A critical review of ginkgolic acids in Ginkgo biloba leaf extract (EGb): toxicity and technologies to remove ginkgolic acids and their promising bioactivities
Abstract
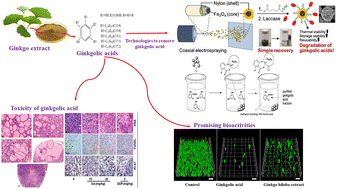
Ginkgo biloba leaf extract (EGb) is high in bioactive components (over 170), which are used in food additives, medicine, cosmetics, health products, and other sectors. Nonetheless, ginkgolic acids (GAs) in Ginkgo biloba (GB) have been identified as the primary source of EGb's adverse effects such as embryotoxicity, cytotoxicity, neurotoxicity, and inhibition of enzyme systems. As a result, the Chinese, European, and United States pharmacopeias all mandate that the GA concentration in EGb be less than 5 μg g−1. This review looked at the toxicity of ginkgolic acid (from in vitro and in vitro trials) as well as the technologies (such as adsorption/desorption, enzymatic degradation, counter-current chromatography, liquid–liquid microextraction, dual-frequency ultrasonic-solvent extraction, deep eutectic solvent, etc.) used to lower the GA to the desired concentration. These technologies’ advantages, disadvantages, viability, and future trends were compared. In addition, several pharmacological significances of GA extraction, such as anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, etc., were discussed, as well as future directions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function Review Articles 2022


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...