Asymmetric small organic molecule-based NIR-II fluorophores for high performance tumor phototheranostics†
Abstract
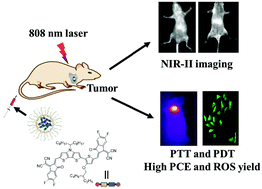
Small organic molecules hold great promise for phototheranostics due to their well-defined chemical structures and optical properties, excellent biodegradation and biocompatibility, high purity, and outstanding repeatability. Nevertheless, numerous small molecules exhibited weak absorption in the near-infrared I (NIR-I) region (particularly 808 nm, the optimal tissue transparent window in the NIR-I region), expedient NIR-I fluorescence emission, and single-mode therapy, which greatly hinder their phototheranostic performances. Herein, versatile nanoparticle DTPT NPs based on a single-component asymmetric small organic molecule were successfully constructed as a proof-of-concept example for high-performance phototheranostics. The developed DTPT NPs possessed strong absorption at 808 nm, excellent near-infrared II (NIR-II) fluorescence emission, prominent reactive oxygen species, and hyperthermia production ability (photothermal conversion efficiency was as high as 61.6%). Furthermore, upon a single 808 nm laser irradiation, the tumor inhibition rate of the versatile DTPT NPs was demonstrated to be 90.8%, profiting from the satisfactory NIR-II fluorescence imaging and photothermal/photodynamic performances. Moreover, the NPs showed superb safety to normal tissues, further demonstrating the potential application of NPs in clinical practice. This study provides an idea to construct small molecule-based nanoplatforms for high performance phototheranostics.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Materials Chemistry Frontiers HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...