E Se tea alleviates acetaminophen-induced liver injury by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway†
Abstract
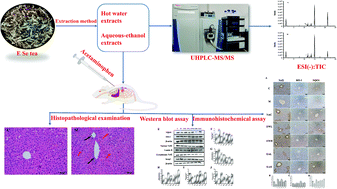
E Se tea is a traditional herbal tea used in the prevention of liver diseases. However, the hepatoprotective effect of E Se tea has not been investigated. This study aimed to determine the protective effect of E Se tea on acetaminophen (APAP)-induced acute liver injury and its potential mechanism. Hot water extracts and aqueous-ethanol extracts of E Se tea were obtained, which were analyzed to determine the chemical constituents of the tea. Phlorizin and phloretin were found to be the dominant chemical compounds. Histopathological analysis showed that E Se tea extract inhibited APAP-induced inflammatory infiltration, necrosis, and cellular vacuolization of hepatocytes in the liver tissue. The E Se tea extract could significantly ameliorate liver injury, inhibit an inflammatory response, and reduce oxidative stress. Western blot analysis revealed that E Se tea extract upregulated the expressions of nuclear Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO1 proteins and downregulated the expressions of cytoplasmic Nrf2 and Keap1 proteins in the hepatocyte. qPCR results showed that E Se tea extract also increased the expression of antioxidant genes (SOD2, Gpx1, GCLC and GCLM). These findings exhibited that E Se tea, enriched in dihydrochalcones, can be used to effectively prevent and manage liver dysfunction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...