Thin-film transistors for emerging neuromorphic electronics: fundamentals, materials, and pattern recognition
Abstract
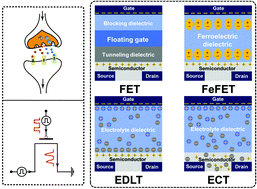
The main goal of the field of neuromorphic electronics is to develop novel microelectronic components that emulate the memory and computing functionalities of the biological synapse. As a three-terminal device, thin-film transistors (TFTs) have natural advantages in the mimicking of synaptic functions with physically separated input and output terminals. This unique feature endows TFT-based artificial synapses with potential for concurrent actualization of signal transmission and learning functions, where signal transmission is carried out via the semiconductor channel and synaptic weights are modulated independently via the gate terminals. Here, the recent successful simulation of pattern recognition with TFT-based artificial synapses from device- to system-level is comprehensively reviewed, focusing on the working principles, reliability concerns, material requirements, and algorithm implementation. Typical types of TFTs are addressed in detail, including charging-based field-effect transistors (FETs), ferroelectric field-effect transistors (FeFETs), electric-double-layer transistors (EDLTs), and electrochemical transistors (ECTs). At last, the challenges are discussed to shed light on future studies.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry C Emerging Investigators


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...