Identification of ligand linkage vectors for the development of p300/CBP degraders†
Abstract
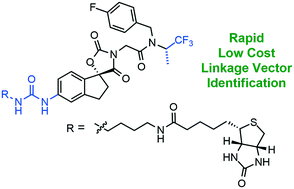
To develop new degrader molecules from an existing protein ligand a linkage vector must be identified and then joined with a suitable E3 ligase without disrupting binding to the respective targets. This is typically achieved through empirically evaluating the degradation efficacy of a series of synthetic degraders. Our strategy for determining optimal linkage sites utilises biotinylated protein ligands, linked via potential conjugation sites of an inhibitor to confirm whether target protein is maintained after forming a conjugate. This method provides low-cost, qualitative evidence that the addition of a linker moiety at a specific position can be tolerated, guiding further optimisation. We demonstrate the application of this method through the exploration of linkage vectors on A-485, a known ligand of p300/CBP, and found a conjugation site through a urea moiety. Pomalidomide was then conjugated through this site with several different linkers and cell viability and degradation were assessed for this library using a myeloma cell line, MM1.S. Compound 18i, with a PEG4 linker, was found to be the most effective p300 degrader and linker length greater than 10 atoms afforded enhanced degradation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigators


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...