Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Heterolytic carbon–iodine bond cleavage by a palladium(I) metalloradical†
Matthew J. G.
Sinclair
 and
Adrian B.
Chaplin
and
Adrian B.
Chaplin
 *
*
Department of Chemistry, University of Warwick, Gibbet Hill Road, Coventry CV4 7AL, UK. E-mail: a.b.chaplin@warwick.ac.uk
First published on 11th July 2022
Abstract
The well-defined Pd(I) metalloradical [Pd(PtBu3)2]+ reacts with aryl and alkyl iodides at room temperature, yielding [Pd(PtBu3)(μ-I)]2 and phosphonium salts. Pd(II) aryl/alkyl derivates, reflecting net radical oxidative addition of the substrate to the metalloradical, are generated during the reaction and two examples have been isolated and crystallographically characterised.
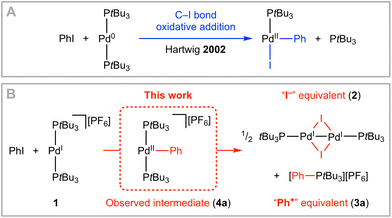
The transition-metal-mediated activation of carbon–halogen bonds is the basis of widely exploited catalytic methods for the construction of organic molecules. Oxidative addition to low-coordinate Pd(0) complexes is a pervading theme, with work by Hartwig and co-workers in 2002 involving isolation of T-shaped aryl Pd(II) halide products a key mechanistic reference point (Scheme 1A).1,2 Whilst the Pd(0)/Pd(II) redox couple remains the workhorse, processes invoking single electron transfer and Pd(I) and Pd(III) intermediates have been attracting growing attention.3 Well-defined monomeric examples of the former are rare,4 but as part of work in our group we recently reported the synthesis of [Pd(PtBu3)2][PF6] 1 by one-electron oxidation of [Pd(PtBu3)2] with [Fc][PF6].5 Using 1 as an exemplar, we herein present our preliminary findings exploring the activation of aryl and alkyl iodides by palladium metalloradicals.
Treatment of 1 (20 mM) with 1.1 equivalents of phenyl iodide in 1,2-difluorobenzene (DFB) solvent6 resulted in complete consumption of the metalloradical within 24 h at room temperature and generated a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 mixture of the known Pd(I) iodide dimer [Pd(PtBu3)(μ-I)]22 and phenyl phosphonium salt [PtBu3Ph][PF6] 3a with >97% selectivity (Scheme 1B). This outcome can be viewed as heterolytic cleavage of the C–I bond and this interpretation is reinforced by immediate conversion of 1 into 2 upon addition of excess KI/18-crown-6 in DFB at room temperature. The decisive role of 1 was confirmed by a control experiment involving treatment of PtBu3 with excess phenyl iodide which did not lead to formation of 3a, even under considerably more forcing reaction conditions.
2 mixture of the known Pd(I) iodide dimer [Pd(PtBu3)(μ-I)]22 and phenyl phosphonium salt [PtBu3Ph][PF6] 3a with >97% selectivity (Scheme 1B). This outcome can be viewed as heterolytic cleavage of the C–I bond and this interpretation is reinforced by immediate conversion of 1 into 2 upon addition of excess KI/18-crown-6 in DFB at room temperature. The decisive role of 1 was confirmed by a control experiment involving treatment of PtBu3 with excess phenyl iodide which did not lead to formation of 3a, even under considerably more forcing reaction conditions.
When the reaction was repeated using 1.5 equivalents of phenyl iodide a larger proportion of 3a was generated and periodic monitoring using UV/vis and NMR spectroscopy indicated complete consumption of 1 within 4 h, sigmoidal reaction kinetics (Fig. 1A), and intermediate formation of a diamagnetic species assigned to three-coordinate Pd(II) aryl [Pd(PtBu3)2Ph][PF6] 4a (λmax = 305 nm, δ31P 61.0). Whilst a complex overall mechanism is evident from the reaction profile, observation of 4a reconciles formation of 3a by reductive elimination. The resulting Pd(0) is presumably converted into 2 or lost from solution,7 with the latter pathway evidently more pronounced in the presence of excess phenyl iodide. Addition of 5 equivalents of PtBu3 retarded, but did not prevent, reaction of 1 with phenyl iodide.
Intrigued by the generation of 4a, which corresponds to net radical oxidative addition of the substrate to 1, we explored reactions with aryl iodides bearing electron donating methoxy substituents to facilitate isolation of the corresponding Pd(II) aryl derivatives by attenuating onward reductive elimination. Gratifyingly, reactions of 1 with 2-methoxyphenyl iodide and 2,6-dimethyoxyphenyl iodide in DFB at room temperature resulted in formation of the persistent Pd(II) aryls [Pd(PtBu3)2Ar][PF6] (Ar = 2-(MeO)C6H4, 4b; 2,6-(MeO)2C6H3, 4c) alongside [PtBu3X]+ (X = 2-(MeO)C6H4, 3b; I) and 2 within 24 h. These low coordinate complexes were successfully isolated from solution, in modest yield following purification by column chromatography (32%, 4b; 38%, 4c), and fully characterised; including in the solid state by single crystal X-ray diffraction (Fig. 1B and C). The spectroscopic features of 4b/c are congruent with those attributed to 4a, with absorption maxima at λmax = 310/321 nm and 31P resonances at δ 62.0/65.3. Isolated 4b undergoes slow reductive elimination of 3b in DFB at room temperature (t1/2 = 3 days), alongside precipitation of palladium black. The rate is unchanged in the presence of excess PtBu3, but in this case liberated Pd(0) was retained in solution as [Pd(PtBu3)2]. In contrast, 4c showed no onward reactivity after 14 days in DFB at room temperature.
We tentatively propose that the aforementioned reactions involve a combination of (a) concerted oxidative addition of the C–I bond to [Pd(PtBu3)]+ followed by halogen atom abstraction from the resulting Pd(III) derivative,8 and (b) auto-catalytic aryl halide activation,9e.g.1 + ArI + 2 → 3 + 1½2, where the C–I bond is added across the Pd(I)–Pd(I) bond in 2.† The former may initiate the latter, which we suggest becomes the main kinetic pathway in the case of phenyl iodide where reductive elimination of 3a is fast. Work by Schoenebeck and co-workers with Pd(I) dimers provides precedent for the proposed C–I bond activation step in (b).10
To explore the reaction scope, 1 was also reacted with adamantyl and tert-butyl iodide. Consistent with intermediate formation of [Pd(PtBu3)2Ad][PF6] 4d, treatment of 1 with 1.5 equivalents of adamantyl iodide in DFB at room temperature resulted in heterolytic C–I bond cleavage and a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 mixture of 2 and [PtBu3Ad][PF6] 3d with >75% selectivity after 8 days. In the case of tert-butyl iodide, however, the putative Pd(II) alkyl [Pd(PtBu3)2tBu][PF6] 4e appears to undergo rapid β-hydrogen elimination as a mixture of 2, [PtBu3H][PF6], and isobutylene was obtained under the same conditions, but after 24 h.
2 mixture of 2 and [PtBu3Ad][PF6] 3d with >75% selectivity after 8 days. In the case of tert-butyl iodide, however, the putative Pd(II) alkyl [Pd(PtBu3)2tBu][PF6] 4e appears to undergo rapid β-hydrogen elimination as a mixture of 2, [PtBu3H][PF6], and isobutylene was obtained under the same conditions, but after 24 h.
Taken together, these findings unequivocally demonstrate the capacity of Pd(I)-based metalloradicals to activate C–I bonds under mild conditions. Whilst the associated mechanism is complex, generation of Pd(II)-aryls/alkyls suggests that through judicious selection of substrates and reaction conditions this reactivity could be effectively harnessed in catalysis.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.Acknowledgements
We thank the EPSRC (MJGS; DTP studentship) and Royal Society (ABC; UF100592, UF150675) for financial support.Notes and references
- (a) J. P. Stambuli, M. Bühl and J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124, 9346–9347 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) F. Barrios-Landeros, B. P. Carrow and J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 8141–8154 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Note [Pd(PtBu3)(Ph)I] has been shown to decompose to 2 and biphenyl: E. Galardon, S. Ramdeehul, J. M. Brown, A. Cowley, K. K. Hii and A. Jutand, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2002, 41, 1760–1763 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) X. Sun, X. Dong, H. Liu and Y. Liu, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2021, 363, 1527–1558 CrossRef CAS; (b) Q. Simpson, M. J. G. Sinclair, D. W. Lupton, A. B. Chaplin and J. F. Hooper, Org. Lett., 2018, 20, 5537–5540 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) Q. Liu, X. Dong, J. Li, J. Xiao, Y. Dong and H. Liu, ACS Catal., 2015, 5, 6111–6137 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) J. Liu, M. M. Bollmeyer, Y. Kim, D. Xiao, S. N. MacMillan, Q. Chen, X. Leng, S. H. Kim, L. Zhao, K. M. Lancaster and L. Deng, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 10751–10759 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) J. Luo, G. N. Tran, N. P. Rath and L. M. Mirica, Inorg. Chem., 2020, 59, 15659–15669 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) M. C. MacInnis, J. C. DeMott, E. M. Zolnhofer, J. Zhou, K. Meyer, R. P. Hughes and O. V. Ozerov, Chem, 2016, 1, 902–920 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Troadec, S. Tan, C. J. Wedge, J. P. Rourke, P. R. Unwin and A. B. Chaplin, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 3754–3757 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. D. Pike, M. R. Crimmin and A. B. Chaplin, Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 3615–3633 RSC.
- This suggestion is supported by an increased baseline UV/vis absorption over time and the reactivity of isolated 4b.
- A Pd(III) species resulting from the reaction of a Pd(I) dithiapyridinophane complex with phenyl iodide has recently been reported: G. N. Tran, B. S. Bouley and L. M. Mirica, ChemRxiv., 2022. DOI:10.26434/chemrxiv-2022-9c7kg-v2.
- F. Barrios-Landeros, B. P. Carrow and J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 5842–5843 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) C. Fricke, T. Sperger, M. Mendel and F. Schoenebeck, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 3355–3366 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) K. J. Bonney, F. Proutiere and F. Schoenebeck, Chem. Sci., 2013, 4, 4434–4439 RSC.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Full experimental details, including characterisation of new compounds and spectroscopic data for selected reactions, and mechanistic sketch. CCDC 2172989 (3a), 2172990 (3b), 2172991 (4b), 2172992 (4c) and 2172993 ([PtBu3H][PF6]). For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d2dt02152h |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2022 |