Spectral and thermometric properties altering through crystal field strength modification and host material composition in luminescence thermometers based on Fe3+ doped AB2O4 type nanocrystals (A = Mg, Ca; B = Al, Ga)†
Abstract
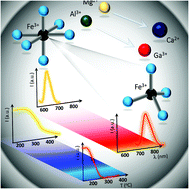
The growing interest in the use of luminescence thermometry for noncontact temperature reading under very specific conditions imposes the need to develop an approach allowing modification of the luminescence parameters of a thermometer accordingly to requirements. Therefore, in response to these expectations, this manuscript reports an approach to modulate the spectral position and luminescence thermal quenching rate of Fe3+ ions by modifying the crystal field strength and the host material composition of nanocrystalline AB2O4 type nanocrystals (A = Mg, Ca; B = Al, Ga). It was proved that in a group of MgAl2O4, MgGa2O4, CaAl2O4, and CaGa2O4 nanocrystals doped with Fe3+ ions, the emission spectral range, as well as the relative thermal sensitivity (from 0.2%/°C for MAO to 2.07%/°C for CGO) and the operating temperature range, can be easily modified by the host material composition. For instance, a maximal relative thermal sensitivity of 2.58%/°C is obtained for Fe3+, Tb3+ co-doped CaAl2O4 nanocrystals. The proposed approach is a step toward the intentional designing of a highly sensitive luminescence thermometer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...