Effects of alkaloid-rich extracts obtained from Grifola frondosa on gut microbiota and glucose homeostasis in rats†
Abstract
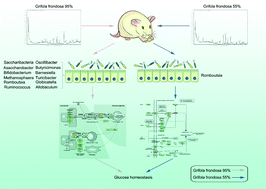
Grifola frondosa (GF), also known as maitake (a type of mushroom), has been widely used as a food item and it exhibits various health-beneficial hypoglycemic activities. Rats fed with a fat/high-sucrose-based diet were used to determine the hypoglycemic activity of 95% and 55% GF ethanol extracts (labeled as GF95 and GF55, respectively). The activity was determined by monitoring the fasting blood glucose level. Oral glucose tolerance tests were conducted, and the levels of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase were studied to study the hypoglycemic activity. The HPLC-ESI-TOF-MS technique was used to analyze the samples, and the results revealed that alkaloids were present in abundance in GF95 and GF55. It was also observed that GF55 contained some organic acids and GF95 contained extra small amounts of phenoloid. The levels of intestinal microbiota were analyzed, and the results from transcriptome analysis indicated that GF55 reduced the relative abundance of Romboutsia and affected RT-Db1, thereby improving the extent of glucose metabolism achieved. GF95 downregulated the mRNA level of Socs1 by increasing the levels of Oscillibacter, Butyricimonas, Barnesiella, Turicibacter, Methanosphaera, Asaccharobacter, Globicatella, Bifidobacterium, Allobaculum, and Romboutsia. The expression of Pik3rl was upregulated when the levels of Ruminococcus and Saccharibacteria increased. The hypoglycemic activity was induced under these conditions. The obtained data indicated that the efficiency of GF95 to control glucose levels was higher than the efficiency of GF55. This suggested that GF95 can be potentially used to protect against hyperglycemia.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...