Intermolecular binding preferences of haloethynyl halogen-bond donors as a function of molecular electrostatic potentials in a family of N-(pyridin-2-yl)amides†
Abstract
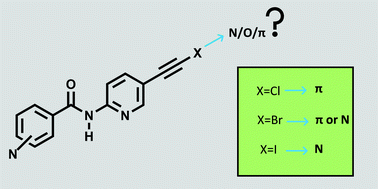
In order to explore how σ-hole potentials, as evaluated by molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) calculations, affect the ability of halogen atoms to engage in structure-directing intermolecular interactions, we synthesized four series of ethynyl halogen-substituted amide containing pyridines (activated targets); (N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamides (Bz-act-X), N-(pyridin-2-yl)picolinamides (2act-X), N-(pyridin-2-yl)nicotinamides (3act-X) and N-(pyridin-2-yl) isonicotinamides (4act-X), where X = Cl/Br/I. The molecules are deliberately equipped with three distinctly different halogen-bond acceptor sites, π, N(pyr), and O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C, to determine binding site preferences of different halogen-bond donors. Crystallographic data for ten (out of a possible twelve) new compounds were thus analyzed and compared with data for the corresponding unactivated species. The calculated MEPs of all the halogen atoms were higher in the activated targets in comparison to the unactivated targets and were in the order of iodine ≈ chloroethynyl < bromoethynyl < iodoethynyl. This increased positive σ-hole potential led to a subsequent increase in propensity for halogen-bond formation. Two of the four chloroethynyl structures showed halogen bonding, and all three of the structurally characterized bromoethynyl species engaged in halogen bonding. The analogous unactived species showed no halogen bonds. Each chloroethynyl donor selected a π-cloud as acceptor and the bromoethynyl halogen-bond donors opted for either π or N(pyr) sites, whereas all halogen bonds involving an iodoethynyl halogen-bond donor (including both polymorphs of Bz-act-I) engaged exclusively with a N(pyr) acceptor site.
C, to determine binding site preferences of different halogen-bond donors. Crystallographic data for ten (out of a possible twelve) new compounds were thus analyzed and compared with data for the corresponding unactivated species. The calculated MEPs of all the halogen atoms were higher in the activated targets in comparison to the unactivated targets and were in the order of iodine ≈ chloroethynyl < bromoethynyl < iodoethynyl. This increased positive σ-hole potential led to a subsequent increase in propensity for halogen-bond formation. Two of the four chloroethynyl structures showed halogen bonding, and all three of the structurally characterized bromoethynyl species engaged in halogen bonding. The analogous unactived species showed no halogen bonds. Each chloroethynyl donor selected a π-cloud as acceptor and the bromoethynyl halogen-bond donors opted for either π or N(pyr) sites, whereas all halogen bonds involving an iodoethynyl halogen-bond donor (including both polymorphs of Bz-act-I) engaged exclusively with a N(pyr) acceptor site.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Halogen bonding in organic synthesis and catalysis and Supramolecular chemistry in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...