Computationally designed p-coumaric acid analogs: searching for neuroprotective antioxidants†
Abstract
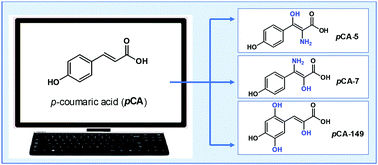
p-Coumaric acid is a ubiquitous molecule, widely distributed in the vegetal kingdom and often found in the human diet. A systematic, rational search for new p-coumaric acid derivatives was performed using a computer-assisted protocol based on chemical properties. A total of 156 derivatives were generated by adding functional groups to the initial structure and employing a selection score (SS) developed for that purpose. A reduced subset of 10 p-coumaric acid derivatives was selected, which have the best drug-like behavior and lower toxicity. Reactivity indexes, pKa values, and bond dissociation energies were computed to estimate the antioxidant capability. According to the obtained results, three p-coumaric acid derivatives have been classified as the most promising candidates to act as chemical antioxidants. These derivatives are predicted to be better for that purpose than p-coumaric acid itself, through the electron transfer and/or H transfer mechanisms. In addition, they may act as new scaffolds of non-nitrocatechol inhibitors against COMT for the treatment of Parkinson's disease without the side effects of the known inhibitors. The presented results are expected to encourage additional inquiries on these molecules, using both theoretical and experimental approaches.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...