Switchable supramolecular ensemble for anion binding with ditopic hydrogen-bonded macrocycles†
Abstract
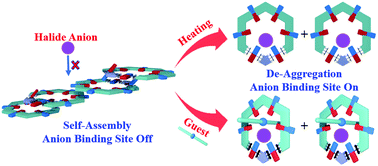
Hydrogen-bonded (H-bonded) macrocycles that recognize cationic and/or anionic species via non-covalent interactions have found a variety of applications in separation, catalysis, analysis and creation of functional molecules. One of the major challenges in this aspect is to manipulate their dynamic associations in the recognition events for applications. In this study, we report a novel supramolecular strategy using a ditopic H-bonded amide macrocycle that is capable of controlling the binding process in response to external stimulus due to its assembly-and-disassembly-induced anion binding. The presence of an incorporated pyridinium moiety provides the host with a strong tendency to self-associate into 1D interlocked aggregates via intermolecular hydrogen bonds, pi–pi stacking and cation–π interaction, as indicated by the X-ray single-crystal structure analysis. A switchable ensemble is realized through adjusting the intermolecular interaction associated with both the anionic and cationic sites through changing the temperature and introducing a guest. In solution, macrocycle aggregation blocks anion binding but is disrupted upon addition of EMIMBF4, thereby enabling the opening of the anion binding site. A catalytic reaction with bromodiphenylmethane as the substrate reacting with methanol reveals a greatly enhanced yield (over 40% increase) by heating and adding a guest with respect to the case with low temperature, demonstrating the potential of the supramolecular element constructed from H-bonded macrocycles for controllable catalysis.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Macrocycle-based Supramolecular Elements


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...