Blends of polymer semiconductor and polymer electrolyte for mixed ionic and electronic conductivity†
Abstract
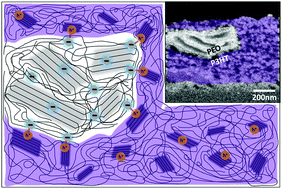
Many applications exploit the interplay between ions and electrons and require materials that can effectively support the storage and transport of both carriers. Organic Mixed Ionic Electronic Conductors (OMIECs) offer not only mixed conductivity but also ease of processability and property tunability, making them promising candidates for such applications. One approach to achieve mixed conductivity is blending a semiconducting polymer that conducts electrons with a polymer electrolyte that conducts ions. This system is synthetically simple and we hypothesized that it offers control of ionic/electronic transport and coupling through phase separation and film morphology. To realize this we blended the common semiconducting polythiophene poly(3-hexylthiophene-2,5-diyl) (P3HT) with the common polymer electrolyte poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) and studied the effect of blend composition and PEO molecular weight (Mw) on mixed conductivity and film morphology. Spectroelectrochemistry and electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance measurements reveal the electrochemical properties, while X-ray diffraction patterns and electron microscopy images of contrast agent-stained films disclose the blend morphology. By correlating the structure and properties we find that mixed conductivity is optimal at a “sweet-spot” composition that contains sufficient PEO to support ionic conductivity and sufficient P3HT to generate high interfacial area. We also find that high Mw PEO supports phase separation and connectivity of P3HT domains effectively providing good electronic conductivity, but suppresses the P3HT:PEO interfacial area required for the coupling between the ions and holes. Good dispersion of PEO and coupling with P3HT is better supported by low Mw PEO. Overall, we show that the morphology tunability attained by polymer blends can be directed towards optimal mixed conductivity suggesting that blends of semiconductors and electrolyte polymers are a promising approach towards high performance mixed conductivity systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...