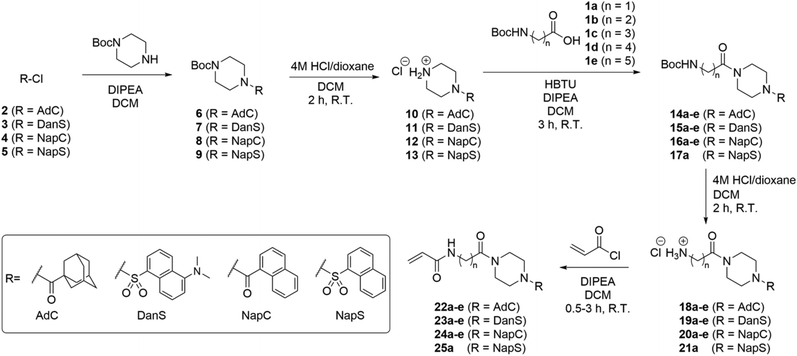
The structure-based design of TG2 inhibitors has been greatly enabled by the publication of the first crystallographic structure of the open conformation of the enzyme.16 This structure was obtained after reaction of the enzyme with a peptidic irreversible inhibitor, and arguably represents the structure of the transamidase-active enzyme, or its acyl–enzyme intermediate. As identified by the original authors, the surface of the open conformation of TG2 features a distinctive hydrophobic pocket, several angstroms away from the mouth of the tunnel leading down to the active site cysteine residue, CYS277. Our primary design criteria were to fill this hydrophobic pocket with a small series of ligands attached to a central piperazine scaffold, and to vary the length of the pendant tether to which a terminal acrylamide warhead was attached. Our initial choice of hydrophobic moieties included three that were previously observed to confer affinity to other series of inhibitors, namely, the adamantyl group identified21 by Badarau et al., the naphthyl group identified26 by Akbar et al., and the dansyl group studied by both research groups (Fig. 1).21,26 For the tether length, we chose to vary the number of methylene units from n = 1, studied by Badarau et al., to n = 5, resembling the peptidomimetic scaffold used by Akbar et al.21,26Synthesis
The synthesis of inhibitors 22–25(a–e) was performed according to the route shown in Scheme 1. Compounds 6–9 were prepared through functionalization of Boc-piperazine with a hydrophobic group (dansyl, naphthoyl, adamantanecarbonyl, or naphthalenesulfonyl) via the commercially available acyl- or sulfonyl chlorides (3–5), except for adamantanecarbonyl chloride (2) which was prepared from the corresponding carboxylic acid. Deprotection of the piperazinyl Boc group was performed under acidic conditions: although it is common to perform Boc deprotections using trifluoroacetic acid, we found this gave sticky solids with overall lower purity by TLC analysis. Conversely, the use of HCl in dioxane provided the amine HCl salts (10–13) as free-flowing powders following precipitation using DCM or Et2O.We initially planned to install the acryloyl group on the Ω-amino acids prior to coupling with the piperazine, but discovered that the acryloyl coupling reaction proceeded inefficiently, and the products were difficult to isolate. Therefore, we prepared Boc-protected amino acids 1a–e, which, despite the addition of steps to the overall synthetic route, improved the yield, efficiency, and ease of synthesis at each step.
The coupling of functionalized piperazines 10–13 and Boc-protected amino acids 1a–e was mediated by HBTU/DIPEA, which enabled rapid and clean conversion to the corresponding amides. We determined that the amides could be isolated by extraction through successive washes with dilute acid, brine, and saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate. Following extraction, all amides 15–18 were pure by 1H NMR except for compounds 15a and 15b, which required further purification by chromatography.
The subsequent Boc deprotection reactions were also performed using HCl/dioxane, which variably gave 18–21 as fine powders or foams, depending on linker chain length and hydrophobic unit. Coupling of the amines with acryloyl chloride gave the final inhibitor compounds, 22–25. The first series of compounds to be synthesized was the naphthoyl series, which was purified at the final step by column chromatography. However, we later determined that the majority of compounds 23–25 could be obtained in >96% purity (as determined by HPLC analysis, see ESI†) simply following extraction and/or successive precipitation/washes with diethyl ether. This suggests that the naphthoyl series compounds (24a–e) could also have been purified in this way.
Kinetic evaluation
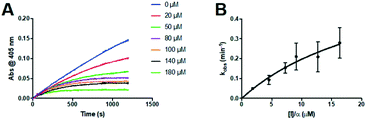
The series of inhibitors prepared herein were evaluated for their inhibition of recombinant human TG2 using an established kinetic assay.26 The acyl transferase activity of TG2 was determined by monitoring the release of p-nitrophenolate product from the chromogenic substrate AL5.36 Incubation with inhibitor resulted in the time-dependent loss of this activity, due to irreversible inhibition. The curves of absorbance versus time were fitted accordingly to a mono-exponential association equation, providing first order rate constants of inhibition, kobs (Fig. 2A). These rate constants, measured at varied concentrations of inhibitor, were then fitted to a hyperbolic equation consistent with saturation kinetics, providing the inhibition parameters kinact and KI (Fig. 2B).The first series of inhibitors tested contained a naphthoyl hydrophobic group and a linker of varying length to which the pendant acrylamide warhead was tethered (Table 1). We were surprised to note that the shortest chain provided the most potent inhibition of TG2. We expected that inhibitors bearing the longest linkers would show the greatest affinity since we had observed this trend among many series of peptidomimetic TG2 inhibitors.22,26,27,38 However, it is clear from the data shown in Table 1 that the shortest linker apparently positions the reactive acrylamide at the optimal distance from the active site cysteine, providing an efficiency (kinact/KI ratio) for compound 24a of 27![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500 M−1 min−1, whereas the longer chain derivatives 24b–e were roughly an order of magnitude less efficient.
500 M−1 min−1, whereas the longer chain derivatives 24b–e were roughly an order of magnitude less efficient.
| Cmpd. | n (CH2) | k inact (min−1) | K I (μM) | k inact/KI (103 M−1 min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24a | 1 | 0.69 ± 0.26 | 25.0 ± 13.9 | 27.5 ± 18.6 |
| 24b | 2 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 51.6 ± 19.2 | 2.4 ± 1.0 |
| 24c | 3 | 0.45 ± 0.06 | 134.0 ± 25.8 | 3.3 ± 0.8 |
| 24d | 4 | 0.44 ± 0.08 | 141.9 ± 37.4 | 3.1 ± 1.0 |
| 24e | 5 | 0.46 ± 0.15 | 109.3 ± 55.5 | 4.2 ± 2.6 |
In order to interrogate the effect of a different hydrophobic unit on the inhibition profile, the adamantyl series was also tested. Again, it was noted that the inhibitor having the shortest linker in the series (22a) also manifested the most potent inhibition, with a KI value of 3.2 μM (Table 2). The efficiency of compound 22a, as shown by its kinact/KI ratio, was also over an order of magnitude greater than that of naphthoyl derivative 24a, indicating substantial preference for the adamantyl moiety. Compound 22a is also known as EB-2-16,34 and as compound 3e in the study by Badarau et al.;21 however, in that publication, its kinact/KI ratio was reported to be 171![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 875 M−1 min−1, whereas in this study we measured a value of 412 × 103 M−1 min−1. This difference may be due to the two different assays employed. While we used a direct chromogenic assay in this study, Badarau et al. used an indirect coupled-enzyme assay to measure kinact and KI.39 It is possible that the initial lag period that is common to coupled enzyme assays may mask the initial phase of the inhibition reaction and under-report the rate constants of inactivation. This would result in slightly lower kinetic parameters than those measured herein by a direct chromogenic assay, which is more responsive over the initial time period of inhibition.
875 M−1 min−1, whereas in this study we measured a value of 412 × 103 M−1 min−1. This difference may be due to the two different assays employed. While we used a direct chromogenic assay in this study, Badarau et al. used an indirect coupled-enzyme assay to measure kinact and KI.39 It is possible that the initial lag period that is common to coupled enzyme assays may mask the initial phase of the inhibition reaction and under-report the rate constants of inactivation. This would result in slightly lower kinetic parameters than those measured herein by a direct chromogenic assay, which is more responsive over the initial time period of inhibition.
| Cmpd. | n (CH2) | k inact (min−1) | K I (μM) | k inact/KI (103 M−1 min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n.d.: no inhibition detected up to 100 μM. | ||||
| 22a | 1 | 1.34 ± 0.22 | 3.2 ± 1.0 | 412 ± 142 |
| 22b | 2 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 22c | 3 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 22d | 4 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 4.5 ± 1.2 | 41.9 ± 11.5 |
| 22e | 5 | 0.36 ± 0.08 | 38.0 ± 15.4 | 9.5 ± 4.5 |
The dansyl series was the third library to be screened for TG2 inhibition. Increasing linker length again led to greatly diminished potency, with compound 23a having the shortest linker and showing the highest potency (Table 3). It is important to note that 23a was also first developed by the Griffin group. Compound 23a is also known as EB-1-155,34 or compound 3h in the publication by Badarau et al.21 Comparison of their kinact/KI value of 297![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 692 M−1 min−1, to the value of 1508 × 103 M−1 min−1 measured herein, suggests that the coupled-enzyme assay again provided lower values than the direct chromogenic assay.
692 M−1 min−1, to the value of 1508 × 103 M−1 min−1 measured herein, suggests that the coupled-enzyme assay again provided lower values than the direct chromogenic assay.
| Cmpd. | n (CH2) | k inact (min−1) | K I (μM) | k inact/KI (103 M−1 min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Values obtained using double reciprocal fitting. | ||||
| 23a | 1 | 2.25 ± 1.44 | 1.49 ± 1.27 | 1508 ± 1608 |
| 23b | 2 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 64.5 ± 12.7 | 3.9 ± 0.9 |
| 23c | 3 | 0.54 ± 0.31a | 74.2 ± 42.9a | 7.3 ± 0.5a |
| 23d | 4 | 0.55 ± 0.33 | 42.0 ± 4.3 | 13.1 ± 1.6 |
| 23e | 5 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 27.4 ± 1.6 | 8.6 ± 0.6 |
Finally, we evaluated one additional inhibitor that allowed two relevant structural comparisons. Inhibitor 25a bears a naphthalenesulfonyl group in the place of the naphthoyl group of 24a, while lacking only the dimethylamino group of 23a. We hoped that the larger sulfonyl linkage would allow the naphthoyl group to bind deeper in the hydrophobic pocket of TG2, while allowing the piperazine–glycine linker to position the acrylamide warhead effectively. As shown in Table 4, inhibitor 25a did show enhanced affinity relative to its carbonyl analogue 24a, with the sulfonyl linkage decreasing the KI value to 6.5 μM, while maintaining a kinact of 0.70 min−1, resulting in a kinact/KI ratio of 108 × 103 M−1 min−1. Interestingly, the dimethylamino group of 23a appears to substantially contribute to binding affinity, with its roughly 15-fold greater efficiency compared to 25a being due to both its higher kinact value and its lower KI value.
| Cmpd. | n (CH2) | k inact (min−1) | K I (μM) | k inact/KI (103 M−1 min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23a | 1 | 2.25 ± 1.44 | 1.49 ± 1.27 | 1508 ± 1608 |
| 24a | 1 | 0.69 ± 0.26 | 25.0 ± 13.9 | 27.5 ± 18.6 |
| 25a | 1 | 0.70 ± 0.13 | 6.51 ± 1.90 | 108 ± 38 |
Inspection of the kinetic parameters reported for the most potent inhibitors (i.e.22a, 23a and 25a) reveals significant standard error, deriving from the error of the hyperbolic fitting. In the Kitz & Wilson kinetic experiment used herein, as inhibitors become more efficient, they inactivate the enzyme very quickly, resulting in shorter reaction times and smaller end point absorbances (see Fig. 2A). This increases the error in the fitting of kobs. Further, as kinact increases for better inhibitors, it becomes increasingly difficult to measure kobs values that approach kinact (at saturation, see Fig. 2B), leading to error in the separate fitting of both KI and kinact. These errors are then propagated, leading to even greater relative error in the kinact/KI ratio. Therefore, we also performed simple linear regression on the kobs values measured at the lowest concentrations of each inhibitor, allowing us to estimate the value of the kinact/KI ratio without introducing as much error from fitting of the separate parameters. These ratios, reported for the best inhibitors of each series (22a, 23a, 24a and 25a) in Table S1 in the ESI,† are all within experimental error of the ratios determined by hyperbolic fitting (Table 1–4), which lends confidence to the data treatment.
GTP binding evaluation
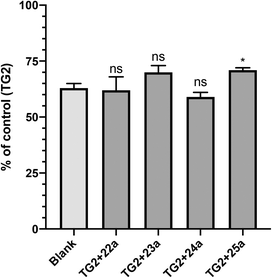
GTP binding is critical to the G-protein function of TG2, which has been implicated in a number of disease states.40–42 However, it was not obvious to us that a small molecule inhibitor would be capable of preventing TG2 from adopting its closed conformation, forming its GTP binding site, and binding GTP.17 Therefore, we decided to investigate whether our most efficient small molecule inhibitors, namely 22a, 23a, 24a and 25a, were indeed capable of blocking this activity. The results are presented in Fig. 3, as a fraction of the positive control, which represents maximum GTP binding to TG2, along with the blank (no TG2) representing zero GTP binding.It is evident from Fig. 3 that all of the inhibitors tested are capable of inhibiting GTP binding, at least partially. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first explicit demonstration of the inhibition of GTP binding by these compounds, including those published previously (22a and 23a).21,34 It is interesting to note that these results appear to be aligned with those from another recent investigation,20 in which we showed that sulforaphane, a very small irreversible inhibitor of TG2, is also able to partially inhibit GTP binding. Further studies are underway to determine the minimum steric bulk that is required to alter the conformational equilibrium of TG2 to completely abolish GTP binding.
Molecular docking analysis
As mentioned above, we were surprised to find that inhibitors bearing a shorter alkyl chain proved to be the most efficient of each series, since this is the opposite trend of what we have observed in series of peptidomimetic inhibitors. In an attempt to explain these unexpected results, we performed extensive molecular modelling studies, hoping to elucidate a functional binding model. Molecular Operating Environment (MOE) was therefore used to perform docking analysis on all inhibitors shown above. The computational binding affinities were prioritized based on a numerical value called the S-score, which decreases with improved predicted binding affinity.43,44 Regarding the target protein, we used the structure of TG2 after reaction with a peptidic irreversible inhibitor (PDB code 2Q3Z), shown in Fig. 4.16 The structure was prepared using the preparation tool from MOE. Water molecules, salts and ions were removed from the structure and all hydrogen atoms were displayed. The structure was verified, and corrected manually, for any problems or warnings such as chain breaks, termini missing or unreasonable charges. Two tryptophan residues, namely TRP241 and TRP332, form a tunnel leading to the active site nucleophilic residue CYS277 (orange) that is alkylated upon reaction with an acrylamide. These three residues are displayed in magenta. Moreover, six residues create the hydrophobic cavity targeted by our inhibitors, namely ALA304, LEU312, ILE313, PHE316, ILE331 and ILE421, all displayed in blue.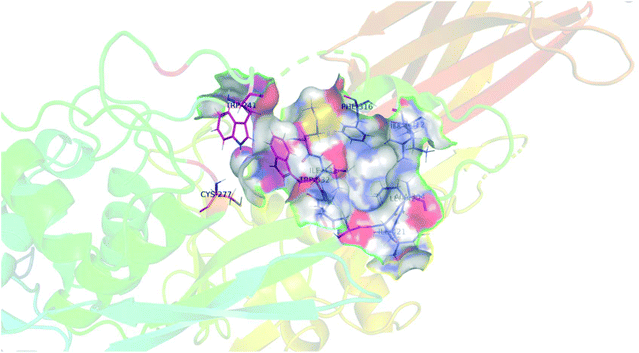 | ||
| Fig. 4 Structural representation of TG2 binding site (PDB: 2Q3Z) in magenta, tryptophan residues TRP241 and TRP332 form a tunnel leading to the active site nucleophilic residue CYS277 (orange). Six residues create the hydrophobic cavity, namely ALA304, LEU312, ILE313, PHE316, MET330, ILE 331 and ILE421, all displayed in blue. | ||
Each ligand was docked according to both a non-covalent and a covalent approach, using a rigid-body method that is considered superior for covalent complexes.44,45 The non-covalent approach involves calculation of S score values, prior to covalent bonding between the ligand and the receptor. Subsequently, the covalent bond is manually created between residue CYS277 and the acrylamide warhead of the bound inhibitor, followed by minimization of the system, which allows the ligand to adopt its final conformation. Alternatively, the covalent approach involves calculation of the potential binding affinities with the requirement of in silico covalent bond formation between CYS277 and the acrylamide warhead. To evaluate both sets of docking results, the S score values and the extent of insertion of each hydrophobic moiety into the hydrophobic cavity were considered. For the latter, the distances (d) between the centroids of the hydrophobic pocket and each hydrophobic structural moiety were measured. All results are presented in Table 5.
| Hydrophobic moiety | Cmpd. | n CH2 | Non-covalent approach | Covalent approach | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S score | d (Å) | S score | d (Å) | |||
| Adamantanecarbonyl | 22a | 1 | −5.97 | 6.5 | −5.12 | 6.5 |
| 22b | 2 | −5.96 | 6.8 | −5.28 | 6.5 | |
| 22c | 3 | −6.12 | 5.4 | −5.72 | 6.1 | |
| 22d | 4 | −6.05 | 5.5 | −5.86 | 4.5 | |
| 22e | 5 | −6.81 | 5.5 | −6.00 | 5.9 | |
| Dansyl | 23a | 1 | −5.40 | 7.8 | −4.86 | 6.1 |
| 23b | 2 | −6.78 | 4.9 | −5.71 | 5.5 | |
| 23c | 3 | −6.49 | 6.7 | −5.41 | 8.6 | |
| 23d | 4 | −6.48 | 4.5 | −5.41 | 5.9 | |
| 23e | 5 | −6.97 | 3.5 | −6.53 | 6.8 | |
| Naphthoyl | 24a | 1 | −6.24 | 7.0 | −5.77 | 5.0 |
| 24b | 2 | −6.28 | 4.7 | −6.00 | 4.9 | |
| 24c | 3 | −6.90 | 5.0 | −5.82 | 4.7 | |
| 24d | 4 | −6.92 | 4.7 | −6.05 | 4.2 | |
| 24e | 5 | −7.30 | 4.6 | −6.41 | 4.6 | |
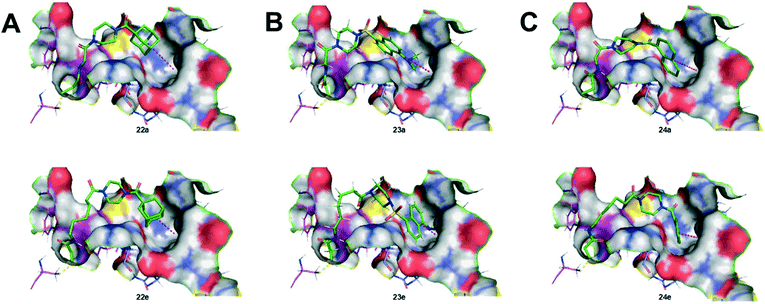
As we originally expected, docking of the longer chain derivatives provided better potential binding affinity as well as deeper insertion into the hydrophobic cavity. For each series of hydrophobic moiety, the inhibitor comprising a 5-carbon tether displays the best S score value compared to the inhibitors bearing a spacer of only 1 carbon. The same trend is observed for the insertion depth of each hydrophobic moiety in the hydrophobic cavity of TG2. Understandably, inhibitors with longer chains tend to show deeper insertion, hence improved hydrophobic interactions with the enzyme. Furthermore, the dansyl 23(a–e) and the naphthoyl 24(a–e) series were predicted to bind more deeply than the adamantyl series 22(a–e), based on the average insertion distances of 5.4, 5.2 and 5.9 Å, respectively. Representations of the inhibitors predicted to show the weakest and strongest affinity for each series are shown in Fig. 5. In summary, the binding models predicted by docking, and the experimental data obtained through kinetic studies are inconsistent with each other. For example, molecular modelling predicts that the inhibitor with the longest tether to acrylamide on one end, and a naphthoyl group on the other (i.e.24e) should be the best inhibitor, when in reality, 24e is one of the least efficient tested herein.
In contrast, the inhibitor bearing a dansyl group and the shortest tether (i.e.23a, aka EB-1-155) was predicted by molecular modelling to have the lowest affinity, but in reality it is the best tested herein, and indeed one of the most efficient inhibitors known for TG2.26 In light of this, we repeated our docking simulations, using a different structure deposited in the PDB. Structure 3S3J was obtained after inhibition of TG2 with a peptidic irreversible inhibitor (Cbz-DON-Val-Pro-Leu-OH) that is different than the one used to generate 2Q3Z (Ac-Pro-DON-Leu-Pro-Phe-NH2). That being said, the substrate binding sites of both crystallographic structures are very similar (see Fig. S1, ESI†). Unsurprisingly, the docking simulations performed with 3S3J provided the same trend in S scores as in 2Q3Z, again in opposition to our observed kinetic results (see Table S2, ESI†).
The discrepancy between the molecular modelling predictions and the experimental evidence obtained by kinetic studies leads us to question whether these crystallographic structures are appropriate for the docking of our small molecule inhibitors. Although 2Q3Z and 3S3J are the most relevant crystallographic structures deposited in the PDB, it is important to note that they were both obtained after inhibition with peptidic inhibitors, whose C-terminal residues may define the very shape of the hydrophobic pocket ‘D-site’. However, in the absence of inhibitor, any enzyme may adopt a conformation that differs from its crystallographic structure, and this may be especially true for TG2, an enzyme known to undergo dramatic and dynamic conformational changes.16,46,47 The free enzyme may simply adopt a conformation sufficiently different from that of the crystallographic structure, that precludes the use of that structure to predict how small molecule inhibitors may bind to the enzyme. This underlines the pressing need for additional protein crystallography studies with small molecule inhibitors. But in the absence of such structures, rigorous kinetic data from SAR studies will be critical for the design of future inhibitors.
Materials and methods
Synthesis
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexanes
1 hexanes![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate) after 10 min. The reaction mixture was diluted in DCM (10 mL) and washed with 5% AcOH (2 × 10 mL) and brine (2 × 10 mL). The organic phase was dried with MgSO4 and solvent removed under reduced pressure.
ethyl acetate) after 10 min. The reaction mixture was diluted in DCM (10 mL) and washed with 5% AcOH (2 × 10 mL) and brine (2 × 10 mL). The organic phase was dried with MgSO4 and solvent removed under reduced pressure.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v solution of DCM and HCl (4 M in dioxane) at an overall concentration of ∼0.25 M. The reaction proceeded until starting material was consumed as determined by TLC analysis (solvent system 1) (approximately 2 h). The reaction mixture was evaporated in vacuo and coevaporated with DCM. The resulting residue was triturated with Et2O, which was decanted off to give the product as a powdery solid. The HCl salts recovered were carried forward without further purification.
1 v/v solution of DCM and HCl (4 M in dioxane) at an overall concentration of ∼0.25 M. The reaction proceeded until starting material was consumed as determined by TLC analysis (solvent system 1) (approximately 2 h). The reaction mixture was evaporated in vacuo and coevaporated with DCM. The resulting residue was triturated with Et2O, which was decanted off to give the product as a powdery solid. The HCl salts recovered were carried forward without further purification.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexanes
1 hexanes![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate, stained with ninhydrin), the solvent was evaporated in vacuo, then the reaction mixture was redissolved in EtOAc (∼20 mL). The organic phase was washed with 5% AcOH (3 × 10 mL), brine (20 mL), NaHCO3 (20 mL) and brine again (20 mL). The organic phase was dried over MgSO4 and evaporated. The resulting product was washed with Et2O or pentane as needed.
ethyl acetate, stained with ninhydrin), the solvent was evaporated in vacuo, then the reaction mixture was redissolved in EtOAc (∼20 mL). The organic phase was washed with 5% AcOH (3 × 10 mL), brine (20 mL), NaHCO3 (20 mL) and brine again (20 mL). The organic phase was dried over MgSO4 and evaporated. The resulting product was washed with Et2O or pentane as needed.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 pentane
1 pentane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Et2O (140 mg, 72%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 4.62 (br. s, 1H), 3.67 (m, 4H), 3.60 (m, 2H), 3.45 (m, 2H), 3.13 (m, 2H), 2.36 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 2.05 (s, 3H), 1.99 (m, 6H), 1.71 (m, 6H, overlaps with H2O resonance), 1.62 (app. s, 4H), 1.53 (m, 2H), 1.43 (s, 9H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 176.23, 156.18, 79.39, 45.72, 45.06, 41.90, 40.20, 39.20, 36.70, 32.78, 29.85, 28.56, 28.54, 22.27. HRMS (ESI) calc'd for C26H43N3O4Na ([MNa]+): 484.3151, found: 484.3148.
Et2O (140 mg, 72%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 4.62 (br. s, 1H), 3.67 (m, 4H), 3.60 (m, 2H), 3.45 (m, 2H), 3.13 (m, 2H), 2.36 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 2.05 (s, 3H), 1.99 (m, 6H), 1.71 (m, 6H, overlaps with H2O resonance), 1.62 (app. s, 4H), 1.53 (m, 2H), 1.43 (s, 9H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 176.23, 156.18, 79.39, 45.72, 45.06, 41.90, 40.20, 39.20, 36.70, 32.78, 29.85, 28.56, 28.54, 22.27. HRMS (ESI) calc'd for C26H43N3O4Na ([MNa]+): 484.3151, found: 484.3148.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 DCM and HCl (4 M in dioxane) at an overall concentration of ∼0.1 M. Disappearance of the starting material was monitored by thin layer chromatography (10% MeOH in DCM), and upon completion, the reaction mixture was evaporated in vacuo. The solid was resuspended in Et2O, and the solvent decanted off to give a white solid. The product was carried forward without further purification.
1 DCM and HCl (4 M in dioxane) at an overall concentration of ∼0.1 M. Disappearance of the starting material was monitored by thin layer chromatography (10% MeOH in DCM), and upon completion, the reaction mixture was evaporated in vacuo. The solid was resuspended in Et2O, and the solvent decanted off to give a white solid. The product was carried forward without further purification.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 DCM/hexanes). Fractions containing product were collected, and solvent removed in vacuo to give a white foam.
1 DCM/hexanes). Fractions containing product were collected, and solvent removed in vacuo to give a white foam.
TG2 inhibition assay
Recombinant TG2 was expressed and purified from E. coli as previously described.50 TG2 activity was determined according to a previously published colorimetric activity assay using the chromogenic substrate Cbz-Glu(γ-p-nitrophenyl ester)Gly (AL5).36 In order to determine irreversible inhibition parameters for each inhibitor, enzymatic assays were run under Kitz and Wilson conditions, in the presence of 100 μM AL5 substrate, in triplicate.51 Buffered solutions of 50 mM of 3-(4-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid (MOPS) (pH 6.9), 7.5 mM CaCl2, 100 μM AL5, and various concentrations of inhibitor (from 0.5 to 900 μM, depending on the inhibitor) were prepared in a 96-well polystyrene microplate with a final volume of 200 μL at 25 °C. AL5 and inhibitor stocks were prepared in DMSO ensuring that the final concentration of this co-solvent did not exceed 5% v/v. If necessary, working stocks of each inhibitor were diluted with water to maintain less than 5% v/v DMSO. To initiate the enzymatic reaction, 5 mU mL−1 TG2, or water for the blank, was added to the well and the formation of the hydrolysis product, p-nitrophenolate, was followed at 405 nm for 20 min using a BioTek Synergy 4 plate reader. Observed first-order rate constants of inactivation (kobs) were obtained by fitting the inhibition data sets with non-linear regression to mono-exponential eqn (1) using GraphPad Prism software.| Abst = Absmax × (1 − e−kobst) | (1) |
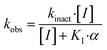 | (2) |
GTP binding assay
GTP binding was measured using a method reported previously.26 TG2 (10 μg) was incubated at 25 °C for 30 min with or without irreversible inhibitor (at a concentration of 2 × KI) with 3.0 mM CaCl2 in 100 mM MOPS (pH = 6.54). The buffer was then exchanged to 100 mM MOPS (pH = 7.0), 1 mM EGTA, and 5 mM MgCl2 to remove calcium using a 10 kDa molecular weight cut off membrane (Amicon tube). The fluorescent, nonhydrolyzable GTP analogue BODIPY GTP-γ-S (purchased from Invitrogen), whose fluorescence increases when bound to the protein, was then added to give a final concentration of 3.0 μM, and fluorescence was then measured on a microplate reader after 10 min of incubation (Ex/Em: 490/520 nm).Protein and ligand preparation for molecular modelling
Two crystals were selected as a target receptor enzyme, and were imported from their PDB files, namely 2Q3Z and 3S3J. The structure was prepared using the preparation tool from MOE. First, water molecules, salts and ions were removed from the structure. All hydrogen atoms were then added (electrostatics: 1/r2, dielectric: 2, solvent: 80, van der Waals: 12–6) and the protein structures were finally verified, and corrected manually, for any problems or warnings such as chain breaks, termini missing or unreasonable charges. Finally, the binding site was created via the site finder tool from MOE. Ligands were drawn in ChemDraw and imported to MOE; partial charges were calculated using a MMFF94x forcefield and the system was eventually minimized following a 0.0001 kcal mol−1 Å−2 gradient. After solvation, minimization was repeated.Molecular docking
The “compute” tool from MOE was used to perform docking analysis of each ligand one by one following both non-covalent and covalent approaches. For the non-covalent approach, ligand placement was achieved using the Triangle Matcher protocol (London dG) to produce 30 poses. In addition, a Rigid Receptor refinement protocol was performed (GBVI/WSA dG) and a total of 5 to 15 final poses were obtained. Finally, using the builder tool from MOE, the covalent bonds between residue CYS277 and the acrylamide warhead of the bound inhibitors were manually created, prior to minimization of the system (0.001 kcal mol−1 Å−2). For the covalent approach, a covalent bond formation between CYS277 and the acrylamide warhead was required using the “1,4 Michael Mercapto Addition” reaction, and ligand placement was achieved using the Rigid Receptor (GBVI/WSA dG) protocol to produce 30 poses.Conclusions
We designed a small library of inhibitors based on known hydrophobic ligands, a known warhead, and varying lengths of tethers. Most of these inhibitors were novel, whereas two members of our series (22a and 23a) were first published by the Griffin group.21 We used a rapid and direct chromogenic assay to measure the kinetic parameters kinact and KI for each of the inhibitors studied herein, allowing for the first time the direct comparison of all inhibitors. Notably, inhibitors 22a, 23a and 25a were far superior to any others. Importantly, we also provided the first direct evidence for their ability to inhibit GTP binding, at least partially. Intriguingly, molecular modelling did not prove useful for guiding structure-based design, in that the results from the docking studies predicted the exact opposite trends of what we observed experimentally. This discrepancy suggests that different crystallographic structures, obtained with small molecule inhibitors, may reveal TG2 in a different conformation, providing a more appropriate starting point for the structure-based design of such inhibitors. In the meantime, kinetic studies such as those presented herein can provide the empirical data required to drive forward the design of next generation TG2 inhibitors.List of abbreviations
| Cmpd. | Compound |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| DIPEA | N,N-Diisopropylethylamine |
| HBTU | 2-(1H-Benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate |
| qu | Quintet (multiplicity) |
| TLC | Thin-layer chromatography |
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
JWK is grateful to the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) for funding. AMMR also thanks NSERC for a CREATE graduate bursary.Notes and references
- S. Gundemir, G. Colak, J. Tucholski and G. V. Johnson, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2012, 1823, 406 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. L. Eckert, M. T. Kaartinen, M. Nurminskaya, A. M. Belkin, G. Colak, G. V. Johnson and K. Mehta, Physiol. Rev., 2014, 94, 383 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Lorand and R. M. Graham, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2003, 4, 140 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. P. Katt, M. A. Antonyak and R. A. Cerione, Drug Discovery Today, 2018, 23, 575 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. W. Keillor, C. M. Clouthier, K. Y. P. Apperley, A. Akbar and A. Mulani, Bioorg. Chem., 2014, 57, 186 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. S. Johnson, M. Fisher, J. L. Haylor, Z. Hau, N. J. Skill, R. Jones, R. Saint, I. Coutts, M. E. Vickers, A. M. El Nahas and M. Griffin, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 2007, 18, 3078 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Shweke, N. Boulos, C. Jouanneau, S. Vandermeersch, G. Melino, J. C. Dussaule, C. Chatziantoniou, P. Ronco and J. J. Boffa, Am. J. Pathol., 2008, 173, 631 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. C. W. Benn, W. Weber, E. Klotzsch, V. Vogel and S. A. Pot, Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng., 2019, 10, 156 CrossRef.
- W. Dieterich, T. Ehnis, M. Bauer, P. Donner, U. Volta, E. O. Riecken and D. Schuppan, Nat. Med., 1997, 3, 797 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Schuppan and W. Dieterich, Chem. Biol., 2003, 10, 199 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Tabolacci, A. De Martino, C. Mischiati, G. Feriotto and S. Beninati, Med. Sci., 2019, 7, 1–19 Search PubMed.
- M. L. Fisher, J. W. Keillor, W. Xu, R. L. Eckert and C. Kerr, Mol. Cancer Res., 2015, 13, 1083 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Szondy, I. Korponay-Szabo, R. Kiraly, Z. Sarang and G. J. Tsay, Biomedicine, 2017, 7, 15 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. H. Jang, D. S. Lee, K. Choi, E. M. Jeong, I. G. Kim, Y. W. Kim, J. N. Chun, J. H. Jeon and H. H. Park, PLoS One, 2014, 9, e107005 CrossRef PubMed.
- N. S. Caron, L. N. Munsie, J. W. Keillor and R. Truant, PLoS One, 2012, 7, e44159 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. M. Pinkas, P. Strop, A. T. Brunger and C. Khosla, PLoS Biol., 2007, 5, e327 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. W. Keillor and G. V. W. Johnson, Expert Opin. Ther. Targets, 2021, 25, 721 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. E. Begg, S. R. Holman, P. H. Stokes, J. M. Matthews, R. M. Graham and S. E. Iismaa, J. Biol. Chem., 2006, 281, 12603 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Song, H. Hwang, C. Y. Im and S. Y. Kim, J. Med. Chem., 2017, 60, 554 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. A. Rorke, G. Adhikary, H. Szmacinski, J. R. Lakowicz, D. J. Weber, R. Godoy-Ruiz, P. Puranik, J. W. Keillor, E. W. J. Gates and R. L. Eckert, Mol. Carcinog., 2022, 61, 19 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Badarau, Z. Wang, D. L. Rathbone, A. Costanzi, T. Thibault, C. E. Murdoch, S. El Alaoui, M. Bartkeviciute and M. Griffin, Chem. Biol., 2015, 22, 1347 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wityak, M. E. Prime, F. A. Brookfield, S. M. Courtney, S. Erfan, S. Johnsen, P. D. Johnson, M. Li, R. W. Marston, L. Reed, D. Vaidya, S. Schaertl, A. Pedret-Dunn, M. Beconi, D. Macdonald, I. Munoz-Sanjuan and C. Dominguez, ACS Med. Chem. Lett., 2012, 3, 1024 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Schaertl, M. Prime, J. Wityak, C. Dominguez, I. Munoz-Sanjuan, R. E. Pacifici, S. Courtney, A. Scheel and D. Macdonald, J. Biomol. Screening, 2010, 15, 478 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Pardin, S. M. Gillet and J. W. Keillor, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2006, 14, 8379 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. W. Keillor and K. Y. Apperley, Expert Opin. Ther. Pat., 2016, 26, 49 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Akbar, N. M. R. McNeil, M. R. Albert, V. Ta, G. Adhikary, K. Bourgeois, R. L. Eckert and J. W. Keillor, J. Med. Chem., 2017, 60, 7910 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Wodtke, J. Wodtke, S. Hauser, M. Laube, D. Bauer, R. Rothe, C. Neuber, M. Pietsch, K. Kopka, J. Pietzsch and R. Loser, J. Med. Chem., 2021, 64, 3462 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. de Macedo, C. Marrano and J. W. Keillor, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2002, 10, 355 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Pardin, J. N. Pelletier, W. D. Lubell and J. W. Keillor, J. Org. Chem., 2008, 73, 5766 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Schuppan, M. Maki, K. E. A. Lundin, J. Isola, T. Friesing-Sosnik, J. Taavela, A. Popp, J. Koskenpato, J. Langhorst, O. Hovde, M. L. Lahdeaho, S. Fusco, M. Schumann, H. P. Torok, J. Kupcinskas, Y. Zopf, A. W. Lohse, M. Scheinin, K. Kull, L. Biedermann, V. Byrnes, A. Stallmach, J. Jahnsen, J. Zeitz, R. Mohrbacher, R. Greinwald and C. E. C. T. Group, N. Engl. J. Med., 2021, 385, 35 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Halim, K. Caron and J. W. Keillor, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2007, 17, 305 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Marrano, P. de Macedo, P. Gagnon, D. Lapierre, C. Gravel and J. W. Keillor, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2001, 9, 3231 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Marrano, P. de Macedo and J. W. Keillor, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2001, 9, 1923 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. R. Griffin, D. Rathbone and L. E. Badarau, WO2014057266A1, 2014.
- C. P. Dominguez, M. Prime, R. Marston, F. A. Brookfield, S. M. Courtney, D. Macdonald, J. Wityak, C. J. Yarnold and D. Vaidya, WO2014047288A2, 2014.
- A. Leblanc, C. Gravel, J. Labelle and J. W. Keillor, Biochemistry, 2001, 40, 8335 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. P. McEwen, K. R. Gee, H. C. Kang and R. R. Neubig, Anal. Biochem., 2001, 291, 109 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Wodtke, C. Hauser, G. Ruiz-Gomez, E. Jackel, D. Bauer, M. Lohse, A. Wong, J. Pufe, F. A. Ludwig, S. Fischer, S. Hauser, D. Greif, M. T. Pisabarro, J. Pietzsch, M. Pietsch and R. Löser, J. Med. Chem., 2018, 61, 4528 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Day and J. W. Keillor, Anal. Biochem., 1999, 274, 141 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. E. Achyuthan and C. S. Greenberg, J. Biol. Chem., 1987, 262, 1901 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Seo, Y. Moon, J. Choi, S. Yoon, K. H. Jung, J. Cheon, W. Kim, D. Kim, C. H. Lee, S. W. Kim, K. S. Park and D. H. Lee, Am. J. Cancer Res., 2019, 9, 597 CAS.
- J. Stamnaes, D. M. Pinkas, B. Fleckenstein, C. Khosla and L. M. Sollid, J. Biol. Chem., 2010, 285, 25402 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. A. Attique, M. Hassan, M. Usman, R. M. Atif, S. Mahboob, K. A. Al-Ghanim, M. Bilal and M. Z. Nawaz, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 2019, 16, 923 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. S. Pagadala, K. Syed and J. Tuszynski, Biophys. Rev., 2017, 9, 91 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. G. Alberg and S. L. Schreiber, Science, 1993, 262, 248 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. M. Clouthier, G. G. Mironov, V. Okhonin, M. V. Berezovski and J. W. Keillor, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 12464 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. G. Mironov, C. M. Clouthier, A. Akbar, J. W. Keillor and M. V. Berezovski, Nat. Chem. Biol., 2016, 12, 918 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Zhang, S. Wu, Z. Xi and L. Yi, Tetrahedron, 2017, 73, 6651 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Vachal, J. M. Fletcher, T. M. Fong, C. C. Huang, J. Lao, J. C. Xiao, C. P. Shen, A. M. Strack, L. Shearman, S. Stribling, R. Z. Chen, A. Frassetto, X. Tong, J. Wang, R. G. Ball, N. N. Tsou, G. J. Hickey, D. F. Thompson, T. D. Faidley, S. Nicolich, J. Achanfuo-Yeboah, D. F. Hora, J. J. Hale and W. K. Hagmann, J. Med. Chem., 2009, 52, 2550 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Roy, O. Smith, C. M. Clouthier and J. W. Keillor, Protein Expression Purif., 2013, 87, 41 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Kitz and I. B. Wilson, J. Biol. Chem., 1962, 237, 3245 CrossRef CAS.
- S. R. Stone and J. Hofsteenge, Biochem. J., 1985, 230, 497 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Computational modelling details; HPLC retention times and analysis of purity for all final compounds; and 1H and 13C NMR spectra for all final compounds. See DOI: 10.1039/d1md00382h |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2022 |