In situ chemical oxidation: peroxide or persulfate coupled with membrane technology for wastewater treatment
Abstract
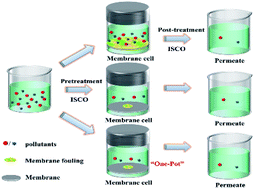
Refractory organic pollutants in wastewater have the characteristics of persistence and toxicity, which seriously threaten the health and safety of humans and other organisms. Many researchers have committed to developing effective wastewater treatment technologies in the past few decades. The coupling of membrane technology with persulfate/peroxide-based in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) not only can successfully overcome the shortcomings of the two single technologies, such as membrane fouling and difficult reuse of some catalysts, but also effectively achieve complementary advantages of pollutant filtration and degradation. Therefore, it has received extensive attention from researchers and is expected to be large-scale applied to actual wastewater treatment. In this review, according to different membrane materials, the common membrane types are briefly summarized, and then the synthesis methods of the catalytic membrane are introduced. In addition, various process configurations coupling membrane filtration with ISCO are researched. Two main modes of the coupling processes can be defined: (i) a one-pot coupling process which simultaneously oxidizes and separates organic pollutants; (ii) a two-stage coupling process, including a pretreatment stage for the removal of foulant forming molecules in the membrane feed water, and a post-treatment stage to further degrade the pollutants of membrane concentrate and permeation fluid. Finally, the major challenges and application prospects of membrane filtration coupled with ISCO in wastewater treatment are discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...