Calcium phosphate bone cement with enhanced physicochemical properties via in situ formation of an interpenetrating network†
Abstract
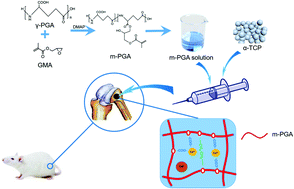
Calcium phosphate cement (CPC), which exhibits excellent biocompatibility and bioactivity, is a well-established material for the repair of bone defects. However, its disadvantages such as poor washout resistance and low mechanical strength limit its clinical applications. In this study, CPC with enhanced washout resistance and mechanical properties has been developed by the in situ crosslinking of glycidyl methacrylate modified γ-polyglutamic acid (m-PGA) within the cement matrix, forming an interpenetrating network. Compared with unmodified CPC, the final setting time of the composite cements was shortened and its washout resistance was significantly improved. In addition, the composite cements showed enhanced mechanical strength and degradation properties. An in vitro study demonstrated that the composite cements exhibited good biocompatibility. The in vivo results showed that the composite cements promoted bone formation. These results suggest that the biocompatible, injectable α-tricalcium phosphate (α-TCP)/m-PGA cements may have the potential to be used as bone filling materials for future clinical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...