Identification of a pyrone-type species as the active site for the oxygen reduction reaction†
Abstract
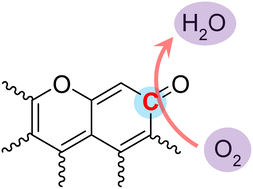
A bicyclic pyrone-type species on oxygen-doped carbon catalysts was identified as the active site for the oxygen reduction reaction in acidic solution. It has much higher activity than that of typical nitrogen-doped carbon catalysts (0.219 e s−1 site−1vs. 0.021–0.088 e s−1 site−1 at 0.6 VRHE). The ortho-carbon atom in the carbonyl ring of the pyrone-type species was revealed as the reactive site by theoretical calculations.
- This article is part of the themed collection: ChemComm Milestones – First Independent Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...