Trimethylsulfonium lead triiodide (TMSPbI3) for moisture-stable perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
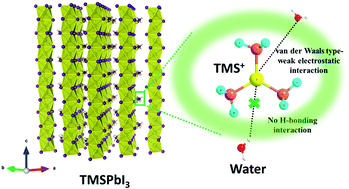
Conventional, high-efficiency, hybrid organic–inorganic perovskites (e.g., methylammonium lead iodide (MAPbI3) and formamidinium lead iodide (FAPbI3)) having ammonium-based organic cations exhibit poor moisture stability mainly due to the effective hydrogen bonding interaction of nitrogen in the ammonium-based cations with water molecules. Recently, a sulfonium-based cation, trimethylsulfonium (TMS+), has attracted growing attention for the development of moisture-stable hybrid perovskite solar cells (PSCs). This research investigated the photovoltaic performance of trimethylsulfonium lead triiodide (TMSPbI3) based PSCs and their moisture stability both experimentally and theoretically. The results revealed that TMSPbI3 exhibited a relatively large optical band gap (Eg = 2.32 eV) and high absorption coefficient (α = 2.30 × 104 cm−1 at 500 nm) with a hexagonal one-dimensional crystal structure. The PSCs with a device structure of FTO/c-TiO2/m-TiO2/TMSPbI3/CuSCN/Au exhibited a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 2.22% with no hysteresis in the I–V curve, and high moisture stability at ambient temperature (25 ± 3 °C, ca. 50% relative humidity) with a PCE loss of only ca. 4.6% after 500 h. This result could be attributed to the absence of the hydrogen bonding interaction of TMS+ with water molecules, leading to the effective stabilization of TMSPbI3 compared to MAPbI3 and FAPbI3, verified by density functional theory calculations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...