Towards understanding the active sites for the ORR in N-doped carbon materials through fine-tuning of nitrogen functionalities: an experimental and computational approach
Abstract
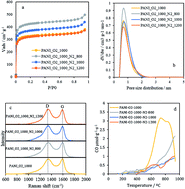
The design of advanced N-doped carbon materials towards oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalysis is only possible if the nature of the active sites is fully understood. There is an important piece of research seeking to overcome this challenge through experimental or theoretical results. However, the combination of both approaches is necessary to deepen the knowledge about this subject. This work presents excellent agreement between experimental results and computational models, which provides evidence of the nature of the most active sites in N-doped carbon materials. N-doped carbon materials have been experimentally obtained through double stage treatment of polyaniline in distinct atmospheres (both oxygen-containing and inert atmospheres) at different temperatures (800–1200 °C). According to temperature programmed desorption (TPD), Raman spectroscopy, N2-adsorption isotherms at −196 °C and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), this synthesis method results in the selective formation of nitrogen species, without significant changes in structural order or porosity. ORR catalytic tests evidence the highly efficient catalysis, with platinum-like performance in terms of the current density and onset potential, of N-doped carbon materials selectively containing graphitic-type nitrogen species. Computational chemistry, through DFT calculations, shows that edge-type graphitic nitrogen is more effective towards ORR catalysis than pyridinic, pyrrolic, pyridonic, oxidized and basal-type graphitic nitrogen species.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...