Fluorescence resonance energy transfer enhanced photothermal and photodynamic antibacterial therapy post a single injection†
Abstract
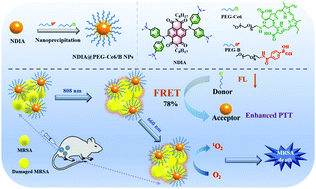
Refractory MRSA infections seriously threaten human health, which compromises antibiotic efficacy. Although phototherapy has exhibited great feasibility in the fight against drug-resistant pathogens, a single-modal therapeutic agent without targeted performance has resulted in low drug utilization and obvious side effects. Herein, near-infrared (NIR) light-triggered theranostic nanoparticles (NDIA@PEG-Ce6/B NPs) were prepared by employing naphthalene diimide derivative NDIA as a photothermal agent, PEGylated chlorin e6 (PEG-Ce6) as a photosensitizer and PEGylated phenylboronic acid (PEG-B) as a bacteria-targeting agent. Upon laser irradiation, the singlet oxygen produced by Ce6 can efficiently kill bacteria through photodynamic therapy. Moreover, the fluorescence emission of Ce6 can be absorbed by the photothermal agent NDIA with a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) efficiency of 78% to reinforce the photothermal effect of NDIA, and the photothermal conversion efficiency of NDIA@PEG-Ce6/B NPs was up to 49.7%. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial experiments indicated that NDIA@PEG-Ce6/B NPs could targeted assembly and effectively destroy multidrug-resistant bacteria through synergistic photothermal and photodynamic therapy with 99.999% antibacterial efficacy under NIR light illumination. The study provides a nanosystem for the antibacterial treatment of synergistic photodynamic and photothermal therapy for subcutaneous abscesses, as well as a novel FRET strategy for further design of light-triggered antibacterial nanoplatforms.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Materials Chemistry Frontiers HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...