Genomics-driven discovery of a new cyclodepsipeptide from the guanophilic fungus Amphichorda guana†
Abstract
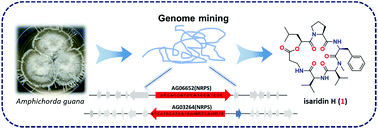
Two potential non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) were identified in the genome of a guanophilic fungus Amphichorda guana by bioinformatics analysis and gene knockout experiments. Liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC-MS) guided isolation led to the discovery of a new cyclodepsipeptide isaridin H (1) and seven known analogs, desmethylisaridin E (2), isaridin E (3), isariin A (4), iso-isariin B (5), iso-isariin D (6), isariin E (7), and nodupetide (8). The absolute configuration of isaridin H (1) was achieved by Marfey's method. Isaridin H (1) showed significant antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea and Alternaria solani.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...