Recent advancements of nanomaterial-based therapeutic strategies toward sepsis: bacterial eradication, anti-inflammation, and immunomodulation
Abstract
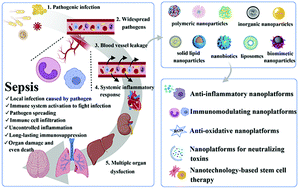
Sepsis is a life threatening disease that is caused by a dysregulated host immune response to infection, resulting in tissue damage and organ dysfunction, which account for a high in-hospital mortality (approximately 20%). However, there are still no effective and specific therapeutics for clinical sepsis management. Nanomaterial-based strategies have emerged as promising tools for improving the therapeutic efficacy of sepsis by combating lethal bacterial infection, modulating systemic inflammatory response, preventing multiple organ failure, etc. This review has comprehensively summarized the recent advancements in nanomaterial-based strategies for the management of sepsis and severe complications, in which those nanosystems act either as inherent therapeutics or as nanocarriers for the precise delivery of agents. These formulations mechanically possess antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and anti-oxidative effects, achieving multifunctional synergistic treatment efficacy against sepsis. Furthermore, several cell membrane-derived biomimetic nanoplatforms have been used as decoys to trap and neutralize the pathogenic toxins. The critical role of other adjuvant therapies in sepsis management, including the combination of nanotechnology and stem cell therapy, is also highlighted. Overall, this review provides insights into innovative nanotechnology-based strategies applied in sepsis treatment.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...