Edible and highly biocompatible nanodots from natural plants for the treatment of stress gastric ulcers†
Abstract
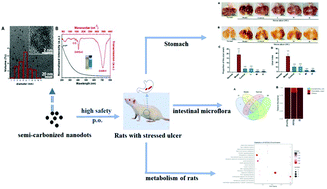
The incidence rate of stress ulcers has increased in recent years, with an increase in life pressure, unavoidable trauma and other factors. The therapy of acute stress ulcers has always been an important challenge. Carbon dots (CDs) have been reported to show excellent biological activities, but research on the stress ulcer curative effect of CDs is unprecedented. Here, we prepared a series of semi-carbonized nanodots (SCNDs) from natural plants or herbs as precursors and the as prepared SCNDs were later proved to be effective in the treatment and inhibition of stress gastric ulcers in a rat model. One kind of SCND from edible and medicinal plants, charred Atractylodes macrocephala (SCNDs-1), is demonstrated in detail for its strong anti-stress gastric ulcer effect with inhibition up to 90% and shows extremely high biocompatibility and ultra-low toxicity. These SCNDs lead to the reduction of inflammatory factors and oxidative stress, and the protection of the gastric mucosa. The SCNDs also reduce the excessive neuroendocrine response caused by stress, regulate the energy metabolism and the structure of intestinal flora, improve the damage to the body caused by the stress state, thus alleviating the occurrence of stress-induced gastric ulcers. This work provides new insights into the preparation of carbon nanomaterials from natural plants through a semi-carbonization process and opens new ways to apply bio-active and bio-safe SCNDs in the modern pharmaceutical field.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Nanoscale HOT Article Collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...